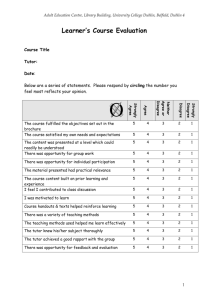
Introduction - School of Computing
advertisement

Dublin Institute of Technology MSc in Computing (Assistive Technology) Programme Document (Part A) Background Information This document was prepared by the Programme Committee on behalf of the School of Computing March 2007 Table of Contents 1 Introduction ...................................................................................................... 1 2 Programme aims and objectives ..................................................................... 2 2.1 Programme Aims ......................................................................................... 2 2.2 2.2.1 2.2.2 Programme Objectives and Learning Outcomes ...................................... 3 Postgraduate Diploma in Computing (Assistive Technology) ...................... 3 MSc in Computing (Assistive Technology) .................................................. 5 3 Market Demand and Support from Industry and Government Policy ...... 7 3.1 Justification for the Programme................................................................. 7 4 Job Placement of Graduates ........................................................................... 9 5 Admission Requirements and Standards ...................................................... 9 5.1 Admission Criteria ....................................................................................... 9 5.2 Access for students with a disability......................................................... 10 5.3 Intake policy and Procedures ................................................................... 10 6 Programme Structure and Content ............................................................. 11 7 Staff ................................................................................................................. 11 7.1 Academic Staff Resources ......................................................................... 11 7.2 Staff Teaching on the Programme............................................................ 11 7.3 7.3.1 Research and Development Interests ....................................................... 12 Staff Professional Development .................................................................. 12 7.4 Teaching Techniques and Programme Delivery ..................................... 13 8 Accommodation/Resources ........................................................................... 13 8.1 Teaching Facilities ..................................................................................... 13 8.2 Library ........................................................................................................ 14 8.3 8.3.1 8.3.2 Accommodation and Facilities .................................................................. 16 Staff Accommodation .................................................................................. 16 Computer Facilities ...................................................................................... 17 8.4 8.4.1 8.4.2 Technical and Administrative Support .................................................... 19 Technical Requirements for This Programme ............................................. 19 Additional Facilities Required to Run the Programme ................................ 19 9 Internationalisation of School ....................................................................... 20 10 Assessments .................................................................................................... 20 10.1 11 External Examiners’ report ...................................................................... 20 Programme Management and Quality Assurance Arrangements ............ 21 11.1 Programme team and Programme management structures ................. 21 11.2 Programme Monitoring and Quality Assurance .................................... 21 12 Student Handbook and Information Channels for Students ..................... 21 13 Programme Development Plan ..................................................................... 22 14 Appendix A – Module responsibilities ......................................................... 23 15 Appendix B – Programme Committee Membership .................................. 24 16 Appendix C – Curriculum Vitae .................................................................. 25 1 Introduction This document is the first part of the documentation required for the validation of the MSc in Computing (Assistive Technology) programme. This documentation has been prepared in accordance with the DIT Quality Assurance and Enhancement Handbook and to satisfy the DIT’s Quality Assurance requirements for programme review. The material for the review process is presented in two parts. This document constitutes Part A. The Part B document presents detailed information about the programme structure and content, including the programme curriculum and syllabi, admission criteria, programme assessment and progression. Technology is advancing rapidly and as with the rest of society, this has had a major impact on people with disabilities. For most people, technology can make life easier, expanding life’s choices and opportunities. For people with disabilities, however, technology makes possible daily activities that were hitherto impossible. Assistive technologies (AT) have a central role to play in equalising opportunities for people with disabilities in all aspects of life. These technologies have been recognised at an international and European level as a means of generating an inclusive society by assisting people to overcome the barriers that exist within their environment.1 AT devices include a variety of tools and equipment from the low-tech, such as a white cane making it possible for a person with a visual difficulty to be mobile; to devices such as hearing aids to enable someone with a hearing impairment use a telephone, or a wheelchair enabling a person to move around their home, work or school. However, in the last ten years there have been great advances in the development of high-tech electronic devices. These include remote-control devices, personal alarm systems and specialised computer software including voicerecognition and speech synthesis. Types of high-tech assistive technology which can facilitate independent living include: Computer access - alternative means of access to computers and technology, eg switches using eye-movement control or suck-and-puff, specialised software and voice recognition systems, alternative keyboards, interface devices switches with scanning, scanners & optical character recognition, trackballs and touch screens Environmental controls - accessible remote controls (eg switch or voicecontrolled) for turning on and off lights, using the telephone, opening and closing doors, windows, curtains, operating household devices Augmentative and alternative communication - devices for people who have communication difficulties which include text-to-speech, symbol-to-speech, text-reading-to-speech, click-to-type, and loop-system hearing aids Mobility - alternative control of powered wheelchairs such as using a switch instead of a joystick to operate a wheelchair, suck-and-puff switch control, seat-raising devices, posture changing devices. 1 European Commission (2003) Access to Assistive Technology in the European Union http://europa.eu.int/comm/employment_social/publications/2004/cev503003_en.htlm 1 Closely related to AT is the concept of Design for All or Universal Design which is a holistic approach to create goods, services or buildings that are accessible and understandable to everybody regardless of age, size, ability or other physical characteristics. It is not exclusively addressed to the needs of people with disabilities, but it is inclusive to their requirements. AT is central to the application of the “Design for All” principles. In many cases it is only through the use of AT that goods, services, and buildings can be made accessible to those with additional needs. In the report “Access to Assistive Technology in the European Union” 2, it was recommended that the “Design for All” principle should include people with special needs as much as possible from the outset in the design of products and services. The concept is promoted for two main purposes: on the one hand to meet the needs of consumers who have often experienced difficulty in using products, and on the other hand to meet needs of companies who want to expand their potential market. The most prominent use of the “Design for All” concept can be seen in Computing where this principle is applied to both software and webpages. Due to the need for legal compliance in the United States of America under the ‘Americans with Disabilities Act’ (1990)3 and the inclusion of “Design for All” principles in Section 508, as well as the accessibility guidelines promoted by the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)4 and the availability of various validation tools, a range of online courses have appeared for learning about this subject. Aside from the technical aspects of these courses, there are components about awareness of the barriers posed by inaccessible design. In 2003, the Microsoft Corporation commissioned Forrester Research, Inc.5, to conduct a comprehensive, two-part study to measure the current and potential market of AT in the United States and to get a better understanding how AT is being used today. The findings in this study show that a majority of working-age adults are likely to benefit from the use of AT. They concluded that 60% (101.4 million) of workingage adults are likely or very likely to benefit from its use. 2 Programme aims and objectives 2.1 Programme Aims The primary aim of the MSc in Computing (Assistive Technology) programme focuses on understanding, designing, developing, testing and using, Assistive 2 ibid. 3 http://www.usdoj.gov/crt/ada/adahom1.htm http://www.w3.org/WAI/ 5 Microsoft Corporation, and conducted by Forrester Research, Inc., between 2003 and 2004. http://www.microsoft.com/enable/research/default.aspx 4 2 Technology. Additionally it will provide graduates with a set of I.T. skills that are highly in demand particularly with relation to the accessibility of software. The practical aims of this programme are to develop the student’s professional, technical and research abilities, developing a broad background in Assistive Technology and a deep practical knowledge of inclusive and universal design, development and integration with exposure to leading edge topics relevant to the area. Therefore, this programme is to produce, at postgraduate level, computing graduates educated in the perspectives, methodologies and core competencies of computing in Assistive Technology. The introduction of this programme is timely and relevant to the current and projected needs of organisations in Ireland and Europe. The programme will provide graduates that are required to facilitate the provision of information technology services to support a diverse range of users. The programme is designed to equip graduates with the necessary skills and competencies to assist organizations using information technology to meet the challenges posed by requirements to be increasingly accessible. The aims of the programme are in keeping with the mission of the Dublin Institute of Technology which is “to provide a comprehensive technological education service for Irish society and industry having regard to the technological, commercial, social and cultural needs to the community it serves”. Further it is closely aligned with Ireland’s and the EU’s stated aims to develop a “comprehensive and holistic strategy to spur on the growth of the ICT sector and the diffusion of ICT in all parts of the economy”6. Graduates will be equipped with the relevant practical and technical skills required to enable them to practice at a professional level in the field of Assistive Technology in industrial and academic environments. The programme will provide a unique opportunity for personnel already employed in the information technology industry to obtain a highly relevant postgraduate qualification on a part-time basis. 2.2 Programme Objectives and Learning Outcomes Programme Objectives and Learning Outcomes are outlined in this section at two levels: the Post Graduate Diploma in Computing (Assistive Technology) and the MSc in Computing (Assistive Technology). Learning outcomes are categorised using the National Qualifications Authority of Ireland (NQAI) range of standards of knowledge, skill and competence. 2.2.1 Postgraduate Diploma in Computing (Assistive Technology) A student may choose to exit from the MSc programme with a Postgraduate Diploma in Computing (Assistive Technology) having successfully accumulated the requisite number of credits for this award. Specific details of this award are outlined in the Part B programme document. 6 “Facing the Challenge - The Lisbon strategy for growth and employment” Report from the High Level Group chaired by Wim Kok, November 2004, p. 22. 3 Programme Objectives The primary objectives of the Postgraduate Diploma programme are to: impart a sound understanding of the general principles of Assistive Technology to students who have a strong academic track record in computer science or other numerate discipline; provide sufficient experience of selected, leading-edge topics, methodologies and technologies within computing for Assistive Technology to significantly advance the career prospects of graduates within the IT industry; equip students with knowledge to enable them to develop and apply technologies in the area of Assistive Technology. Programme Learning Outcomes Knowledge On successful completion of this Postgraduate Diploma programme, the graduate will be able to demonstrate: Detailed knowledge and understanding of fundamental topics in computing for Assistive Technology and the manner in which they are combined in the overall process of inclusive design. Detailed understanding of selected specialised computing topics useful in the area of Assistive Technology. Awareness of ethical and professional issues relevant to computing in Assistive Technology. Know-How and Skill On successful completion of this Postgraduate Diploma programme, the graduate will be able to: Perform problem analysis from written descriptions. Derive limited requirements specifications from an understanding of problems. Create and/or justify designs to satisfy given requirements. Effectively design and develop accessible systems. Perform independent information acquisition and management, using the scientific literature and Web sources. Define and contextualise computing research problems in the area of Assistive Technology, questions or issues. Propose and scope a research project of reasonable scale. Communicate effectively by oral, written and visual means. Prepare technical reports to a professional standard. Prepare and present seminars to a professional standard. 4 Competence On successful completion of this Postgraduate Diploma programme, a graduate will be able to: Engage in and take significant responsibility for the successful specification and resolution of Assistive Technology projects in both technical and managerial roles. Communicate the specification and resolution of Assistive Technology projects in both technical and managerial roles. Work effectively as an individual and as a member of a team. Take significant responsibility for the work of individuals and groups. Take limited/partial responsibility for leading and initiating Assistive Technology activities. Demonstrate an awareness of how Assistive Technology can be used in a variety of organisational types and the impact of Assistive Technology initiatives on such organisational types. Demonstrate an appreciation of the wider inclusive society and the challenges faced by and responsibilities of individuals and organisations in such a society. Appreciate the importance of continued academic/professional development within the field of computing for Assistive Technology. Demonstrate an awareness of the resources available to keep up to date with new developments in Assistive Technology. Demonstrate an awareness of personal responsibilities within professional codes of conduct relevant to computing in Assistive Technology. Take responsibility for their own learning. Learn from experiences gained in different contexts. Demonstrate the ability to comprehend multiple perspectives. 