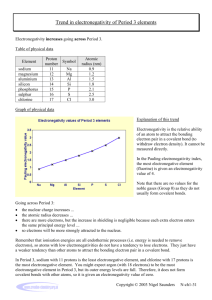
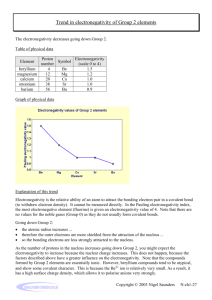
Electronegativity trends
advertisement
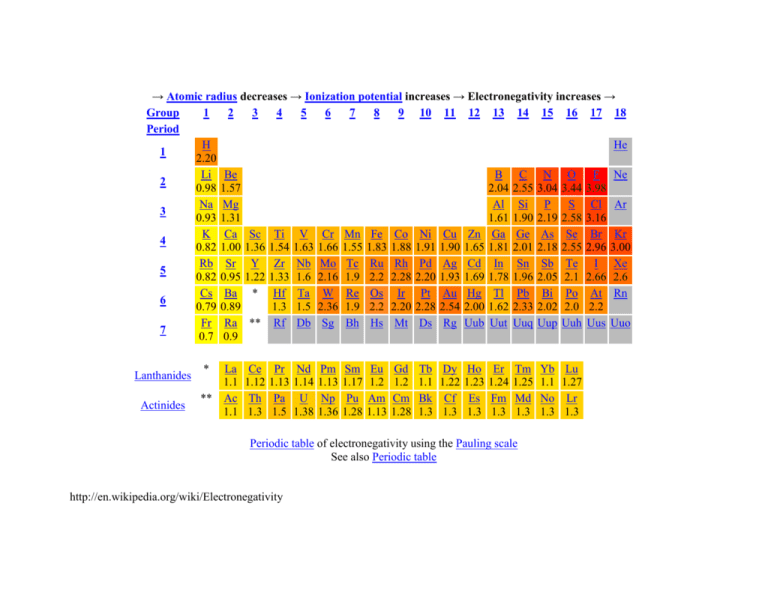
→ Atomic radius decreases → Ionization potential increases → Electronegativity increases → Group 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Period H He 1 2.20 Li Be B C N O F Ne 2 0.98 1.57 2.04 2.55 3.04 3.44 3.98 Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar 3 0.93 1.31 1.61 1.90 2.19 2.58 3.16 K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr 4 0.82 1.00 1.36 1.54 1.63 1.66 1.55 1.83 1.88 1.91 1.90 1.65 1.81 2.01 2.18 2.55 2.96 3.00 Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe 5 0.82 0.95 1.22 1.33 1.6 2.16 1.9 2.2 2.28 2.20 1.93 1.69 1.78 1.96 2.05 2.1 2.66 2.6 Cs Ba * Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn 6 0.79 0.89 1.3 1.5 2.36 1.9 2.2 2.20 2.28 2.54 2.00 1.62 2.33 2.02 2.0 2.2 Fr Ra ** Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Ds Rg Uub Uut Uuq Uup Uuh Uus Uuo 7 0.7 0.9 Lanthanides Actinides * La 1.1 ** Ac 1.1 Ce 1.12 Th 1.3 Pr 1.13 Pa 1.5 Nd 1.14 U 1.38 Pm 1.13 Np 1.36 Sm 1.17 Pu 1.28 Eu 1.2 Am 1.13 Gd 1.2 Cm 1.28 Tb 1.1 Bk 1.3 Dy 1.22 Cf 1.3 Ho 1.23 Es 1.3 Er 1.24 Fm 1.3 Tm 1.25 Md 1.3 Periodic table of electronegativity using the Pauling scale See also Periodic table http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronegativity Yb 1.1 No 1.3 Lu 1.27 Lr 1.3 Electronegativity trends Each element has a characteristic electronegativity ranging from 0 to 4 on the Pauling scale. The most strongly electronegative element, fluorine, has an electronegativity of 3.98 while weakly electronegative elements, such as lithium, have values close to 1. The least electronegative element is francium at 0.7. In general, the degree of electronegativity decreases down each group and increases across the periods, as shown below. Across a period, non-metals tend to gain electrons and metals tend to lose them due to the atom striving to achieve a stable octet. Down a group, the nuclear charge has less effect on the outermost shells. Therefore, the most electronegative atoms can be found in the upper, right hand side of the periodic table, and the least electronegative elements can be found at the bottom left. Consequently, in general, atomic radius decreases across the periodic table, but ionization potential increases. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronegativity