4.2

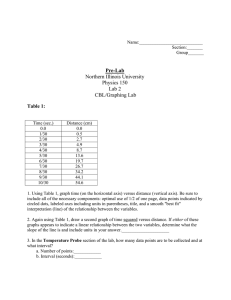
A function f has a local maximum (or relative maximum) at c if f (c)
≥
f (x) when x is near c [this means that f (c)
≥
f (x) for all x in some open interval containing c]. Similarly, f has a local minimum at c if f (c)
≤
f (x) when x is near c
Example:
1. f (x) = x 2 . Identify min and max values.
2. f (x) = x 3 . Identify min and max values.
Note: If f has a local max or min at c, then c is a critical number of f
The Closed Interval Method: To find the absolute max and min values of a continuous function f on a closed interval [a , b]
1. Find values of f at the critical numbers of f in (a , b)
2. Find the values of f at the endpoints of the interval
3. The largest of the values from steps 1 and 2 is the abs. max value, the smallest of these values is the abs. min value
Rolle's Theorem: Assume that f(x) is continuous on [a , b] and differentiale on (a , b). If f(a) = f(b), then there exists a number c between a and b such that f ' (c) = 0
Example 7: Show that f (x) = x 3 + 9x -
4 has at most one real root.