here - science

Further Physics
(Physics
– P2)
Year 11 Autumn term. P3.1 – Medical Applications of Physics
This document contains
Page 1: lesson outline with overview of resources
Page 2 –11: individual lesson plans
P3.1 – Medical applications of physics
1
Intro and keywords
Resources
Printed resources in folder: wave equation worksheet, keyword quiz, reflection, plenary questions, slide 5
In powerpoint – will need to print slide 16 for cards and 19
2
X-rays
3
Ultrasound
Speaker (to get messy) cornflour and water mixture in speaker cone.
Signal generator.
4
Refractive index
5
Total internal reflection
6
Lenses
Glass or Perspex rectangular blocks
Protractors
Ray boxes with lenses, psus
A4 Blank paper
D block
Protractors
Ray boxes with lenses, psus
A4 Blank paper
Wiggly glass block demo
Print out of info on uses to summarise
Ray box
Shape cut out of card as object or cross wires
Convex lens
Screen
Metre rule
Smoke/Lens box
Sheets in folder – students will need copies of each one.
7
Lenses and Ray Diagrams
8
The Eye and Camera
Eyeball for dissection and tiles and scalpels
White lab coats
Goggles
Old SLR camera (dismantled)
A3 paper, colouring pens/pencils
Big A3 print outs – laminated - of starter material in folder, 8 copies, one for each group of 4. different power lenses
9
Power of Lenses
10
LASER eye surgery
Laser set up with spray or chalk dust to see it
Computer room
Collins separate sciences text book
This material will be assessed by the y11 mock in November
Year 11 Autumn term. P3.1 – Medical Applications of Physics
Activity and Resources.
Lesson 1
P3.1 –
Title:
Introduction
Text book
Collins further pages p134-135
Keywords
Reflection, refraction, diffraction, transmission, sound, light, mechanical, electromagnetic spectrum, frequency, period, wavelength, incident ray, wave speed, echo
Lesson objective; Lesson outcomes
Specification p3.1 keywords
Objective: Be able to define keywords in the topic and select appropriate equations.
HSW: AF2 – Understanding the applications and implications of
science
Outcomes:
• ALL MUST be able to use the resources given to select
the correct equations for the topic.
• MOST SHOULD be able to define the key terms
associated with the topic.
• SOME COULD explain the importance of physics in
medical applications.(X-Rays, Ultrasound)
Suggested teaching activities
Starter
Seating plan
Introduce course
Give out books
Main Activities
Keyword quiz
Look at planner pages
Labeling waves (print slide 5)
Wave equation worksheet
Refraction, reflection, diffraction revision – draw it
EM spectrum revision – watch video and write out order
Plenary –
Consolidate
Exam race – use exam style questions to be answered within the group
Tell me 2 things
Additional Resources and web links –
Printed resources in folder: wave equation worksheet, keyword quiz, reflection, plenary questions, slide 5
Teaching and learning / Assessment
Differentiation: Outcome and assistances in practical
V – PowerPoint on screen and practical
A – discussion
K – Practical
L – discussion
R/W –diagrams and explanations
Key skills: observing, recording, analysing,
PLTS:.
Team workers – Work collaboratively with others.
ECM:
Assessment –
Teacher assessment in plenary
Q & A assessment throughout
HW: homework doddle –
Safety:
Year 11 Autumn term. P3.1 – Medical Applications of Physics
Activity and Resources.
Lesson 2
P3.1 –
Title: X-
Rays
Text book
Collins further pages
Keywords
Frequency, wavelength,
CT (CAT) scan, cells, tumour, cancer, filament, cathode, anode, tungsten, ionisation,
CCD.
Lesson objective; Lesson outcomes
Specification
P3.1.1 X-rays a) X-rays are part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
They have a very short wavelength and cause ionisation. b) X-rays can be used to diagnose and treat some medical conditions. c) Precautions to be taken when X-ray machines and CT scanners are in use.
Objective: Be able to describe what X-Rays are, how they are used and the precautions to take when using them
HSW: AF2 – Understanding the applications and implications of
science
Outcomes:
• ALL MUST be able to state 3 properties of X-Rays, 3 uses, 1 danger and 3 precautions we can take around them.
• MOST SHOULD be able to describe how X-Rays are formed and explain why they are used to check broken bones.
• SOME COULD explain the dangers of X-Rays and compare
• them to other medical uses of waves to explain why we use X-Rays in the way we do.
