syllabus - Capital High School
advertisement
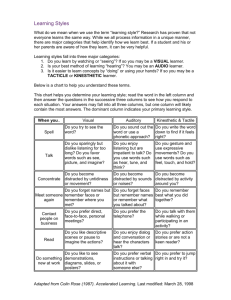
CAPITAL HIGH SCHOOL BUSINESS EDUCATION MOS: WORD CORE CIP Code: 110620 Course Title: MOS: Word Core Course Description: MOS: Word Core is an exploratory course designed to teach the competencies necessary to complete the Microsoft Office Specialist (MOS) core test for Word 2002. Purpose of Course: To provide skills to productively use Microsoft Word 2002. The Microsoft Office Specialist (MOS) program is helping meet the demand for qualified and knowledgeable people in the modern workplace. Graduation Requirement: Elective course; fulfills 1 occupational education credit per semester Prerequisite: DigiTools Course Level: 9th to 12th grade Class Fees: None Course Length: 90 hours (1 semester) SYLLABUS MOS: Word Core is a 90-hour exploratory course designed to teach the competencies necessary to complete the Microsoft Office Specialist (MOS) core test for Word 2002. It is a foundational course for students in the Business and Marketing Pathway and prepares students for any of the five career clusters (identified by the U.S. Department of Education States Career Clusters) in the Business and Marketing Pathway. COURSE OVERVIEW The outline below gives an overview of the components of the MOS: Word Core course. This framework includes the performance task/assessment, standards and competencies, and connection to Washington State Education Reform Initiatives including EALRs and Goals 1-4. The standards for this framework are taken from the Microsoft® Office Specialist (Office Specialist) program, a globally recognized standard for demonstrating desktop skills with the Microsoft Office suite of business productivity applications. COURSE OUTLINE Integrated Standards 3 weeks Inserting and Modifying Text 3 weeks Creating and Modifying Paragraphs 3 weeks Formatting Documents 3 weeks Managing Documents 3 weeks Working with Graphics 3 weeks Workgroup Collaboration D:\533575438.doc Rules, Expectations, Introductions, Ergonomics Career Development, Ethical Responsibilities, Leadership, Safety and Security, Teamwork Insert, modify, and move text and symbols Apply and modify text formats Correct spelling and grammar usage Apply font and text effects Enter and format Date and Time Apply character styles Modify paragraph formats Set and modify tabs Apply bullet, outline, and numbering format to paragraphs Apply paragraph styles Create and modify a header and footer Apply and modify column settings Modify document layout and Page Setup options Create and modify tables Preview and Print documents, envelopes, and labels Manage files and folders for documents Create documents using templates Save documents using different names and file formats Insert images and graphics Create and modify diagrams and charts Compare and Merge documents Insert, view and edit comments Convert documents into Web pages COURSE STRATEGIES Teaching Strategies for Students with Different Learning Styles. There are many different learning styles. Some people learn best from reading material. Others need to see a demonstration or learn by feeling. Still others may learn best from auditory cues. It is important to remember, however, that no matter what learning style works best for any individual, learning style is not an indicator of intelligence. Two people of similar levels of intelligence may learn best in two different styles of learning. Learning style is also not necessarily a rigid behavior. Many individuals may have a dominant learning style; however, most also have the flexibility to adapt learning style to the demands of the material to be learned. Different learning styles include print, visual, auditory, tactile, and kinesthetic learning. Print Learners. The print learner prefers to see the data in print—preferably printed in words. For example, a print learner would prefer to study the illustration. Visual Learners. The visual learner needs to “see” the concept. One way for the learner to “see” the concept is mental visualization. Illustrations and visual aids are important to the visual learner. Auditory Learners. The auditory learner will best learn by hearing. Auditory learners who read a textbook chapter benefit from hearing reinforcement of key concepts spoken out loud. Auditory learners also benefit from verbalizing concepts, such as listing steps involved in the process or verbally explaining a formula and/or calculations to other students in a small group. Tactile Learners. The tactile learner learns best by touching or handling objects. Tactile learners may benefit from using the computer to key entries or projects and then print reports and papers. Kinesthetic Learners. The kinesthetic learner learns best by taking an active part in the instruction. Motion is an important part of kinesthetic learning. A student might benefit from the opportunity to perform calculations to solve formulas using drills or prepared worksheets. Course Technology's SAM XP and TOM are a powerful skills assessment and training package for Microsoft® Office XP. On the training side, TOM uses rich multimedia to keep students engaged while they learn valuable Office XP skills in a variety of learning styles. TOM is performance-based learning. For each skill you want to master, a TOM activity offers four learning modes: Prepare - Review important conceptual information about a skill, including definitions of key terms and detailed graphics illustrating commonly used features of the application. • Observe - Watch a narrated animation that allows you to see and hear how a skill is completed in the application. • Practice - Master a skill by working step-by-step through a guided task in a realistic simulation of the application. • Apply - Test your knowledge by working on your own, in a realistic simulation of the application, without step-bystep guidance. Students can access Prepare, Observe, Practice, and Apply at any time, moving among them in any order to create the learning program that best suits them. Students can also access any learning mode as many times as they like. SAM XP lets students prove their knowledge by working in an authentic simulated Office environment. SAM XP is a dynamic, Web-based application that tests and evaluates your skills in the Microsoft® Office XP suite of applications. TEACHER PREPARATION Teacher as Facilitator. Teachers are invited to empower students to become autonomous and be accountable for their own learning. A traditional way of teaching is “teacher-centered” where the teacher lectures and assigns readings and/or tasks. This type of teaching