unit_10 - CLSU Open University
advertisement

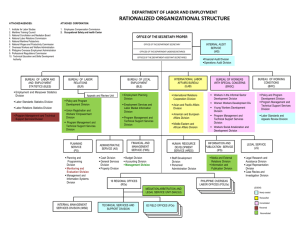
UNIT X THE DEPARTMENT OF INTERIOR AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT Introduction This is the ultimate unit of this self-learning material. It delves on the role of the Department of Interior and Local Government and its relation with local government units. Objectives of the Unit Objectives Unitthe student should be able to: At the endof of the this unit, Understand the role of the Department of Interior and Local Government in local governance; and Explain clearly the structure of the Department of Interior and Local Government and enumerate its powers and functions. Suggested Timeframe: 5 hours 146 Lesson 1. Role of the Department of Interior and Local Government in Local Governance Lesson 1 Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: 1. Describe the role of the Department of Interior and Local Government in local governance; and 2. Enumerate the powers and functions of the Department of Interior and Local Government. Powers and Functions of the DILG The DILG is the national agency primarily tasked to assist the President in the exercise of general supervision over local government units. The President of the Philippines exercises only general supervision over local governments (Sec. 25, LGC). This is in consonance with the declared basic policy of the State to allow the territorial and political subdivisions autonomy (Sec. 2, Art. X, Constitution). The President exercises supervisory authority directly over provinces, highly urbanized cities, and independent component cities through the province with respect to component cities and municipalities; and through the city and municipality in relation to barangays. The Department is mandated to perform the following powers and functions: Advise the President on the promulgation of policies, rules, regulations and other issuances relative to the general supervision of local government units; Establish and prescribe rules, regulations and other issuances and implementing laws on the general supervision of local government units; 147 Provide assistance in the preparation of national legislation affecting local government units; Establish and prescribe plans, policies, programs and projects to strengthen the administrative, technical and fiscal capabilities of local government offices and personnel; Formulate and implement policies, plans, programs and projects to meet national and local emergencies arising from natural and man-made disasters; and Perform such other functions as may be provided by law (Sec. 2, Chapter I, Title XII, Administrative Code). The Department of Local Government, created under Title XII of Executive Order No. 292, otherwise known as the Administrative Code of 1987, was reorganized into a Department of Interior and Local Government by R.A. No. 6975, also known as the Department of Interior and Local Government Act of 1990. Participation of Local Executives in the Administration of the PNP Powers of Local Government Officials over the PNP Units Governors are deputized by the Code as representatives of the Commission in their respective territorial jurisdictions. Relative to this and as such, the local government executives are required under Sec. 51 of the DILG Act of 1990 to perform or discharge certain functions which are enumerated hereunder. 1. Provincial Governor: 1.1 The power to choose the Provincial Director from a list of three (3) eligibles recommended by the PNP regional director. 1.2 As chairman of the provincial peace and order council, the governor shall oversee the implementation of the provincial 148 public safety plan, which is prepared taking into consideration the integrated community safety plans. 2. City and Municipal Mayors 2.1 The city and municipality mayors exercise operational supervision and control over PNP units in their respective jurisdictions except during the thirty-day period and thirty (30) days following or after any national, local or barangay election. During these periods, the local police forces are placed under the supervision and control of the Commission on Elections. The power of operational supervision and control includes the power to employ and deploy units or elements of the PNP, through the station commander, to ensure public safety and effective maintenance of peace and order within the locality. Definition of Terms Supervision means overseeing or the power or authority of an office, in this case the President, to see that subordinate officers perform their duties. If the latter fail to or neglect to fulfill them, then the former may take such action or steps as prescribed by law to make them perform their duties (Mondaño v. Silvosa, 97 Phil. 43). Operational Supervision and Control shall mean the power to direct, superintend, oversee and inspect the police units or forces. Employ refers to the utilization of units or elements of the PNP for purposes of protection of lives and properties, enforcement of laws, maintenance of peace and order, prevention of crimes, arrest of criminal offenders and bringing the offenders to justice, and ensuring public safety, particularly in the suppression of disorders, riots, lawless violence, rebellions or sedition, conspiracy, insurgency, subversion other related activities. Deploy means the orderly and organized physical movement of elements or units of the PNP within the province, city and municipality for purposes of employment as hereinabove. 