Chapter 1 Notes
advertisement

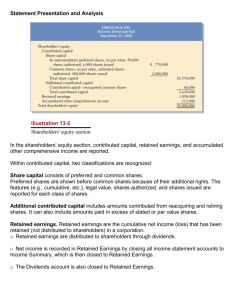
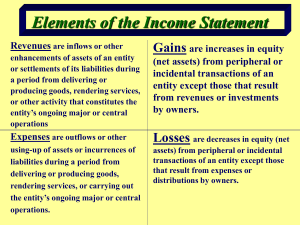
BTB110 Accounting Introduction (as per Chapter 1 – Warren's Survey of Accounting) The following concerns the role of accounting in Business. In general, a business is an organization in which basic resources (inputs) such as material and labour are assembled and processed to provide goods or services (outputs) to customers. Businesses come in all shapes and sizes. The objective of most businesses is to maximize profits by providing goods or services to meet customer needs. Types of Businesses operated for profit: a) Manufacturing – these businesses convert basic inputs into products that are sold to individual customers b) Merchandising – sells products to customers, but does NOT make the products they sell; products are purchased from other businesses ( eg. a manufacturer) c) Service – these businesses provide services rather than products to customers Forms of Businesses Businesses operated for profit can take one of four forms: a) proprietorship – owned by one individual, is easy to organize with a low organizing cost. However, the resources of this business form are limited to the resources of the owner b) partnership – owned by two or more individuals, and organized in much the same way as are sole proprietorships. Same risk as sole proprietorships with respect to limited resources. c) corporations – organized under provincial or federal law as a separate legal entity. Ownership is allocated on the basis of ownership of shares of company stock. Although about 10% of all companies are organized as corporations, they account for approximately 90% of total dollars earned d) limited liability companies (LLC) – organized as a corporation but can elect to be taxed as a partnership. Owner liability is limited to their investment in the business. How Do Business Make Money? The decisions companies make regarding pricing policies are often based on how a company plans to gain an advantage over its competitors, make money and maximize profits. Business have different ways of maximizing profits: a) low price emphasis – a business designs and sells ans produces products at a lower cost than its competitors. The products and services are no-frills and standardized. b) premium-price emphasis – a business tries to design and sell products that serve a unique market need (niche market) allowing it to charge premium prices. Business Stakeholders A business stakeholder is a person or entity that has an interest in the economic performance and well-being of a business. Stakeholders of Note: a) capital market stakeholders provide major financing for a business. b) product or service market stakeholders are the buyers of services or products from the business and vendors to the business. c) government stakeholders collect taxes and fees from the business and its employees. d) internal stakeholders are the individuals employed by the business Business Activities No matter what company we are discussing, all engage in the business activities – financing, investing and operating. a) Financing activities involve obtaining funds to begin and operate a business. Business seeks financing through capital markets. Financing can be in the form of borrowing or issuing shares of ownership. Most major businesses use both means of financing. When a business borrows money, it incurs a liability (debt financing). A business may borrow money by issuing bonds. Bonds are a form of long-term financing. The face value of a bond is expected to be repaid at a set date at some point in the future. Interest on the bond is usually payable semi-annually. A company may also borrow money by issuing a notes payable. Notes payables may be either longterm or short-term financing. When the note is repaid, so also is the interest on the note. A business can also finance its operations by issuing shares of ownership in the form of company stock. There can be different forms of stock, but the best known are common shares and preferred shares. Capital stock is a term used to cover the many different forms of stocks. Investors who purchase stock are referred to as shareholders. The resources owned by a business are called its assets, and the distribution of company earnings to shareholders is called dividends. b) Investing activities are used to obtain the necessary assets to start and operate a business after the financing has been obtained. Depending on the nature of the business, a variety of many different assets must be purchased. Most assets have physical characteristics, although but some assets may be intangible in nature (patent rights, goodwill). Assets can have many different forms; tangible assets include cash, land, property, plant and equipment; intangible items include rights to payments, goodwill, patents, etc. Rights to payments from customers are called accounts receivable. A company may also prepay for items such as insurance or rent. Such items, which are assets until they are consumed, are noprmally reported as prepaid expenses. c) Operating activities represent the implementation of a company's business emphasis. These activities include the sale of its merchandise to earn revenue. If goods are sold, the revenue is labeled as Sales. If a service is sold, the revenue is labeled as Fees Earned. To earn revenue, a business incurs costs such as wages of employees, salaries of managers, rent, insurance, advertising, freight, utilities. Cost used to earn revenue are called expenses. Expenses can be identified in several ways. The cost of the merchandise sold can be called cost of goods sold or cost of sales. Other expenses are often classified as selling or