Earth Science Vocabulary
advertisement

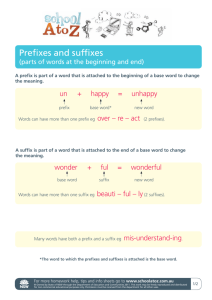
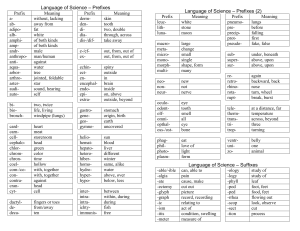
Name: _____________________________________ Date:____________ Period:____ Earth Science Vocabulary Vocabulary is the total words used, understood, and at the command of a person or a group of people. Understanding vocabulary is essential when you are trying to communicate something. To understand and appreciate earth science it is necessary to know the vocabulary of this branch of science. To help you learn this vocabulary there is a simple system that can be used to learn the meaning of words. Here’s how the system works: Many words in science consist of three parts: a prefix, a stem or root, and a suffix. Here’s an example. GEO MORPH OLOGY Prefix Root Suffix You can figure out the meaning of this word if you know the meaning of each of the three parts. As you will learn, each of the parts has these meaning: Geo – means “Earth” Morph – means “form or shape” Ology – means “study of” So, the word geomorphology refers to the branch of earth science that “studies the forms and shapes of the earth’s surface.” At first if would seem that our task has become more difficult rather than simpler. We now have three things to memorize – a prefix, root, and suffix – instead of a single word. The thing that makes this system easier is that many prefixes, roots, and suffixes are used over and over again. Once you learn them, you can use them to analyze other new words. General Directions: Listed on page 2 are groups of prefixes, roots/stems, and suffixes that often occur in scientific terms in earth science. The other pages contain practice exercises that will help you develop your vocabulary by using these prefixes, roots, and suffixes. NOTE: Many of the roots listed can be used as prefixes and/or suffixes. Prefixes and suffixes can also appear as roots. Page 1 of 5 Name: _____________________________________ Prefixes that stand for Numbers Prefix Meaning semi-, hemihalf uni-, monoone di-, bitwo trithree quadra-, tetrafour quinqu-, pentafive sex-, hexsix sept-, heptaseven octaeight nonanine decaten centi-, hectohundred millithousand megamillion (or very much) Common Prefixes Prefix Meaning antiagainst circumaround contogether diaacross epioutside extrabeyond forebefore innot interbetween isosame metachange multimany neonew paleoold, ancient periaround polymany postafter prebefore (time) probefore(place) reagain retrobackward subunder, below superabove, better than transacross, through ultramore than unnot Common Roots Prefix anthropaqua- Meaning human water Date:____________ Period:____ astra-, astroatmoautobar-, barobiocentrocosmocyclodynamecogeogram-, graphhelioheterohomohydrolitholunamacro, magnmesometermicromorphpetrophonphotoscopseismospherespectstratostructteleterrthermtoxumbrzoo- star vapor, gas self pressure life center universe round force environment earth drawn, written sun different same water stone moon large, great middle measure small form, shape rock sound light see earthquake round, layer of the earth sight, view horizontal build distant earth heat poison shadow animal Common Suffixes Prefix Meaning able-, idle-, ilecapable of al-, arypertaining to, belonging to eer-, istperson who is doing something ichaving to do with oidlike, resembling ology, ogy, nomystudy of izeto cause to happen cidedeath ismbelief in ion-, mentresult of an action Page 2 of 5 Name: _____________________________________ Date:____________ Period:____ Practice Exercises Divide each term below into its component parts – prefix, root, and/or suffix – and then write the meaning of that prefix, root, and/or suffix. 1. thermometer: ________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. hemisphere: _________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. telescope: ___________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. microscope: _________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. hydrodynamic: ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. paleozoology: _______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 7. cosmology: _________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 8. geothermal: _________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 9. barometer: __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 10. lithostratigraphic: ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Page 3 of 5 Name: _____________________________________ Date:____________ Period:____ For each underlined word in the sentence below, (1) write the meaning of its prefix, root, and/or suffix, and then (2) write the meaning of that word as a whole as it is used in that sentence. 1. The satellite launched by NASA went into a heliocentric orbit. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. Yesterday the seismograph at Hawaii University recorded P waves and S waves. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. I was able to see Venus last night in my telescope. __________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Marble and limestone are both examples of metamorphic rock. ________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. The student observed that the rock was polymineralic and identified it as granite. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. A lab in earth science will involve finding the diameter and circumference of a globe. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 7. The paleontologist used an ultramicroscope to study the fossils. _______________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ “Create” your own word. Write each of the parts – prefix, root, and/or suffix – and their meanings, and then write out your word and its meaning. Finally, use your word in a sentence.. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Page 4 of 5 Name: _____________________________________ Date:____________ Period:____ Fill in the blanks using words from the following word bank. centimeter(s) barometer microbiology photometrist petrologist atmosphere lithosphere hydrosphere isobar isotherm geocentric subterrestrial paleoanthropology 1. The ________________________ surrounding the Earth has several layers. 2. Josh measured the length of the string in ____________________________. 3. A ________________________________________ once told me that all rocks originally came from magma. 4. My cousin, who studies the Incas and Aztecs, is majoring in __________________________ in college. 5. The ________________________________ showed a pressure reading of 1020 millibars. 6. The __________________________________ includes the crust and the upper mantle of Earth. 7. We pulled the excavated carcass of the wooly mammoth from _________________________ depths, almost 300 feet down! 8. ___________________________________ includes the study of bacteria, dust mites, amoebas, and other small organisms. 9. Ptolemy’s proposal of the _____________________________ model was proven to be incorrect because the earth is not the center of the universe. 10. The ___________________________ on the weather map showed that Chicago and Cincinnati have the same pressure readings. 11. A ______________________________ would be employed by a light bulb manufacturing company to assess the correct intensity of light radiation from their bulbs. 12. Fishes, whales, and sharks live in the _______________________________. 13. The meteorologist pointed to a(n) __________________________ on the map that connected Raleigh and Louisville, which are both at 60 degrees F. Page 5 of 5