Document
advertisement

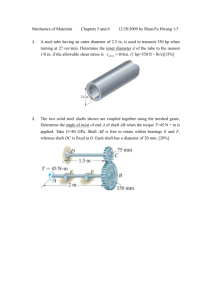
Tutorial: Torsion Problem 1 (br141) A hollow cylindrical steel shaft is 1.5m long and has inner and outer diameters respectively of 40 and 60mm. (a) What is the largest torque that can be applied to the shaft if the shearing stress is not to exceed 120MN/m2 (b) What is the corresponding angle of twist. T 4084Nm 0.075rad (4.3) Problem 2 (hrn8.0) A shaft 20mm diameter and 500mm long carries a torque of 400Nm determine shear stress and angle of twist (G=80GN/m2) [254.6MN/m2, 9.11o] Determine the diameter necessary in order to halve the stress. [25.2mm] Determine the diameter necessary in order to halve the angle of twist. [23.8] Problem 3 (hrn8.1) A solid steel shaft A of 50mm diameter rotates at 250rev/min. Find the greatest power that can be transmitted for a limiting shearing stress of 60 MN/m2 in the steel. … It is proposed to replace A by a hollow shaft B, of the same external diameter but with a limiting shearing stress of 75 MN/m 2. Determine the internal diameter of B to transmit the same power at the same speed. [38.6 kW, 33.4 mm] Problem 4 () A solid shaft of diameter 40mm used to transmit power between one point and another. If the limiting shear stress is 120MN/m2 and the speed of rotation is 300RPM. Calculate the max power which may be transmitted. [ 47.4kW]. If the shaft is replaced by a hollow shaft 50mm external diameter and of equal weight (same CSA), calculate the new power which may be transmitted if limited to the same maximum shear stress. [80.5kW]. Problem 5 (Hib5-74 p220) A rod is made from two segments: AB is steel and BC is brass. It is fixed at its ends and a torque of 800Nm is applied at the interface B. If the steel portion AB has a diameter of 30mm and the brass section has a diameter of 40mm determine the reaction torques at A and C, the Gst = 80GN/m2 shear stress in each section and the angle of Gbr = 40GN/m2. twist at B. [ 1 86.7 2 27.1MN / m2 1,2 3.1 ] Problem 6 () The rod shown is gripped tightly at one end and twisted by applying a torque at the other end. Determine the diameter of B so that its shear stress will be Gst = 80GN/m2. double that in A. [ d 15.87mm ] If the free end is turned to an angle of 5 degrees determine, the twist ratio, the torque required and the stresses induced in each section. [ B 1.081 A ; T 75.2Nm ; A 47.87MN / m2 ; B 95.82MN / m2 ] 29 November 2010 Tutorial: Torsion 29 November 2010