2.2.2 MSc in Computing (Assistive Technology) Programme Objectives The primary objectives of the MSc in Computing (Assistive Technology) programme are to: impart a sound understanding of the general principles of Assistive Technology to students who have a strong academic track record in computer science or other numerate discipline; provide an in-depth treatment of selected, leading-edge, research-based topics within computing for Assistive Technology; equip students with knowledge to enable them to develop and apply technologies in the area of Assistive Technology; 5 provide sufficient breadth and depth of experience in up-to-date methodologies and technologies to significantly advance the career prospects of graduates within the IT industry, and/or equip them to undertake research in computing. Programme Learning Outcomes Knowledge On successful completion of the MSc programme, the graduate will be able to demonstrate: Detailed knowledge and understanding of fundamental topics in computing for Assistive Technology and the manner in which they are combined in the overall process of inclusive design. Detailed understanding of selected specialised computing topics useful in the area of Assistive Technology. Detailed knowledge and understanding of selected, leading-edge, researchbased topics within computing for Assistive Technology. Detailed knowledge and understanding of research methodology and practice. Awareness of ethical and professional issues relevant to computing in Assistive Technology. Know-How and Skill On successful completion of the MSc programme, the graduate will be able to: Perform problem analysis from written descriptions. Derive requirements specifications from an understanding of problems. Create and/or justify designs to satisfy given requirements. Develop original ideas in a research context. Effectively design and develop accessible systems. Define and contextualise computing research problems in the area of Assistive Technology, questions or issues. Propose, scope, plan and manage a research project of significant size. Perform independent and efficient time management. Communicate effectively by oral, written and visual means. Prepare technical reports to a professional standard. Prepare a dissertation to acceptable academic standard. Present and defend research findings in an academically acceptable format. Prepare and present seminars to a professional standard. 6 Competence On successful completion of the MSc programme, a graduate will be able to: Engage in and take significant responsibility for, the specification and successful resolution of Assistive Technology projects in both technical and managerial roles. Communicate the specification and resolution of Assistive Technology projects in both technical and managerial roles. Confidently defend research findings. Work effectively as an individual and as a member of a team. Take significant responsibility for the work of individuals and groups. Take significant responsibility for leading and initiating Assistive Technology activities. Demonstrate an awareness of how Assistive Technology can be used in a variety of organisational types and the impact of Assistive Technology initiatives on such organisational types. Demonstrate an appreciation of the wider inclusive society and the challenges faced by and responsibilities of individuals and organisations in such a society. Appreciate the importance of continued academic/professional development within the field of computing for Assistive Technology. Demonstrate an awareness of the resources available to keep up to date with new developments in Assistive Technology. Take responsibility for their own learning. Learn from experiences gained in different contexts. Demonstrate an awareness of personal responsibilities within professional codes of conduct relevant to computing in Assistive Technology. Demonstrate the ability to comprehend multiple perspectives. 3 Market Demand and Support from Industry and Government Policy 3.1 Justification for the Programme Ireland has one of the highest concentrations of information and communications technology (ICT) activity and employment in the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) counties. According to ICT Ireland, almost 100,000 people are employed in the ICT sector. In 2001, exports of ICT products and services from Ireland represented 33% of all exports. Ireland is currently the largest 7 exporter of software products in the world and in 2003 manufactured one third of all Personal Computers sold in Europe7. The National Skills Bulletin 2005 identifies current and future skills shortage of IT professionals8. In particular, it notes that “Demand (for IT staff) is expected to continue to be high, whereas the supply is expected to remain at current levels or fall. Post 2006, it is expected that demand for ICT skills will exceed supply and eventually exceed it by a substantial margin”. This shortage has been exacerbated by the down turn in the technology sector in 2001 as recruitment numbers of leaving certificate students dropped in line with the downturn in the IT sector. The Expert Group on Future Skills Needs (EGFSN), established in 1997, is a body appointed by the Irish Government to advise it on aspects of education and training related to the future skills requirements of the enterprise sector of the Irish Economy. Its membership is composed of representatives from business, employees, education, Government departments and State agencies. The EGFSN’s latest report of 2005 recommends a focus on continuing education for those already in the workforce. It also notes that as the ICT market recovers, colleges need to allow for a major expansion in the demand for graduate diploma conversion courses. The European Disability Forum estimates that from 10% to 20% (almost 50 million people) of the European population has a disability. Much attention has been given in recent years to the fact that the population of the western world is ageing rapidly. Research would indicate that most individuals within this ageing population are likely to acquire some form of disability, from natural or external causes which will, according to current estimates, lead to an increase in the number of people registered as having a disability to 17% by 2020. This increase will create an even greater demand for technologies, which will allow people to participate more fully in society and enjoy a greater quality of life. If Ireland is to leverage its position as a leader in the IT sector, it must not only help in the education of IT students, but also it must identify and focus on specific knowledge intensive domains within the IT sector such as Assistive Technology, to grow expertise and research into these domains. The MSc in Computing (Assistive Technology) is aimed directly at consolidating the IT knowledge of individuals with formal or experiential computing knowledge to increase their abilities to apply that knowledge in assistive technology. The MSc will provide a pathway for those with a technical or numerate qualification who have some computing experience to widen their knowledge of IT in a specific discipline, and thus provide them with a pathway to working in the assistive technology sector. 7 8 Forfas (2003): The Fourth report of the Expert Group on Future Skills Needs. FAS (2005), National Skills Bulletin 8 4 Job Placement of Graduates Given that this is a new programme, there is no history of job placement for graduates. However, it is anticipated that there will be strong demand for graduates in two roles; As AT practitioners who design, develop and maintain assistive technologies, and As IT professionals with a deep awareness of the design and development of accessible software and web-based products. The latter role is becoming more and more significant, particularly in light of the range of recent European Union (EU) initiatives that examine this issue, most significant an initiative called "i2010 – A European Information Society for Growth and Employment" which holds the view that "All citizens have the right to benefit from new opportunities that the Information Society offers." To ensure all citizens have access to the information society, IT professionals must be aware of the accessibility as it applies to web and software design and development. Thus, the introduction of this programme is timely and relevant to the current and projected needs of organisations in Ireland. 5 Admission Requirements and Standards 5.1 Admission Criteria The programme does not accept any applications for direct entry to the Postgraduate Diploma in Computing (Assistive Technology) and all accepted students must initially enrol for the MSc in Computing (Assistive Technology) programme. This MSc programme requires applicants to have experience of the issues involved in designing and implementing computer systems from a simple to moderate degree of complexity in either an industrial or an academic context. The minimum admission requirements for entry to the MSc programme are as follows: (1) B.Sc. (Honours 2.2. or better) in Computer Science or an allied discipline with computer science as a significant programme component. Each such programme will be assessed by the Admissions and Exemptions Committee. Or (2) Applicants with at least 3 years experience in a relevant industry with a qualification in computer science or related discipline of at least equivalent to NQAI level 7. Although not meeting (1) these candidates may be assessed at interview by the Admissions and Exemptions Committee. Or 9 (3) Any other relevant qualification as recommended by the Admissions and Exemptions Committee and approved by the Director of Science Faculty, DIT. Although not meeting (1) or (2) these candidates may be assessed at interview by the Admissions and Exemptions Committee. Where demand for the programme exceeds the number of available places, selection will be made by the Admissions and Exemptions Committee based on academic merit and relevant experience. 5.2 Access for students with a disability In keeping with the DIT policy on Disabled Students and the philosophy of the programme, this School actively promotes access to its programmes for students with a disability. 5.3 Intake policy and Procedures Applicants must apply directly in writing to the Office of Post Graduate Studies. All applications will be reviewed by the Admission Committee of this programme. The responsibilities of the Admission Committee are detailed in Part B of the programme documentation. 10 6 Programme Structure and Content The programme structure and content is detailed and available in Part B of the documentation. 7 Staff 7.1 Academic Staff Resources The School of Computing is directed by a Head of School of Computing, a Head of Department of Computer Science and a Structured Lecturer. The School has thirty eight full-time academic staff, three technical staff and a school secretary. The School also has four pro-rata lecturers. It is the policy of the School, in keeping with its ethos of an industrially-oriented education system, to have a number of lecturers on contract who are currently employed in the ICT industry sector. They provide lectures, seminars and supervise final year projects at both under graduate and post graduate levels. PhD Masters BSc/BA Total SL3 SL2 SL1 ST L L 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 15 19 PRORATA 1 3 4 TWT TOTAL 2 9 11 8 27 3 38 Table 2 Staff Profile for the School of Computing Additionally there are 15 part-time staff in the School including Project Supervisors from industry. Technical Staff 3 Computer Technicians (1 PWT, 2 TWT) Administrative Staff 1 School Secretary (PWT) 7.2 Staff Teaching on the Programme Staff assigned to teaching on the programme can be found in Appendix A. Individual staff curriculum vitae are shown in Appendix C. 11 7.3 Research and Development Interests There has been a major increase in the research and development interest and activities within the School during the past four years. This has resulted in a substantial increase in the number of academic publications and externally generated funding for the School. This is reflected in the table of publications: Number of academic publications 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 7 35 36 37 48 Table 3 Number of publications by staff from School of Computing 2002 - 2006 The principal areas of research and development within the School are: Assistive Technology Legacy Systems E-commerce Systems Assistive Technology E-Learning Pedagogy Quality Factors in Software Software Development Intelligent Agents Case-based Reasoning Artificial Intelligence Computational Linguistics/Natural Language Processing Mobile Computing Distributed Databases Database Technology Internationalisation of Education Geographical Information Systems Music Technology 7.3.1 Staff Professional Development The School of Computing supports an extensive programme of staff development for both academic and technical staff. There are currently twelve staff members undertaking study and research for a PhD degree. Two of these have recently submitted their PhD theses in 2006 and a further cohort will be submitting in late 2007. Staff development is supported by the school budget, by externally funded income and by a dedicated budget of 38,000 euro annually, provided by the Dublin Institute of Technology for a five-year period commencing in 2002. The school has appointed three senior research professors with a proven track record of successful PhD Supervision to the school on a part-time basis whose sole function within the School is the supervision of staff on the PhD programme. 12 Staff are encouraged to avail of and participate in courses which are primarily presented to upskill industrial personnel. These are funded by the School. There is also a very comprehensive staff development programme provided by the Learning and Teaching Centre which staff are encouraged to avail of and which have been proved to be of major benefit to the School in developing innovative teaching techniques. 7.4 Teaching Techniques and Programme Delivery In line with the ethos of a post-graduate programme, there will be considerable emphasis placed on independent research and study, discussion groups, problemsolving skills, effective communications and the ability to work in teams. Students will be expected to develop independence in, and responsibility for their own learning. The programme will continue to use guest speakers from industry and the School as a core teaching technique in order maximise the students’ exposure to a variety of industry scenarios, systems and perspectives. This will form the basis for the Case Studies in IT module, but will also be used throughout the remaining modules wherever relevant. This technique has in the past proven invaluable for enabling students to broaden their horizons and knowledge, particularly in selecting a specialist area for their dissertation. A Virtual Learning Environment (VLE) will be employed to distribute teaching materials and to support student interaction with both other students and academic staff. This resource is particularly important for students who are also working in industry as they have a particular need to be able to access teaching materials outside of the college. Students are expected to proactively use this resource. To facilitate the completion of assignment, students will be provided with an outline timetable of the assignments at the beginning of each semester. This will be important to help students to plan their time and co-ordinate their work industry. Learning, teaching and assessment methods for individual modules are provided in more detail in the module descriptors in Part B of the programme documentation. 