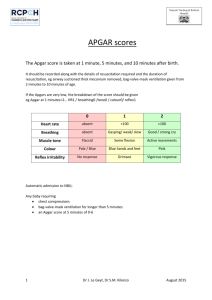
Tests for newborn
advertisement

VARIANT 1. 1. The neonatal period is the interval from: a) birth until 28 days after birth; b) birth until 7 days after birth; c) 8 til 28 days after birth; d) the 28th week of intrauterine life till the end of 7 day of infant’s life. 2. Name the chemical changes in the blood of neonate that help initiate the first respiration: a) low oxygen concentration; b) high carbon dioxide; c) low pH; d) a relatively cooler atmosphere. 3. What is the function of brown adipose tissue ? a) greater heat loss; b) conservation of heat; c) intensified heat production; d) hemopoiesis. 4. Apgar scoring system includes: a) heart rate; b) blood pulse; c) muscle tone; d) reflex irritability. 5. The child was born at term 32-33 wks of gestation with weight 1650 g. Make the diagnose. a) prematurity of I stage; b) prematurity of II stage; c) prematurity of III stage; d) term newborn. 6. Describe sucking reflex of the infant. VARIANT 2. 1. The early neonatal period is the interval from: a) Birth until 28 days after birth; b) birth until 7 days after birth; c) 8 til 28 days after birth; d) the 28th week of intrauterine life till the end of 7 day of infant’s life. 2. Name the primary thermal stimulus that help initiate the first respiration: a) a relatively cooler atmosphere; b) low oxygen concentration; c) high carbon dioxide; d) low pH. 3. Brown fat owes its name to: a) its larger content of fat acids; b) its larger content of lysosomes; c) its larger content of mitochondrial cytochromes; d) its larger nucleus. 4. Evaluations of all categories of Apgar scoring system are made at: a) 1 minute after birth; b) 1 and 5 minutes after birth; c) 2 and 5 minutes after birth; d) 1 and 10 minutes after birth. 5. The child was born at term 36-37 wks of gestation with weight 2350 g. Make the diagnose. a) prematurity of I stage; b) prematurity of II stage; c) prematurity of III stage; d) term newborn. 6. Describe rooting reflex of the infant. VARIANT 3. 1. The late neonatal is the interval: a. From birth until 28 days after birth; b. from birth until 7 days after birth; c. from 8 til 28 days after birth; d. the 28th week of intrauterine life till the end of 7 day of infant’s life. 2. The surface tension of the fluid in the alveoli of a newborn is reduced by: a) surfactant; b) detergent; c) lung fluid; d) exudate fluid. 3. Brown adipose tissue is located: a) between the scapula; b) around hips; c) around the neck; d) behind the sternum. 4. Total scores of 0 to 3 according to Apgar scoring system represent: a) severe distress; b) moderate difficulty in adjusting to life; c) absence of difficulty in adjusting to life; d) all variants are right. 5. The child was born at term 30-31 wks of gestation with weight 1400 g. Make the diagnose. a) prematurity of I stage; b) prematurity of II stage; c) prematurity of III stage; d) term newborn. 6. Describe grasp reflex of the infant. VARIANT 4. 1. The perinatal period is the interval from: a) Birth until 28 days after birth; b) birth until 7 days after birth; c) 8 til 28 days after birth; d) the 28th week of intrauterine life till the end of 7 day of infant’s life. 2. The surfactant is produced by: a) the lymphatic vessels; b) the pulmonary capillaries; c) the alveolar epithelium; d) the endothelium. 3. Deeper layers of brown adipose tissue are located: a) around the kidneys; b) around trachea; c) around the liver; d) around the heart. 4. Total scores of 4 to 6 according to Apgar scoring system represent: a) severe distress; b) moderate difficulty in adjusting to life; c) absence of difficulty in adjusting to life; d) all variants are right. 5. The child was born at term 39-40 wks of gestation with weight 3400 g. Make the diagnose. a) prematurity of I stage; b) prematurity of II stage; c) prematurity of III stage; d) term newborn. 6. Describe Babinski's reflex of the infant. VARIANT 5. 1. The intranatal period is the interval from: a) the beginning of delivery until the birth; b) birth until 28 days after birth; c) birth until 7 days after birth; d) 8 til 28 days after birth. 