lecture distribution
advertisement
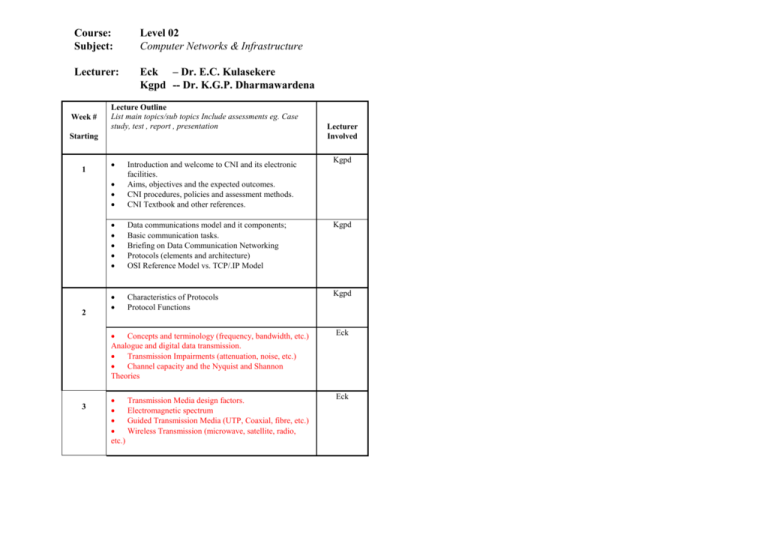
Course: Subject: Level 02 Computer Networks & Infrastructure Lecturer: Eck – Dr. E.C. Kulasekere Kgpd -- Dr. K.G.P. Dharmawardena Week # Lecture Outline List main topics/sub topics Include assessments eg. Case study, test , report , presentation Starting 1 2 3 Lecturer Involved Kgpd Introduction and welcome to CNI and its electronic facilities. Aims, objectives and the expected outcomes. CNI procedures, policies and assessment methods. CNI Textbook and other references. Data communications model and it components; Basic communication tasks. Briefing on Data Communication Networking Protocols (elements and architecture) OSI Reference Model vs. TCP/.IP Model Kgpd Characteristics of Protocols Protocol Functions Kgpd Concepts and terminology (frequency, bandwidth, etc.) Analogue and digital data transmission. Transmission Impairments (attenuation, noise, etc.) Channel capacity and the Nyquist and Shannon Theories Eck Transmission Media design factors. Electromagnetic spectrum Guided Transmission Media (UTP, Coaxial, fibre, etc.) Wireless Transmission (microwave, satellite, radio, etc.) Eck 4 5 Synchronous and Asynchronous transmission Line Configuration (topology and duplicity) Interfacing and its characteristics. Overview of Data Link Control and Flow Control mechanisms Flow Control Techniques (Stop-n-Wait, Sliding Windows) Error Detection methods (parity, CRC – polynomial only) Error Control (Stop-and-Wait ARQ) Error Control (Go-back-N and Selective Reject ARQ) Eck Eck Multiplexing and its usage in Data Communications. Time-Division Multiplexing (Synchronous & Asynchronous) Statistical Time-Division Multiplexing Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Inverse Multiplexing. 6 7 8 Classification of networks (LAN, MAN, WAN, etc.) Motivation behind WAN technologies; Switching networks and their architecture; Circuit switching, packet switching, message switching. Review with the students the material Switching Techniques VCPS vs. DPS and the effect of packet size on efficiency Internal vs. External Switching Basic elements of routing; Routing strategies in WAN X.25 protocols, services, and specifications Frame Relay and its relation to X.25 Critical comparison between the X.25 approach vs. Frame Relay approach. ATM switching technology; ATM architecture in relation to the OSI reference model; ATM logical connections and control signalling; ATM cell structure and its effect on the performance of ATM networks Kgpd Eck Eck Eck Eck Kgpd 9 10 ISDN and Integrated Services Networks. ISDN and Integrated Services Networks. Review of LAN Applications IEEE model for LAN vs. OSI Reference Model; LAN topology and its relation to LAN technologies; Medium Access Control (MAC) and the MAC frame format; Logical Link Control (LLC) services and its frame format; 11 12 Internetworking devices & the need to connect LANs Bridges and their architecture and routing issues Routing in bridges (fixed routing and spanning tree) Other Internetworking devices (routers, gateways, etc.) Performance issues in LAN systems (access delay, applied load, and throughput) Ethernet technology and its protocols and access methods; Ethernet-related technologies (fast Ethernet, switched Ethernet and gigabit Ethernet standards) Ring and token bus technologies and their specifications; Performance issues in Token Ring and alternatives Token priority and early token release. FDDI technology and how it differs from token ring. TCP/IP terminology and the meaning of TCP and IP; History of TCP/IP and ARPA project. TCP/IP architecture and protocols 13 14 Responsibilities and services of the IP layer; Addressing concept in TCP/IP protocols and how the IP layer maps the entities to a network and a host. Other IP-related protocols like ICMP and ARP. Transport services provided by a transport protocol; Connection-oriented vs. connectionless-oriented issues Service provided by the TCP protocol; The structure of the IP datagram and its header; Distributed applications and their protocols; Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP); Kgpd Kgpd Kgpd Kgpd Kgpd Kgpd Kgpd Kgpd Eck Electronic mail (SMTP & MIME) protocols and operations. Other application protocols (http, URL and URI concepts, etc.) Review of the CNI material for the final examination;





![Internetworking Technologies [Opens in New Window]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007474950_1-04ba8ede092e0c026d6f82bb0c5b9cb6-300x300.png)