Suggested teaching activities
Starter
Literacy exercise displayed on board. Students connect info learnt about EM-spectrum last lesson.
Draw a sketch diagram of the EM spectrum and describe 2 dangers and precautions to take around X-
Rays. Then discuss how they think they may be produced.
Introduction
Use the powerpoint slides to introduce how X-Rays are created, what they are used for and what precautions we must take around them.
Main Activities
Sort the cards into groups of properties, medical uses, dangers and precautions.
Memory board to describe how they are produced
Think pair share to explain uses and dangers.
Plenary –
Pop quiz (based on outcomes)
Additional Resources and web links –
In powerpoint – will need to print slide 16 for cards and 19
Teaching and learning / Assessment
Differentiation: Outcome and assistances in practical
V – PowerPoint on screen and practical
A – discussion
K – Practical
L – discussion
R/W –diagrams and explanations
Key skills: observing, recording, analysing,
PLTS:.
Team workers – Work collaboratively with others.
ECM: stay safe – how to identify and minimize risk
Assessment –
Teacher assessment in plenary
Q & A assessment throughout
HW: homework doddle –
Safety:
Year 11 Autumn term. P3.1 – Medical Applications of Physics
Activity and Resources.
Lesson 3
P3.1 –
Title:
Ultrasound
Text book
Collins further pages 138
Keywords frequency, speed, time, distance,
Hertz, sonar, A-
Scan, echo
Lesson objective; Lesson outcomes
Specification a) Electronic systems can be used to produce ultrasound waves, which have a frequency higher than the upper limit of hearing for humans. b) Ultrasound waves are partially reflected when they meet a boundary between two different media.
The time taken for the reflections to reach a detector can be used to determine how far away such a boundary is. c) Calculation of the distance between interfaces in various media. s = v x t
Objective: Be able to describe what Ultrasound is and how we can calculate distances using it.
HSW: AF2 – Understanding the applications and implications of
science
Outcomes:
• ALL must be able to construct an image using Ultrasound readings
• MOST SHOULD modify equations in order to calculate distance
• SOME COULD argue your opinion on the use of Ultrasound
• during pregnancy. Justify your answer
Suggested teaching activities
Starter
Connect to last lesson – what did the learn last time. What would they like to know today?
Human hearing test – use signal generator and speaker to generate different frequencies – as per powerpoint
Watch echolocation youtube clip – blind man who uses sound clicks to navigate
Main Activities
AO1 – numeracy - Worksheets – ultrasound imaging and practice with calculations
WOW – cornflour and water in speaker (nothing to do with ultrasound but looks amazing)
AO3 – literacy – arguing whether ultrasound the best way to see unborn babies
Plenary –
Going Up – describe the lesson to your partner in the time it takes for a lift to reach the top floor –
120seconds
Additional Resources and web links –
Speaker (to get messy) cornflour and water mixture in speaker cone. Signal generator.
Teaching and learning / Assessment
Differentiation: Outcome and assistances in practical
V – PowerPoint on screen and practical
A – discussion
K – Practical
L – discussion
R/W –diagrams and explanations
Key skills: observing, recording, analysing,
PLTS:.
Team workers – Work collaboratively with others.
ECM:
Assessment –
Teacher assessment in plenary
Q & A assessment throughout
HW: homework doddle –
Safety:
Year 11 Autumn term. P3.1 – Medical Applications of Physics
Activity and Resources.
Lesson 4
P3.1 –
Title:
Ultrasound
Uses
Text book
Collins further pages 138
Keywords
Refractive index, deviation,
Snell’s Law, apparent depth
Lesson objective; Lesson outcomes
Specification a) Refraction is the change of direction of light as it passes from one medium to another.
(c) refractive index = sin i / sin r)
Objective: Be able to select and apply Snell’s Law.
HSW: AF2 – Understanding the applications and implications of
science
Outcomes:
• ALL MUST be able to carry out a practical safely
• MOST SHOULD calculate the refractive index of glass
• SOME COULD be able to apply the refraction equation to
• different situations
Suggested teaching activities
Starter
Review what the wrote about ultrasound being used in prenatal-scans last lesson.