8 Accommodation/Resources 8.1 Teaching Facilities Lectures, tutorials and practicals will be held at the Kevin Street and Aungier Street sites. The School of Computing has nine dedicated computer laboratories, six in the Kevin Street site and three in the Aungier Street site. Details may be found in Section 8.3.2 Computer Facilities. Computer laboratories are open and available to students from 8 a.m. to 9.30 p.m. during the academic year. A more restricted access is operated during holiday periods. 13 Lectures and tutorials normally take place in lecture theatres and rooms but on occasion where appropriate in the computer laboratories. Many of the lecturing rooms have been fitted with ceiling mounted projectors. Four rooms have been enabled with wireless networking (WiFi) to enable greater flexibility in teaching. 8.2 Library Students have access to Kevin Street College library and the libraries of the other five constituent colleges. In addition, students can have access to the libraries of Trinity College. Extensive inter-library facilities are available. Kevin Street College library has over 6,000 volumes dealing with mathematical and computer science topics and computerised search facilities. Situation: Area: Seating: Staff: e-mail contacts: Opening hours: Term time Vacation Library holdings: Periodicals: The library comprises the entire second floor of the Kevin St. Annex Building. 1200 m2. 405 on the main library floor 2 (professional grade) 5 (non-professional grade) julie.defoubert@dit.ie Librarian tina.hayes@dit.ie Senior Library Assistant kstlibrary@dit.ie General Enquiries 9.30 a.m. - 9.30 p.m. Monday-Thursday 9.30 a.m. - 5.15 p.m. Monday-Friday Bookstock: 50,000 vols. approx. 440 hardcopy titles See e-journals information below Systems: All seven constituent site libraries plus the Library Central Services Unit use the Millennium system for WebOPAC provision and circulation, acquisitions, cataloguing, document supply and serials management. General Library Information: Students and staff may borrow from any of the six DIT Library sites on production of their DIT ID card and have electronic access to their library account whereby they may view, renew and place holds on items. Undergraduate students can request letters of referral to use TCD Library or other academic libraries. Academic staff and postgraduates are eligible to apply for an ALCID card which is a reciprocal access scheme allowing staff and postgraduate 14 students access to libraries of member institutions. See the Library website for more details. Electronic Resources Information: WebOPAC (Online Public Access Catalogue) provides a complete list of DIT Library holdings, including books, and journals plus access to users library account using an ID number and PIN. www.library.dit.ie. The WebOPAC and the Library Website both provide links to electronic information resources including subject databases, subject web-links, electronic journals, other library catalogues and web guides. The DIT Library website is accessed at www.dit.ie/library. Metafind, a meta search facility which allows simultaneous searching of library catalogues, internet search engines and subject databases may also be accessed here. Databases: DIT Library subscribes to over 60 databases with user single sign-on facilitated by the Athens Access Management system. These include Web of Science which provides a cited reference searching facility, INSPEC, Science Direct, British Standards Online (fulltext) and the IEEE Electronic Library Online which supports database functionality and fulltext journal access. E-Journals: DIT Library has subscriptions to over 16,000 electronic fulltext journals across a range of subjects. Access is available via the library website or the WebOPAC. Current Awareness services such as Zetoc enable the creation of Electronic Tables of Contents via the British Library extensive periodical databases. Information Skills Training: Library orientation sessions are given at the beginning of every academic year, enabling students at different levels to find and use hardcopy and web resource. Seminars on research resources specifically related to a programme can be arranged by appointment at any time during the academic year. An information skills e-module on WebCT is currently being devised to support students in using library resources. Contact julie.defoubert@dit.ie for more information. Internet Access: a dedicated room on the library premises contains 12 PCs for internet use. Access via a student username and password and use is on a ‘walk-in’ basis. The library also has 3 general use internet PCs and 5 WebOPAC PCs on the library floor. To enable wider laptop usage the Library implements WIFI wireless technology. Access from Home: Electronic resources as outlined above are available to registered library users on a remote basis. Details are available on the staff and student intranets. Study Facilities: A student collaborative study room is available for small groups of students working on group or problem based learning projects. A separate AV room equipped with a TV, DVD and video machines is also available 15 Inter library Loans: Material not available in DIT Library is available via the Inter Library Loans system which aims to offset any limitations on periodical title subscriptions. Our major document supplier is the British Library, but loans of books, and theses or purchase of journal articles may be arranged from any academic library. Requests are submitted and supplied electronically where possible. A charge is levied to offset the overall cost of this service (€6 for undergraduates and €8 for all other users). Assistive Technology: a dedicated PC, scanner and internet point with assistive technology software (Kurzweil) is available. PC login access is via a password provided by the Disability Office. Reprographics: an outsourced maintenance service provides 4 photocopiers (A3, A4 and acetates) and a networked printer for student use. Copyright guidelines apply. 8.3 Accommodation and Facilities All teaching and practical work is accommodated between the Kevin Street and the Aungier Street site. 8.3.1 Staff Accommodation Members of the Computer Science staff are accommodated in a number of offices in two main locations in the Kevin Street site. Kevin Street Room A324 16 m2 Room A324 Room K347 A Room K347 B Room K345 28 m2 14 m2 14 m2 11 m2 Departmental Office Staff Office Staff Office Staff Office Staff Office School Secretary Room A112 Room K26 Room K26A Room K113A Room K115A Room K201 50 m2 30 m2 42 m2 25.25 m2 26.25 m2 33 m2 Staff Office Staff Office Staff Office Staff Office Staff Office Staff Office Head of School Structured Lecturer Head of Department 1 Senior Lecturer 1 (Teaching) 3 Technicians 6 Academic Staff 4 Academic Staff 5 Academic Staff 5 Academic Staff 6 Academic Staff 21 m2 Staff Office 4 Staff Members 34 New Bride Street Ground Floor 16 8.3.2 Computer Facilities The School of Computing delivers a comprehensive range of IT services tailored to the needs of staff and students. It is the policy of the school to provide the highest level of service and support to all users. The school maintains a Microsoft Active Directory infrastructure which provides centralised account and password management allowing staff and students of the school access to any PC maintained by the school. Upon registration a user account is automatically created for the student facilitating access to the School’s resources. Email addresses are provided to all students by the DIT Central IT Services. 8.3.2.1 Server Facilities The school operates a mixed server environment comprising of Microsoft Windows 2000, Microsoft Windows 2003, Suse Linux, Debian Linux and Sun Solaris. Services available to students of the school include: Microsoft Active Directory authentication services Internal web hosting on Microsoft Internet Information Services version 6.0 SQL relational databases: Microsoft SQL Server 2000, Postgres and Oracle 10g. Networked home directories for both Unix and Windows environments Accessible network file shares storing course materials A virtual server networking environment using User Mode Linux 9 Solaris 8 graphical Unix desktop environment provided to SunRay thin clients. Unix multi user development environment on Debian Linux On-line e-learning environments (Moodle and WebCT) 8.3.2.2 Hardware Facilities The School of Computing currently maintains 8 computer laboratories comprising of a total of 172 PCs running Microsoft Windows XP and 1 dedicated Unix laboratory which consists of 1 Sun V280 server running Sun Solaris 8 that currently supports 20 Sun-Ray 150 thin clients. One lab is currently being updated and rewired to support the teaching of Cisco networking modules. The School of Computing Laboratories are ergonomically designed and equipped with air conditioning and ceiling mounted projectors. Labs are open to students from 8am to 9:30 pm Monday to Friday and 10am to 4 pm on Saturdays. In addition to the lab projectors the School provides 15 portable projectors to aid the delivery of lectures and programme material via electronic presentations. DIT provides a wireless Internet access service in selected areas of the campus allowing all staff and students of DIT to continue their research in classrooms, recreational areas and the library. In addition to the fixed computing facilities, the School provides 30 wireless enabled laptops available on a temporary loan basis to students of the School. 17 Print services are provided to all students of the school in every laboratory via Hewlett Packard LaserJet 4100 laser printers. Students are required to provide their own paper. Toner and support are provided by the School of Computing. Lab A115 A116 Location Kevin St Kevin St Equipment 20x SunRay 150 terminal Clients 12x Dell GX260 (P4, 2.4Ghz, 512MB RAM, 20GB Hard-disk, CDROM, ZIP-drive, 100Mbit NIC) 8x Dell GX270 (P4, 2.8Ghz, 512MB RAM, 40GB Hard-disk, CDRW-drives, ZIP-drive, 100Mbit NIC) A117 Kevin St 20x Dell GX270 (P4, 3.2Ghz, 2048MB RAM, 80GB Harddisk, DVD/CDRW combo, ZIP-drive, 1Gbit NIC) A305 Kevin St 24x Dell GX270 (P4, 2.4Ghz, 1024MB RAM, 40GB Harddisk, CDRW-drive, ZIP-drive, 1Gbit NIC) A306 Kevin St 24x Dell GX280 (P4, 2.8GHz, 1GB RAM, 80GB Hard-disk, CDRW-drive, ZIP-drive, 1Gbit NIC) A308 Kevin St 20x Dell GX270 (P4, 2.4Ghz, 512MB RAM, 40GB Hard-disk, CDRW-drive, ZIP-drive, 1Gbit NIC) 4x Dell GX260 (P4, 2.4Ghz, 512MB RAM, 40GB Hard-disk, CDRW-drive, ZIP-drive, 1Gbit NIC) 1-005 Aungier St 25x Dell GX260 (P4, 2.4Ghz, 512MB RAM, 40GB Hard-disk, CDROM, ZIP-drive, 1Gbit NIC) 1-006 Aungier St 25x Dell GX260 (P4, 2.4Ghz, 512MB RAM, 40GB Hard-disk, CDROM, ZIP-drive, 1Gbit NIC) B37 Aungier St 10x Dell GX270 (P4, 2.8Ghz, 512MB RAM, 40GB Hard-disk, CDROM, ZIP-drive, 100Mbit NIC) 8.3.2.3 Software Facilities The School of Computing provides access to all software required by students to complete their programme through a standard image on all School of Computing PCs. This standard environment provides a consistent user experience across all labs. The following table presents a list of software applications are available to students of the school: 18 ActivePerl 5.8.3 build 809 Netbean 3.6 IDE Java J2EE SDK 1.4.2 (inc. J2SE) Java J2RE 1.4.2 Java Web Services 1.3 (inc. Tomcat 5) MS SQL Server Client 2000 Project 2002 + updates Borland C++ 5.02 Cobol 6.1A SSADM Derive 5.04 MatLAB 6.5.1 MiniTab 13 Hugs98 (Nov2003r2) Windows 2000 OS + SP4 + Updates Adobe Acrobat 6.0 Pro .Net Framework Norton Antivirus + Updates MS Office 2003 + updates Oracle Spatial VMWare-Player MS Project Eclipse 3.0 JUnit 3.8.1 CafeOBJ 1.4.6 Apache Ant 1.6.2 Z-Eves 2.3 BCC55 Visio modeler 3.1 FDM Query iUMLite Winzip 9 JbuilderX OCL Compiler MS Visual .Net Rational Rose Oracel 9i StarOffice 7.0 +J2RE 1.4.2 Putt Terminal Client Netscape 7.1 Turbo Pascal 1.5 Nunit Spim Simulator Macromedia Studio 8 8.4 Technical and Administrative Support The school employs three computer technicians who design, implement, operate and support all School of Computing services. The School technicians deliver support to staff and students via both an email based ticketing system and on an informal basis via drop-in support. There is one school secretary who staffs the School office and currently supports all the academic staff. 8.4.1 Technical Requirements for This Programme In this programme, a Virtual Learning Environment will be used to enable students to access online teaching and learning material and to support interaction between students and academic staff. The VLE that will be employed will be available for use by students and academic staff from the outset of the programme. No additional funding is required to support the use of a VLE for the programme. 8.4.2 Additional Facilities Required to Run the Programme Students who wish to complete their assignments outside the college, will be expected to have access to their own computer facilities. 19 9 Internationalisation of School It is important that modern Schools of Computing should have an international dimension. It opens horizons, both for staff and students and enriches all aspects of their academic experience. The School of Computing has developed strong relationships with third-level institutions in the United Kingdom and particularly in China in recent years. The programme of studies leading to a BSc (Hons) in Computer Science (DT228) is currently being offered in English at the Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT) in China. This programme will offer a BSc (Hons) degree from both DIT and HIT. This joint programme has been identified by the Department of Education of the Government of the Peoples Republic of China as being a possible prototype which may be offered elsewhere in the recently established Schools of Software Engineering throughout China. The School of Computing was successful in 2003 in achieving substantial funding of 600,000 euro from the EU Asia Link Programme to develop an undergraduate BSc in Computing incorporating the industrial focus currently being offered by the School of Computing with appropriate Chinese industrial and social culture. A number of the academic staff of the School have spent time in HIT during the past years developing and implementing aspects of the programme including curriculum development, programme delivery and in particular, quality assurance issues. The School of Computing is responsible for the Project with the University of Wolverhampton and HIT as partners. The School of Computing has a large number of non-EU students, approximately 15% of the total whole time student cohort. This has beneficial effects on the School as a whole but particularly for their fellow students. It widens intellectual horizons and introduces a multi-cultural atmosphere from which we can all learn. The School also welcomes EU students who wish to pursue their studies in Computing in the DIT. 10 Assessments The structure and nature of Examinations and Assessments is documented in Part B of the Programme Documents. 10.1 External Examiners’ report It is the practice of the School of Computing to nominate external examiners for each of its programmes, both academic and industrial. In this programme, there will initially be two external examiners, one academic and one industrial. The duties and the detailed responsibilities of the external examiners are described in the General Assessment Regulations (Modular Programmes). 20 11 Programme Management and Quality Assurance Arrangements This section describes the programme management structures. 11.1 Programme team and Programme management structures In keeping with the Quality Assurance Handbook: The Programme Team consists of the following staff: Head of School of Computing Head of Department of Computer Science, All whole-time academic staff of DIT who lecture on the programme, The Programme Committee for the programme as selected by the Programme Team is to be found in Appendix B. It comprises of: Head of School of Computing Head of Department of Computer Science Dissertation Co-ordinator Additional staff teaching on the programme Student representatives The chairperson is elected by the Programme Committee. The Committee meets at least once a semester and the Programme Team at least each academic year. 11.2 Programme Monitoring and Quality Assurance The procedures to be implemented and followed to assure the quality of the programme are in accordance with the Quality Assurance Handbook. In particular, an annual report form (Form Q5) will be prepared and discussed by the programme committee. 12 Student Handbook and Information Channels for Students A student handbook will be provided and made available online for students. This will be regularly updated to inform students of current and ongoing development on the programme. In addition, a full set of documentation for the programme will be available in the library. Meetings between staff and students will take place each semester. This forum will allow students to provide feedback on programme content and teaching strategies. 21 Student representatives will be present at Programme committee meetings, enabling students to provide input, ideas and feedback into programme review and development discussions. 13 Programme Development Plan It is proposed that programme will start in the first semester of academic year 2007/2008. A formal review of the programme will take place every five years in accordance with Dublin Institute of Technology’s Quality Assurance procedures. However, it is the policy of the School of Computing to internally review syllabi for the programme biannually to take account of the rapid evolution of the IT industry. 22 14 Appendix A – Module responsibilities The following is a list of the modules and nominated lecturers. Core Modules Module Code Module Title Nominated Lecturer ASTC1101 Foundations of Assistive Technology Dyslexia and Assistive Technology Universal Design Damian Gordon Assistive Technology Professional Skills I Problem Solving, Communication and Innovation Man and Machine Ger Craddock Assistive Technology Professional Skills II Case Studies in Assistive Technology Research Methods and Proposal Writing Ger Craddock ASTC1201 ASTC1301 ASTC1401 ASTC1501 ASTC1601 ASTC2101 ASTC2201 ASTC2301 John Gilligan Ciaran O’Leary Brian McNamee Dave Carroll Deirdre Lawless Fred Mtenzi Option Modules Module Code Module Title Nominated Lecturer ASTC2401 Damian Gordon ASTC2501 Inclusive Learning Through Technology Ubiquitous Computing ASTC2601 Accessible Web Design Brendan Tierney ASTC2701 Biomedical Devices James Condron ASTC2801 Project and Change Management Robotics Susan McKeever ASTC2901 Michael Collins John Kelleher 23 15 Appendix B – Programme Committee Membership Role Name Head of School of Computing Head of Department of Computer Science Brendan O’Shea Dissertation Co-ordinator Additional staff teaching on the programme Damian Gordon Dave Carroll, Michael Collins, James Condron, Ger Craddock, John Gilligan, John Kelleher, Deirdre Lawless, Fred Mtenzi, Susan McKeever, Brian McNamee, Ciaran O’Leary, Brendan Tierney. Student representatives To be elected. Bing Wu 24 16 Appendix C – Curriculum Vitae STAFF CURRICULUM VITAE 25 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Brendan O’Shea SL III (Head of School) Full time 2. Academic Qualifications BSc, MSc, PhD 3. Experiences 1966-67 Junior Lecturer, University College, Galway 1970-71 Lecturer, University of Leeds 1971-75 Lecturer (L1), College of Technology, Kevin Street. 1975-79 Lecturer (L2), College of Technology, Kevin Street 1979-2001 Science. Asst. Head, Department of Mathematics, Statistics & Computer 2001-Present Head, School of Computing 4. Scholarly Interests Discrete Mathematics Computer Aided Learning Medical Informatics Software Development Web Metrics Sports Nutrition Sports Science Smart Card Technology 5. Publications “Algorithms for the solution of systems of coupled 2nd order differential equations” Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, Vol. 4, No. 1, 1978. “A nutritional study of Irish athletes” (with Barry et al.), Brit. J. of Sports Med. 15 (1981) 99-109. “Dietary survey of a central Dublin population” (with Doherty et al.) Journal of Irish Medical Association 71 (1978) No. 17. 26 “A control study of dietary factors in Renal Stone formation”, (with Griffiths et al.), Brit. Journal of Urology 53 (1981) 416-420). “A case-control study of the dietary intake of Renal Stone patients (with Griffith et al.) Paper 1 Urological Research, Vol. 14 (1986). “A case-control study of the dietary intake of Renal Stone patients (with Griffith et al.) Paper 2 Urological Research, Vol. 14 (1986). “An integrated approach to marathon training”. Proceedings of the Eighth Mid. East Sports. Sc. Symposium, pp. 20-25 (1988). “A nutritional study of Olympians.” Proceedings of the Eight Mid. East Sports Sc. Symposium, pp. 63-65 (1988). “Nutrition in sport.” Education; Vol 4. No. 7. 3-7. (1988). “Food for Sport and Fitness”. Barry, Kevany and O’Shea, CDVEC publications (1982). “ “Dietary Principles for Optimum Performance.” Sports Science Symposium; proceedings from ninth World Veteran Championships, pp 87-92. (1989). “Establishment of an Irish nutrient database.” Flair Eurofoods - Enfant project, pp 126-126. (1989). “PCDIET: Nutrition Analysis Program for the IBM and Power Mac computers” Mathias, P. and O’Shea, B. Proceedings of the Third Macedonian Conference on Dietetics and Nutrition (1997). Brendan O’Shea, Bing Wu and Cindy Liu (2003) Industry-Oriented Education to Meet the Requirements of Software Industry and Beyond, IT Education Vol. 1, No. 1 pp66-69, Dec 2003 Fitzpatrick, R., Smith, P. and O'Shea, B. (2004) Software Quality Revisited, Proceedings of the Software Measurement European Forum (SMEF 2004, Rome), Istituto di Ricerca Internazionale S.r.l., Milan, Italy, p307/315, ISBN 88-86674-33-3. Fitzpatrick, R., Smith, P. and O'Shea, B. (2004) Software Quality Challenges, Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Software Quality at the 26th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2004), Edinburgh, Scotland, IEE, Stevenage, Herts, UK. Fitzpatrick, R., Smith, P. and O'Shea, B., 2005 Web site engagibility: A step beyond usability, invited paper Proceeding of HCI International 2005, Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction, Las Vegas, USA, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc (LEA) 27 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Bing Wu SL2 (Assistant Head of School) Full Time 2. Academic Qualifications BSc, MSc, PhD 3. Experiences May 2001 – Present Senior Lecturer II, School of Computing, DIT, Dublin Nov. 1998 – Apr.2001 Lecturer II Department of Computer Science DIT, Dublin Jan. 1997 – Sept. 1998 Research Fellow Department of Computer Science Trinity College Dublin Jan. 1992 - Aug. 1996 Researcher Department of Computation, UMIST, UK leading to Ph.D Feb. 1985 - Dec. 1991 Lecturer Department of Computer Science, NUDT, China 4. Scholarly Interests Applications of modern database systems Information system engineering and re-engineering Legacy system migration and integration Healthcare informatics and Bioinformatics Distributed information systems E-business, E-Service Object-oriented modelling and design approaches 5. Publications Wan, B S and Wu, B (1986): Formal language National-Defence Publication 296 pagers ISBN 7-81024-027-7. This book was conferred with the ‘Best Textbook Award’ by the Chinese National Education Committee in 1993. Recent Papers in Refereed Journals and Conferences (since 1998) K Dube, E Mansour and B Wu (2005) Supporting Collaboration and Information Sharing in Computer-Based Clinical Guideline Management. Accepted for The 18th IEEE International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS05). Dublin, Ireland. June (2005). P Banks, L Moor, C Liu and B Wu (2004) Dynamic visual acuity : a review The South African Optometrist Vol. 63 No. 2 June 2004 28 D Lawless, B Wu, X Xu, C Yuan and K Bechkoum (2004) Requirements For An Industry-Oriented IT Education Model To Support The Emerging Knowledge Economy in China in Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Knowledge Economy and Development of Science and Technology. "Knowledge Economy meets Science and Technology" (KEST 2004) Beijing, China. September 17-20. B O’She, B Wu and C Liu (2003) Industry-Oriented Education to Meet the Requirements of Software Industry and Beyond IT Education, Vol. 1 No.1 (ISSN 1672-5913) China, December 2003 Yingyu Wan, Fred Mtenzi, and Bing Wu (2003) Distributed Construction of Weakly Connected Dominating Sets for Clustering Mobile Ad Hoc Networks, Third IT&T Annual Conference, 22-23 October, 2003 Xiaohai Wei, Fredrick Mtenzi, Bing Wu and Yingyu Wan (2003), An Energy Efficient Routing Algorithm With Priority for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (PDSR), Proceedings of the Third IASTED International Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications, Editor: Lambertus Hesselink, pages 628-632, ISBN: 0-88986-3741, ACTA Press, 2003. D Nugent, K. Dube and B Wu (2003) (DAAS) A Web-Based System for User-Specific Dietary Analysis and Advice for the Public Health Domain In the Proceedings of the 7th international Conference for Young Computer Scientists, Harbin, China, August 810, 2003 Yingyu Wan, Fred Mtenzi, and Bing Wu (2003) A best-possible approximation for minimum-energy multicast problem in wireless ad hoc networks, XVI Conference of the European Chapter on Combinatorial Optimization, 5 June - 7 June 2003 Molde, Norway R. Jones, K. Dube and B Wu (2003) TOPME: AN XML-BASED CLIENT-SERVER FRONT-END FOR THE DISTRIBUTED MANAGEMENT OF CLINICAL PROTOCOLS FOR TOPS In the Proceedings of the 7th international Conference for Young Computer Scientists, Harbin, China, August 8-10, 2003 R. Eiband, P Kennedy, D Cotter, R Ryan, U MacEvilly, B Wu (2003) : Analysis of Atlantic Salmon Skin Mucus: COPS – A computer-based system for protein pattern analysis of 1 D SDS-PAGE gels 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Bioinformatics & Bioengineering (BIBE 2003) Bethesda, Maryland March 10-12, 2003 K.Dube, B.Wu and J. Grimson (2002): Using ECA Rules in Database Systems to Support Clinical Protocols, the 13th International Conference on Database and Expert Systems Applications (DEXA 2002). Aix en Provence, France, September 2002 (LNCS2453) Eibrand, R. Kennedy, P., Cotter, D., Ryan,R. MacEvilly, U., Wu, B. (2002)., COPS – Computerised Proteomics System for Protein Pattern Analysis of 1D SDS-PAGE Gels of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Skin Mucus. In Proceedings of the Swiss Proteomics Society, Lausanne, Switzerland 87-90. 29 K.Dube, B.Wu and J. Grimson (2002): Framework and Architecture for the management of Event-Condition-Action (ECA) Rule-Based Clinical Protocols, the 15th IEEE Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems. Maribor, Slovenia, June 2002 L. Moore, B. Wu, and C. Liu (2001) Computer Software Application in the Testing of Dynamic Visual Acuity and Recognition times Sport Vision 2001, Loughborough, UK. April (invited talk). K. Dube and B. Wu (2001) : Supporting Clinical Laboratory Test Ordering Protocol Specification, Execution and Management: an Event-Condition-Action Rule and Database Approach Healthcare Informatics Journal (HIJ), Sheffield Academic Press, UK. March, 2001 B. Wu and K. Dube (2001) : Applying Event-Condition-Action Mechanism in Healthcare: a Computerised Clinical Test-Ordering Protocol System (TOPS). The Third International Symposium on Cooperative Database Systems for Advanced Applications Beijing, China. B. Wu and K. Dube (2001) PLAN : a Framework and Specification Language with an Event-Condition-Action (ECA) mechanism for Clinical Test Request Protocols in the Proceedings of Thirty-fourth Annual Hawaii International Conference on Systems Sciences (HICSS-34), the Information Technology in Health Care Track, Maui, Hawaii. K. Dube and B. Wu (2000) : Supporting Clinical Laboratory Test Ordering Protocol Specification, Execution and Management: an Event-Condition-Action Rule and Database Approach 5th Annual Conference and Scientific Symposium of Healthcare Informatics Society of Ireland, Saggart, Co.Dublin. (Best Research Paper Award). K. Dube and B. Wu (2000) : Specification, Implementation, Management and Execution of Clinical Test Ordering Protocols: a Database Approach. in the Proceedings of the First European Workshopon Computer-based Support for Clinical Practice Guidelines (EWGLP 2000). Leipzig, Germany. P. O'Byrne and B. Wu (2000): LACE Frameworks and Technique -- Identifying the Legacy Status of an Information System from the Perspectives of its Causes and Effects in the Proceedings of the International Symposium on Principles of Software Evolution, Kanazawa, Japan F. Knox, D. Berry, P. Gaffne, B. Wu, G. Stephens, M. Sharp, W. Grimson, J. McGrory (1999): INCA: The Development of an Integrated Network Clinical Analyser, 4th Annual Conference and Scientific Symposium of Healthcare Informatics Society of Ireland, Malahide, Dublin. D. Berry, B. Wu, S. Pardon, F. Duignan, W. Grimson, P. Gaffney, F. Clarke, J. Feely(1999) A Test Request Protocol System IFCC WorldLab Conference, Bologna, Italy. 30 J. Bisbal, D. Lawless, R. B. Wu, and J. Grimson (1999) “Legacy Systems Migration : A Brief Review of Problems, Solutions and Research Issues”, IEEE software. Vol.16, No.5 B. Wu, D. Lawless, J. Bisbal, and J. Grimson, (1998) "Legacy System Migration : the Database Engineering Prospective", Invited paper (keynote speaker), in the Proceedings of the 18th Database Conference (DATASEM '98), Brno, Czech Republic. B. Wu, D. Lawless, J. Bisbal and J. Grimson (1998) “Facing Challenge : migrations of Legacy Information Systems” in the Proceedings of the 3rd national conference of young Chinese scientists. Beijing, China. J. Bisbal, B. Wu, D. Lawless and J. Grimson (1998) “Building Consistent Database Sampling to Support Information Systems Evolution and Migration”, in the Lecture Notes of Computer Science (LNCS 1460) 31 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Dave Carroll, BSc, MSc, MBCS Structured Lecturer Full-Time 2. Academic Qualifications Dublin City University MSc in Computer Applications 1996 Dublin City University BSc in Information Technology 1993 Dublin Institute of Technology, Kevin St, Dublin 8. Structured Lecturer in Computer Applications 2001 To Date Dublin Institute of Technology, Kevin St, Dublin 8. Lecturer 1 in Computer Science 1999 2001 Dublin Institute of Technology, Mountjoy Square, Dublin 1. Lecturer 1 in Computer Applications Information Technology and Multimedia 1983 1999 1980 1983 3. Experiences Various companies in private sector. Service Manager/Chief Engineer - Broadcast and industrial video systems 4. Scholarly Interests Human Computer Interaction, Assistive Technology, IT Skills Acquisition Models, IT Training Delivery Models, Quality Assurance in Industry Oriented Software Education. Currently pursuing PhD research in IT Skills Acquisition and IT Training Delivery Models under the supervision of Prof. Gordon Bull and Dr. Brendan O’Shea. 5. Publications/Presentations Lawless, Deirdre; Gordon, Damian; O’Leary, Ciarán; Carroll, Dave; Mtenzi, Fred and Collins, Michael (2005) Educational model for industrially oriented software 32 engineering education. Poster at DIT Showcase on Learning and Teaching, May 2005. Carroll, D (2005). EMERSION Industry Oriented Education Model - QA System Requirements Overview. CEIS-SIOE 2005: 1st China-Europe International Symposium on Software Industry Oriented Education, 10-11 January 2005, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China. Presentation delivered at CEIS-SIOE 2005 Session Four: Quality Assurance in Industry Oriented Software Education. Carroll, D (2004). Evaluation of IT Skills Certification Schemes. 3rd Annual Research Conference, 16-17 December 2004, School of Computing, Dublin Institute of Technology Presentation on current PhD research work. Carroll, D (2002). Training Delivery Models for IT Skills Acquisition. 1st Annual Research Conference, 16-17 December 2004, School of Computing, Dublin Institute of Technology PhD research presentation. 6. Membership of Professional Bodies British Computer Society Member (Professional Grade) 2004 Association of Computing Machinery Member (Professional) 2001 IEEE Computer Society Member 2001 33 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Paul Kelly SL1 Full time 2. Academic Qualifications B.Sc. M.Sc. 3. Experiences Industrial: 4 years Academic:20 years 4. Scholarly Interests Virtual learning environments, software agents, Learning Disabilities and Assistive Technology 5. Publications A Guide to C Programming (3rd Edition), Gill and Macmillan, 1999. A Guide to C++ Programming, Gill and Macmillan, 2001. 