Abstract: - Rabbit - University of Miami
advertisement

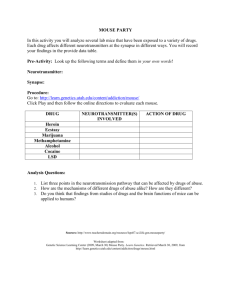
Senior Project
USB Webcam Mouse
May 06, 2005
Jeremy Stephens
Candice Cooper
Kenan Ozdamar
Advisor: Dr. Mohamed Abdel-Mottaleb
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Abstract
Introduction
Objectives
Implementation
I. Phase 1
Materials Needed
Approach
Observations
II. Phase 2
Materials Needed
Approach
Camera Settings
MATLAB Image Acquisition Toolbox
Attempt I
Attempt I Observations
Attempt II
Attempt II Observations
Attempt III
Project Continuation
Future Applications
Conclusion
Code
University of Miami
Page 2
Page 2
Page 3
Page 4
Page 6
Page 7
Page 7
Page 7
Page 7
Page 8
Page 10
Page 10
Page 10
Page 11
Page 11
Page 15
Page 15
Page 17
Page 17
Page 20
Page 23
Page 25
Page 27
Page 28
3/6/2016
Abstract:
Personal Computing has evolved quickly with the adaptation of new hardware
and software. In particular the development of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) and the
growth of broadband internet access are helping to fuel the improvement of web cameras.
The nature of technology, especially computers, is to combine multiple devices into a
single multipurpose device in the hopes of increasing performance and to reduce size. It
seems logical that the next technological advancement should be the combination of web
cameras and a standard mouse. This will reduce the number of input devices per
computer, increase usability, and improve user performance.
University of Miami
Page 3
3/6/2016
Introduction:
Capturing and processing streaming video has in the past been a difficult task
because of the accessibility of cameras and the amount of processing power needed to
translate the video into a usable form. PC web cameras originally ran on a serial interface
and then moved to USB 1.0. Recently web cameras migrated into using USB 2.0 and
even FireWire. These new technologies have increased the amount of bandwidth that was
needed to send high resolution fast paced images to the processor. Processors have
themselves advanced and have increased in speed and overall performance to handle the
increased load of today’s applications.
Technology has advanced to the point where we can take real time, real life
events and capture them as computer input. Currently the mouse and keyboard are the
main direct interface devices used to initiate and control actions on a computer. Both are
bulky and outdated and require that you perform actions other then what you’re used to in
normal day-to-day living. It is not natural to sit at a desk with one hand on a keyboard
while your other hand is on a mouse, but many people have become used to it because it
has been necessary.
This project captures video by means of a web camera in real time and translates
them into mouse events on a computer. For example, when a user’s hand moves to the
right the pointer of the mouse should move to the right. This is the first step in computers
being able to interface with humans as opposed to humans having to control computers.
University of Miami
Page 4
3/6/2016
A computer with a web camera has eyes into our world and when programmed could
perform actions based on what it sees going on around it.
University of Miami
Page 5
3/6/2016
Objectives:
To create a stand alone application that could be installed and run on a standard
installation of Microsoft Windows® that would:
Capture streaming video by means of a standard USB web camera.
Analyze the video captured to distinguish movements of an object in front of the
camera.
Calculate the necessary movement required by the mouse pointer in relation to the
movement captured from the video and perform that movement.
Have an intuitive Graphical User Interface (GUI) to control whether the
application is running or suspended.
University of Miami
Page 6
3/6/2016
Implementation:
Phase I:
Materials Needed:
Logitech QuickCam® Pro 4000
Logitech Software Development Kit (SDK)
o Connect to the USB Webcam.
o Capture video using the objects and methods provided in the API.
Microsoft Foundation Classes (MFC)
o To create a Microsoft Windows® Graphical User Interface (GUI) for
the application.
Win32 API
o To connect to and control the Microsoft Windows® mouse drivers.
Approach:
To create a stand alone application the goal was to tie directly into the Microsoft
Windows operating system using a C++ program. This would allow us to access the web
camera directly through the USB port, compute the image processing, and control the
mouse pointer. The Logitech Software Development Kit was created as an API to access
the streaming video directly from the camera in a raw data format. The image processing
University of Miami
Page 7
3/6/2016
could then be performed on the raw data. The mouse could then be moved by rewriting
the current mouse drivers with a set of drivers that reference the installed application
rather then the input from the current mouse hardware.
