The Master List of Sociology Terms

Master List of Sociology Terms
Fall Semester 2012
Silverman
Unit ONE: Sociological Foundations & Methods
1.
Sociology – the systematic study of human society and social behaviors
2.
Social phenomena – an observable fact or event that involves human society
3.
Sociological perspective – a systematic method of viewing the behavior of groups
4.
Sociological imagination – the ability to see connections between the larger world and our personal lives
5.
Social psychology – the study of the way in which an individual’s behavior and personality are impacted by the social environment
6.
Macro-sociology – an approach to the study of sociology that emphasizes the analysis of social systems and populations on a large scale, at the level of social structure
7.
Micro-sociology – an approach to the study of sociology that emphasizes the nature of everyday human social interactions on a small scale
8.
Social Darwinism – a theoretical perspective in which societies evolve toward stability and perfection through survival-ofthe-fittest
9.
Bourgeoisie – owners of the means of production in a capitalist society (i.e. middle class, management)
10.
Proletariat – workers in a capitalist society; sell labor for wages
11.
Function – the consequence that an element of society produces for the maintenance of its social system (i.e. religion as a means of maintaining social order)
12.
Verstehen
– an empathetic understanding of the meaning that others attach to their actions, as discussed by Max Weber
13.
Functionalist perspective – a theoretical perspective that views society as a set of interrelated parts that work together to produce a stable social system
14.
Dysfunction – the negative consequence that an element has for the stability of its social system; creates disruption, not stability (i.e. crime)
15.
Manifest function – the intended and recognized consequence of some element of society
16.
Latent function – the unintended and unrecognized consequence of some element of society
17.
Conflict perspective – a theoretical perspective that focuses on those forces in society that promote competition and change
18.
Interactionist perspective – a theoretical perspective that focuses on how individuals interact with one another in society
19.
Empirical research – research that relies on the use of experience, observation and experimentation to collect data
20.
Independent variable – a variable that causes a change in another variable
21.
Dependent variable – a variable that is changed by an independent variable
22.
Sample – a group of people who are selected from a given population to participate in a scientific study
23.
Motivation – Influences that account for initiation, direction, intensity & persistence of behavior
24.
Social Psychology – the study of the interaction between people, groups and social structures
25.
Social Cognition – the ways in which people store, remember & use information about other individuals in the social world
26.
Attitude – an overall evaluation of your social world; lasting patterns of beliefs & opinions that predispose one’s reactions to objects, people & events
27.
Persuasion – outside efforts to change one’s attitude
28.
Stereotype – fixed & overly-simplistic generalizations in regards to the traits, behaviors & attitudes of a particular group of people
29.
Prejudice – negative attitude in regards to members of a certain group
30.
Attribution – inferences generated to explain the reasons for events, the behavior of others and the behavior of oneself
31.
Conformity – a change in beliefs or actions that results in adherence to group norms
32.
Compliance – a change in behavior prompted by a direct request rather than social norms; obedience
Unit TWO: Culture & Social Structure
33.
Culture – all the shared products of a particular human group; include both physical objects & the beliefs, values and behaviors shared by the group
34.
Material culture – physical objects created by human groups; sociologists and anthropologists use the term artifacts to refer to the physical objects of material culture
35.
Non-material culture – abstract human creations, such as language, ideas, beliefs, rules, skills, family patterns, work practices, and political & economic systems
36.
Society – a group of interdependent people who have organized in such a way as to share common culture and feelings of unity
37.
Language – the organization of written or spoken symbols into a standardized system
38.
Sapir-Whorf hypothesis – the idea that differences in language shape the way its speakers view reality
39.
Values – shared beliefs about what is good or bad, right or wrong, desirable or undesirable
40.
Norms – shared rules of conduct that dictate how people should act in certain situations; expectations for behavior
41.
Folkways – norms that describe socially acceptable behavior, without having great moral significance attached to them
(i.e. cover your mouth when you yawn)
42.
Mores – norms that have great moral significance attached to them (i.e. do not rob a bank)
43.
Real culture – the values and standards of behavior that people actually follow
44.
Ideal culture – the values and standards of behavior that people profess to hold
45.
Cultural universals – common features that are found in all human cultures (i.e. dancing, cooking, gift-giving…)
46.
