Full Description
advertisement

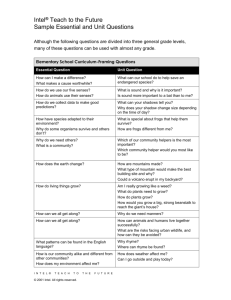
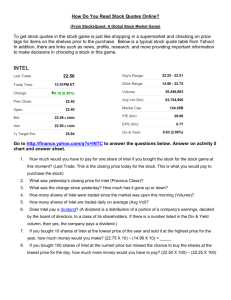
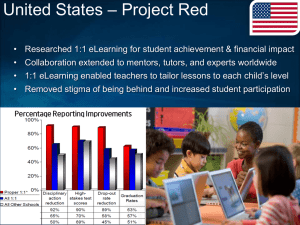
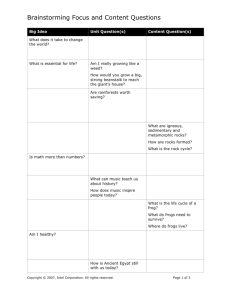
1. Title of subject Introduction To Machine Architecture 2. Subject code TMA1271 3. Status of subject Core 4. Version Date of Previous Version: Year 2006 Date of New Version : December 2007 5. Credit Hours 4 42 Hours of Lecture 28 Hours of Laboratory LAN Credit Hours Equivalence: 4.00 6. Semester Trimester 3, Beta level 7. Pre-Requisite Digital Systems (TCE1111) 8. Methods of Teaching 42 Hours of Lecture 28 Hours of Laboratory 9. Assessment Course Work : 40% Final Exam : 60% Total : 100% 10. Teaching staff Kannan Ramakrishnan Ng Hu Tan Saw Chin 11. Objective of subject This course provides thorough discussions on the fundamentals of computer organization and architecture and relates this to contemporary design issues. This will cover system buses, structures and functions of different central processing units, control units, characteristics and functions of different instruction sets, addressing modes, memory, input/output, parallel processing and multi-core computing. 12. Synopsis of subject This course will cover historical development of computers and evolution of Intel multi-core processors and IBM power processors. Topics such as elements of system bus design, interrupts, organization of registers (with Intel 8085, Intel 8086, and Motorola 68000 microprocessors as examples), study of instruction cycle and pipelining, study of arithmetic and logic unit with integer and floating-point arithmetic algorithms, study of hardwired and microprogrammed control unit, and study of instruction set characteristics, functions, formats, addressing modes (with Intel 8085 and Intel 8086 as examples) will be included. In addition, the following topics in memory and input/output will also be covered with details: Principles of cache memory and elements of cache design, types and organization of semiconductor main memory, structure and function of input/output modules with different data transfer techniques, and interfacing of Intel 8085/8086 microprocessors with 8255 programmable peripheral interface device. Topics in advanced computer architecture such as symmetric multiprocessors, software/hardware solutions for cache coherence problem, configuration of clusters, organization of non-uniform memory access, and motivation behind multi-core computing with architecture and performance characteristics of different multi-core processors will also be introduced. Kursus ini merangkumi sejarah pembangunan komputer dan evolusi pemproses teras-berbilang Intel serta pemproses berdaya tinggi IBM. Topik-topik seperti elemen-elemen rekabentuk sistem, sampukan, organisasi pendaftaran (menggunakan pemproses Intel 8085, Intel 8086 dan Motorola 68000), pembelajaran kitar arahan dan penalian paip, unit logik aritmetik, algoritma aritmetik integer dan titik ampung, mikroatur cara terdawai keras, ciri-ciri arahan set, fungsi, format serta mod pengalamatan berlandaskan pemproses Intel 8085 dan 8086 adalah pengkhususan subjek ini. Topik-topik berteraskan ingatan dan masukan/keluaran juga akan diperkenalkan secara terperinci : Prinsip-prinsip serta elemen rekabentuk ingatan para , kepelbagaian jenis dan organisasi semikonduktor ingatan utama, fungsi-fungsi modul masukan/keluaran dengan kepelbagaian aturcara pemindahan data serta antaramuka pemproses Intel 8085/8086 menggunakan peranti boleh aturcara 8255. Tidak ketinggalan topik-topik lanjutan dalam bidang senibina komputer . Ia meliputi pemproses berbilang simetri, penyelesaian perisian dan perkakasan untuk masalah kekoherenan para, konfigurasi kelompok, organisasi ketidakseragaman akses ingatan, dorongan disebalik pengkomputeran teras-berbilang serta rekabentuk dan ciri-ciri prestasi pelbagai pemproses teras-berbilang. 