Observations:
We were unable to accomplish the above approach for several reasons. The
Software Development Kit provided from Logitech is an outdated version made
specifically for their older model cameras. After contacting the company we found that
they didn’t have an updated version, and had no plans to create one. The possible
solutions to this were to use an older model camera with the SDK or to create a new
approach.
The older model cameras provided from Logitech as well as any other web
camera manufacturer did not support the resolution and frame rate needed to run a high
speed efficient interface. A frame rate of 8fps-15fps which is what many older model
cameras have is far to low to create a mouse with fluid movement. The normal human
eye can detect changes at a rate of on average 30fps. To create mouse movement at this
rate the camera needs to receive and process images at a rate at or exceeding 30fps.
Resolutions lower then 320x240 pixels is not enough to create a well defined
image. At lower resolutions each pixel represents a larger area and the image becomes
undefined enough that you cannot detect the true edge of an object.
University of Miami
Page 8
3/6/2016
Under the assumption that the SDK from Logitech would work with newer
cameras we attempted to create the application using methods from the API. After several
attempts at connecting with the camera we were only able to get “Assertion Failures”
upon execution.
University of Miami
Page 9
3/6/2016
Phase II:
Materials Needed:
Logitech QuickCam® Pro 4000
MATLAB Version 7.0
o Connect to the USB Webcam.
o Capture streaming video.
o Process the incoming video.
Java
o Control the mouse movement and function.
Approach:
To create an application that utilized MATLAB to connect to and process the
incoming video from the USB Webcam and java to control the mouse functionality. The
project would perform the same functionality as the Phase I approach however it would
be dependant on MATLAB being installed on the computer.
University of Miami
Page 10
3/6/2016
Camera Settings:
The resolution we choose to use for this project, was 320 x 240 pixels at 15
frames per second. This was an ideal setting for the current project because it gave us a
high enough resolution to distinguish particular shapes and fast enough to provide a
reasonable mouse movement. More importantly the images could be processed with the
current hardware.
Table 1
Resolution
Pixels per Frame
Frame Rate
Pixels per Second
320 x 240
76,800
15 fps
1,152,000
320 x 240
76,800
30 fps
2,304,000
640 x 480
307,200
15 fps
4,608,000
640 x 480
307,200
30 fps
9,216,000
Ideally the maximum resolution and frame rate would provide the best mouse
movement, however it took too long to process the incoming frame before the next frame
would arrive.
University of Miami
Page 11
3/6/2016
MATLAB Image Acquisition Toolbox:
MATLAB supports image acquisition through its Image Acquisition Toolbox.
The toolbox supports a wide range of operations for acquiring images through the
toolbox, including:
Acquiring images through many types of image acquisition devices, from
professional grade frame grabbers to USB-based Webcams.
Viewing a preview of the live video stream Triggering acquisitions (includes
external hardware triggers)
Configuring callback functions that execute when certain events occur
Bringing the image data into the MATLAB workspace
The Image Acquisition Toolbox uses an object oriented approach. With the
toolbox you create an object that represents the connection between MATLAB and
specific devices (such as a webcam). Using an object oriented approach we can control
various properties of the object which control aspects of the image acquisition process.
The toolbox uses components called hardware device adaptors to connect to
devices through their drivers. The toolbox includes adaptors that support devices
produced by several vendors of image acquisition equipment. In addition, the toolbox
includes an adaptor for generic Windows video acquisition devices. The following figure
shows these components and their relationship.
University of Miami
Page 12
3/6/2016
Figure 1
The toolbox provides support for several companies such as Matrox. The toolbox
also provides support for everyday camera’s used through USB and FireWire ports.
To see what kind of camera is connected to the system and other important
information, use the imaqhwinfo command. The InstalledAdaptors field will specify
what type of camera(s) is connected to the computer. It is also possible for more then one
camera to be connected to a computer. Every device is given a unique device number
which will need to be explicitly used if the system is using more then one camera. One
University of Miami
Page 13
3/6/2016
can also retrieve more information about a device, such as video encoding and frame
resolution by using the same imaqhwinfo function but also explicitly specifying th device
number as an argument.
Once you get all the necessary information about the hardware you wish to
connect to, you can establish a connection to it by creating an image acquisition object.
The MATLAB toolbox uses two types of image acquisition objects. A video input
object which represents the connection between MATLAB and the device at a high level,
and a video source object which represents a collection of one or more physical data
sources.
Figure 2
To create a video input object call the videoinput specifying the adaptor name, device
ID, and video format as arguments. However, only the adaptor name is required.
