Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes Practice Questions
advertisement

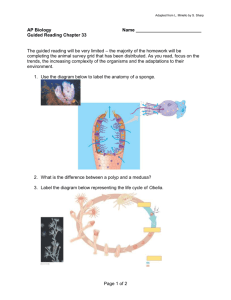
Porifera, Cnidaria, & Platyhelminthes Practice Questions Part I. Label the diagrams shown below. Choose from the following labels: mouth bud tentacle GVC endoderm basal disc ectoderm eyespot cilia nerve cords GVC flame cells mouth brain pharynx auricle Part II. Life Cycle. Label the life cycle diagram below. Choose from the following labels: sperm larva flagella new sponge develops dividing cells (spongocoel) egg larva released Part III. Fill in the blank. Fill in the missing structure/process for each statement below. 1. In a jellyfish, food enters the body and wastes are removed from the body through the _____________. 2. In sponges, waste water is removed through the _________________. 3. In a jellyfish and all flatworms, the process of diffusion is used for these two life processes: _________________________ and ______________________ 4. In a sponge, the ___________________ transport nutrients and make egg and sperm cells. 5. Spicules provide __________________________ for the sponge. 6. Water is drawn into the sponge by the beating of the _______________, which are attached to the collar cells. 7. Sponges are not capable of _________________ since they have no nerve cells. 8. Hydra have a nervous system made up of a loosely connected band of nerve cells called a _______________. 9. In a hydra, the _________________ sting and immobilize the prey, then the __________________ grab the prey and stuff it into the mouth. 10. In a sponge, the ________________ trap the food particles, while the _________________ digest the food particles. 11. All three phyla of animals are capable of __________________, a process in which the animal regrows missing parts. 12. Budding is a type of ________________ reproduction because it involves only one parent. 13. In harsh conditions, sponges produce internal buds which can break off and grow into adult sponges when the conditions improve. This process is called _______________. 14. The planaria will move by secreting ____________ and pushing through it with its ___________. 15. Planaria and flukes feed with a tube called a ______________ that shoots from its mouth and brings food into the body. 16. In planaria, flukes, and jellyfish, food is digested inside a hollow tube in the body called a _____________. Enzymes made in the inside cell layer called the _______________ digest their food. 17. In all flatworms, tubes called ____________ filter and remove waste. 18. A ________________ feeds on the digested food of its host organism. 19. Flukes and tapeworms are considered to be _______________ because they live inside of a host organism and cause harm to them. 20. A _____________ feeds on the blood and tissues of its host organism. 21. A planaria is capable of detecting light through its ___________________. 22. A planaria is capable of learning to go through mazes because of their ____________. 23. Both a tapeworm and a fluke infection can be detected by examining the _____________ for the presence of the eggs. 24. How a fluke and a tapeworm infection can be treated with ____________. Part IV. Short answer. 25. How do all three groups of animals compare in terms of the type of symmetry seen? 26. How do Porifera, Cnidaria, and planaria compare in terms of their diet? 27. How do Porifera, Cnidaria, and free-living flatworms compare in terms of their habitat? 28. How do all three groups of animals compare in terms of their gender? 29. How do the medusa and polyp body forms seen in the Phylum Cnidaria compare? 30. How can someone become infected with a tapeworm? What would be some symptoms of infection? 31. How can a person become infected with a fluke? What would be some signs of infection? 33. How can you prevent becoming infected with a tapeworm or a fluke?