34 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Andrea Curley Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications 2004 1995 1994 MSc in IT for Strategic Management (Distinction), D.I.T. BSc in Computer Science and Software Engineering (2.1), D.I.T. Diploma in Computer Science, (Distinction), D.I.T. 3. Experiences 2000-05 Ericsson Telecommunications Test team Lead/ Senior Designer in the 3G/UMTS I&V Department 3G/UMTS Integration & Verification Engineer 2G/GSM Integration & Verification Engineer 1994-2000 Riverdance 4. Scholarly Interests Web Content Protection Music Technology Telecommunications 35 1. Personal Details Name: Art Sloan Grade: Lecturer Full time/Part-time: Full-Time 2. Academic Qualifications Higher National Diploma in Computer Science Graduate Diploma in Computer Science Master of Science (Faculty of Economics) in Analysis, Design and Management of Information Systems 3. Experiences 1989 – 1992: Systems Engineer, British Aerospace Military Aircraft, Warton, Lancashire 1992 - 1993: Database Programmer, KPMG, Belfast 1993 – 1994: Analyst/Programmer, Applied Scientific Ltd, Limerick Also: Analyst/Programmer, Accutron Ltd, Limerick 1994 – 1999: Lecturer (MIS and Computing), various 3rd-level institutions in Ireland incuding UCD, NCIR, Carlow Inst of Tech and Dundalk Inst of Tech 199 – Present: Lecturer (PWT), DIT, Kevin Street 4. Scholarly Interests Currently a PhD student (part-time) at the Dublin Institute of Technology 5. Publications EdTech 2003 Conference Paper: Comparing the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator to the Multiple Intelligence Inventory EdTech 2004 Conference Paper: Learning Outcomes in Web-Based Education ITTE Conference Paper: Constructivism in Web-Based Education 36 1. Personal Details Name: Brian Mac Namee Grade: Lecturer Full time/Part-time: Full time 2. Academic Qualifications 2000 BA (mod) Computer Science, University of Dublin, Trinity College. 2004 PhD, Department of Computer Science, University of Dublin, Trinity College 3. Experiences 2000-05 (Part-Time) Technical Trainer, International Academy of Computer, Dublin, Ireland 2002-03 (Part-Time) Lecturer, University of Dublin, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland 2004-05 R & D Software Engineer, Agilent Technologies, Dublin, Ireland 4. Scholarly Interests Machine Learning Artificial Intelligence Computer Games Augmented Reality 5. Publications B Mac Namee, S Dobbyn, P Cunningham & C O'Sullivan, “Simulating Virtual Humans Across Diverse Situations”, In Proceedings of Intelligent Virtual Agents ’03, pp 159-63. (2003) B Mac Namee & P Cunningham, “Creating Socially Interactive Non Player Characters: The µ-SIC System”, International Journal of Intelligent Games & Simulations, Vol.2 No.1. (2003) C Peters, S Dobbyn, B Mac Namee & C O'Sullivan, “Smart Objects for Attentive Agents”, In Proceedings of the International Conference in Central Europe on Computer Graphics, Visualization and Computer Vision. (2003) B Mac Namee, S Dobbyn, P Cunningham & C O'Sullivan, “Men Behaving Appropriately: Applying the Role Passing Technique to the ALOHA System”, Proceedings of Artificial Intelligence and the Simulation of Behaviour '02. (2002) 37 B Mac Namee, P Cunningham, S Byrne & O Corrigan, “The Problem of Bias in Training Data in Regression Problems in Medical Decision Support”, Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, Volume 24, Issue 1, pp 51-70. (2002) B Mac Namee & P Cunningham, “Proposal for an Agent Architecture for Proactive Persistent Non Player Characters”, Proceedings of the Twelfth Irish Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Science, pp. 221 - 232. (2001) 38 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Brendan Tierney Lecturer Full Time 2. Academic Qualifications Diploma in Applied Science BSc (Applied Science) MSc (Computer Applications) Graduate Diploma in Applied Project Management 3. Experiences 1993-1996 – Oracle Corporation (Ireland & UK) – Consultant 1996-1998 – Deloitte & Touche Management Consultants (Ireland) – Senior Database Consultant 1998-2001 - Norkom Technologies (Ireland, Belgium & USA) - Project Manager & Senior Technical Consultant 4. Scholarly Interests Databases, Data Mining, Data Warehousing, Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Management, Organisational Analysis & Statistics 5. Publications Tierney, B., Jackson, M., 2004, 'Contextual Semantic Integration for Ontologies', British National Conference on Databases, Doctoral Consortium, Tuesday 6th July, 2004. Zhao, S., Tierney, B., 2004, 'Bi-Directional Mapping between Ontology Versions: A Requirement for Data Sharing in Distributed Environments', Second International Conference on Computer Science and its Applications (ICCSA-2004), San Diego, California, USA, June 28-30, 2004. Tierney, B., Jackson, M., 2004, 'Contextual Extensions for Ontology Integration', Second International Conference on Computer Science and its Applications (ICCSA-2004), San Diego, California, USA, June 28-30, 2004. Tierney, B., Jackson, M., 2003, 'Using Ontologies in Knowledge Discovery in Data', International Conference on Emerging Technologies, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA, August 25-26, 2003. Hofmann, M., Tierney, B., 2003, 'The Involvement of Human Resources in Large Scale Data Mining Projects', International Symposium on Information and Communication Technologies, Dublin, Ireland, 24 - 26 September, 2003. Hofmann, M., O'Mahony, M., Tierney, B., 2003, 'A Framework to Utilise Urban Bus Data for Advanced Data Analysis', 10th World Congress on Intelligent Transport Systems, Madrid, Spain, 16 - 20 November, 2003. 39 Tierney, B., Jackson, M., 2003, 'Using Semantics for Knowledge Discovery in Data', 20th British National Conference on Databases, Coventry, England, 15 - 17 July, 2003. Tierney, B., 2002, 'An introduction to Business Intelligence and Knowledge Discovery in Data', CRM2Day, May, 2002. 40 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Bryan Duggan Lecturer Full-time 2. Academic Qualifications 2003 MSc in IT for Strategic Management, Dublin Institute of Technology 1996 First Class Honours Degree in Computer Science and Software Engineering, University of Dublin, Trinity College 1993 Diploma in Computer Science, (Credit Standard), Dublin Institute of Technology Kevin St. 3. Experiences DIT Kevin St National College of Ireland AIB Dec, 2003 - To Date Sep, 2002 – Dec, 2003 Lecturer Assistant Lecturer May 2002 Java and Internet Security specialist Vice President with Responsibility for Internet Projects Internet specialist Web developer C Programmer Bear Stearns Sept 1998 – Sept 2001 Lotus Womex SIS Sept 1997 – Sept 1998 Sept 1996 – Sept 1997 Sept 1993 – Sept 1996 4. Scholarly Interests I am presently pursuing a PhD entitled “Modeling Creativity in Traditional Irish Music using Case Based Reasoning”. I am also interested in Music Technology and Games Programming 5. Publications Duggan, B.: Creating Effective Efficient & Desirable Voice Enabled Web Systems, presented at the 8th ERCIM Workshop "User Interfaces For All", Palais Eschenbach, Vienna, Austria, 28-29 June 2004 Duggan, B. and Deegan, M.: Considerations in the usage of Text To Speech in the Creation of Natural Sounding Voice Enabled Web Systems, International Symposium on Information and Communication Technologies, Trinity College Dublin September 24-26, 2003 41 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Ciarán O’Leary Lecturer (Permanent) Full time 2. Academic Qualifications BSc (Hons) Computer Applications, Dublin City University MSc Computer Science, Trinity College, Dublin Member of the Institution of Engineers of Ireland 3. Experiences 1999 Web Developer Solomon Smith Barney, New York City, USA 1999 – 2001 IT Contractor (Part Time) IT Training with Irish Academy of Computer Training and Computer Learning Centre Ireland. Java Developer with Labyrinth on Digifone Online website. 2000 – Date Lecturer Lecturer with the School of Computing, Dublin Institute of Technology 4. Scholarly Interests I am currently pursuing a PhD in the area of Behaviour Based and Distributed AI. Other research interests include Distributed and Internet Systems and E-Learning. 5. Publications 'Leary, Ciarán; Humphrys, Mark and Walshe, Ray, A novel application of Web Services in Computer Science education. In proceedings of The International Conference on Computer as a tool (EUROCON 2005). Belgrade, Serbia & Montenegro, November, 2005 O’Leary, Ciarán, Reuse and arbitration in diverse Societies of Mind. In proceedings of the 16th Irish conference on Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Science (AICS 2005), Coleraine, Northern Ireland, September 2005 42 Lawless, Deirdre; Gordon, Damian; O’Leary, Ciarán; Mtenzi, Fred; Xu, Xiaofei and Bechkoum, Kamal, "Establishing undergraduate research communities", to be presented at CAL2005, Bristol, England, April 2005. Lawless, Deirdre; Gordon, Damian; O'Leary, Ciarán and Collins, Michael, "Determining Key Skills for IT Graduates in the Emerging Knowledge-Based Economy", presented at All Ireland Society for Higher Education Inaugural Conference, Trinity College, Dublin, 2 - 3 September 2004 Walshe, Ray; Humphrys, Mark and O'Leary, Ciarán, "Complex Brains: Constructing better minds using sub-minds from biotechnology authors", in proceedings of The First IFIP Conference on Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations, Toulouse France August, 22-27, 2004 O'Leary, Ciarán; Humphrys, Mark and Walshe, Ray, "Constructing an animat mind using 505 sub-minds from 234 different authors", in proceedings of The Eighth International Conference on the Simulation of Adaptive Behavior (SAB'04) 13 - 17 July 2004, Los Angeles, CA, USA O'Leary, Ciarán and Humphrys, Mark, "Building a hybrid Society of Mind using components from ten different authors", in proceedings of Seventh European Conference on Artificial Life (ECAL-03), September 2003, Dortmund, Germany O'Leary, Ciarán, "Technology for automated assessment: The World-Wide-Mind", talk presented at EdTech 2003, Waterford, Ireland, May 2003. Gordon, Damian and O'Leary, Ciarán, "Zen and the art of web site evaluation: tools to assist in the successful development of an elearning portal", talk presented at CAL 2003, Belfast, Northern Ireland, April, 2003. Humphrys, Mark and O'Leary, Ciarán, "Constructing complex minds through multiple authors", in From Animals To Animats 7: The 7th International Conference on the Simulation of Adaptive Behavior (SAB-02), August 2002, Edinburgh, Scotland. O'Leary, Ciarán and Humphrys, Mark, "Lowering the entry level: Lessons from the Web and the Semantic Web for the World-Wide-Mind", poster at 1st Int. Semantic Web Conf. (ISWC-02), June 2002, Sardinia, Italy 43 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Cindy Liu Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications B.Sc. Computer Science M.Sc. Computer Science 3. Experiences Nov. 2001– Present Post: Lecturer Computing School, DIT, Kevin Street Nov. 1999 – Nov. 2001 Post: Senior Database Developer Labyrinth Ltd. Upper Hatch Street, Dublin 2 Jan. 1999 – Nov. 1999 Post: Software Researcher Industrial Control Centre, DIT, Kevin Street Mar. 1992 - Apr. 1993 Post: Lecturer Department of Systems Engineering National University of Defence Technology Hunan, China Mar. 1986 – Sep. 1989 Post: Lecturer Department of Systems Engineering National University of Defence Technology Hunan, China Aug. 1982 - Feb. 1986 Post: Software Engineer Xi-Chang Satellite-Lunching Centre Shi-Chuang Province P. R. China 4. Scholarly Interests Computer Application for Sports E-Learning technologies and solutions Database systems and applications 5. Publications P Banks, L Moor, C Liu and B Wu (2004) Dynamic visual acuity : a review The South African Optometrist Vol. 63 No. 2 June 2004 44 Brendan O’Shea, Bing Wu and Cindy Liu (2003) Industry-Oriented Education to Meet the Requirements of Software Industry and Beyond, IT Education Vol. 1, No. 1 pp66-69, Dec 2003 Linda Moore, Cindy Liu and Bing Wu (2001) DOVE: the Development of a Software System for Testing Dynamic Visual Acuity and Recognition Time invited talk in Sports Vision 2001 M.Sc Thesis (1992) The Development of a Software Analysis System for Gymnasts Training Text Book: Xiaoling Liu and MeiXi Zhao (1987) Programming in Assembly Language National University of Defense Technology Printing 45 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Damian Bourke Lecturer Full-Time 2. Academic Qualifications Dip.EE, B.Sc.(Eng.), PGD(ITSM), M.Sc.(ITSM). 3. Experiences 1988 - 1990 Allen Martin Conservation Limited - Software Development, Project Engineer. 1990 – 1993 British Telecommunications Limited – Operations and Maintenance Manager. 1993 – 1995 Concert Communications Limited - Operations and Maintenance Manager. 1996 – 2001 Eircell Limited - Project Engineer, Strategic Planning Manager, Interconnect Manager. 2001 – Present DIT, Kevin Street - Lecturer. 4. Scholarly Interests Communication systems, Computer networks, Network Programming and Distributed Systems. 5. Publications Various dissertations/final year projects in pursuit of the above qualifications. 46 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Damian Gordon L Full time 2. Academic Qualifications M.A. in Computer Science, Trinity College, Dublin Certificate in Java and HTML Programming, School of Computer Technology B.A.(Mod.) in Computer Science, Trinity College, Dublin 3. Experience Jan 2001 – To Date Lecturer for the School of Computing, Dublin Institute of Technology May-August 2000 Researcher for CRITE (Centre for Research in IT in Education), TCD Mar 1999 – Dec 2000 Researcher for Trinity College Dublin, in conjunction with Machine Vision Technology (MVT) Nov 1998 – Feb 1999 Implementation Consultant for Ross Systems Ireland Ltd. Mar 1996 - July 1998 Business Systems Analyst/Developer (Team Leader) for Phimac Computing Ltd. Oct 1995 - Jan 1996 Visiting Researcher to the Department of Computer Science, National University of Ireland, Maynooth. 4. Scholarly Interests eLearning eLearning, Virtual Learning Environments, pedagogically inspired models in ICT Education, constructivistic learning approaches. Knowledge Management Knowledge Acquisition and Representation, Ontology Design, Knowledge Management for Assistive Technology, Ontological Representations of ICT Training Computer Vision Automated Inspection, shape-from-specularity, shape-from-shading, shape-frommotion, photometric stereo, Gestalt psychology, illusory contour formation, biologically inspired models. 47 5. Publications Gordon, D., eBeckett: An Investigation of the Additional Dimensionality provided by an On-line Environment for Beckett Studies, Beckett at 100: New Perspectives, Febuary 2006. Lawless, D., Gordon, D., O'Leary, C., Mtenzi, F., Xu, X., Bechkoum, K. Establishing Undergraduate Research Communities, CAL 2005, April 2005. Craddock, G., Gordon, D., Scherer, M., Inclusive Learning through Technology: Individualized Curriculum in Special Ed, ATIA 2005 Conference and Exhibition, Orlando, Florida, January 2005 Gordon, D., Craddock, G., Lynch, B., Using the de Bono 6-Hats Technique as a Learning Styles Model, ELSIN Seminar 2004, University of Durham, UK, September 2004 Lawless, D., Gordon, D., O'Leary, C., Collins, M. Determining Key Skills for IT Graduates in the Emerging Knowledge-Based Economy, All Ireland Society for Higher Education Inaugural Conference, Trinity College, Dublin, September 2004 Gordon, D., Bull, G., The Nexus Explored: A Generalised Model of Learning Styles, SITE 2004, March 2004. Gordon, D., Bull, G., Blood from the Shoulder of Pallas: Using Learning style as a guide when developing Learning Materials using a Virtual Learning Environment, CAL 2003, April 2003. Gordon, D., O'Leary, C., Zen and the Art of Web Site Evaluation: Tools to Assist in the Successful Development of an eLearning Portal, CAL 2003, April 2003. 48 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Deirdre Lawless Lecturer Full Time 2. Academic Qualifications MSc . Computer Science, University of Dublin, 1999. BSc. Computer Science, University College Dublin, NUI 1990. 