Naming Ionic Compounds Notes
advertisement

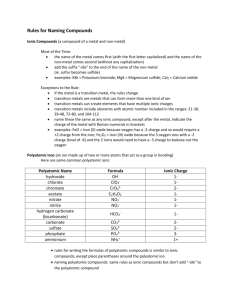
Naming Ionic Compounds Yesterday we talked about how to use the crossing over method to figure out the formulas for ionic compounds, and today we’re going to start to talk about what the names of these formulas are. What happens to electrons in an ionic compound? They are transferred What types of atoms are they usually being transferred from and to? From a metal to a nonmetal So, ionic compounds form between a metal and a nonmetal. Which one is the positive ion? The metal That leaves the nonmetal to be the negative ion. There are two parts to an ionic compound, and there are two parts to its name. Here are the two steps to follow to name a binary ionic compound: 1. The metal has the same name as its element 2. The nonmetal has the same name as its element, except the suffix has been replaced with an -ide Once we do some examples this should seem pretty easy. Let’s start with NaCl. What two elements are in this compound? Sodium and chlorine Which one is the metal? Sodium That leaves the chlorine for the nonmetal. So, let’s follow the rules to name this: 1. Sodium stays the same 2. Chlor-ine becomes chlor-ide So, what’s the name of this compound? Sodium chloride Try these next few in your notebook: MgO, KF, CaBr2, BeS Can you do it the other way around? Look on the periodic table for the charges of the ions and use them to write the formulas for these ionic compounds in your notebooks: Sodium iodide, hydrogen chloride, silver fluoride Those were specifically for binary ionic compounds. Remember those polyatomic ions? Well, they can form ionic compounds with metals also, but naming them is easy. Look at the table and tell me what you think the name of this compound is: AgNO3 Silver nitrate So, to name an ionic compound with a polyatomic ion in it, you still just keep the name of the metal, and then you just add the name of the polyatomic ion that you’re given on the table after it. Try these: Mg(OH)2, CaS2O3 The trick here is just to know to suspect a polyatomic ion if there are more than two elements in the ionic compound. Let’s practice naming and formula writing. For each of the following, write the name and draw the dot diagram of the compound: MgS, SrCl2, Li2O Write the formula for each of these compounds: Hydrogen cyanide, Potassium chloride, Barium sulfate, Calcium fluoride The Stock System Let’s review what we did yesterday: Try to write the formulas of these from their names: Sodium cyanide, calcium carbonate, copper nitrite What’s the problem with copper? It has more than one oxidation state What’s one possible formula for copper nitrite? What charge does the copper have there? CuNO2 +1 What formula could copper nitrite have if the copper has a + 2 charge? Cu(NO2)2 Now there is just one more thing that you need to know about naming ionic compounds. You’ve seen that some elements can be polyvalent – they can have more than one possible charge. This is true of most of the transition metals – the elements in the middle of the periodic table. For elements like those the type of name that we’ve been giving to the compound is not descriptive enough. The name copper nitrite could mean either CuNO2 or Cu(NO2)2 so there is one more thing that we have to add in order to say which one we mean. If you are naming a compound with a polyvalent ion in it you must use the stock system. This system is the same as what we had been doing by keeping the name of the metal and adding an –ide on the end of the nonmetal, but now we’re going to add in a Roman numeral after the metal to show which oxidation state that it has. So, for example, instead of just calling Cu(NO2)2 copper nitrite we can call it copper (II) nitrite to show that we’re using the +2 oxidation state of the copper, which would need 2 nitrites to go with it. Let’s try some examples. What are the names of two compounds that could be formed by iron and chlorine? Iron (II) chloride and iron (III) chloride. Knowing that the oxidation numbers have to add up to zero, we can figure out the formula for iron (II) chloride because we’re told what the charge on the iron is. If iron is +2, how many chlorines do we need to go with it to make the whole compound neutral? 2 So how do you write the formula for iron (II) chloride? FeCl2 What is the formula for iron (III) chloride? FeCl3 Here is a worksheet for practice (Do “The Stock System” worksheet)