Dissection For Mussels/Clams WS Name: PreLab Questions: 1. To
advertisement

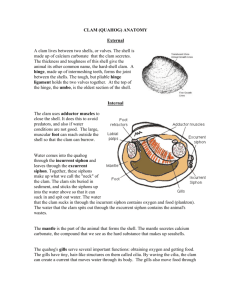
Dissection For Mussels/Clams WS Name: PreLab Questions: 1. To what phylum does the clam belong? 2. What does the name of the phylum translate (from the Latin language) to mean? 3. List six common members of the phylum Mollusca. 4. What does it mean when an organism is bilaterally symmetrical? 5. What element (from the Periodic Table) is a major component of a calcareous shell? 6. Name the three main body regions of a mollusk. 7. To what class does the clam and mussel belong? 8. What does the name of the class translate to mean? 9. What does it mean if an animal is called a bivalve? 10. List five common members of the class Pelecypoda. External Anatomy Questions: 1. Describe the location of the hinge in relation to the two shell-halves. 2. What is the name of the oldest part of the clamshell? 3. ATTEMPT (sometimes this is difficult) to count the number of concentric growth lines (think about tree rings) on the shell. What is your best estimate? Label the drawings of the clamshell: dorsal, ventral, anterior, posterior, right valve, left valve, umbo, and hinge. The terms can be used more than once if necessary. Dissection Questions 1: 1. Describe what happened when acid was placed on the exposed prismatic layer. 2. Describe a situation where what you observed might actually be applied to the clam in its natural environment. 3. Name the material (chemical) that makes up the clamshell. 4. What do you believe the chemical formula of the material is? Shell Anatomy Questions. 1. How many layers make up the "shell" of the clam? 2. How many layers make up the "mantle" of the clam? 3. Which part of the clamshell forms pearls? 4. A pearl is formed as a reaction to a ___________between the shell and mantle. Internal Anatomy Questions: 1. What forms the "scars" on the valves? 2. Describe the inner layer of the shell. Label the drawing with the following structures: anterior adductor muscle, posterior adductor muscle, incurrent siphon, excurrent siphon, mantle, and right valve On the diagram, label each of these parts: visceral mass, reproductive organ, stomach, anus, digestive gland, intestine, anus, pericardial cavity, heart, and kidneys. Conclusion Questions: 1. Name the three main classes of mollusks and give an example of each. 2. How are mollusks classified (which phylum)? 3. What structures hold the two shells together in a bivalve mollusk? 4. What type of feeder is the clam? 5. As water goes through the clam's body, what does it bring in? 6. As the water goes through the clam's body, what does it take out? Reproduction Questions: 1. What is the advantage of being attached to the gills or fins of a host? 2. What is a glochidium? 3. What type of relationship does the fish and larva have?