3-4 Questions
advertisement

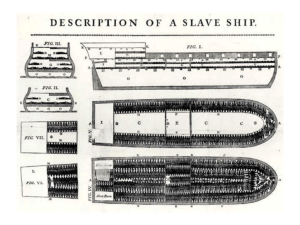
Chp 3 Section 4 pp. 96-100 Turbulent Centuries in Africa Intro: [Read quote by Olaudah Equiano] Enslaved Africans formed part of an international trade network that arose during the first global age. Africa was a diverse continent with ancient traditions, Islam, and Christianity all coexisting in some parts, as the Europeans arrived they brought their own traditions and virtually destroyed the culture [on the surface] of the Africans. 1. A. Middle Passage: Slaves were transported from Africa to the Americas, first to Spanish Colonies then later to the American Colonies. Pure hell on earth for the seized Africans, stuffed on ships men, women, and children, not uncommon for ½ of a load of slaves to die on the Middle Passage. Read Equiano’s quote p. 98 B. Asante: Kingdom in what is today Ghana, united by Osei Tutu, claimed divine right, set up government with qualified people regardless of birth right, created Monopolies in gold and slave trade, became wealthy and powerful in the late 1600s C. Usman dan Fodio: Islamic Preacher in the Fulani people of Nigeria, he denounced local rulers and convinced the poor to follow him and overthrew the Hausa govt. and set up a Powerful Islamic state that increased literacy, brought peace and improved trade. D. Boer: Dutch Farmers living in Cape Colony which is today South Africa drove Africans out of the area or enslaved them E. Shaka: Great Zulu leader who adapted fighting techniques to hand to hand combat, conquered large areas of south central Africa, eventually comes into conflict with Borers F. Great Trek: Boer Farmers leaving Cape Colony after it was taken over by the British and slavery outlawed, and traveling north from Southern Africa in the 1830s several thousand made this migration, coming into contact and defeating Africa tribes along the way, eventually defeating the ZULU. Spears no match for Dutch Guns. 2. A. Triangular Trade: Ships from Europe to Africa to trade gold, silver, and European goods for Slaves--- Ships from Africa to Caribbean Islands to trade Slaves for molasses and sugar—Ships from Caribbean to Europe to sell molasses and sugar B. Repeal: Take back, as in take back the ban on slave trade by Almany of Futa Toro C. Monopolies: Total control of a business or industry 3. A] Describe the attempts by Africans to stop the slave trade. King Affonso wrote to the King of Portugal, asking him to end the slave trade, the almamy of Futa Toro passed a law forbidding anyone to transport slaves through his land. B] What was the impact of the slave trade on life in Africa? The population of some regions of Africa decreases dramatically. Some societies and stats were destroyed. The African states that profited from the slave trade grew more powerful. 4. What steps did the Asante ruler take to ensure his power? Claimed to rule by divine right, created an efficient bureaucracy, conquered neighboring peoples, engaged in the slave trade, and avoided conflict with European powers. 5. How did southern Africa become a battleground for rival groups? Various groups like the Dutch, Zulu, and British migrated there and competed for control of the area, the trading ports on the cape of Hope were extremely valuable.