may not take into account individual learning styles. Project-based learning is “learner-centric”. In this model, teachers may introduce ideas and projects and students use the tools and resources available to them to find answers and complete projects. From the beginning, the students know the goals and base their learning by doing tasks that engage their minds. Students are encouraged to use critical thinking skills, teaming skills and “tools” that will increase reading, writing, and communications skills. ESSENTIAL ACADEMIC LEARNING REQUIREMENTS (EALRS) READING The student understands and uses different skills and strategies to read [1.0]. Use vocabulary (word meaning) strategies to comprehend text [1.2]. Build vocabulary through wide reading [1.3]. The student reads different materials for a variety of purposes [3.0]. Read to learn new information [3.1]. Read to perform a task [3.2]. Read for career applications [3.3]. The student sets goals and evaluates progress to improve reading [4.0]. Assess reading strengths and need for improvement [4.1]. D:\533575438.doc WRITING The student understands and uses a writing process [1.0]. Prewrites to generate ideas and plan writing [1.1]. Produces draft(s) [1.2]. Revises to improve text [1.3]. Edits text [1.4]. Publishes text to share with audience [1.5]. COMMUNICATION The student uses listening and observation skills to gain understanding [1.0]. Uses listening and observation skills and strategies to focus attention and interpret information [1.1] The student uses communication skills and strategies to interact/work effectively with others [2.0] Uses interpersonal skills and strategies in a multicultural context to work collaboratively, solve problems, and perform tasks [2.2] MATHEMATICS The student understands and applies the concepts and procedures of mathematics [1.0]. Understand and apply concepts and procedures from number sense [1.1]. The student understands how mathematical ideas connect within mathematics, to other subject areas, and to real-life situations [5.0]. Relate mathematical concepts and procedures to real-world situations [5.3]. HEALTH & FITNESS The student analyzes and evaluates the impact of real-life influences on health [3.0]. Understand how environmental factors affect one’s health (air, water, noise, chemicals) [3.1]. THINKING PROBLEM SOLVING SCHOOL AND WORK CONNECTION CONTENT CAREER DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK: The technical core of Career Development will develop concepts related to career exploration, selection, and preparation integrated throughout the student's educational experiences. Students through this technical core standard will: Understand a variety of career options and how they are influenced by personal strengths, weaknesses, interests, and wants. Use a variety of career resources to learn about career opportunities. Use career-planning skills. Use workplace readiness skills. ETHICAL RESPONSIBILITIES FRAMEWORK: The technical core of Ethical Responsibilities will develop an understanding of legal and ethical responsibilities and typically accepted practices, including expectations and the implications of practices on business systems. Students through this technical core standard will: Identify the laws and regulations that affect business. Understand ethical concepts as related to the business environment. LEADERSHIP FRAMEWORK: The mission of teaching Leadership will be to develop skills that empower students to assume and model responsible roles in family, community, and work. Identify appropriate leader characteristics and styles. Identify the purpose of various professional organizations. SAFETY AND SECURITY FRAMEWORK: The technical core of Safety and Security will develop an understanding of existing and potential hazards to customers and employees. Students will prevent injury or illness through safe work practices and follow health, safety, and security policies and procedures. Students through this technical core standard will: Know appropriate response to an emergency. Know basic security procedures and protocols. Know appropriate organizational and regulatory guidelines for area of work. Know how to reduce risks and hazards in the workplace. TEAMWORK FRAMEWORK: The technical core of Teamwork will develop active participation in a wide variety of work teams. Students will understand the various roles of team members and will interact effectively and sensitively with all team members. Students through this technical core standard will: Use a variety of team membership skills in different workplace settings. Understand how to work with team members from diverse backgrounds in the workplace. Know how to manage conflict within the workplace. DIVERSITY FRAMEWORK: The technical core of Diversity will develop an appreciation for and respectful interaction with diverse populations, the elimination of harassment, bias and stereotyping, and non-traditional training and employment opportunities. Students through this technical core standard will: Demonstrate an appreciation for diversity of culture, ethnicity, physical capacity, age, and gender as societal strengths. Respectfully interact with diverse populations in schools, communities, and workplaces. Recognize and support the elimination of harassment, bias, and stereotyping. D:\533575438.doc LEADERSHIP TRAITS/HABITS FOR EMPHASIS Dependability (e.g., attendance, punctuality, tools, deadlines). Self-discipline (e.g., correct technique, working with distractions, paying attention, respect for equipment). Following oral instructions. Following written instructions. Problem-solving techniques. GRADING SCALE GRADE A+ A AB+ B BC+ C CD+ D DF (Attempted) F (Not done) POINTS 12.0 11.4 10.9 10.7 10.2 9.7 9.5 9.0 8.5 8.3 7.8 7.3 3.6 0 PERCENT 98 - 100 92 - 97 90 - 91 88 - 89 82 - 87 80 - 81 78 - 79 72 - 77 70 - 71 68 - 69 62 - 67 60 - 61 0 - 59 0 GRADE SUMMARY Training (TOM) Assignments Exams Tests Final 25% 25% 30% 10% 10% CLASSROOM RULES No eating or drinking in the classroom Be in class before the bell rings CHS attendance policies will be followed Cheating—1st offense=failure on assignment, parents notified 2nd offense=referral to administration If you are absent, it is your responsibility to find out what you missed You are allowed the number of days absent (ex.) plus one (+1) to turn in the missed work—work not turned in by the deadline will receive a 0 Quizzes and tests are closed book and no notes are allowed . RESOURCES Internet Explorer Shelley Cashman Series: Microsoft Word 2002, Sam & Tom XP, Website (http://samxp1.course.com) D:\533575438.doc