149 Lesson 2. Organizational Structure of the DILG Lesson 2 Objectives This lesson aims to attain the general objective of describing the various offices comprising the organizational structure of the Department of Interior and Local Government. It seeks to achieve the following specific objectives, namely: 1. Enumerate and describe offices constituting the department proper including their powers and functions and other matters; and 2. Explain the set-up of the various bureaus that comprise the Department of Interior and Local Government and its association with the regional offices as well as discuss the powers and functions of the same. Set-Up of the DILG The Department is composed of the Department Proper and the bureaus and offices of the Department of Local Government, the National Police Commission, the Philippine Public Safety College, and the following bureaus: the Philippine National Police, the Bureau of Fire Protection, and the Bureau of Jail Management and Penology (Sec. 6, R.A. No. 6975). The staff and line offices of the DLG referred to above consist of the following: Bureau of Local Government Supervision; Bureau of Local Government Development; National Barangay Operations Office; Project Development Services; Department Services; Office of Public Affairs; and Regional and Field Offices 150 The Department Proper The department proper consists of the existing staff services as provided for by E.O. 292 and Office of the Secretary, which consists of the Secretary and his immediate staff, and the Offices of the Undersecretaries and Assistant Secretaries. The Secretary is assisted by two (2) Undersecretaries, one (1) for local government and the other for peace and order and three (3) career Assistant Secretaries. At least one of the undersecretaries belongs to the career executive service (Sec. 7, R.A. 6975). The Secretary The secretary is the head of the department and acts as ex-officio chairman of the National Police Commission. The secretary is appointed by the President of the Philippines, which appointment to be valid and effective, must be confirmed by the Commission on Appointments1. R.A. No. 6975 prohibits the appointment of a retired or resigned military officer or police official as Secretary within one year from the date of his retirement or resignation. (Sec. 8). Powers, Term of Office and Compensation In the Secretary is vested the authority and responsibility for the exercise of the powers and functions of the Department. The secretary holds office at the pleasure of the President of the Philippines. He is entitled to receive the compensation, all the allowances and other emoluments to which heads of departments are entitled (Sec. 9, R.A. 6975). In addition to the powers and functions exercised by the Secretary enumerated in sec. 3 of E.O. 292, the Secretary as head of the Department: Periodically prepares and submits reports, which include a Quarterly Anti-Crime Operations Report and such other reports as the President and Congress may require; Chairs and presides (NAPOLCOM); and Delegates authority to exercise any substantive or administrative function to the members of the NAPOLCOM or other officers of rank within the Department (Sec. 10, R.A. 6975). over the National Police Commission 151 Department Services The Department maintains five (5) services, namely: Planning Service; Financial and Management Service; Legal Service; Administrative Service; and Electronic Data Processing Service. Planning Service The Planning Service’s responsibility is to provide the Department with efficient and effective services relating to planning, programming, research and statistics (Sec. 7, E.O. No. 292). Financial and Management Service The Financial and Management Service is responsible in providing the Department with efficient and effective staff advice and assistance on budgetary, financial and management improvement services (Sec. 8, E.O. No. 292). Legal Service The Legal Service provides the Department with efficient and effective legal counseling services, assistance to the Secretary in the review or determination of subordinate bodies or agencies, collaboration with the solicitor general in handling cases affecting the Department, and investigation of administrative cases involving Department personnel and local officials (Sec. 9, E.O. No. 292). Administrative Service The Administrative Service provides the Department with efficient and effective services related to personnel, information, records, supplies, equipment, collection, disbursement, security and custodial work, and other 152 kinds of services not related to other services mentioned above (Sec. 10, E.O. No. 292). Electronic Data Processing Service The Electronic Data Processing Service’s responsibility is to provide adequate and up-to-date data and management information inputs, including monitoring of all field operations, to serve as basis foe effective planning, management and control, policy formulation and decision-making (Sec. 11, E.O. No. 292). Bureaus and Offices As stated earlier in this module, the Department consists of the bureaus and offices of the Department of Local Government as provided in Sec. 4 of E.O. No. 292 and those provided in R.A. No. 6975. The bureaus and offices of the Department of Local Government were the Bureau of Local Government Supervision, the Bureau of Local Government Development, Office of Public Affairs, Local Government Academy, National Barangay Operations Office and Office of Project Development Services. Under R.A. 6975, the DILG has two bureaus, namely: the Bureau of Fire Protection and the Bureau of Jail Management and Penology. The Philippine National Police is considered and is in the status of a bureau. The Bureau of Local Government Supervision Sec. 12, Chapter 4 of Title XII, E.O. No. 292 provides that the Bureau of Local Government Supervision, headed by a Bureau director who is appointed by the President of the Philippines upon the recommendation of the Secretary, undertakes the following functions: Advise and assist the Secretary in the exercise of the power of supervision of the President over local government units, particularly in the formulation and implementation of national laws, policies and standards concerning local government operations and their personnel; Establish and prescribes guidelines for the administration of the Katarungang Pambarangay Laws; 153 Monitor compliance with national laws and policies by local government units; Provide assistance in the preparation of national legislation affecting local government units and in the promotion of local autonomy; Extend consultation services and advice to local government units involved in promoting local autonomy; Provide assistance to local governments in the promotion of citizens’ participation on local government activities; and Provide financial and technical assistance, as well as secretarial services to the Leagues of Provinces, Cities, and Municipalities. Bureau of Local Government Development The Bureau of Local Government Development is headed by a Bureau Director who is appointed by the President of the Philippines upon the strength of the recommendation of the Secretary. What functions are performed or are to be performed by the Bureau of Local Government Development (BLGD)? Sec. 13, Chapter 4 of title XII of E.O. No. 292, enumerates seven (7) major functions of the BLGD, namely: Establish and prescribe