2. Surfactant acts like: a) detergent; b) lung fluid; c) exudate fluid d) blood. 3. The emptying time of the stomach in neonatal period is: a) 1-1.5 hrs; b) 2-2.5 hrs; c) 2.5-3 hrs; d) 3.5-4 hrs. 4. Total scores of 7 to 10 according to Apgar scoring system represent: a) severe distress; b) moderate difficulty in adjusting to life; c) absence of difficulty in adjusting to life; d) all variants are right. 5. The child was born at term 27-28 wks of gestation with weight 900 g. Make the diagnose. e) prematurity of I stage; f) prematurity of II stage; g) prematurity of III stage; h) prematurity of IV stage. 6. Describe Babinski's reflex of the infant. VARIANT 6. 1. The late antenatal period is the interval from: a) the 28th till the 40th week of intrauterine life. b) birth until 7 days after birth; c) 8 til 28 days after birth; d) the 28th week of intrauterine life till the end of 7 day of infant’s life. 2. The of: a) b) c) d) defficient secretion of surfactant in neonate leads to the development pneumonia of neonate; respiratory distress syndrome; asphyxia; absence of the first breath. 3. Passage of meconium should occur within the first: a) 36 hours; b) 24 hours; c) 12 hours; d) 6 hours. 4. A score of 1 (according to Apgar scoring system) is given to: a) Some flexion of extremities; b) Slow or irregular respiration; c) Good crying; d) Active motion. 5. The child’s ASS score at 1 min. is 6. Make conclusion. a) severe distress; b) moderate difficulty in adjusting to life; c) absence of difficulty in adjusting to life; d) all variants are right. 6. Describe Moro reflex of the infant. VARIANT 8. 1. The late neonatal is the interval: a. From birth until 28 days after birth; b. from birth until 7 days after birth; c. from 8 til 28 days after birth; d. the 28th week of intrauterine life till the end of 7 day of infant’s life. 2. The respiratory distress syndrome is the result of: a) Airway obstruction; b) infection related to accumulation of pulmonary secretion; c) ineffective airway clearance; d) surfactant defficiency. 3. What stools appear on the 2nd-3rd day of infants life? a) meconium; b) transitional stools; c) typical milk stools; d) diarrheal stools. 4. A score of 2 (according to Apgar scoring system) is given to: a) Some flexion of extremities; b) Slow or irregular respiration; c) Good crying; d) Active motion. 5. The newborn child at 1 min. after birth shows pink body with bluish extremities, heart rate 135 beats/minute, shallow and irregular respirations, the extremities are flexed and close to the body and the fist is tightly clenched, the response to passing a catheter is a loud, angry cry. What is his Apgar score? a) 10 points; b) 9 points; c) 8 points; d) 6 points. 6. Describe Perez reflex of the infant. VARIANT 9. 1. The late antenatal period is the interval from: a) birth until 7 days after birth; b) 8 til 28 days after birth; c) the 28th week of intrauterine life till the end of 7 day of infant’s life. d) the 28th till the 40th week of intrauterine life. 2. Respiratory distress syndrome more frequently develops in: a) preterm infants; b) term infants; c) postmature infants. 3. The yellow to golden in colour and pasty in consistency stools are called: a) meconium; b) transitional stools; c) typical milk stools; d) diarrheal stools. 4. A score of 2 (according to Apgar scoring system) is given to: a) Some flexion of extremities; b) Slow or irregular respiration; c) Cough or sneeze; d) Completely pink color of skin. 5. The newborn child at 1 min. after birth shows pink body with bluish extremities, heart rate 96 beats/minute, shallow and irregular respirations, the extremities are flexed and close to the body and the fist is tightly clenched, the response to passing a catheter is a facial grimace. What is his Apgar score? a) 9 points; b) 8 points; c) 7 points; d) 6 points. 6. Describe crawling reflex of the infant. Right answers to tests to newborn. V.1: 1-a; 2-a+b+c; 3-c; 4-a+c+d; 5-b. V.2:1-b; 2-a; 3-c; 4-b; 5-a. V.3:1-c; 2-a; 3-a+c+d; 4-a; 5-c. V.4:1-d; 2-c; 3-a+b; 4-b; 5-d. V.5:1-a; 2-a; 3-c; 4-c; 5-h. V.6:1-a; 2-b(допуск.c,d); 3-b; 4-a+b; 5-b. V.7:1-c; 2-d; 3-b; 4-c+d; 5-c. V.8:1-d; 2-a; 3-c; 4-c+d; 5-d.