Main Activities
Snell’s Law experiement
Plenary –
Numeracy Calculations
Additional Resources and web links –
Glass or Perspex rectangular blocks
Protractors
Ray boxes with lenses, psus
A4 Blank paper
Teaching and learning / Assessment
Differentiation: Outcome and assistances in practical
V – PowerPoint on screen and practical
A – discussion
K – Practical
L – discussion
R/W –diagrams and explanations
Key skills: observing, recording, analysing,
PLTS:.
Team workers – Work collaboratively with others.
ECM: stay safe – how to identify and minimize risk
Assessment –
Teacher assessment in plenary
Q & A assessment throughout
HW: homework doddle –
Safety: ray boxes will get hot. Allow them to cool before packing up otherwise students could burn their fingers.
Care must be taken with them as lightbulbs are fragile, if broken, sharp glass could be spread causing cuts. If glass is smashed it must be swept up by teacher asap.
Year 11 Autumn term. P3.1 – Medical Applications of Physics
Activity and Resources.
Lesson 5
P3.1 –
Title: TIR
Text book
Collins further pages
Keywords
Critical angle, refraction, snell’s law, opyical fibres, endoscope
Lesson objective; Lesson outcomes
Specification a) Total internal reflection and critical angle. refractive index = 1 / sin c b) Visible light can be sent along optical fibres.
c) The laser as an energy source for cutting, cauterising and burning.
Objective: Be able to describe why things get charged up with static and what forces are felt.
HSW: AF2 – Understanding the applications and implications
of science
Outcomes:
• ALL WILL
• Carry out a practical safely.
• MOST SHOULD
• Use Snell’s Law to show how the critical angle is related to the refractive index.
• SOME COULD
• Explain in detail how TIR is used by doctors.
•
Starter
Show video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rFbnxnf6HRQ&feature=plcp
Optical fibre demo
Main Activities
Do critical angle prac
Relate n=1/sin c
Do questions - numeracy
Demo wiggly block – use info on powerpoint slides to summarise optical fibres, mention that the laser as an energy source for cutting, cauterizing and burning. And can be sent down and optical fibre.
Plenary –
Recap and T/F quiz (use white boards)
Which PLT have you used today?
Additional Resources and web links –
D block
Protractors
Suggested teaching activities
Ray boxes with lenses, psus
A4 Blank paper
Wiggly glass block demo
Print out of info on uses to summarise
Teaching and learning /
Assessment
Differentiation: Outcome and assistances in practical
V – PowerPoint on screen and practical
A – discussion
K – Practical
L – discussion
R/W –diagrams and explanations
Key skills: observing, recording, analysing,
PLTS:.
Team workers – Work collaboratively with others.
ECM: stay safe – how to identify and minimize risk
Assessment –
Teacher assessment in plenary
Q & A assessment throughout
HW: homework doddle –
Safety: ray boxes will get hot. Allow them to cool before packing up otherwise students could burn their fingers.
Care must be taken with them as lightbulbs are fragile, if broken, sharp glass could be spread causing cuts. If glass is smashed it must be swept up by teacher asap.
Year 11 Autumn term. P3.1 – Medical Applications of Physics
Activity and Resources.
Lesson 6
P3.1 –
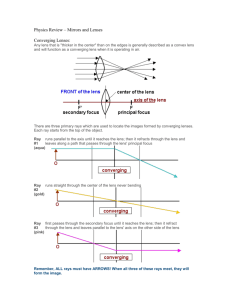
Title: Lenses
Text book
Collins further pages 144
Keywords
Converge, convex, diverge, power, focal length, magnification, object, real image, virtual image, parallel
Lesson objective; Lesson outcomes
Specification b) A lens forms an image by refracting light. c) In a convex or converging lens, parallel rays of light are brought to a focus at the principal focus.
The distance from the lens to the principal focus is called the focal length. refractive index = sin i / sin r d) The nature of an image is defined by its size relative to the object, whether it is upright or inverted relative to the object and whether it is real or virtual. e) The nature of the image produced by a converging lens for an object placed at different distances from the lens. f) The use of a converging lens as a magnifying glass. g) The nature of the image produced by a concave or diverging lens.
Objective: To understand the nature of the image produced in converging lens and to understand the uses of a converging lens in a camera.
HSW: AF2 – Understanding the applications and implications of
science
Outcomes:
• ALL MUST be able to carry out a practical safely
• MOST SHOULD be able to describe how to make converging lenses stronger.
• SOME COULD explain how lenses may be used.
