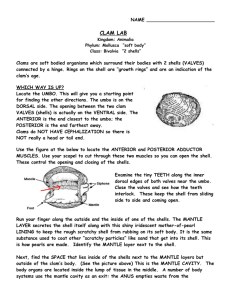
An invertebrate with a soft un-segmented
advertisement

An invertebrate with a soft un-segmented body often enclosed in a hard shell containing calcium carbonate; examples include snails, clams,& squids MOLLUSK Free swimming, ciliated larva seen in mollusks and some annelids TROCHOPHORE The epidermal layer (outside surface) of mollusks; In a clam, it makes the shell MANTLE A rough, flexible tongue-like strip covered with tough, abrasive teeth used in feeding by most mollusks except bivalves A aquatic mollusk with a shell divided into two halves connected by a hinge, such as a clam oyster, or scallop BIVALVE In a mollusk the body region, located between the head-foot and the mantle, that contains the heart, digestive, excretory, & reproductive organs VISCERAL MASS A space between the mantle and the visceral mass in mollusks (In a clam, it’s the space seen when the shell is opened) MANTLE CAVITY A mass of nerve cells is called a _________ GANGLION (pl. GANGLIA) RADULA Process during larval development of gastropods in which the visceral mass twists 180° so the tail ends up in towards the front of the body near the head TORSION What do we call circulatory fluid (blood) in an animal with an open circulatory system What do we call the fluid filled body cavity or space in an invertebrate with an open circulatory system The tube through which water ENTERS the mantle cavity of a bivalve = ? HEMOCOEL HEMOLYMPH INCURRENT SIPHON A tube through which water EXITS the mantle cavity of a bivalve In animals, a respiratory organ specialized for the exchange of gases with water EXCURRENT SIPHON Name the fan-like structures at the anterior end of a clam that move food trapped on the gills forward and into the mouth GILL Name the muscles used by a bivalve to open and close its shell PALPS ADDUCTOR MUSCLE Name the pigment cells located in the outer mantle in cephalopods that can produce a sudden color change for camouflage A free swimming, predatory mollusk with a circle of tentacles extending from the head such as an octopus, squid, cuttlefish or a chambered nautilus CHROMATOPHORES A mollusk that has one or no shell and moves by gliding on a muscular foot such as a snail, slug, and nudibranch GASTROPOD Mollusks are ______________ Invertebrate protostomes Invertebrate deuterostomes Vertebrate deuterostomes Name the excretory organ found in clams KIDNEY CEPHALOPOD Clams have ______________ development DIRECT INDIRECT Bivalves and gastropods have _______ circulation. OPEN CLOSED To which body system do kidneys belong? EXCRETORY Give the function for kidneys. This word describes organisms that stay in one place and don’t move much Collect & remove nitrogen waste; osmoregulation Cephalopods have ________ circulation OPEN The name MOLLUSK comes from the Latin word meaning ____________ CLOSED All aquatic mollusks except cephalopods have ____________ development. DIRECT SESSILE INDIRECT The name BIVALVIA comes from the Latin words meaning ________________ TWO SHELLS SALT All clams ______________ have separate sexes The mollusks with the most advanced brain are the _____________ BIVALVES are hermaphrodites GASTROPODS CEPHALOPODS Mollusks have a(n) ________________ acoelom Marine clams live in _____________ water. FRESH SOFT pseudocoelom eucoelom Bivalves have ___________ symmetry no radial bilateral An organism that has both male and female reproductive organs is called a(n) _______ HERMAPHRODITE Mollusk group in which most organisms have 1 SHELL GASTROPODS Mollusk group in which most organisms have NO SHELL CEPHALOPODS Name the KINGDOM for clams. ANIMALIA Name the CLASS for clams. BIVALVIA TRUE OR FALSE: The space seen when you open a clam’s shell is its coelom. Mollusk group in which organisms have 2 SHELLS BIVALVIA (BIVALVES) Name the only group of mollusks that does NOT have cephalization BIVALVES Name the PHYLUM for clams. MOLLUSCA (MOLLUSKS) Give the KINGDOM, PHYLUM, & CLASS for clams. Kingdom: Animalia; Phylum: Mollusca; Class: Bivalvia The space surrounding the heart in a clam is called the ______________ space. PERICARDIAL CAVITY (COELOM) FALSE: it’s the mantle cavit.; the coelom is the pericardial cavity Mollusks have a________________ Tell the all purpose word for reproductive organs Ventral nerve cords/dorsal heart GONADS Dorsal nerve cords/ventral heart Organisms that strain food out of water are called ______________ feeders FILTER digestive, excretory, reproductive Give TWO functions for gills in a clam. GAS EXCHANGE & TRAP FOOD The umbo on a clam’s shell is located closer to the ___________ end. ANTERIOR POSTERIOR Bile works to help break down _______ carbohydrates fats proteins Which part in a clam collects and removes digestive waste? INTESTINE Name the muscular part of a clams body used for locomotion FOOT Name the THREE body systems that used the mantle cavity as an EXIT. The bump on a clams shell is called the _____ UMBO The part in a clam that makes bile is the ? DIGESTIVE GLAND Which body part in a clam finishes digestion and absorbs nutrients? DIGESTIVE GLAND Name the exit opening for digestive waste. ANUS Name the part that starts digestion and grinds up food. STOMACH To which body system does the heart belong? To which body system does the intestine belong? CIRCULATORY To which body system do gonads belong? REPRODUCTIVE Give a function for the heart? PUMP BLOOD Name the substance is produced by the digestive gland that helps break down fats BILE Name the chemical that makes clam shells hard. CALCIUM CARBONATE To which body system do ganglia belong? NERVOUS DIGESTIVE To which body system does the gills belong? RESPIRATORY Give a function for the intestines in a clam collect/remove digest waste Name the muscles that control the opening and closing of the clam’s shell ADDUCTOR MUSCLES Tell the number of ganglia and nerve cords found in a clam. 3 pairs of ganglia; 2 pairs of nerve cords Which part in a clam traps food? GILLS Tell one way clams are different from earthworms. Earthworms: closed circulation; direct development; cerebral ganglia & 1 nerve cord;hermaphrodites; breath through skin; nephridia; cephalization Clams: open circulation; indirect development; multiple ganglia/nerve cords; separate sexes; breathe with gills; kidneys; no cephalization Tell one way clams are different from earthworms. Earthworms: closed circulation; direct development; cerebral ganglia & 1 nerve cord;hermaphrodites; breath through skin; nephridia; cephalization Clams: open circulation; indirect development; multiple ganglia/nerve cords; separate sexes; breathe with gills; kidneys; no cephalization Tell one way clams and earthworms are alike. Both: invertebrate protostomes; eucolom; Sexual reproduction; ventral nerve/dorsal heart 2 opening digestive system Tell one way clams and earthworms are alike. Both: invertebrate protostomes; eucolom; Sexual reproduction; ventral nerve/dorsal heart 2 opening digestive system