13. Learning Outcomes By the end of this course, students should be able to: Describe the evolution of computer architectures. Identify and explain the structures and functions of the primary components of computer such as system buses, registers, ALU, control unit, memory, inputoutput devices and also the characteristics of instructions sets of typical microprocessors. Demonstrate the ability to write simple assembly language programs and also programs for the programmable peripheral interface device with different interfacing techniques. Formulate the best solution and organization of single processor systems, symmetric multiprocessors, clusters, non-uniform memory access and chip-level multiprocessors in response to problems associated with computer architectures. Programme Outcomes Ability to apply soft skills in work and career related activities 14. Details of subject % of contribution 5 Good understanding of fundamental concepts 40 Acquisition and mastery of knowledge in specialized area Acquisition of analytical capabilities and problem solving skills 20 20 Adaptability and passion for learning Cultivation of innovative mind and development of entrepreneurial skills 5 5 Understanding of the responsibility with moral and professional ethics 5 Topics Covered Hours 1.Introduction 4 Basic Concepts (Organization and Architecture, Structure and Function), Computer Evolution and Performance (Brief History of Computers, Designing for Performance, Intel multi-core processors and IBM Power processors Evolution), System Buses (Computer Components, Computer Functions, Interconnection Structures, Bus Interconnection). 2.CPU structure and function 9 Processor Organization (ALU, Registers, Control Unit), Register Organization (User-Visible Registers, Control and Status Registers), Examples (Architecture of Intel 8085, Intel 8086, and Motorola 68000 microprocessors), Instruction Cycle (Fetch, Execute, Interrupt, Indirect), Instruction Pipelining (Pipelining Strategy, Pipeline performance, Dealing with branches), Control Unit Operation (Micro-operations, Control of the processor, Hardwired Implementation, Micro-programmed Control Unit). 3.Instruction Set Design 9 Instruction Sets- Characteristics and functions (machine instruction characteristics, types of operands, types of operations), Examples (Instruction Set of Intel 8085, and Intel 8086 Microprocessors), Addressing Modes (Different types), Examples (Addressing modes of Intel 8085, and Intel 8086 microprocessors), Instruction formats (Design issues), Examples (Instruction format of Intel 8085 and Intel 8086 microprocessors). 4. Computer Arithmetic 4 Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU), Integer Representation (Sign-Magnitude, Twos Complement, and Ones Complement), Integer Arithmetic (negation, addition, subtraction, unsigned and twos complement multiplication and division algorithms), Floating-Point Representation (principles, IEEE 754 single and double formats), Floating-Point Arithmetic (addition and subtraction, multiplication and division, precision considerations). 5. Memory System Architecture 4 Computer Memory System Overview (Characteristics of memory systems, Memory Hierarchy, locality of reference principle),Cache memory (Principles, Elements of Cache Design), Semiconductor main memory (Types, organization, error correction), Advanced DRAM Organization (SDRAM, RDRAM, CDRAM, DDR SDRAM, DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM). 6.Input/Output 6 External Devices (Human Readable, Machine Readable, Communication devices), I/O Modules (structure and function), Data Transfer Techniques (Programmed I/O, Interrupt-Driven I/O, Direct Memory Access), I/O Channels and Processors, Architecture, Programming and Operation of 8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface (PPI), Interfacing of Intel 8085/8086 microprocessors with 8255 PPI. 7.Parallel Processing and Multi-Core Computing Multiple Processor Organizations (SISD, SIMD, MISD, MIMD), Symmetric multiprocessors, Cache Coherence and the MESI Protocol, Clusters, Non-uniform Memory Access. 