administrative expenses, depending on the nature of the cost. If revenues earned are greater than costs incurred, a net income will be the result. Conversely, there is a net loss when expenses exceed revenues for a given period. What is Accounting and Its Role in Business In a general sense accounting is defined as an information system that provided reports to stakeholders about the economic activities and conditions of a business. Accounting serves many purposes. A primary purpose is to summarize the financial performance of the firm for external users such as banks and government agencies. The branch of accounting that is associated with preparing reports for users external to the business is termed financial accounting. Accounting used to guide management in making decisions about the business is the branch called management accounting. There is considerable overlap between management and financial accounting in the sense that managers can use financial reports to external users in considering the impact of their decisions. The major objectives of financial accounting – 1) to report financial conditions of a business at a particular point in time 2) to report changes in the financial condition of a business over a period of time Financial Statements There are four basic financial statements which relate to the two financial accounting objectives noted above: 1) 2) 3) 4) Income Statement – reports change in financial condition Retained Earnings Statement – reports change in financial condition Balance Sheet – reports financial condition Statement of cash flows – reports change in financial condition. Normally, these reports are prepared in the order given above. 1) The income statement is a summary of the revenues earned and expenses incurred for a specific period of time, such as a month or a year. Formula Used: Revenues – Expenses = Net Income (Net Loss if expenses > revenue) 2) The retained earnings statement is a summary of the changes in the earnings retained by a corporation for a specific period of time, such as a month or a year. Formula Used: Retained Earnings (beginning of period) + Net Income - Dividends paid = Retained Earnings (end of period) 3) The balance sheet lists the assets, liabilities and stockholders’ equity as of a specific date, usually on the last day of a month or year. Formula Used: Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity* *Shareholders’ Equity = Capital Stock + Retained Earnings 4) The statement of cash flows is a summary of the cash receipts and cash payments for a specific period of time, such as a month or a year. Formula Used: Sources and Allocation of Cash from Financing, Investing and Operations Interrelationships Among Financial Statements The financial statements are prepared in the order given above because an interrelationship with these statements. The result of the Income Statement is the Net Income (output). The output of the Income Statement becomes input to the Statement of Retained Earnings. Net Income is added to the opening balance of Retained Earnings , and ultimately affects the value of Stockholders’ Equity. The value calculated for Retained Earnings is added to the Capital Stock balance to determine a value for Stockholders’ Equity. Stockholders’ Equity is a major component of the Balance Sheet. Even the Balance Sheet and the Statement of Cash Flows are interrelated. The cash balance on the Balance Sheet is a ‘control figure’ for the cash flow statement. If a matching of the figures cannot be achieved, then it stands to reason that either one or the other is in error. Accounting Concepts Accounting rules called ‘generally accepted accounting principles’ (GAAP) determine the proper content of financial statements. 1. Business Entity Concept – applies accounting to a specific entity about which stakeholders need economic data. In general, when speaking of corporations, the accounting of the corporation is separated from the accounting of individual stockholders. Therefore, only the transactions and events of the corporation would be included in its financial statements. 2. Cost Concept - determines the amount initially entered in financial records for purchases. The only amount that affects financial statements is the historical cost or the purchase price. 3. Going-Concern Concept –A business normally expects to continue operations for an indefinite period of time. This is called the going concern concept. 4. Matching Concept –in accounting, revenues for a period are matched with the expenses incurred to generate that revenue. Under the matching concept, revenues are normally recorded at the time of the sale of the product or service. Recording revenue is generally called revenue recognition . 5. Objectivity Concept – this concept requires that entries in the accounting records and financial statements be based on objective evidence. We say that we need a paper trail in order to be objective. 6. Unit of Measure Concept – Money is common to all business transactions and thus is considered the unit of measure for reporting. 7. Adequate Disclosure –Financial statements including footnotes and other disclosures should contain all relevant data a reader needs to understand the financial condition and performance of a company. 8. Accounting Period Concept – The process by which accounting data are recorded and summarized in financial statements is a period process. Data are recorded and the income statement, retained earnings statement and statement of cash flows are prepared for a period of time, such as a month or a year. The balance sheet is then prepared at the end of the period. As this cycle (period) is completed, the process begins anew for the next accounting period.