Ethnocentrism – the tendency to view one’s own culture and group as superior to others
47.
Culture relativism – the belief that cultures should be judged by their own standards rather than by applying the standards of another culture
48.
Folk culture – traditionally practiced by a small, homogeneous, rural group living in relative isolation
49.
Pop culture – found in a large, heterogeneous society that shares certain habits despite differences in personal characteristics.
50.
Counterculture – a group that rejects the values, norms and practices of the larger society and replaces them with a new set of cultural patterns
51.
Subculture – a group with its own unique values, norms and behaviors that exists within a larger culture
52.
Culture shock – the disorientation that people feel when they encounter cultures radically different from their own
53.
Globalization – a process by which regional economies, societies and cultures have become integrated through a global network of communication, transportation and trade
54.
Social structure – the network of interrelated statuses and roles that guide human interaction
55.
Status – socially defined position within a group or society
56.
Role – the behavior expected of someone occupying a particular status
57.
Ascribed status – a status assigned according to the standards that are beyond a person’s control (i.e. age, sex, family heritage, race, etc.)
58.
Achieved status – a status acquired by an individual on the basis of some special skill, knowledge or ability
59.
Social institution – a system of statuses, roles, values and norms that is organized to satisfy one or more of the basic needs of society (i.e. education)
60.
Group – a set of two or more people who interact on the basis of shared expectations and who possess some degree of common identity
61.
Preindustrial society – a type of society in which food production – carried out through the use of human and animal labor
– is the main economic activity
62.
Hunting & gathering society – a type of society characterized by the daily collection of wild plants and the hunting of wild animals
63.
Pastoral society – a type of society characterized by a reliance on domesticated herd animals as the main form of subsistence
64.
Horticultural society – a type of society characterized by a reliance on vegetables grown in garden plots as the main form of subsistence
65.
Agricultural society – a type of society characterized by the use of draft animals and plows in the tilling of friends
66.
Industrial society – a type of society in which the mechanized production of goods is the main economic activity
67.
Urbanization – the concentration of population in cities
68.
Postindustrial society – a type of society in which economic activity centers on the production of information and the provision of services
69.
Mechanic solidarity – close-knit social relationships, common in preindustrial societies, that result when a small group of people share the same values and perform the same tasks
70.
Organic solidarity – impersonal social relationships, common in industrial societies, that arise with increased job specialization
Gemeinschaft
– societies in which most members know one another, relationships are close, and activities center on the 71.
72.
family and the community
Gesellschaft
– societies in which social relationships are based on need rather than emotion, relationships are impersonal and temporary, and individual goals are more important than group goals
73.
Formal group – a group in which the structure, goals and activities of the group of clearly defined
74.
Informal group – a group in which there is no official structure or established rules of conflict
75.
Primary group – a small group of people who interact over a relatively long period of time on a direct and personal basis
76.
Secondary group – a group in which interaction is impersonal and temporary in nature
77.
In-group – a group that an individual belong to and identifies with
78.
Out-group – any group that an individual does not belong to, nor identify with
79.
Instrumental leaders – leaders who are task-oriented
80.
Expressive leaders – leaders who are emotion-oriented
Unit THREE: Socialization & Social Control
81.
Personality – the sum total of behaviors, attitudes, beliefs and values that are characteristic of an individual
82.
Sociobiology – the systematic study of the biological basis of all social behavior
83.
Id – Sigmund Freud's term for the personality component that includes all of the individual's basic biological needs that demand immediate gratification
84.
Ego – according to Sigmund Freud, the rational, reality-oriented component of personality that imposes restrictions on the innate pleasure-seeking drives of the id
85.
Superego – according to Sigmund Freud, the part of the personality that represents the conscience, formed in early life by internalization o f the standards of parents and other models of behavior
86.
Sensory motor stage – in Piaget’s stages of cognitive development, a period between birth and age two during which a child relies on sensory impressions. During this stage children learn through assimilation and accommodation
87.
Preoperational stage – in Piaget's stages of cognitive development, a period between ages two and six during which a child learns to use language. During this stage, children do not yet understand concrete logic, cannot mentally manipulate information, and are unable to take the point of view of other people
88.
Concrete operational stage – in Piaget’s stages of cognitive development, a period between ages seven and adolescence during which a child begins to understand concrete logic
89.