3. Experience September 2002 – date School of Computing, Faculty of Science, Dublin Institute of Technology, Kevin Street Dublin 8. Lecturer Modules Knowledge Based Decision Support Systems, BSc. Computer Science 4th Year. Algorithms for Artificial Intelligence, BSc. Computer Science 3rd Year. Intelligent Systems Development, BSc. Computer Science 3rd Year Information Systems, BSc. Information Technology 1st Year. Research Local project manager of the Emersion project funded by EU Asia-Link project, awarded March 2003. Emersion will establish, implement and evaluate an industryoriented education model and system in China, particularly for the information technology sector. August 2000 – May 2002 Amdocs, Regus House, Harcourt Road, Dublin 2. R&D Project Lead/Manager for international leader in development of customer care and billing systems for the telecommunications industry in start-up research and development centre in Dublin. October 1998 – July 2000, CIE,Oriel Street, Dublin 1. Web Development Team Lead July 1996 - October 1998, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2. Research assistant on the MILESTONE(MIgrating Legacy SysTems to OpEN Environments) project involving Broadcom Éireann Research, Telecom Éireann, Ericsson and the Department of Computer Science, Trinity College Dublin. October 1996–June 1998 ,Institute of Technology Tallaght, Dublin 24. Associate Lecturer, School of Business Sept. 1990 – July 1996, CIE ,Oriel Street, Dublin 1. Systems Designer 4. Scholarly Interests 49 Information systems engineering and re-engineering, particularly legacy system migration. Knowledge Engineering. Knowledge Management in particular the applications of modern database systems, with active mechanisms End-user controlled software development. ICT Education and E-learning. 5. Publications “Establishing Undergraduate Research Communities”, Deirdre Lawless, Damian Gordon, Ciarán O’Leary, Fred Mtenzi, Xiaofei Xu,Kamal Bechkoum, CAL 05 – Virtual Learning ?, April 2005. "Determining Key Skills for IT Graduates in the Emerging Knowledge-Based Economy", Deirdre Lawless, Damian Gordon, Ciarán O'Leary, Michael Collins, All Ireland Society for Higher Education Conference, September 2004. "Requirements For An Industry-Oriented IT Education Model To Support The Emerging Knowledge Economy in China", Deirdre Lawless, Bing Wu, Xiaofei Xu, Cheng Yuan, Kamal Bechkoum, Second International Conference on Knowledge Economy and Development of Science and Technology, September 2004. “Legacy Information System Migration: A Methodology and its Trial Implementation”, Deirdre Lawless, M.Sc. Thesis, June 1999. “Legacy Information System Migration: A Brief Review of Problems, Solutions and Research Issues”, Jesus Bisbal, Deirdre Lawless, Bing Wu, Jane Grimson, IEEE Software, September 1999. “Requirements for a General Migration Tool-kit”, Deirdre Lawless, Technical Report ML0026, MILESTONE Project, Trinity College Dublin, October 1997. “Legacy Systems Migration: A Method and its Tool-kit Framework”, Bing Wu, Deirdre Lawless, Jesus Bisbal, Jane Grimson, Vincent Wade, Donie O’Sullivan and Ray Richardson, In Proceedings of the Joint 1997 Asia Pacific Software Engineering Conference and the International Computer Science Conference (APSEC’97/ICSC’97), Hong Kong, China, December 2-5, 1997. "An Overview of Legacy Information Systems Migration", Jesus Bisbal, Deirdre Lawless, Ray Richardson, Bing Wu, Jane Grimson, Vincent Wade, and Donie O’Sullivan. In Proceedings of the Joint 1997 Asia Pacific Software Engineering Conference and International Computer Science Conference (APSEC'97/ICSC'97), Hong Kong, China, 2 - 5 December 1997. “Legacy System Migration: A Legacy Data Migration Engine”, Bing Wu, Deirdre Lawless, Jesus Bisbal, Jane Grimson, Vincent Wade, D O’Sullivan, and Ray Richardson. In Proceedings of the 17th International Database Conference (DATASEM ‘97), pp. 129-138, Brno, Czech Republic, October 12 - 14, 1997. 50 1. Personal Details Name: Office Location Tel: E-mail: Denis Manley K113a 402 – 4949 denis.manley@comp.dit.ie 2. Education and Qualifications Schools Attended Millstreet Community School Cork R.T.C. D.I.T. Kevin Street D.I.T. Kevin Street National Distance Education Centre D.C.U. D.I.T. Kevin Street Examination Taken Second Level Leaving Certificate 1986 Subject Maths Physics Chemistry Biology Applied Maths Third Level Degree in Applied Sciences Certificate in COBOL Programming Diploma in Information Technology Degree in Information Technology MSc. In Information Technology 3. Work Experience Company Kevin Street D.I.T. Kevin Street D.I.T. From 1981 1987 1990 1993 1994 To 1986 1990 1992 1994 1998 1998 2000 Level Honours Honours Honours Honours Honours Grade A A A A B Grade B.Sc. (hons) 2.1 Distinction Year 1992 Distinction 1996 College Trinity College D.I.T. Kevin St. D.C.U. B.Sc. (hons) 1.1 Distinction 1998 D.C.U. 2000 D.I.T Kevin St. From To Sept 2000 Jan 1999 --------June 2000 51 1994 Position and Duties Lecturer in Computer Science Supervisor of computer labs. Enfer Scientific, 21 Upper Fitzwilliam Street Dublin 2 Sept 1993 Aug 1998 Supervisor of introductory C labs. Laboratory Technician incl. maintenance of the computer system Bon Secours Hospital Tralee Co. Kerry. Jan 1993 Aug 1993 Laboratory Technician West Middlesex Hospital, London, England June 1990 Sept 1990 Laboratory Technician Cork University Hospital, Cork. Sept 1989 June 1990 Laboratory Technician PROJECTS MSc papers The strategic implications of electronic commerce for Businesses Smart Cards: Their features and strategic implications. Neural networks an alternative computing paradigm for strategic management An Investigation of Electronic Commerce issues using Biometric Verification Techniques Implemented on Smart Cards. Strategic issues influencing the adoption of Internet retailing PhD Title: An Investigation into computational methods for understanding gene regulation 4. Research Interests Bio-informatics: namely pattern matching techniques that can be used to analyze and store biological information. Modelling biological processes and computational Analysis of biological processes Setting up a Bioinformatics Course 5 Publications (International only) An Investigation into computational methods for understanding gene regulation IEEE SMC 2004 The Hague, The Netherlands. 52 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Edina Hatunić-Webster Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications M.Sc. Computer Science; 1993, Computer Science Department, University College Dublin; M.Sc. Thesis: “Hatunić, E., Design and Implementation of a Security System for a Complaint Handling Management Application, M.Sc. Dissertation, Department of Computer Science, University College Dublin, February 1993” B.Sc. Mathematics with Computer Science; 1989, Faculty of Science and Mathematics, University of Sarajevo, Bosnia-Hercegovina 3. Experiences Sep.2004 – Present Dublin Institute of Technology, School of Computing Lecturer in Computing Lecturing K268/3 Software Engineering Lab assistant for the following courses: FT228/3 User Interface Programming (Labs and Tutorials), FT228/2 Operating Systems and FT228/4 Distributed Systems Supervising 5 Final Year Projects Mar.2003 – Apr.2003 Institute of Art, Design and Technology, Dun Laoghaire Mathematics and programming tutor Run an advice clinic for first year students having problems with mathematics and programming LogicaCMG (Logica Mobile Networks) Technical Leader/Senior Designer/Team Manager 1998 – 2003 Designed and developed client functionality for the Operations & Maintenance Interface of Logica’s MMS and SMS products (using Java/Swing). Designed and implemented the licensing feature for the Logica’s SMSC. 53 Participated in code and product reviews. Presented solutions to UI design issues. Evaluated and recommended tools and procedure for the CMF GUIs unit and regression testing (JUnit , SilkTest) Managed development team of 2–7 developers, including supervision and training of two new hires. Followed ISO9001 quality procedures. Designed and developed the Event Viewer – a Java/Swing fault management application. Led the development team to deliver on time the following SMSC components: database schema development and support, SNMP subagent, Metrics Module (a Webbased Java client and Java server connecting to an Oracle database). Projects within the team utilised Java, C, JDBC, CORBA and Oracle technologies. Negotiated project outsourcing for the Metrics Product. Designed and developed a user interface utility (a Java application) that allows activation representatives to activate and reprogram CDMA phones. Presented the product demo version to the customer. Evaluated and introduced new tools into development process (JDK, InstallShield). Critical Path 1995 – 1998 Technical Leader/ Senior Software Engineer Developed a Web-based GUI (a Java applet) used to administer ISOCOR E-mail server. Designed and implemented a MAPI based address book, using DAP (Directory Access Protocol) to access X500 directory services. Designed and implemented extensions to the ISOPRO for MAPI E-mail client to provide automatic compression/decompression and virus checking of message attachments. Wrote project proposals. Synaptics Ltd 1993 – 1995 Software Engineer Extended the X.500 attribute syntaxes, added new attributes and objects to support the project specific distributed directories and provided security for the directory using X.509 certificates. CNDS Research Group, Department of 1991 - 1993 Computer Science, UCD Research Assistant Designed and developed a security system for a Telecommunications Management Network (TMN) application – Complaint Handling Management Application. Mentored undergraduate student projects. Presented work at a Departmental Seminar. Chosen to present at the 1992 UCD Postgraduate Day IRIS – ENERGOINVEST 1989 - 1991 Software and Security Specialist Designed and developed a security library during the work on the CEC's COST-11 Ter 'Computer Networks Security' and CEC's COST-225 'Secure Communications' projects. The library is a part of a commercial product. 54 4. Scholarly Interests Health Informatics, Computer Security 5. Publications Technical Assistant for the book: “S. Muftic, A. Patel, P. Sanders, R. Colon, J. Heijnsdijk and U. Pulkkinen, ‘Security Architecture for Open Distributed Systems’, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 1993”. “Muftic, S. and Hatunic, E. 'CISS: Generalised Security Libraries', Computers & Security, 11 (1992) 653-659.” “Hatunic, E., Clissmann, C., Patel, A. (UCD), Hurley, B. and Fitzgerald, A. (Broadcom Ltd.), 'Provision of Security to a TMN Complaint Handling Application', 6th RACE TMN Conference, Madeira, September 1992.” One of the collaborative colleagues for the book: ‘Muftic, S., ‘Security mechanisms for computer networks’, Ellis Horwood Computer Communications And Networking Series, 1989 55 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Emmet Caulfield Assistant Lecturer Pro-Rata 2. Academic Qualifications B.Eng. in Electronic Engineering, higher second class honours, 1995. 3. Experiences RISC assembly language programming (Kestral Security Products Ltd.), mixed signal hardware design (Kestral), software development (Kestral), Unix & Korn shell training (various), training materials development (L.M. Ericsson Ireland Ltd.), Internet & web programming (Netrogen, various), IP telephony (TCSI Ltd., SIP Projects Ltd.), financial web service development, plasma surface engineering (Plasma Coating Group, DCU), business automation and consulting (DiverseyLever Ireland Ltd.). See: http://netrogen.com/about/emmet.php 4. Scholarly Interests Database management systems and models, object modeling, operating systems, Open Source software. 5. Publications None. 56 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Frank Deignan L Part-time 2. Academic Qualifications B. Sc., M. Sc., FBCS, AFIMA, C. Eng. 3. Experiences 1971 – 1974: Mathematical/Systems Programmer, University of Wales, Cardiff 1974 – 1977: Associate Research Fellow, University College London 1977 – 2002: Various roles including Principal Consultant, Systems Architect, ICL/Fujitsu 2002 – Present Part – time Lecturer, DIT 4. Scholarly Interests Knowledge Management eBusiness Networking 5. Publications Asynchronous Transfer Mode – ATM, F Deignan, Ingenuity: ICL Systems Journal, Volume 9, Issue 2, November 1994 Networking Services, F Deignan and D Hollingsworth, Prentice Hall, 1993, ISBN 013-630393-5 57 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Frank Deignan L Full Time 2. Academic Qualifications MSc (Computer Science), BSc(Eng), DipEE, DipTechEng. 3. Experience Industrial: PC based control software for industrial processes. Distributed database ,data entry and data communications systems development and maintenance Embedded systems development. Academic: Lecturer in DIT for 13 years. Ongoing programming support for a range of research projects across a number of faculties between DIT and UCD. 4. Scholarly Interests Assistive technology for Linux Microprocessor based control systems Power electronics. 5. Publications 58 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Fredrick Japhet Mtenzi Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications B.Sc, Master management Science, PhD 3. Experiences Fred’s industrial experience involves analysis, design and implementation of Management Information Systems in two large Banks and Ministry of Labour and Children in Tanzania. He has participated in a number of projects which were sponsored by UNICEF and World Bank as a computer networking consultant. He has been researching in collaboration with one of the largest shopping chains on the appropriate networking technologies they can use in their shopping chains in rural Tanzania. He has been lecturing in third level institutions for more than fifteen years. Among the universities he has worked include University of Dar es salaam – Tanzania, University College Dublin – Ireland and Dublin Institute of Technology – Ireland. He has supervised research students at undergraduate, masters, doctorate and postdoctorate level. In the last five years has worked also as a visiting academic to Harbin Institute of technology and University of Dar es salaam. He is a member of various societies such as IEEE, ACM, Irish Computer society, British Computer society and IASTED. He has been a programme committee member in a number of conferences such as Communications and Computer Networks CCN2004 and Communications Systems ACIT 2005. 