•
Suggested teaching activities
Starter
Describe what lenses are and how they are used – use powerpoint
Main Activities
Demonstrate smoke lens box
Lenses practical
Plenary –
Tweet what you’ve learnt
Additional Resources and web links –
Ray box
Shape cut out of card as object or cross wires
Convex lens
Screen
Metre rule
Smoke/Lens box
Teaching and learning / Assessment
Differentiation: Outcome and assistances in practical
V – PowerPoint on screen and practical
A – discussion
K – Practical
L – discussion
R/W –diagrams and explanations
Key skills: observing, recording, analysing,
PLTS:.
Team workers – Work collaboratively with others.
ECM: stay safe – how to identify and minimize risk
Assessment –
Teacher assessment in plenary
Q & A assessment throughout
HW: homework doddle –
Safety: ray boxes will get hot. Allow them to cool before packing up otherwise students could burn their fingers.
Care must be taken with them as lightbulbs are fragile, if broken, sharp glass could be spread causing cuts. If glass is smashed it must be swept up by teacher asap.
Year 11 Autumn term. P3.1 – Medical Applications of Physics
Activity and Resources.
Lesson 7
P3.1 –
Title: Lenses and ray diagrams
Text book
Collins further pages 144-145
Keywords
Converge, convex, diverge, power, focal length, magnification, object, real image, virtual image, parallel
Lesson objective; Lesson outcomes
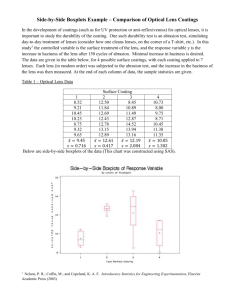
Specification h) The construction of ray diagrams to show the formation of images by converging and diverging lenses. i) The magnification produced by a lens is calculated using the equation: magnification = image height / object height
Objective: Construct ray diagrams to show the formation of images by diverging lenses and converging lenses.
How to calculate the magnification produced by a lens using the
formula
HSW: AF2 – Understanding the applications and implications of
science
Outcomes:
• ALL MUST know what the object, real image and virtual image is for a lens.
• MOST SHOULD be able to draw ray diagrams for images formed by converging and diverging lenses.
• SOME COULD be able to work out the magnification of a
• lenses.
Suggested teaching activities
Starter
Learn keywords, object, real image, virtual image
Main Activities
Introduce how to work out magnification
Lenses ray diagrams sheets (mathematical ability)
Plenary –
Lenses quiz
Additional Resources and web links –
Sheets in folder – students will need copies of each one.
Teaching and learning / Assessment
Differentiation: Outcome and assistances in practical
V – PowerPoint on screen and practical
A – discussion
K – Practical
L – discussion
R/W –diagrams and explanations
Key skills: observing, recording, analysing,
PLTS:.
Team workers – Work collaboratively with others.
ECM:
Assessment –
Teacher assessment in plenary
Q & A assessment throughout
HW: homework doddle –
Safety:
Year 11 Autumn term. P3.1 – Medical Applications of Physics
Activity and Resources.
Lesson 8
P3.1 –
Title: Eye and Camera
Text book
Collins further pages 146-147
Keywords
Optic nerve
Optic disc
Retina
Iris
Pupil
Cornea
Ciliary muscle
Lens
Suspensory ligament
Lesson objective; Lesson outcomes
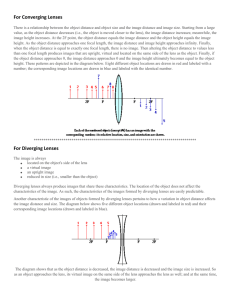
Specification a) The structure of the eye.
The structure of the eye is limited to:
■ retina
■ lens
■ cornea
■ pupil /iris
■ ciliary muscle
■ suspensory ligaments. d) Comparison between the structure of the eye and the camera.
Objective: Be able to describe the structure of the eye and the camera and describe how they work.
HSW: AF2 – Understanding the applications and implications of
science
Outcomes:
• ALL MUST be able to label the structure of the eye and a camera.
• MOST SHOULD be able to describe what the parts of an eye and a camera do.
• SOME COULD be able to compare the differences between how a camera and an eye work.
