anatomy_lab6_13_3_2011
advertisement

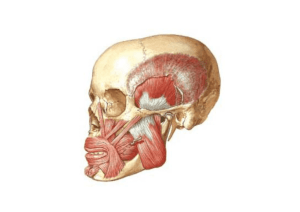
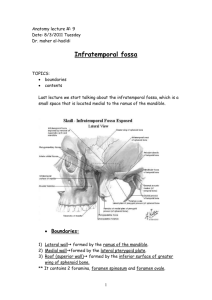
Infratemporal fossa anatomy lab#6 date: 13-3-2011 Boundaries: Anterior : infratemporal surface of maxilla which contains “posterior superior alveolar foramina” Posterior : head and neck of mandible , and the styloid process Laterally : Ramus of mandible Medially : lateral pterygoid plate Roof : Lateral pterygoid plate and Infratemporal part of greater wing of sphenoid which contains: Foramen ovale behind it foramen spinosum behind it spine of sphenoid Contents: 3 muscles : lateral pterygoid , medial pterygoid , temporalis 1 Artery : maxillary artery 2 Veins : maxillary vein and pterygoid plexus 3 Nerves : mandibular nerve V3 , chorda tympani , otic ganglion When we want to see the Infratemporal fossa in the lab we move the parotid gland, the masseter muscle, and the temporalis muscle. The ramus of the mandible removed in the lab to see the underlying structures. Muscles : Lateral pterygoid : it has 2 heads : superior and inferior (it is the key for infratemporal fossa because it divides the maxillary artery into divisions ) Superior head origin : from great wing of sphenoid Inferior head origin : from outer surface of lateral pterygoid plate Insertion : pterygoid fossa of neck of mandible , TMJ fibrous capsule , TMJ articular disk Action : protrusion and depression Medial pterygoid It has 2 heads : superficial and deep Deep origin : inner (medial) surface of lateral pterygoid plate . Superficial origin : tuberosity of maxilla . Insertion : inner surface of ramus and angle of the mandible Action : elevation and side to side movement Maxillary artery (the largest branch of external carotid artery) : The external carotid artery at the parotid gland divides into superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery which starts behind the neck of mandible then pass medial to the neck of mandible then to the lateral or medial surface the lateral ptrygoid , then it will dive through pterygomaxillary fissure to enter ptrygopalatine fossa . in its way it divides into 3 branches : 1st mandibular part “for spaces” it gives 5 branches 1) Inferior alveolar artery “the most important one”, which descend down with the inferior alveolar nerve 2) Middle miningeal artery (cut in the lab) 3) Accessory middle miningeal (not always exist but if it exists it pass through foramen ovale 4) Anterior tympanic : tympanic membrane 5) Deep auricular : external auditory meatus 2nd pterygoid part : passes lateral or medial to the lateral pterygoid and gives branches to muscles “lateral and medial pterygoid , masseter , temporalis” it gives 4 branches 1) deep temporal arteries 2) pterygoid arteries 3) masseteric artery 4) buccal artery 3rd pterygopalatine part (u can study it from Dr slides “slide num 20 cuz ma 7ka eshe gded) *Maxillary vein drains in Retromandibular vein which originate from superficial temporal and maxillary vein *Pterygoid venous plexus is a connection between facial nerve and cavernous sinus *otic ganglion and corda tempani can’t be seen Mandibular nerve is the largest branch of the V3 (trigeminal nerve ) pass through foramen ovale which gives miningeal branch which go back and pass through foramen spinosum . it ”mandibular nerve” descend down then it gives 6 motor branches to muscles. four muscles of mastication and the mylohyoid nerve which goes to mylohyoid muscle and anterior belly of digastric muscle (so total is 6) *Sensory beanches of mandibular nerve From anterior to posterior : Buccal , lingual , inferior alveolar , auriculotemporal 1)Buccal nerve : pass between 2 heads of lateral pterygoid , then pass medial to ramus of mandible , then in the cheeks , then it will go to the skin outer and mucosa inner to buccinator muscle The difference between it and the buccal branch of facial nerve ? 1)buccal nerve is inner ,and buccal branch of facial is outer 2)Lingual nerve: pass between lateral and medial pterygoid muscle the medial to the ramus of the mandible , then it will pass via groove close to the root of third molar then it will go the mouth to the anterior 2/3 of tongue and provide “general sensation”, but corda tempani carries the “special sensation” , the posterior third from glossopharyngeal nerve , the epiglottis from vagus nerve , so when we want to force our selves to vomit we put our finger on the epiglottis 3) Inferior alveolar nerve : pass between lateral and medial pterygoid muscle the medial to the ramus of the mandible , it will go to the inner surface of the mandible and enter through mandibular foramen supply the lower teeth and emerge as mental nerve 4)Auriculotemporal nerve : the only one which return back originate as 2 root , surround middle miningeal artery , and pass medial to TMJ بيلف لف حوليه and become behind it , pass anterior to external auditory meatus , the only one that cross the zygomatic arch , then supply auricle of the ear and temple muscle dedicated to all my friend wish you the best done by :Mohammad Ghanim