Describing and Explaining Graphs in Humanities and Geography
advertisement

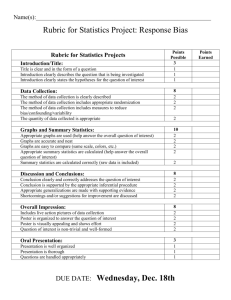
Describing and Explaining Graphs in Humanities and Geography When you describe graphs, you must look at the graph carefully. Then you write what you see. This is a simple guide to help you. Is there a low point on the graph? What is the low amount? When did it occur? Useful words Minimum, low, small, trough Is there a high point on the graph? What is the high amount? When did it occur? Useful words Maximum, high, large, peak Is there a general pattern? What is it like? Useful words Up, down, Increase, decrease Rise, fall, Grows, declines Sharp, gentle Straight, steady, level Slowly, rapidly Sections, parts Even, uneven distribution Large, slight difference Pie Charts Useful words A majority More than half The largest / smallest section Quarter, half, third Percentages Dominated by When you explain graphs, you must use what you know about the subject of the graph. For each point you made in your description, why did this happen? Comparing Use numbers to help you make comparisons. Twice as many than Useful words Half the range than 75% more/less than Describing and Explaining Maps in Humanities and Geography When you describe maps, you must look at the map carefully. Then you write what you see. Don’t forget to write about what is NOT there. This is a simple guide to help you. Firstly, use accurate place names to identify the location. Use the map title to introduce your description. Useful words This is a map showing world population distribution. Is there a general pattern? What is it like? Useful words North, south, east, west MEDC, LEDC North of the Equator, south of the Equator Inland, coast More, less Most, least Sparse, clustered, random When you explain maps, you must use what you know about the subject of the map. For each point you made in your description, why do you think it is like this?