plans, programs, and projects to strengthen the administrative and technical capabilities of local government offices and personnel; Provide technical assistance to enhance the administrative, fiscal and technical capabilities of local government officers and personnel; Formulate, prescribe and periodically evaluate local development policies, plans, programs and projects designed to enhance the participation of local government units in planning and implementation; Establish a system of incentives and grants to local governments and prescribes policies, procedures and guidelines in the implementation of self-help assistance projects; 154 Formulate and develop models, standards and technical materials on local government development; Extend consultation service and advice to local government units involved in development programs; and Establish a viable system of strategies and approaches for local governments anchored on citizens’ participation within a holistic and integrated framework for the development of communities. Office of Public Affairs The Office of Public Affairs is mandated to: Provide technical assistance in the modernization and maintenance of a Department-wide micro-telecommunications systems; Provide mechanisms for the operationalization of the intent of the provisions of public information, coverages and documentation of the activities of the Department; Perform functional supervision over regional information centers in providing the citizenry with relevant information on the programs of the Department and the Government’s thrust towards the participation of the citizens in the democratic processes; Formulate plans and programs to implement the administrative and technical capabilities of public officers and personnel both on the central and regional levels; Extend consultation services and advice in the implementation of Regional Information Services; Assess information needs of the people through opinion polls and surveys; Provide assistance on various public programs of the Department; Establish and implement policies, plans, programs and projects to meet local emergencies arising from natural and man-made disasters; and Undertake projects assigned by the Secretary in the effective delivery of public services (Sec. 14, Chapter 3, Title XII, E.O. No. 292). 155 Local Government Academy The Academy is under the direct supervision of a Board of Trustees composed of the Secretary of the Interior and Local Government as Chairman and four (4) other members appointed by the President of the Philippines upon the recommendation of the Secretary. The Academy is responsible for human resource development and training of local government officials and Department personnel (Sec. 15, Chapter 3, Title XII, E.O. 292). National Barangay Operations Office A Director, appointed by the President of the Philippines upon the recommendation of the Secretary, heads the National Barangay Operations Office. The Office is mandated by Sec. 16, Chapter 3, Title XII, E.O. 292, to perform the following functions, as follows: Formulate policies, plans and programs that will promote community and citizen participation in the political development of the barangay through the mobilization and participation of barangay assemblies; Initiate projects on innovative barangay development strategies and approaches in close coordination with the Bureau of Local Government Development; Provide secretariat services to the Association of Barangay Councils and serve as a clearing house on matters affecting barangay officials’ insurance, hospitalization, educational and other benefits as provided by law; Provide continuing information dissemination to barangay units on national development efforts and issues in order for barangay assembly members to participate meaningfully in national development; Establish and maintain master lists of barangay, barangay officials and barangay socio-economic profiles; and Provide situational and political analysis for the Secretary on barangay affairs. 156 Office of Project Development Services The Office is tasked to perform the following functions, to wit: 1. Formulate innovative approaches and strategies designed to promote technical capabilities of local government; and 2. Assist in the development of program components for the implementation of tested and appropriate systems and processes at the local level (Sec. 17, Chap. 3, Title XXII, E.O. No. 292). In addition to the major functions hereinabove stated, foregoing bureaus and offices may be required to perform other functions as may be delegated by the Secretary or as required by law. Regional Offices To implement the policies and programs of the department in different regions of the country are its regional and field offices. For this reason, there is in each of the administrative regions of Philippines established, operated and maintained regional offices (Sec. 11, R.A. 6975; Sec. 18, E.O. No. 292). Each regional office is headed by a regional director who is assisted by two (2) assistant regional directors: one (1) for jail management and another for fire protection (Ibid). Within its administrative region, the regional office performs the following functions: Implement law, rules, and regulations, other issuances, policies plans, programs and projects of the Department; Provide efficient and effective service to local government; Coordinate with regional offices of other departments, offices and agencies matters affecting local administration and development; Assist local government units in developing their capabilities for local government administration and development; and Perform such other functions as may be delegated by the Secretary or as provided by law (Sec. 18, E.O. 292). 157 Activity One of the major issues confronting local government executives nowadays is the control of local police units and forces. Find out the pros and cons of subjecting to the control of municipal and city mayors local PNP units and forces by interviewing local chief executives and PNP officials and men. Report your findings in the class. Unit Summary Unit X presented the role of the Department of Interior and Local Government in local governance particularly in regard to the exercise by the President of the power of general supervision over local government units. This unit likewise explained the organizational structure of the DILG including the various department services and the bureaus and offices that constitute it.