4. Scholarly Interests Data quality issues in Data warehousing, Internet price comparison using intelligent agents, Combinatorial Optimization, Approximation Algorithms, NP-Completeness and the Travelling Salesman Problem, Distributed Systems and Components Based Software Engineering, Design and Implementation of Energy aware routing algorithms for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANET) Security issues in MANET and sensor networks Knowledge Management High performance E-Commerce 5. Publications 59 Fredrick Mtenzi and John Kyaruzi, A new search technique in Planar Convex Networks, University Science Journal, December 1993 Fredrick Mtenzi, Personal Computers into interactive future, Computer Center Newsletter, December 1993 Fredrick Mtenzi, Artificial Neural Systems: A necessary tool for Financial decision Making, Institute of Finance Management (IFM) Journal, 1993 Fredrick Mtenzi, Experimental design methodology for large, symmetric, sparse, Travelling Salesman Problem, (accepted for publication on the European Journal of Operations Research). Fredrick Mtenzi, Integer Linear Programming formulations for the Sparse TSP, (accepted for publication on the European Journal of Operations Research). Fredrick Mtenzi, Lower Bound for the Sparse TSP, University Science Journal, June 2002, pp 30-41 Fredrick Mtenzi, Tour Construction Heuristics for the Sparse TSP, Working Paper MIS, Business Research Programme, Graduate School of Business, University College Dublin Fredrick Mtenzi, Tour Improvement Heuristics for the Sparse TSP, Working Paper MIS, Business Research Programme, Graduate School of Business, University College Dublin Fredrick Mtenzi, Random Methods for the Sparse TSP, Working Paper MIS, Business Research Programme, Graduate School of Business, University College Dublin Yingyu Wan, Fred Mtenzi, and Bing Wu, Distributed Construction of Weakly Connected Dominating Sets for Clustering Mobile Ad Hoc Networks, Third IT&T Annual Conference, 22-23 October, 2003 Yingyu Wan, Fred Mtenzi, and Bing Wu, A best-possible approximation for minimum-energy multicast problem in wireless ad hoc networks, XVI Conference of the European Chapter on Combinatorial Optimization, 5 June - 7 June 2003 Molde, Norway Fredrick Mtenzi, Randomised Algorithms for the Sparse Travelling Salesman Problem, The 7th International Conference for Young Scientists, August 9 – 10, 2003, Harbin Institute of technology, China. Xiaohai Wei Fredrick Mtenzi Bing Wu and Yingyu Wan, An Energy Efficient Routing Algorithm With Priority for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (PDSR), , Proceedings of the Third IASTED International Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications, Editor: Lambertus Hesselink, pages 628-632, ISBN: 0-88986-3741, ACTA Press, 2003. Xiaohai Wei, Guoliang Chen, Yingyu Wan, Yinlong Xu and Fredrick Mtenzi. Minimal Re-Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. In Proc. of first IEEE and IFIP International Conference on Mobile and Wireless Communications and Optical communications Networks (WOCN 2004), pages 204-207, 2004 Xiaohai Wei, Guoliang Chen, Yingyu Wan and Fred Mtenzi, Optimized priority based energy efficient routing algorithm for mobile ad hoc networks Pages 231-239, Volume 2, Issue 3, Pages 203-349 (July 2004) Quality of service in ad hoc networks, Ad Hoc Networks, Ad Hoc Networks Copyright © 2004 Elsevier B.V. Peter Cahill and Fredrick Mtenzi, Speech Synthesis for PDA, ITB Journal Issue Number 9, Pages 63-74, May 2004 60 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Hugh Mcatamney Assistant Lecturer part time 2. Academic Qualifications B.Sc managament – University of Dublin Trinity College M.Phil IT – Dublin Institute of Technology 3. Experiences Lecturer in DIT since 1995 President of Triathlon Ireland since 2000 4. Scholarly Interests Virtual Reality Game Engineering / Learning E-Learning 5. Publications The National Gallery of Ireland Virtual Gallery’, National Gallery of Ireland Symposium, Dublin. ‘The National Gallery of Ireland Virtual Gallery’, Proceedings of the VSMM 6th International Conference on Virtual Systems and Multimedia. Ogaki City, Japan. October 2000. 'An Investigation into the Use of the Virtual Reality Modeling Language (VRML) as a Means of Distribution of Virtual Tourism' , Proceedings of the Hospitality Information Technology Association (HITA) Conference, Edinburgh, 1999 There are over 40 citations of my work. A list of these is available in a publications document at Http://www.dmc.dit.ie/2002/research.html 61 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Jane Ferris Assistant Lecturer Temporary WholeTime 2. Academic Qualifications BSc (Hons) Msc (Dist) Materials Engineering with Management IT for Strategic Management 3. Experiences Lecturer in the DIT (2000 – present) 4. Scholarly Interests 5. Publications 62 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: John Gilligan Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications B.Sc (Hons) NUI MSc NUI 3. Experiences Lecturer Computer Science University College Dublin 1986-1988 Lecturer Computer Science DIT 1985 – Present Course Chair FT225 Degree in Applied Science/Computing Researcher on EU ICARUS ERAE project in Formal Specifications 1989 Funded Research IAD/ PAT Grants, ETCI Grants , British Irish Council, Equal 4 , Inclusive Learning Through Technology McMahon Foundation, DIT Seed. External Project Assessor IDA 1999 External Examiner Masters UCD 2003 –2004 Member of Scientific Committee AAATE 03 Conference Chaired Human Computer Interaction session AAATE 03 Conference Internal Assessor DIT Masters Validation in Music Technology 1998 External Assessor Limerick Institute of Technology Masters 2004 4. Scholarly Interests Assistive Technology , Education and Technology Artificial Intelligence, Knowledge Based Systems , Formal Specifications 5. Publications Various Technical reports “Towards a repository of Assistive Technology plans” John Gilligan and Prof. Peter Smith, AAATE 03 Conference Dublin Paper accepted for Balancing Equation Conference Southampton 05 63 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: June Barrett Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications BA (mod) Natural Sciences - Trinity College Dublin PgD – Computer Science - University College Cork MSc – Computer Applications - Dublin City University 3. Experiences 1996-Present Lecturer Dublin Institute of Technology Lecturing in Procedural & Object Orientated Programming, Databases, Systems Analysis & Design. Project co-ordination for final year projects on BSc (Ordinary). Supervision of MSc research for the MSc (ITSM ). Disabilities co-ordinator for the School of Computing. 1986 – 1996 FAS Ireland’s National Training and Employment Authority Project Manager for European Project (EURAS). To develop a European database for recruitment and job placement. Senior Analyst on payroll, personnel, course recruitment database systems. Programmer on various internal and external information systems. 4. Scholarly Interests Object Orientated Programming and OO Systems Design. Database System Architectures, Data Warehousing and Data Mining. Education for students with disabilities. 5. Publications 64 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Ken O’Brien Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications B.E M.Eng.Sc. 3. Experiences Software development, systems analysis, systems programming, systems administration, network planning, and implementation consulting, software engineer 4. Scholarly Interests data communication, operating systems 5. Publications 1.ESB X.25 Packet Data Network, Institute of Engineers of Ireland 11/4/91; 2.The Planning,Design and Installation of ESB's X.25 Network, CIGRE, Paris 1992; 3.Implementation of WGS84 mapping reference system for Irish Airspace IEI magazine 1998 4. A three phase Thyristor invertor for Constant-Current Control of an Induction Motor, M.Eng.Sc. Thesis 1973. 65 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Mark Deegan L1 Full Time 2. Academic Qualifications B.A. (Ordinary) Mathematics, University of Dublin, Trinity College, 1990 B.A.I. (Honours) Engineering, University of Dublin, Trinity College, 1990 M.Sc. (Computer Science), University of Dublin, Trinity College, 1994 M.I.E.I. (Member of the Institute of Engineers of Ireland) 1990 M.B.C.S. (Member of the British Computer Society) 2004 3. Experiences 1990 – 1999: Lecturer, Department of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Scieice, DIT, Kevin Street. Preparing and delivering courses to undergraduate and masters students. 1994 – 1999: IT Consultant. Providing IT design and support services to a number of major clients in Ireland and the UK. 1994 – Present: Director, Degas Software Studios, Dublin. 1994 – 2000: IT Trainer, Moresoft Institute, Dublin. Preparing and delivering commercial IT training courses on a wide range of subjects. 2000 – 2001: Engineering Program Manager, Sun Microsystems. Managing the sustaining of a number of Sun Microsystems software products including Sun Ray and SunForum (video conferencing software). Promoting the evolution of software development and management processes. 2000: Project Manager, Guinness UDV, Dublin. Responsible for managing the deployment of Siebel and related systems to a 250+ strong sales force. 2001 – Present: Lecturer, School of Computing, DIT Kevin Street. Preparing and delivering courses to undergraduate and masters students. Planning the IT infrastructure of the School of Computing. 4. Scholarly Interests 1: The Development of software support systems for ubiquitous computing in an academic environment. I have a keen interest in the area of ubiquitous computing, and, in particular the area of thin client computing. This was the main business area of the Sun Ray group in which I worked at Sun Microsystems. 2: The formation of Third Level Education Policy in Ireland. I have a keen interest in the evolution of the third level sector in Ireland. I am interested in establishing if any particular long term vision has been or should be applied to the development of the third level sector in Ireland. 5. Publications DEEGAN, Mark. O’DRISCOLL, Ciarán. The Development of Software Support Systems for Ubiquitous Computing in an Academic Environment. School of Computing, DIT Kevin Street, 3rd Annual Research Seminar, December 2004. 66 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Mark Foley Lecturer PWT 2. Academic Qualifications DipACP, MBCS, PgD, MSc, CITP 3. Experience 18 years in business world (banking & IT). IT experience includes, operations, software development, consultancy, project management, networking. 9 years in academic world as full time lecturer. 4. Scholarly Interests IT Management, Geographic Information Systems, Spatial Data Mining, Web Development, Databases 5. Publications M. Foley, A. Alderson and H. Shah (2000) "A framework to guide the strategic manager in the acquisition of software development technologies" - 2nd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems. Staffordshire University, UK; July 2000. 67 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Michael Collins Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications M.Sc. in Computer Science B.Sc. (Hons) in Applied Science (Computer Science and Software Engineering) Diploma in Computer Science Technician Certificate in Electronic Engineering 3. Experiences Lecturer in Computer Science, School of Computing, DIT, Kevin Street, Dublin 8. (Sep 02 – present) Software Engineer, TransactPlus, San Francisco, California, USA. (Apr 01 – Nov 01) Research Software Engineer, Broadcom Eiréann Research, Dublin. (Feb 98 – Jun 99) Localisation Software Engineer, ITP, Bray, Co. Wicklow (Jul 97 – Nov 97) 4. Scholarly Interests Internet Research and Web Technologies Pervasive computing IT Education 5. Publications Lawless, Deirdre, Gordon, Damian, O'Leary, Ciarán, Collins, Michael (2004), "Determining Key Skills for IT Graduates in the Emerging Knowledge-Based Economy", to be presented at All Ireland Society for Higher Education Inaugural Conference, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland, 2nd - 3rd September 2004 68 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Oliver O'Connor L Full time 2. Academic Qualifications BSc, MSc 3. Experiences 1975-1978 Lecturer in Computer Applications RTC Dundalk 1978-1986: Software Engineer/Analyst various industries. 1986-present: Lecturer, DIT, Kevin St. 4. Scholarly Interests Systems Analysis, Systems Development Methodologies, Software Engineering, 69 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time: Patrick Browne Lecturer F 2. Academic Qualifications British Computer Society Exams, School of Computing, DIT Kevin St. B.Sc. in Computer Applications, Dublin City University. M.Sc. in Computer Applications, Dublin City University. 3. Experiences 25 years experience of digital cartography and geographic information systems with the Irish Ordnance Survey. 1 year Software Engineer with ICL. 5 years lecturing at the School of Computing, DIT, Kevin Street 2 years lecturing at the National College of Ireland 4 years tutoring with the Open University. 4. Scholarly Interests Geographic Information Systems, Formal Methods, and Databases 5. Publications 1) “Towards a Unified Spatial-Temporal Data Model and Query Language for Geographical Information Systems" at British National Conference on Databases (Doctoral Consortium) in Edinburgh, July 2004. 2) "Unification of Spatial-Temporal Data Models" Conference on Spatial Information Theory (COSIT03) in Switzerland, Sept. 2003. 3) “Spatial and Temporal Data Models for Geographical Information Systems” by Patrick Browne, Micheal O'hEigeartaigh, Dublin City University, Working Paper 1997. 70 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Patrick Matthews Lecturer Full-time (permanent) 2. Academic Qualifications B.Sc. (Hons) (N.U.I.) 3. Experiences 1987-1992 Researcher on various industry and ECfunded projects, Department of Computer Science, U.C.D. 1992-date Lecturer, Department of Management Information Systems, D.I.T. 4. Scholarly Interests Artificial intelligence applications, Natural language processing, Web development. 5. Publications Using Actions to Generate Sentences. In: AI and Cognitive Science '92, Proceedings of the 5th Irish Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Science. (Springer-Verlag 1992) Transforming Expert System Output into Natural Language in a Process Control Environment (with H. Mok). In: SAC '92: Proceedings of the 1992 ACM/SIGAPP Symposium on Applied Computing. (ACM Press, 1992). 71 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Patricia O’Byrne Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications B.Sc. (Hons) in Computer Science with Mathematics as a minor UCD 1981. PgD (ITSM) 1997, University of Staffordshire. M.Sc. (ITSM) with Distinction, 1999, University of Staffordshire. 3. Experiences Systems Programmer, C.I.E. Applications Programmer, C.I.E. Systems Analyst and Designer, C.I.E. Lecturer, D.I.T. Kevin St. 4. Scholarly Interests Legacy systems, Systems Analysis and Design, Databases, Programming. Research into IT for Strategic Management and supervision of Masters students. 5. Publications O’Byrne, Patricia, Wu, Bing “Lace Frameworks and Technique – Identifying the Legacy Status of an Information System from the Perspectives of its Causes and Effects” 2000 International Symposium on Principles of Software Evolution (ISPSE 2000), Kanazawa, Japan. 72 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Paul Bourke Lecturer Full 2. Academic Qualifications B.Sc, H.Dip in Ed, M.Sc, Dip in L.S., LL.M 3. Experiences Maths Teacher & Sports Coach at St. Benedicts, Ealing, London. Systems Analyst at Wang Laboratories in Limerick, Boston & Sydney. 4. Scholarly Interests Alternative IT interfaces Digital Image Processing Global Lighting Models Liability issues in Software systems IT Intellectual Property Rights Data Protection & Freedom of Information e Government Cyber crime 5. Publications Computers controlled by Eye-movement, ISSC 1998 Electronic Voting: An Irish legal case study, UOS 2004 73 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Richard Lawlor Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications B.Sc., M.Sc.(Maths), M.Sc.(Computing) 3. Experiences 1985-present: Lecturer, DIT Part time member of the Foramal Methods Group in TCD for about 2 years. Actively involved with the franchise of FT228 computer science degree by Harbin Institute of Technology. Delivered some of FT228-1 to the HIT-DIT class. 4. Scholarly Interests Category Theory, Formal modelling of concurrency, Formal Specification, Z, CSP, Unifying Theories of Programming, Programming Paradigms, Functional Programming, Concurrent Programming, Software Engineering. 5. Publications I contributed to an IEEE conference paper on "Image Motion Detection and Analysis". The paper was published in "Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Computer Vision (ICARCV'92). Other contributor was Dr. Jan Yun of DCU. 74 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time Ronan Fitzpatrick Lecturer Full-time 2. Academic Qualifications MSc, CEng, MBCS 3. Experiences 32 years of Industrial appointments 1961 - 1967 Draughtsman 1967 - 1968 1968 - 1969 1969 - 1970 Draughtsman 1970 - 1976 1977 - 1984 1984 - 1986 1986 - 1991 1991 to 1993 SMITH & PEARSON LTD. Trainee O'DWYER STEEL CO. LTD. THOMAS GARLAND & PARTNERS CESCO LIMITED Draughtsman Draughtsman Senior BURKE HIGGINS MCNULTY (STEEL) LTD SHANNON STRUCTURES AND SERVICES LTD. FREELANCE COURSEWARE DEVELOPMENT CBT SYSTEMS LIMITED CBT COURSEWARE CONSULTANT Manager Director/Secretary Developer Developer Consultant 12 years of Academic appointments (Lecturer) 1992 - 1998 1995 1995 1996 INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY - TALLAGHT, PORTOBELLO COLLEGE - DUBLIN GRIFFITH COLLEGE - DUBLIN DCU AT INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, TALLAGHT 1996 – to-date (2004) DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY - KEVIN STREET 1999 – 2001 Ireland’s representative to the International Standards Authority Technical Committee - ISO/TC 159/SC4 WG6 - Human centered design processes for interactive systems. 