University of Miami
Page 14
3/6/2016
Attempt I:
With this attempt we focused on reading the input from the camera. We would
read in a color still image, modify it by turning the Green and Blue colors of the objects
in the image to black. Now with only the Red values being displayed, and everything else
turned to black; it would be easier to find only the red objects in the image. We assumed
that if the pointer we wanted to follow with the camera was to red we would be able to
find it. After altering the first captured image, a second image would be read in and
altered the same manner as the first. Once bother images are read in and changed we
would compare the first colored still with the second. The purpose of this would be to
find the difference in the placement of the red object between the two images. We
thought if the object we were trying to find was red and the background black it would be
easy to spot.
Observations of Attempt I:
We decided that this attempt of the project would not work because this way of
doing things is not considered “real time”, and in order to use this in everyday
applications, the camera would need to detect objects with any color background.
University of Miami
Page 15
3/6/2016
Figure 3
University of Miami
Page 16
3/6/2016
Attempt II:
In this attempt, we focused on capturing streaming video and manipulate the
streaming video. In this attempt we decided to convert the incoming video to black and
white, instead of keeping it in color. We thought that it would be easier to work with. The
same problem still applied with streaming video that applied with still images, we needed
to detect movement. Another obstacle to overcome was that number of pixels we had to
work with when we were inputting streaming video.
We attempted to detected movement by finding the differences between one
frame and another. We did this by reading in the first frame from the camera; resizing the
image by a scale factor of 0.5, and then converting the image to a grayscale image. After
that, the same process was repeated with the second frame. After the two frames were
read in, resized, and then turned into grayscale images, the second frame was subtracted
from the first frame. If there were any values left over we would then conclude that there
was movement between the two frames.
Observations of Attempt II:
What was observed with this approach was that it used up a lot of the processor
time, and was slow.
University of Miami
Page 17
3/6/2016
Figure 4
Image of the first frame before it is modified.
Figure 5
University of Miami
Page 18
3/6/2016
Black and White 1 is the image of the first frame converted to a grayscale, then
converted to black and white, and a histogram of .4 added to it. Black and White 2 is the
same as Black and White 1 but with the second frame instead of the first frame. The BW1
– BW2 is the image of the difference between the two of them.
Figure 6
University of Miami
Page 19
3/6/2016
Attempt III:
The program can be broken down into three parts, an acquisition phase, an image
processing phase, and cursor update.
First, the camera interface is created and all initializations are taken care of. The
default resolution of the camera is 320 X 240 which is fine for this project but can be set
to 640 X 480 if one wishes. The FramesPerTrigger is set to one because we wish to work
with one frame from the video stream at a time. The TriggerRepeat property is set to Inf
because the program calls for an infinite stream that dose not stopped unless explicitly
told to do so by the user.
After all the initializations are taken care of the program goes into in infinite loop
where the algorithm is performed. In a repetitive manner the most current frame is
opened by MATLAB for manipulation. The frame is first converted to grayscale. Using
the grayscale we compute which pixel has the maximum magnitude. This value is dived
by 255 (the max possible value) so it can be used as a ratio. The image is then turned to
black and white using the value previously described as a threshold. Meaning that any
values lower then this threshold will be turned to black. This is done so the only pixels
remaining are those representing the light reflecting orb.
Finally the position of the white spot (the representation of the orb in the image)
is determined. This is done simply in 2 for loops which span very pixel looking for white.
This return the x and y values (represented as i and j in the program). Since the camera
University of Miami
Page 20
3/6/2016
resolution and screen resolution are different, the data must be interpolated to account for
the difference, i and j are multiplied by 4 to get the correct values. Since the camera is
facing the opposite direction of the person in front of it, images are reflected along the y
axis. For example your right hand would be displayed at the left end of the image. To
correct this we subtract the x-value from the max x-value.
University of Miami
Page 21
3/6/2016
Start
Create and
Initialize Camera
Start Image
Acquisition
Get current
frame
Start Image
Acquisition
Covert to
gray
Threshold
Covert to
BW
Move mouse
Interpolate
Determine
Position
Flow Chart
The final location values are sent to java and they represent the new position for
mouse. After it the cursor is moved the program goes back to the beginning of the loop
and the algorithm repeats.
University of Miami
Page 22
3/6/2016
Project Continuation:
The continuation of the project should involve several crucial steps for increasing
the usability and reliability of the system.
To make a true application that can be used as an alternative to the mouse a
solution for the absence of mouse buttons needs to be resolved. Either a system designed
to look for specific events such as two luminescent globes either touching or separating,
or an algorithm that detects specific gestures.
