IPC I Gastrointestinal Lesson Plan
advertisement

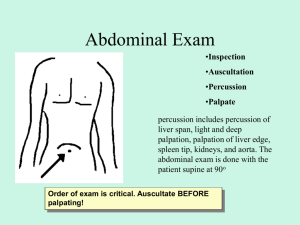
IPC I: Gastrointestinal H&P HPI PMH PSH Abdominal pain: knowing the different systems involved in abdominal pain is very important! GI (of course!), GU (UTI, pyelonephritis, PID, ectopic pregnancy, torsion) and other systems (DKA) o Quadrant: important in forming DDx (see diagram!) o Onset/duration: acute, gradual o Characteristics: sharp, dull, aching, colicky o Pattern/timing: intermittent, continuous, moving o Severity: rate on pain scale o Sexual activity: possibility of pregnancy? STD’s? o Urinary symptoms: dysuria, hesitancy, frequency, hematuria, polyuria, nocturia, weak stream o Associated sx: fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Diarrhea: onset, frequency, amount, color/quality (mucus, watery), blood, recent food, recent travel, associated sx (fever, nausea, vomiting) Nausea/vomiting: onset, frequency, description, quantity, blood, recent foods, ETOH, associated sx (LOC) Heartburn: chest pain, quality, onset/timing (how many hours after dinner?), aggravated by lying down, alleviated with antacids, current meds (PPI, H2 blockers), associated sx (coughing) Jaundice: when it started, color of urine/stool, pruritis Indigestion: onset/duration, association with specific foods, family history, Anorexia: odynophagia, dysphagia, postprandial pain GERD, GI bleeding, PUD, esophageal varices, hepatitis, cirrhosis, alcoholism, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis (acute, chronic), SBO, LBO, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s, IBS, Celiac’s, Hirschprung’s, polyps, hemorrhoids, cancer, renal calculi, pyelonephritis, multiple UTI’s, STD’s, DM EGD, colonoscopy/polypectomy, cholecystectomy, appendectomy, bowel resections Meds/Allergies Especially ASA, NSAID’s! FHx Hx of GI bleeding, cirrhosis, PUD, CA, FAP, IBD, celiac’s, etc. SocHx Diet, smoking, ETOH, IVDA Sexual history!!! Physical Examination Inspection Identify major landmarks on the abdomen: xiphoid process, CVA, iliac crest, vertebrae, costal edge, McBurney’s Appreciate general shape of abdomen (obese, distended) and always note scars! o Distention below umbilicus: ovarian tumor, pregnancy, uterine fibroids, distended bladder o Distended above umbilicus: carcinoma, pancreatic cyst, gastric dilation o Asymmetric distention or protrusion: hernia, tumor, cysts, bowel obstruction, organomegaly Jaundice (look for scleral icterus!), caput medusae, spider angiomas, gynecomastia, ascites, ecchymosis Pulsations, masses, hernias, distention, ripples Auscultation Bowel sounds: hyperactive (gastroenteritis), hypoactive (ileus), absent (much have NO bowel sounds in quadrant for 5 minutes!), normoactive. High-pitched (obstruction). Remember to listen with diaphragm! Bruits: over aorta, renal, and iliac arteries. Remember to listen with bell! Percussion Tympany/dullness: also check for shifting dullness if abdomen distended (ascites). Note that different areas are expected to have some tympany (air in stomach) or dullness (solid masses like liver). Liver span (7-12 cm or >3cm below costal edge) and spleen to check for enlargement. To percuss liver, begin at L midclavicular line where it is tympanic, then percuss towards the head until you hear dullness (inferior edge of liver). Then keep percussing until you hear resonance (superior liver edge going into lungs). CVA tenderness: gently thump on patient’s back above kidneys to check for pain Palpation: light moderate deep palpation x 4 quadrants (may help to have patient bend knees) Feel for masses at different levels (light, moderate, deep). If the mass cannot be palpated when patient lifts their head up (flexing abdominal muscles), then mass is in abdominal cavity, not in abdominal wall. Check for hernias (umbilical, incisional hernias are a result of weakness of the abdominal wall) Check for guarding, rebound (“does it hurt more when I push in or when I let go?”) Liver and speen: try to push fingers under the ribcage and have patient breathe in (may be only able to palpate normal sized livers in thin individuals). Pulses: check for a midline pulsatile mass (aortic aneurysm), femoral Specific tests: see below! Cullen's sign Bluish periumbilical discoloration Retroperitoneal hemorrhage (hemorrhagic pancreatitis, abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture) Kehr's sign Severe left shoulder pain Splenic rupture Ectopic pregnancy rupture McBurney's sign Tenderness located 2/3 distance from anterior iliac spine to umbilicus on right side Appendicitis Murphy's sign Abrupt interruption of inspiration on palpation of right upper quadrant Acute cholecystitis Iliopsoas sign Hyperextension of right hip causing abdominal pain Appendicitis Obturator's sign Internal rotation of flexed right hip causing abdominal pain Appendicitis Grey-Turner's sign Discoloration of the flank Retroperitoneal hemorrhage (hemorrhagic pancreatitis, abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture) Chandelier sign Manipulation of cervix causes patient to lift buttocks off table Pelvic inflammatory disease Rovsing's sign Right lower quadrant pain with palpation of the left lower quadrant Appendicitis Blumberg’s sign Rebound tenderness (pain when releasing deep palpation) Peritoneal irritation Markle’s sign Have patient stand and hit heels on floor or hit heels (unexpectedly) to elicit pain Appendicitis Peritoneal irritaiton