ECE 562
advertisement

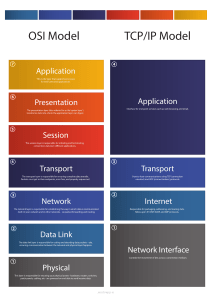
Course Syllabus ECE 562 – Data Communication Networks Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering 1. Course Number and Name: 2. Credit Units/Contact Hours: 3. Course Coordinator: ECE 562 – Data Communication Networks 3/3 Debbie van Alphen 4. Text, References & Software Recommended Text: Data Communications and Networking, 4th edition, McGraw-Hill, 2007 Additional References: Computer Networking, 5th edition, Kurose & Ross, Pearson, 2009 Software: OPNET, WIRESHARK 5. Specific Course Information a. Course Description Layered network architectures and the TCP/IP model. Link layer error and flow control mechanisms. Packet switching. Wired and wireless local and wide area networks. Medium access control procedures. Internetworking with switches, bridges and routers. Routing algorithms. Network security. b. Prerequisite by Topic Students taking this course should have complete familiarity with the topics of probability theory (ECE450, Probabilistic Systems in Electrical Engineering-Design and Analysis) c. Elective Course 6. Specific Goals for the Course a. Specific Outcomes of Instructions – After completing this course the students should be able to: 1. Identify different applications of computer communications networks and understand the current state of the telecommunications industry 2. Understand the concept and importance of TCP/IP layered architecture 3. Understand the functionalities, concepts, standards and technologies involved with voice and data network services and voice/data integration 4. Perform link level analysis including error detection, error control and flow control. 5. Understand circuit & packet switching technologies and their deployments in public networks 6. Understand how wired and wireless local networks such as Ethernet, Token rings and Wi-Fi operate and distinguish between different medium access control procedures 7. Understand the functions and operations of internetworking devices such as hubs, bridges, routers and gateways 8. Understand the hierarchy of IP addressing and subnetting 9. Understand how routing is carried out in large open networking environment and the operations of major routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF and BGP 10. Understand how Internet clients and servers are able to communicate with each other across the Internet and the WWW. 11. Understand the standard Internet applications protocols such as FTP, SMTP, HTTP, DNS, etc. 12. Understand basic network security measures such as encryption, signatures and firewalls 13. Conduct network simulations using OPNET and protocol analysis using Wireshark. b. Relationship to Student Outcomes This supports the achievement of the following student outcomes: a. An ability to apply knowledge of math, science, and engineering to the analysis of electrical engineering problems. b. An ability to design and conduct scientific and engineering experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data. c. An ability to design systems which include hardware and/or software components within realistic constraints such as cost, manufacturability, safety and environmental concerns. e. An ability to identify, formulate, and solve electrical engineering problems. k. An ability to use modern engineering techniques for analysis and design. l. Knowledge of probability and statistics. 7. Topics Covered/Course Outline 1. Basic concepts of networking. Network topologies. The concept of layered architecture modeling including OSI and the TCP/IP protocol suite. Client-server communications. 2. Physical layer functionalities including signaling, modulation, multiplexing, line coding and synchronization. Transmission media. Network performance measures including throughput, delays are presented. Data vs. signaling rates, channel bandwidth and capacity. 3. Link layer functionalities including frame synchronization, error detection and control including ARQ, flow control mechanisms including sliding windows. 4. Circuit, packet and virtual circuit switching technologies 5. Local area network technologies including ETHERNET, Token Rings. Multiple-access schemes such as CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA and Token-passing. MAC addressing. Switched vs. shared ETHERNETs. Performance evaluation, including throughputs and delays, 6. Internetworking devices including repeaters, bridges, switches, routers and gateways. Network layer protocols, including IP, ARP and ICMP. IP addressing schemes. Subnetting 7. Internet routing including protocols used in the Internet such as RIP, OSPF and BGP. 8. Transport layer protocols including UDP and TCP. Ports and sockets. TCP connection establishment. Error, flow and congestion control in TCP. 9. Applications layer protocols such as HTTP, FTP, DNS, SMTP, TELNET 10. Network security measures including encryption, authentication, data integrity and firewalls. Prepared by: Ali Zahid and Debbie van Alphen, Professors of Electrical and Computer Engineering, October 2011 Ali Amini, Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, March 2013


![Internetworking Technologies [Opens in New Window]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007474950_1-04ba8ede092e0c026d6f82bb0c5b9cb6-300x300.png)