The mouse movement needs to be stabilized so that you have better control of the
operating system and the specific location of the mouse at any given time. This can be
accomplished several ways. The most practical at the given time is to add some tolerance
to the movement that the camera detects. A specific tolerance needs to be determined and
needs to be met before the mouse should move. This would fix the problem of the mouse
shaking due to your hand naturally shaking. The shaking motions would be eliminated
and only true movement would be captured and applied.
The application should be remade into a stand alone application that does not
require MATLAB as a framework. This would make the application usable by anyone
running the appropriate operating system and an appropriate web camera. They would
just need to download and install the application to use the features of the Webcam
Mouse.
The incoming streaming video needs to be processed in color. This would solve many
issues involving the reflection of light from multiple sources and the brightness of the
ambient light surrounding the camera. If color was used to process the image then skin
tones could be detected and followed as opposed to just movement in front of the camera.
University of Miami
Page 23
3/6/2016
With the improvement of hardware the Webcam mouse will only improve in
accuracy and its motion will become more stable and fluid. As the cameras bring in
higher resolution video faster and computers can process those frames without preventing
normal computer operations from running the Webcam mouse will become a viable
solution to the lack of innovative computer input devices.
University of Miami
Page 24
3/6/2016
Future Applications:
The Webcam mouse is a good alternative to a conventional mouse. Future
devices, like cell phones, have already been integrating in cameras that can capture video.
It is a matter of time before laptops come standard with web cameras built in. These
devices could benefit from a Webcam mouse because a user would have an input device
that has the ability to recognize gestures as well as track standard movement without the
need for a mouse that in some cases may be larger then the device it would be
controlling. A benefit of the technology is that it can be used by both right and lefthanded individuals. Specific hardware is targeted towards either right-handed or lefthanded users based on shape and button configuration whereas a Webcam mouse is the
same for all users.
Another useful purpose for the Webcam mouse would be during presentations. A
Webcam mouse could serve two purposes. It could video tape the presentation as well as
be used as an input device. A presenter would not need a specific remote or any other
special hardware. The Webcam mouse could track the movement of a standard laser
pointer being projected on the screen and move the mouse to its specific location.
The most user friendly application of the Webcam mouse would be its
development into an Eye Tracking mouse. When used with a normal personal computer
the camera would track a user’s eye movement and either moves the mouse in relation to
the movement of the eye or by calculating a projected line of sight to the screen and
move the mouse to that exact location. This would be ideal for many users that do a lot of
data entry or in areas where a mouse is unpractical, like a construction or machining area.
University of Miami
Page 25
3/6/2016
Users would never have to remove their eyes from the screen and can focus on typing or
in some cases never need hands on input devices at all.
University of Miami
Page 26
3/6/2016
Conclusion:
The Webcam mouse is a viable representation of what can be done in the future
using a web camera and a computer to process streaming video. It proves that a mouse
pointer can be controlled using a camera with no direct input from the user.
The project was difficult in theory and application. It took quite a bit of research
and planning before anything viable was created. The most difficult part was determining
how to move the mouse based on input from a MATLAB program. We found an elegant
and simple solution to that using Java. If MATLAB did not have the Java integration then
the mouse movement would have been nearly impossible. After attempting several
algorithms to process the video we settled on the current one which works faster then
some of the other algorithms but have its limitations in that it can track the wrong object
if the lighting conditions are not perfect. There are many improvements and additions that
can be added to this project given the scope of this technology and possibilities of its
incorporation in many others.
The continuation of project (included in this report) contains some mouse clicking
ability. However the mouse clicking is unreliable, the mouse movement still works very
well in specific lighting conditions.
University of Miami
Page 27
3/6/2016
Code:
MATLAB:
function varargout = projGUI(varargin)
% PROJGUI M-file for projGUI.fig
%
PROJGUI, by itself, creates a new PROJGUI or raises the existing
%
singleton*.
%
%
H = PROJGUI returns the handle to a new PROJGUI or the handle to
%
the existing singleton*.
%
%
PROJGUI('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
%
function named CALLBACK in PROJGUI.M with the given input arguments.
%
%
PROJGUI('Property','Value',...) creates a new PROJGUI or raises the
%
existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
%
applied to the GUI before projGUI_OpeningFunction gets called. An
%
unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
%
stop. All inputs are passed to projGUI_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
%
*See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
%
instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Copyright 2002-2003 The MathWorks, Inc.
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help projGUI
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 04-Mar-2005 13:03:49
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name',
mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @projGUI_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @projGUI_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before projGUI is made visible.