•
Suggested teaching activities
Starter
Structure of the eye group labeling exercise
Main Activities
Make a revision poster of the eye and the camera comparing the similarities and differences
Peer feedback
WOW: dissection
Plenary – wordsplat
Additional Resources and web links –
Eyeball for dissection and tiles and scalpels
White lab coats
Goggles
Old SLR camera (dismantled)
A3 paper, colouring pens/pencils
Big A3 print outs – laminated - of starter material in folder, 8 copies, one for each group of 4.
Teaching and learning / Assessment
Differentiation: Outcome and assistances in practical
V – PowerPoint on screen and practical
A – discussion
K – Practical
L – discussion
R/W –diagrams and explanations
Key skills: observing, recording, analysing,
PLTS:.
Team workers – Work collaboratively with others.
ECM: stay safe – how to identify and minimize risk
Assessment –
Teacher assessment in plenary
Q & A assessment throughout
HW: homework doddle –
Safety: if dissection done. Explain the risk involved with using scalpels. Very sharp.
Could cut hand. Need to take extreme caution when handling them. Walk round lab. Need to wear safety goggles in case of splash. If anything gets into eye rinse out well.
Year 11 Autumn term. P3.1 – Medical Applications of Physics
Activity and Resources.
Lesson 9
P3.1 –
Title:
Text book
Collins further pages
Keywords
Focal length, dioptre
Lesson objective; Lesson outcomes
Specification b) Correction of vision using convex and concave lenses to produce an image on the retina:
■ long sight, caused by the eyeball being too short, or the eye lens being unable to focus
■ short sight, caused by the eyeball being too long, or the eye lens being unable to focus. c) Range of vision. The eye can focus on objects between the near point and the far point. e) The power of a lens is given by:
P = 1 / F f) The focal length of a lens is determined by:
■ the refractive index of the material from which the lens is made, and
■ the curvature of the two surfaces of the lens. g) For a given focal length, the greater the refractive index, the flatter the lens. This means that the lens can be manufactured thinner
Objective: To understand the nature of the image produced in converging lens and to understand the uses of a converging lens in a camera.
HSW:
Outcomes:
• ALL MUST be able to describe how to make converging lenses stronger and describe what long and short sightedness are.
• MOST SHOULD be able to draw ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses correcting sight and apply equations to calculate the power of a lens.
• SOME COULD explain how to make thin glasses stronger.
•
Suggested teaching activities
Starter
Eye test
Main Activities
Simultaneous round table exercise to share information and test it on sight problems.
Give equation for lens power and explain how to make lenses more powerful
Do worksheet
Mark worksheet
Plenary –
Tell me 2 things
Additional Resources and web links –
Could give out different power lenses for students to examine
Teaching and learning / Assessment
Differentiation: Outcome and assistances in practical
V – PowerPoint on screen and practical
A – discussion
K – Practical
L – discussion
R/W –diagrams and explanations
Key skills: observing, recording, analysing,
PLTS:.
Team workers – Work collaboratively with others.
ECM: stay safe – how to identify and minimize risk
Assessment –
Teacher assessment in plenary
Q & A assessment throughout
HW: homework doddle –
Safety:
Year 11 Autumn term. P3.1 – Medical Applications of Physics
Lesson 10
P3.1 –
Title: laser eye surgery
Text book
Collins further pages 148
Lesson objective; Lesson outcomes
Specification c) The laser as an energy source for cutting, cauterising and burning.
Objective:
HSW:
Outcomes:
• ALL MUST
• MOST SHOULD
• SOME COULD
Keywords
Laser, laser eye surgery, cornea, lens
Activity and Resources.
Suggested teaching activities
Starter
Demonstrate a laser beam around the class and read through page 148
Main Activities
Use computers to research what laser eye surgery is, why people hve it done and the risks involved
Plenary –
Students feedback on their work, email powerpoints to teacher and tell each other 2 things – as last slide
Additional Resources and web links –
On powerpoint
Teaching and learning / Assessment
Differentiation: Outcome and assistances in practical
V – PowerPoint on screen and practical
A – discussion
K – Practical
L – discussion
R/W –diagrams and explanations
Key skills: observing, recording, analysing,
PLTS:.
Team workers – Work collaboratively with others.
ECM: stay safe
– how to identify and minimize risk
Assessment –
Teacher assessment in plenary
Q & A assessment throughout
HW: homework doddle –
Safety: laser beam risk. can cause damage to the retina resulting in scotoma (blind spot in the fovea). This wave band is also know as the "retinal hazard region". Do not look into it