6 Multi-Core Computing (Introduction, Motivation, Innovations), Architecture and Performance characteristics of multi-core processors from INTEL, IBM, Advanced Micro Devices, and Sun. Laboratory: 1. Study of Intel 8085 and Intel 8086 based microcomputer kits and the corresponding simulation software. 2. Assembly language programming exercises using Intel 8085 based microcomputer kit. 3. Assembly language programming exercises using Intel 8086 based microcomputer kit. 4. Experiments based on Interfacing 8255 PPI with Intel 8085, and Intel 8086 microprocessors. Total Contact Hours (Equivalent to lecture hours) 42 Text book 1. William Stallings, “Computer Organization and Architecture”, Seventh Edition, Prentice Hall, 2006. Reference Books 1. M. Morris Mano, “Computer System Architecture”, Third Edition, Prentice Hall, 1993. 2. Ramesh S. Gaonkar, “Microprocessor Architecture, Programming, and Applications 15. Text with the 8085”, Fifth Edition, Prentice Hall, 2002. 3. Barry B. Brey, “Intel Microprocessors-Architecture, Programming, and Interfacing”, Seventh Edition, Prentice Hall, 2006 4. Kip R. Irvine, “Assembly Language for Intel-based Computers", Fourth Edition, Prentice Hall, 2003. Current Syllabus 1. Title of subject Introduction To Machine Architecture 2. Subject code TMA1271 3. Status of subject Core 4. Credit Hour 4 42 Hours of Lecture 28 Hours of Laboratory LAN Credit Hours Equivalence: 4.00 5. Semester Trimester 3, Beta level 6. Pre-Requisite Digital Systems (TCE1111) 7. Methods of Teaching 42 Hours of Lecture 28 Hours of Laboratory 8. Assessment Assessment : 40% Final Exam : 60% TOTAL : 100% 9. Teaching staff 10. Objective of subject P. Vijayaprasad Kannan Ramakrishnan Ng Hu Tan Saw Chin This course provides a thorough discussion of the fundamentals of computer organization and architecture and relates this to contemporary design issues. This will cover buses, memory, input/output, instruction sets, CPU structure and functions and parallel processing 11. Synopsis of subject This Course cover historical development of computers and computer architectures, multilevel computer concepts, virtual machines, Computer system orhganisation, computer systems components,information representation,integer and floating-point representation and computer arithmetic. The central processing unit,instruction sets, instruction formats,addressingmodes,CISC and RISC machines, Methods for I/O,memory systems architecture,Pentium 11 and PowerPC Cache Organization,Virtual memory, caching,concurrency, control unit,control unit operation, Microprogramming, Microprocessor systems,architecture if Intel 8085 microprocessor and assembly language programming, I/O ports and I/O programming,introduction to advanced computer architectures, multiple processors organization,symmetric Multiprocessors, Cache coherence and the MESI Protocol, Clusturs, Vector computation. Kursus ini mendedahkan sejarah pembangunan komputer & seni bina komputer, konsep pengkomputeran berbilang aras, mesin maya,organisasi sistem komputer, komponen sistem komputer, perwakilan informasi, integer & perwakilan titik apung dan arimetik komputer. Unit pemprosesan pusat, set suruhan, format suruhan, mod pengalamatan, mesin CISC dan RISC, kaedah I/O, arkitek sistem ingatan, Pentium II & organisasi Power PC Cache, ingatan maya, cache serempak, unit kawalan, operasi unit kawalan, pengaturcaraan mikro, sistem mikropemproses, pengaturcaraan bahasa himpunan, port I/O, pengaturcaraan I/O, pengenalan kepada seni bina komputer lanjutan, organisasi pemproses berbilang, simetri pemproses berbilang, protokol MESI, gugusan dan komputasi vektor. 