Formal operational stage – in Piaget’s stages of cognitive development, a period during which individuals develop an abstract view of the world
90.
Socialization – the interactive process through which people learn the basic skills, values, beliefs and behavioral patterns of society
91.
Self – one’s conscious awareness of possessing a distinct identity that separates you and your environment from other members of society
92.
Looking-glass self – refers to the interactive process by which we develop an image of ourselves based on how we imagine we appear to others
93.
Role-taking – a theory of socialization in which individuals take on or pretend to take on the roles of others
94.
Peer group – primary group composed of individuals of roughly equal age and social characteristics
95.
Mass media – newspapers, magazines, books, television, radio, films and other forms of communication that reach large audiences without personal contact between the individuals sending the information and those receiving it
96.
Total institution – a setting in which people are isolated from the rest of society for a set period of time and subjected to the control of authority
97.
Resocialization – a break with past experiences and the learning of new values and norms
98.
Sanction – rewards or punishments used to enforce conformity to norms
99.
Informal sanction – spontaneous expression of approval or disapproval given by an individual or individuals
100.
Formal sanction – reward or punishment that is given by a formal organization or regulatory body, such as the government, the police, a corporation or a school
101.
Social control – the enforcement of norms through either internalization or sanctions
102.
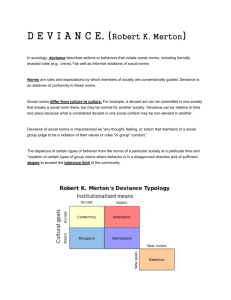
Deviance – behavior that violates significant social norms
103.
Stigma – a mark of social disgrace that sets a deviant apart from the rest of society
104.
Strain theory – theory of deviant behavior that views deviance as the natural outgrowth of the values, norms and structure of society
105.
Control theory – theory of deviant behavior in which deviance is seen as a natural occurrence and conformity is seen as the result of social control
106.
Cultural transmission theory – theory that views deviance as a learned behavior transmitted through interaction with others
107.
Differential association – proportion of associations a person has with deviant versus non-deviant individuals
108.
Techniques of neutralization – the suspending of moral beliefs to commit deviant acts
109.
Labeling theory – theory that focuses on how individuals come to be labeled as deviant
110.
Primary deviance – nonconformity undetected by authority in which the individuals who commit deviant acts do not consider themselves to be deviant, and neither does society
111.
Secondary deviance –nonconformity that results in the individuals who commit acts of secondary deviance being labeled as deviant and accepting that label to be true
112.
White collar crime – crime that is committed by an individual or individuals of high social status in the course of their professional lives
113.
Hate crime – a crime, usually violent, motivated by prejudice or intolerance toward a member of a gender, racial, religious or social group
Unit FOUR: Social Stratification
114.
Social stratification – the ranking of individuals based on unequal access to scare resources and social rewards
115.
Social inequality – the unequal sharing of social rewards and resources
116.
Exogamy – marriage outside of one’s own social category
117.
Endogamy – marriage within one’s own social category
118.
Caste system – system in which scarce resources and rewards are distributed on the basis of ascribed statuses
119.
Class system – system in which scarce resources and rewards are determined on the basis of achieved statuses
120.
Socioeconomic status – a rating that combines social factors such as level of education, occupational prestige and place of residence with the economic factor of income in order to determine an individual’s relative position in the stratification system
121.
Social mobility – movement between or within social classes or strata
122.
Horizontal mobility – type of social mobility in which the individual moves from one position in a social-class to another position in that same social-class
123.
Vertical mobility – movement between social classes or strata in which the individual moves from one social-class to another
124.
Intergenerational mobility – a form of vertical mobility in which status differs between generations in the same family
125.
Poverty level – minimum annual income needed by a family to survive
126.
Race – category of people who share inherited physical characteristics and who are perceived by others as being a distinct group; social construction
127.
Ethnicity – set of cultural characteristics that distinguishes one group from another group
128.
Ethnic group – individuals who share a common cultural background and a common sense of identity
129.
Minority group – category of people who share physical characteristics or cultural practices that result in the group being denied equal treatment
130.
Discrimination – denial of equal treatment to individuals based on their group membership
131.
Prejudice – unsupported generalizations about a category of people
132.