University of Miami
Page 28
3/6/2016
function projGUI_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to projGUI (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for projGUI
global show_flag;
global disp_flag;
show_flag=1;
disp_flag=1;
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes projGUI wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = projGUI_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% clc
% close all;
% clear all;
global show_flag;
global disp_flag;
run_flag = 1;
vid = videoinput('winvideo');
set(vid,'FramesPerTrigger',1);
set(vid,'TriggerRepeat',Inf);
triggerconfig(vid, 'Manual');
University of Miami
Page 29
3/6/2016
import Mouse
m = Mouse
%we start acquiring the images
start(vid);
trigger(vid);
%This is our counter, it lets us know what frame we are in
frame = 0;
%The getdata function transfers the acquired images into the MATLAB workspace.
theImage = (getdata(vid,1,'uint8'));
while (run_flag == 1)
trigger(vid);
frame = frame + 1;
set(handles.text2, 'String',['The Frame No. ' num2str(frame)])
theImage = (getdata(vid,1,'uint8'));
%STREL Create morphological structuring element. SE = STREL('disk',R) creates a flat disk-shaped
structuring element
%with the specified radius, R. R must be a nonnegative integer
structDisk = strel('disk', 3);
%Converts to grayscale
gfr1 = rgb2gray(theImage);
%We determin the threshold. This is done by trial and error, it is a
%number between 0 and 1.
bw1 = im2bw(gfr1, .98);
%figure(3); imshow(im2bw(gfr1));
bw1 = imopen(bw1, structDisk);
if (disp_flag == 1)
set(gcf, 'currentaxes',handles.axes1)
imshow(bw1); axis off; pause(0.01);
set(gcf, 'currentaxes', handles.axes3);
imshow(theImage); axis off;
end
%
%
%
%
%
%
%
%
%
set(gcf, 'currentaxes', handles.axes4);
[X,Y]=meshgrid(1:320,1:240);
surf(X,Y,double((gfr1))/255)
VIEW(-180,84)
for i = 1:320
for j = 1:240
University of Miami
Page 30
3/6/2016
% bw1(j, i)
if bw1(j,i) == 1
break
end
end
if bw1(j,i) == 1
break
end
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
for k = i:320
for l = j:240
if bw1(l,k) == 1
break
end
end
if bw1(l,k) == 1
break
end
end
if(l == 240)
if( k == 320)
%insert click fuction
end
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
j=j*4;
i= 1440 - (i*4);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
sprintf('(k,l) is : ( %d , %d ) \n', k, l);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
m.Move(i, j)
%pause
set(handles.text3, 'String',['X loc= ' num2str(i) ' X loc= ' num2str(j)])
if(show_flag == 0)
stop(vid);
delete(vid);
run_flag = 0;
end;
end
University of Miami
Page 31
3/6/2016
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global show_flag
show_flag=~show_flag
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton3.
function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
global disp_flag;
disp_flag=~disp_flag;
University of Miami
Page 32
3/6/2016
Java:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class Mouse {
public void Move(int XArg, int YArg)
throws AWTException{
Robot robot = new Robot();
robot.mouseMove(XArg,YArg);
}
public void Delay(int time)
throws AWTException{
Robot robot = new Robot();
robot.delay(time);
}
public void LClick()
throws AWTException{
Robot robot = new Robot();
robot.mousePress(InputEvent.BUTTON1_MASK);
robot.mouseRelease(InputEvent.BUTTON1_MASK);
}
public void Left_Click()
throws AWTException{
Robot robot = new Robot();
robot.mousePress(InputEvent.BUTTON1_MASK);
}
public void Left_Release()
throws AWTException{
Robot robot = new Robot();
robot.mouseRelease(InputEvent.BUTTON1_MASK);
}
public void RClick()
throws AWTException{
Robot robot = new Robot();
robot.mousePress(InputEvent.BUTTON2_MASK);
robot.mouseRelease(InputEvent.BUTTON2_MASK);
}
public void Right_Click()
throws AWTException{
Robot robot = new Robot();
robot.mousePress(InputEvent.BUTTON2_MASK);
}
public void Right_Release()
throws AWTException{
Robot robot = new Robot();
robot.mouseRelease(InputEvent.BUTTON2_MASK);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
throws AWTException{
Robot robot = new Robot();
int X = 1430;
int Y = 10;
University of Miami
Page 33
3/6/2016
robot.mouseMove(X,Y);
robot.mousePress(InputEvent.BUTTON1_MASK);
robot.mouseRelease(InputEvent.BUTTON1_MASK);
robot.delay(10);
}
}//ends class Mouse
University of Miami
Page 34
3/6/2016