12. Learning Outcomes By the end of the subject, students should be able to: Understand the details of computer architecture and organization. Explain about the primary computer components such as CPU, memory and input output devices. identify and explain the purpose of different levels of memory. explain different instructions for a processors. Programme Outcomes % of contribution Ability to apply soft skills in work and career related 5 activities Good understanding of fundamental concepts 40 Acquisition and mastery of knowledge in specialized area 20 Acquisition of analytical capabilities and problem solving skills 20 Adaptability and passion for learning Cultivation of innovative mind and development of entrepreneurial skills 5 5 Understanding of the responsibility with moral and professional ethics 5 13. Details of subject Topics Covered Hours 4 1.Introduction Brief History of Computers, Designing for Performance, Pentium and PowerPC Evolution, Computer Component, Computer Functions, Interconnection Structure, Bus Interconnection and PCI. 2.CPU structure and function Processor Organization, Register Organization, The Instruction Cycle, Instruction Pipelining, The Pentium II and PowerPC processors, Micro-operations, Control of The Processor 3.Computer Arithmetic The Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU), Integer representation, Integer arithmetic, Floating-Point Representation, Floating-Point Arithmetic 4.Instruction Set Design Machine Instruction Characteristics, Types of Operands, Type of Operations, Pentium II and PowerPC Data Types and Operation Types, Addressing, Instruction Formats, Pentium II and PowerPC Addressing Modes and Instruction Formats. 5.Memory System Architecture Computer Memory System Overview, Semiconductor Main Memory, Cache Memory, Pentium II and PowerPC Cache Organization, Advanced DRAM Organization. 6.Input/Output External Devices, I/O Modules, Programmed I/O, Interrupt Driven I/O, Direct Memory Access, I/O Channels and Processors, The External Interface: SCSI and FireWire. 7.Microprocessor Systems Stored Program Concepts, Architecture of Intel 8085 Microprocessor, Arithmetic Logic Unit and Timing and Control Unit, Address Buffers and Latches, Addressing Modes, Addressing Modes in 8085 Microprocessor, Instruction Set of Microprocessor, Groups of Instructions, Timing Diagram of Microprocessor Instructions, Flag Register Organisation, Assembly Language Programming, Microprocessor Interfacing, I/O Ports, Memory-mapped and I/O Mapped, Address 4 3 7 4 4 12 Space Partitioning, Memory Interfacing, Programmable Peripheral Interface (8255), 8279 Keyboard Display Interface. 8.Introduction to Advanced Computer Architecture Instruction Execution Characteristics, The Use of a Large Register File, Compiler-Based Register Optimization, Reduced Instruction Set Architecture, RISC Pipelining, The RISC versus CISC Controversy, Multiple Processor Organizations, Symmetric Microprocessors, Cache Coherence and the MESI Protocol, Clusters, Non-uniform Memory Access, Vector Computation. 4 Laboratory: 1. 2. Basic Operation using 8-bit Microprocessor Kits. Assembly Language Program for: a) Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division of Numbers b) Logical Operations c) Sorting of Numbers d) Serial Input and Output 3. Interfacing : Memory and Input/output 4. Interfacing: Memory Total Contact Hours (Equivalent to lecture hours) 14. Text Compulsory 42 1. W. Stalling, “Computer Organizationn and Architecture, 7th Edition”, Prentice Hall 2006. 2. Miles Murdocca , Vincent P. Heuring, “Principles of Computer Architecture, First Edition”, Engineering/Science/Mathematics 1999 Andrew S. Tanenbaum , “Structured Computer Organization, Fourth Edition, Engineering/Science/Mathematics, 1998 D. Patterson and J. Hennessy, “Computer Organization & Design The Hardware/Software Interface”, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 1994. Gaoengar, “Microprocessors: Architecture, Programming and Applications”, John Wiley & Sons, 1995. Reference 3. 4. 5.