4. Scholarly Interests Strategic Management of IT Usability Web site quality 5. Publications 75 Fitzpatrick, R. (1996) Software Quality: Definitions and Strategic Issues, Staffordshire University, School of Computing Report Fitzpatrick, R. and Higgins, C. (1998) Usable software and its attributes: A synthesis of software quality, European Community law and human-computer interaction, In: People and Computers XIII. Proceedings of HCI’98 Conference, Springer, London, UK Fitzpatrick, R. and Dix, A. (1999a) A Process for Appraising Commercial Usability Evaluation Methods, Human-Computer Interaction: Ergonomics and User Interfaces, Proceedings of HCI International ’99, Munich, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey, USA Fitzpatrick, R. (1999b) Strategies for Evaluating Software Usability, Department of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, Dublin Institute of Technology, Kevin Street, Dublin 8, Ireland Fitzpatrick, R. (2000a) Interpreting quality factors for the World Wide Web, Irish Academy of Management Conference, September 2000, Dublin, Ireland (Extended abstract) Fitzpatrick, R. (2000b) Additional Quality Factors for the World Wide Web, Proceedings of the Second World Congress for Software Quality, Yokohama; Union of Japanese Scientists and Engineers, Tokyo, Japan Fitzpatrick, R. (2001) Strategic Drivers of Software Quality: Beyond external and internal software quality, Second Asia-Pacific Conference on Quality Software, Proceedings of APAQS 2001, Hong Kong; IEEE Computer Society Press, California, USA Fitzpatrick, R. (2002) Software Quality Matters, School of Computing Research Paper (ITSM), Dublin Institute of Technology, Kevin Street, Dublin 8, Ireland Fitzpatrick, R. (2003a) Quality Challenges in E-Commerce Web sites, Workshop paper for Exploring the Total Customer Experience: Usability Evaluations of (B2C) E-Commerce Environments at INTERACT 2003: Ninth IFIP TC 13 International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, September 2003, Zurich, Switzerland Presentation Fitzpatrick, R. (2003b) The Software Quality Star: A conceptual model for the software quality curriculum, Workshop paper for Closing the Gaps: Software Engineering and Human-Computer Interaction at INTERACT 2003: Ninth IFIP TC 13 International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, September 2003, Zurich, Switzerland Presentation Fitzpatrick, R. and O'Donnell, K. (2003) Crafting a research paper ITSM Authoring Style, School of Computing, Dublin Institute of Technology, Kevin Street, Dublin 8, Ireland. Fitzpatrick, R. (2003) Engagibility ratios for quality Web sites: Challenges and strategy, Proceedings of the Dublin Institute of Technology, School of Computing PhD Conference, Dublin, Ireland. Fitzpatrick, R., Smith, P. and O'Shea, B. (2004) Software Quality Revisited, Proceedings of the Software Measurement European Forum (SMEF 2004, Rome), Istituto di Ricerca Internazionale S.r.l., Milan, Italy, p307/315, ISBN 88-86674-33-3. Fitzpatrick, R., Smith, P. and O'Shea, B. (2004) Software Quality Challenges, Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Software Quality at the 26th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2004), Edinburgh, Scotland, IEE, Stevenage, Herts, UK. Fitzpatrick, R., Smith, P. and O'Shea, B. (2005) Website engagibility: A step beyond usability, Proceedings of parallel session "Quality models for Human Computer 76 Interaction" in the context of the 3rd international conference on Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction, HCI International 2005, Las Vegas, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey, USA 77 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Sarah Jane Delany Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications BA (Mod) in Mathematics, University of Dublin, Trinity College MSc. in Computer Science (Assistive Technology), Staffordshire University, UK 3. Experiences 1996- : DIT Kevin Street 1993-1996: ESBI Computing, 1987-1993: Andersen Consulting, 4. Scholarly Interests Machine Learning Case-base Reasoning Email / Spam Filtering Concept Drift 5. Publications Delany SJ, Cunningham P, Tsymbal A, Coyle L. (2005) A Case-Based Technique for Tracking Concept Drift in Spam Filtering, Knowledge Based Systems, to appear. Delany SJ, Cunningham P, Tsymbal A, Coyle L. (2004) A Case-Based Technique for Tracking Concept Drift in Spam Filtering9, AI 2004, the 24th SGAI International Conference on Innovative Techniques and Applications of Artificial Intelligence p316. Delany SJ, Cunningham P, Coyle L. (2004) An Assessment of Case-Based Reasoning for Spam Filtering, In: L. McGinty & B Crean (eds.), Proceedings of Fifteenth Irish Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Science, p.9-18. Delany SJ, Cunningham P. (2004) An Analysis of Case-base Editing in a Spam Filtering System, In: Funk P & Gonzales Calero P.A. (eds.), Advances in Case-Based Reasoning, (Proceedings of Seventh European Conference on Case-Based Reasoning), LNAI 3155 pp.128-141 Springer Verlag Barrett R. & Delany SJ., (2004) openMVC: A Non-proprietary Component-based Framework for Web Applications, WWW2004 13th International World Wide Web Conference, p.464-465. Cunningham P., Nowlan N., Delany SJ., Haahr M., (2003) A Case-Based Approach to Spam Filtering that Can Track Concept Drift, The ICCBR'03 Workshop on LongLived CBR Systems, Trondheim, Norway, June 2003 Delany SJ., Cunningham P. & Wilke W., (1998), The limits of CBR in Project Estimation, GWCBR’98 – 6th German Workshop on CBR, Berlin, March 1998 9 Awarded Best Application Paper, to appear in Special Issue of Knowledge Based Systems 78 Technical Reports: Delany SJ., Cunningham P. (2000) The application of Case-Based Reasoning to Early Software Project Cost Estimation and Risk Assessment. TCD Departmental Technical Report 79 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Shane Mulligan Lecturer Full-time 2. Academic Qualifications B.A.(Mod.), M.Sc., Ph. D. 3. Experiences 2002- present: Lecturer in School of Computing, DIT Kevin St. Jan. – July 2003 Research Sabbatical in Toulouse, France 1990 – 2002 Lecturer in Computer Applications, DIT Bolton St. 1986 – 1990 Research Assistant, Numerical Analysis Group, TCD 4. Scholarly Interests Numerical Analysis, High Performance Parallel and Scientific Computing, Finite Element and Finite Difference numerical methods, Parallel Numerical Algorithms, Mathematics in Computing. 5. Publications Seán P. Mulligan, “A numerical solution of the two-dimensional Poisson equation in semiconductor devices”, M.Sc. Thesis, School of Mathematics, University of Dublin, Trinity College, (1991) Seán P. Mulligan, “A comparison of iterative methods for the solution of the linearised Poisson equation in semiconductor device modelling”, INCA (Institute for Numerical Computation and Analysis) Preprint No. 4, (1987). See the INCA WWW site: http://dune.mcs.kent.edu/inca/index.html Seán P. Mulligan, “On block preconditioned iterative methods for unsymmetric linear systems”, INCA Preprint No. 5, (1988) Seán P. Mulligan, “A comparison of preconditioned conjugate gradient methods for the solution of a linearised two dimensional Poisson equation”, in VECTOR AND PARALLEL COMPUTING issues in applied research and development, eds. Jack Dongarra, Iain Duff, Patrick Gaffney, Sean McKee, Ellis Horwood (1989); also presented at the 2nd International Conference on Vector and Parallel Computing, Tromsø, Norway, June (1988) Seán P. Mulligan, “Preconditioned iterative methods for the numerical solution of the stationary semiconductor device equations”, Ph. D. Thesis, School of Mathematics, University of Dublin, Trinity College, (1991) 80 Seán P. Mulligan, “Preconditioned iterative methods for solving the semiconductor device equations”, IMACS 2000 Conference, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, May 2000, and Int. J. Appl. Sci. Comput. Vol. 8, No. 1, (2001) 81 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Susan McKeever Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications B.A.B.A.I Eng (Electronic) from Trinity College Dublin (1st) 2003 M.Sc Assistive Technology, Dublin Institute of Technology 3. Experiences 1989 – 1993 Software Engineer and Team leader with Andersen Consulting Dublin. Worked on a variety of client assignments, including custom and package system implementations. Clients included Microsoft, Shorts Aircraft and Power Supermarkets. 1993 - 1997 IT Consultant for Binder Hamlyn Consultancy in London. Performed numerous client assigments including IT strategy and systems implementation projects. 1997 – 2002 Independent IT project manager in Dublin, with particular expertise in web systems. Clients included AIB, Bank of Ireland and IBM. 4. Scholarly Interests Web technologies System Interface design 5. Publications McKeever S. (2003) "Defining the range of B2B e-commerce formats", IADIS conference, Portugal. McKeever, S., (2003), Understanding Web Content Management systems: evolution, lifecycle and market, Journal of Industrial Management and Data Systems, Volume 103, Number9, pp 686-692 82 1. Personal Details Name: Grade: Full time/Part-time: Svetlana Hensman Lecturer Full time 2. Academic Qualifications BSc in Computer Science (1st Hons) and MSc in Artificial Intelligence (1st Hons) Awarded by Sofia University, Bulgaria - July 2000. PhD in Computer Science University College Dublin, National University of Ireland Submitted: October 2004, viva scheduled for February 24th, 2005. The PhD dissertation explores the idea of automatically building semantic representation of text, as well as embedding this representation in XML documents. By applying VerbNet and WordNet lexical resources we identify the semantic roles, which in turn are used to construct a conceptual graph representation of each sentence. We also use syntactic information and some semi-automatically precompiled domain specific knowledge. Supervisors: Mr. John Dunnion, Prof. Ronan Reilly. 3. Experiences Teaching Experience Lecturer University College Dublin, Belfield, Dublin 4, Ireland. September 2004 – October 2004 Taught an intensive 6-week course in Programming and Object-oriented development for the Master of Management Science course. Lecturer Griffith College Dublin, South Circular Rd, Dublin 2, Ireland Feb 2001 - Jun 2001, Sep 2004 - Oct 2004 Courses taught: Knowledge-based systems Object-oriented development, 3rd year BSc Data structures, 1st year BSc Responsibilities included: planning, organizing and delivering of course material organizing tutorials and preparing demonstrators preparing and correcting assignments preparing and correcting exams Project supervisor 83 Griffith College Dublin, South Circular Rd, Dublin 2, Ireland Feb 2001 - Jun 2001 A course supervisor for the final year projects of 1st year BSc in Computing students. Tutor Griffith College Dublin, South Circular Rd, Dublin 2, Ireland Nov 1999 - Feb 2001 Courses taught: Object-oriented development, 3rd year BSc and 2nd year National Certificate Data structures, 1st year BSc Introduction to programming, 1st year BSc Postgraduate Demonstrator University College Dublin, Belfield, Dublin 4, Ireland Nov 1998 – October 2004 Courses taught: Formal grammars and syntax, 3rd year BSc Introduction to programming, 1st year BSc Data structures, 2nd year BSc Introduction to computing, 1st year BA (Agricultural Department) Databases, 1st year BA (Department of Library and Information Studies) Research Experience INTINN project Jan 2001 – March 2004 University College Dublin, Ireland A project for classification, semantic annotation and developing of automatic markup languages for hypertext documents; a continuation of INTENTS project. INTENTS project Nov 1998 - Dec 2000 University College Dublin, Ireland This project aimed at developing a set of tools for intelligent indexing, navigation and searching of hypertext documents. Tempus exchange student Apr 1998 Visited the Computer Science Department at University College Dublin as a Tempus exchange student and worked on the INTENTS project DBR-MAT project Sept 1996 - Oct 1998 Linguistic Modelling Laboratory, Bulgarian Academy of Science, Bulgaria 84 A joint German-Bulgarian-Romanian project in Knowledge-based Machine Aided Translation, fund-ed by the Volkswagen Foundation (Germany). Our Bulgarian team was engaged in the development of a module for generation of natural language explanations in Bulgarian from an underlying knowledge base of conceptual graphs. CGLex project Sept 1996 - Oct 1998 Linguistic Modelling Laboratory, Bulgarian Academy of Science}, Bulgaria The goal of the project was to create a Natural Language-based tool for Conceptual Graph acquisition. Visiting researcher Sept 1996 Visiting researcher at the Natural Language Group, CS Department, Hamburg University, Germany, working on the integration of the German and Bulgarian modules of CGLex and DBR-MAT projects. 4. Scholarly Interests My research interests include Natural Language Processing, Knowledge Representation, Semantics, Information Extraction, Information Retrieval, Hypertext Markup Languages, Web Technologies. 5. Publications (peer-reviewed) Svetlana Hensman and John Dunnion Using linguistic resources to construct conceptual graph representation of texts In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Text, Speech and Dialogue (TSD), Brno, Czech Republic, September 8-11, 2004. Svetlana Hensman and John Dunnion Automatically building conceptual graphs using VerbNet and WordNet In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Information and Communication Technologies (ISICT), Las Vegas, June 16-18, 2004, pp.115--120. Svetlana Hensman Construction of Conceptual Graph representation of texts In Proceedings of the Student Research Workshop at HLT-NAACL, Boston, USA, May 2, 2004, pp. 49-54. Svetlana Hensman and John Dunnion Applying VerbNet for automatic semantic role identification In Proceedings of the 14th Irish Conference of Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Science (AICS 2003), Dublin, Ireland, September 17-19, 2003, pp. 72-76. Svetlana Hensman and John Dunnion Applying VerbNet for automatic semantic role identification 85 International Conference for Cognitive Modeling in Linguistics, Varna, Bulgaria, September 1-7, 2003, pp. 471-481. Svetlana Damianova, Shazia Akhtar, John Dunnion and Ronan Reilly NewMedia, New Tools, Invited talk for "New Media, New Links: Strategies for Interdisciplinary Collaboration", Lillian Gilbreth Colloquium, New Jersey, USA, March, 2001. Svetlana Damianova, John Dunnion and Ronan Reilly Semantic indexing and knowledge-based searching of documents using conceptual graphs, Poster presentation at "Wiring Memory" colloquium, Dublin, Ireland, September 2001. Svetlana Damianova and John Dunnion IBIS: a system for semantic indexing and knowledge-based searches of hypertext documents, Poster presentation at "What's All the Hype in Hypertext About" workshop, Dublin, Ireland, March 2000. Svetlana Damianova and Kristina Toutanova Using Conceptual Graphs to Solve a Resource Allocation Task In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Conceptual Structures, Blacksburg, Virginia, USA, July 1999, Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence Vol. 1640, pp. 297-314. Galia Angelova, Kristina Toutanova and Svetlana Damianova Knowledge Base of Conceptual Graphs in DBR-MAT Technical Report BG-3-98, Project DBR-MAT (funded by the Volkswagen Foundation), University of Hamburg, Computer Science Faculty, Hamburg, Germany, July 1998. Galia Angelova, Svetlana Damianova, Kristina Toutanova and Kalina Bontcheva Menu-Based Interface to Conceptual Graphs: the CGLex Approach In Proceedings of CGTools Workshop, Seattle, USA, August 1997, Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence Vol. 1257, pp. 603-606. Galia Angelova, N. Boynov, Kalina Bontcheva, and Svetlana Damianova CGLex: A Natural Language Based Tool for Conceptual Graphs In Proceedings of CGTools Workshop, pp. 9-10, Sydney, Australia, August 1996. 86