On-line Sedimentary Rock Identification Lab
advertisement

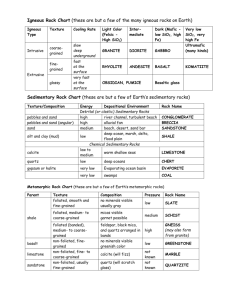
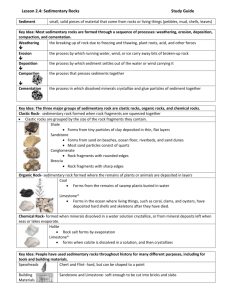
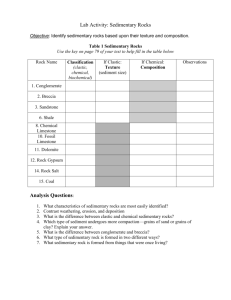
On-line Sedimentary Rock Identification Lab http://facweb.bhc.edu/academics/science/harwoodr/Geol101/Labs/Sediment/ Part 1: a. Go to the website above. b. You will need to read each section in order to complete the questions below. c. It will be necessary for you to click on each underlined word. This will provide you with a complete explanation and illustration of each key term. d. All questions must be completed correctly prior to moving on the Part 2. 1. How is sediment deposited? Sediment is deposited in numeral environment through out the world, by moving air and water. 2. What is sedimentary rock identification based on? It’s based on the rocks composition. 3. In this lab, what does “texture” mean? Texture is the sediment, chemical and biological substances that make up the rock. 4. What are the 3 types of texture? 1. Gravel 2. Calcite 3. Caron 5. What are “clasts?” Clasts are fragments, pieces of rock or minerals. 6. How are chemical sedimentary rocks identified? By identifying the mineral from which they are composed. 7. What are the 4 minerals that need to be identified in order to classify a sedimentary rock? 1. 2. 3. 4. Quartz Halite Gypsum Calcite. 8. How do “biological” rocks form? They form as the result of the accumulation of organic material or biologic activity. 9. What is an obvious characteristic of coal? The dark brown to black color is the most obvious characteristic. 10.Coquina and limestone are both composed of the same mineral. What is it? Calcite 11.What is the difference between coquina and limestone? Almost entirely shell and skeletal fragments. Part 2: a. At the bottom of the web page you will find a link saying “select a sample to identify.” b. You will need to identify each of the 12 sedimentary rocks shown. c. As you identify the rocks, mark your answers to each category: texture; grain size; composition; and rock name on the following pages for each of the 12 rocks. d. There are hints given on each one including reaction to HCl, hardness, and more detailed images – use them! Texture 1 Grain size 4 5 6 7 None Calcite limestone biologic none Coquina Chemical none Calcite, almost entirely shell and skeletal fragments Gypsum biologic none Fossiliferous Limestone Clastic <1/16mm calcite with some shell and skeletal fragments quartz, clay minerals Clastic >1/16mm feldspar, quartz Arkrose Chemical none gypsum Rock gypsum Clastic >2mm Conglomerate Chemical none rounded quartz, feldspar and rock fragments silica (quartz) 8 9 Rock Name Chemical 2 3 Composition Rock Gypsum Siltstone (mud, shale) Chert 10 11 12 clastic 1/16-2mm Quartz, feldspar Sandstone clastic 1/16-2mm Quartz feldspar Sandstone biologic none densely compacted organic material and plant fragments Bituminous Coal