Stereotype – oversimplified, exaggerated or unfavorable generalization about a category of people
133.
Self-fulfilling prophecy – a prediction that results in behavior that makes the prediction come true
134.
Scape-goating – practice of placing blame for one’s troubles on an innocent individual or group
135.
Cultural pluralism – a policy that allows each group within a society to keep its unique cultural identity
136.
Assimilation – the blending of culturally distinct groups into a single group with a common culture and identity
137.
Segregation – physical separation of a minority group from the dominant group
138.
De jure segregation – law-based segregation
139.
De facto segregation – segregation based on informal norms
140.
Subjugation – maintaining control over a group through force
141.
Gender – behavioral and psychological traits considered appropriate for men and women
142.
Gender roles – specific behaviors and attitudes that a society establishes for men and women
143.
Gender identity – the awareness of being masculine or feminine as those traits are defined by culture
144.
Sex – biological/chromosomal traits that determine physical characteristics
145.
Sexism – belief that one sex is by nature superior to the other
146.
Ageism – the belief that one age category is by nature superior to another age category
147.
Graying of America – the phenomenon of the growing percentage of elderly Americans as part as the total U.S. population
148.
Baby-boom generation – collective term for the approximately 76 million children born in the United States from 1946 through 1 964
149.
Dependency ratio – the number of workers for each person retrieving Social Security benefits
Unit FIVE: Social Institutions
150.
Nuclear family – family form that consists of one or both parents and their children
151.
Extended family – family form that consists of three or more generations of a family sharing the same residence
152.
Kinship – network of people who are related by marriage, birth or adoption
153.
Monogamy – marriage of one man to one woman
154.
Polygamy – marriage with multiple partners
155.
Polygyny – form of polygamy in which a man is permitted to marry more than one woman at a time
156.
Polyandry – for of polygamy in which a woman is permitted to marry more than one man at a time
157.
Patriarchy – system in which men are dominant over women
158.
Matriarchy –a family in which the mother holds most of the authority
159.
Egalitarian – a family in which the mother and father share power
160.
Homogamy – tendency for individuals to marry people who have social characteristics similar to their own
161.
Heterogamy – tendency for individuals to marry people who have social characteristics different from their own
162.
Sandwich generation – Americans caught between the needs of their children and aging parents
163.
Schooling – instruction by specially trained teachers who follow officially recognized policies
164.
Hidden curriculum – in schools, the transmission of cultural goals that are not openly acknowledged
165.
Tracking – assignment of students to different types of educational programs
166.
Charter schools – alternative schools which are funded by public money but are privately operated
167.
School choice – a broad movement to provide alternatives to public school systems to which parents can choose to send their children
168.
Religion – system of roles and norms organized around the sacred realm that binds people together in social groups
169.
Ritual – an established pattern of behavior through which a group of believers experience the sacred
170.
Animism – a belief system in which spirits are active in influencing human life
171.
Shamanism – a belief system in which spirits communicate only with one person acknowledged as a specialist
172.
Theism – belief in a god or gods
173.
Monotheism – belief in one god
174.
Polytheism – belief in many gods
175.
Ethicalism – a belief system in which moral principles have a sacred quality
176.
Ecclesia – a type of religious organization in which all people in the society are members by virtue of their birth
177.
Denomination – well-established religious organization in which a substantial portion of the population are members
178.
Sect – relatively small religious organization that typically has split off from a denomination because of doctrinal differences
179.
Cult – religious group founded on the revelations of a person believed to have special knowledge
180.
Religiosity – importance of religion in a person’s life
181.
Secular – non-religious
182.
Media convergence – the idea that mass media are merging and are no longer separate entities
183.
Knowledge-gap hypothesis – as new information enters society, wealthy and better educated members acquire it at a faster rate than poor and less-educated people
184.
Digital divide – the gap between those with access to new technologies and those without it
185.
Social capital – social networks and the reciprocal norms associated with these networks that encourage people to do things for each other
186.
Spiral of silence – belief that as more people accept common opinions the people who disagree are less likely to voice their views
187.
Agenda setting – the argument that the media sets boundaries of public debate by deciding which issues will receive coverage and which will not
188.
Gatekeepers – media executives, editors or reporters who can open or close the “gate” on a particular news story