Study Guide for Test on Plasma Membrane and Cell Transport
advertisement

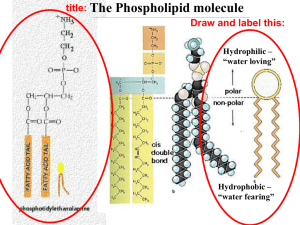
Review for Test on the Plasma Membrane (Chapter 3 sections 3-5) Be able to define selective permeable and explain how the selective permeability of the plasma membrane is necessary to maintain homeostasis of the cell. (Be able to define homeostasis). Understand the following information regarding the plasma membrane (also known as cell membrane): surrounds all cells is composed primarily of phospholipids, with some embedded proteins and other molecules. controls what materials can enter and exit the cell o is selectively permeable o has specific channels to allow needed materials into the cell that can’t pass through the phospholipid membrane Know the basic structure of a phospholipid molecule: phosphate group forms polar end of molecule 2 fatty acid tails (nonpolar) Be able to make a simple diagram of a phospholipid molecule and explain which part of the phospholipid molecule is hydrophobic and which part is hydrophilic Be able to explain that the phospholipids are arranged bilayer (double layer) in the membrane. Be able to diagram the orientation of phospholipids in plasma membrane bilayer: phosphate groups face outward lipid tails face interior of bilayer Know some possible functions of membrane proteins: channels to allow transport of certain molecules markers for cell-to-cell recognition receptors that receive signals from hormones etc. Be able to define diffusion and osmosis. Be able to define hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic solutions. Be able to determine which direction water will move when a cell is placed in each type of solution and whether the cell will shrink, expand and possibly lyse (burst) or remain unchanged. Know that since there is always random motion of molecules that in an isotonic solution water is moving in both directions through the membrane equally with no net change in size. Be able to explain what passive transport means and know that osmosis and diffusion are passive transport. Be able to explain that the limitation of passive transport is that it can only transport molecules from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. Be able to contrast passive transport (osmosis and diffusion) with active transport. Be able to define endocytosis and exocytosis. Be able to give an example of a situation where each of these processes would occur. Be able to define equilibrium and know the difference between a dynamic and a static equilibrium. Know which kind of equilibrium occurs for a cell in an isotonic solution.