CPR Worksheet 2015
advertisement

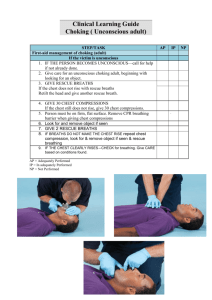
Name ____________ CPR Training Introduction 1. While CPR is never 100% successful, it does________________________________. What Would You Do You need to know BEFORE you are faced with an emergency situation, what you would do……. Are you going to help or not?? Checking an Unconscious Adult and Child Emergency Action Steps 1. ______________ 2. ______________ 3. ______________ 4. __________ the scene for ____________ 5. If the victim is a child, obtain ____________ from a ______________ or _____________. 6. Check the person for ____________________________. 7. If the person doesn’t respond _____________ for _______________, 8. If the person is facedown, ___________ roll the person __________ ______. 9. Keeping the ________, ________ & __________ in a straight line. 10. Open the airway using the ________ _______, chin _________ method. 11. Check for breathing for on more than _________ seconds. 12. Look to see if the person’s chest clearly _____________ and _____________ 13. Listen for _________ _______ from the mouth and nose 14. Feel for __________ ________ against the ______ ____ ____ _________. 15. _____________ breathing is irregular, gasping or shallow. a. Care for the person as if ________________________________________ 16. If an adult is not breathing, quickly check for ____________ __________ 17. Then begin ______________ _____________________ 18. If a child is not breathing, give ________ ________ _____________ 19. If the chest does not rise, ____ ______ the child’s head. 20. If the victim begins vomiting, the ____________ could be _________ 21. If the person is unconscious but breathing, maintain an ______ ____________ Checking An Unconscious Infant 1. Follow the Emergency Steps: a. ___________ b. ___________ c. ___________ 2. Check the __________ _____ _____________ 3. 4. 5. 6. Obtain __________ from a parent or guardian if present Check the Infant for ____________________________ If Infant does not respond, Call ______________ With infant on his/her back, open the ____________, using the ______ _______ ________ ______ technique. 7. Check for breathing for no more than _______ seconds. 8. Then _________, __________ and _____________ for signs of breathing. 9. Normal effective breathing is ____________, ___________ and ______________ 10. Make a complete _________ over the infant’s _____________ and ___________. 11. After ______ successful rescue breath’s; scan the body for severe bleeding. Shock – A life threatening situation where the body is struggling to meet the demands for ___________ and _____________ supply. Signs: 1. Apprehensiveness or _____________ 2. Confused or ________________ 3. Breathing is_________________ 4. Body temperature ____________ 5. Skin becomes ______________, ____________, ____________ and clammy. 6. Pulse rate initially ___________then becomes __________, weak and irregular. 7. Ultimately death because __________________ shut down. How to minimize Shock: 1. Call _________ 2. Put the person in a __________________ position. 3. Control ______________________________. 4. Try and maintain normal _______________________. 5. Reassure the victim until ________________________. 6. Do not give _____________ or __________________. 7. Continue to ______________________. Recognizing and caring for Cardiac Emergencies Signs and symptoms: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 4 Links to Cardiac Chain of Survival: 1. Early ___________________ and access to ______________. 2. Early _____________________ - this keeps the __________flowing to the brain and __________________________. 3. Early __________________ - this establishes a ____________ rhythm. 4. Early _________________ Care – the professional responders continue care. CPR – Adult & Child 1. You will first learn to give _________________ chest compressions followed by two __________ _________________. 2. When practicing, position yourself along side of the victim and place the ___ of one hand in the center of the chest on the breast bone (sternum). Then ______ ______ ______ ___ ____ and lace the fingers together. 3. Your shoulders should be __________ over the hands and fingers are ___ and ____ the chest. Push hard and fast in the middle of chest at least _____ inches deep. 4. Perform ________ chest compressions (at least _____ per min). Each compression should be ____, let the chest rise before you press down again and do not take your hands off the chest just your ________. 5. CPR cycles are performed in cycles; ______ chest compression and ____ rescue breaths. 6. Rescue breaths are performed by using the head lilt, chin lift method. Pinch ________ shut and make a ___________ seal over the mouth. Blow air in for about ___ second. Watch the chest to rise and fall. If air does not go in _________ head and give another breath. 7. Simulating a real response: a. Do not stop CPR unless: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. CPR - Child 1. There are ___ distinct differences between adult and child CPR. 2. After checking for breathing give ___ __________ __________. 3. Quickly scan for severe bleeding and give ____ _________ _____________. 4. Adults do not receive these _____ ________ __________ _____________. 5. Chest compressions for children are _____ _____ inches, for adults they are ____ ________ ____ ________. 6. The cycle of chest compression and rescue breaths is the same for adults and children; ___ _________ __________ followed by ___ _______ _________. CPR –Infant 1. Place one hand on infant’s ____________ to keep airway open. 2. With the other hand place ___ or ___ fingers on the infants _________ just below the _____________ line. 3. If you feel the notch at the end of the breast bone move your fingers slightly towards the infant’s ________. 4. To give chest compressions, position your fingers pointing _____________ down and push _______ and ________ on the chest. Push down about ___________ inches deep 5. Give _______ chest compressions keeping an even _________, counting ____ _________. 6. Each compression should be ________, let the chest ______ completely before pressing down again. 7. Keep your _______________ on the chest. 8. There should be ___________ compressions per ______________. 9. For rescue breaths, tilt ____________ back and lift _________ ___, make a __________ seal over the infant’s _________ and ______. Blow in for about _______ second. Watch for the chest to __________ and _______ after each breath. 10. Cycles are __________ chest compressions and ______ rescue breaths. AED – Adult 1. Following the ____________ of __________ __________ of ____________ can help save lives. 2. The sooner 911 is called the sooner _____________ _______________ __________ will arrive. 3. Early _______ helps circulate blood that contains _____________ to vital _________________. 4. Most people experiencing sudden cardiac arrest need an electrical shock called ___________________. 5. Continue CPR until an _____ is ready to use. 6. An AED stands for ____________ ___________________ ______________________, it is a portable electrical device that analyzes the hearts _______________ and determines if an _______________ _________ is needed to help restore the heart to an effective ______________. 7. Most AED’s have ______________ instructions. 8. The AED ____ _____ _____ what to do. 9. Make sure the person’s _____________ is ___________ and _______. 10. Use gauze to dry the person’s ______ where the pads will be _________. 11. Place one pad on the _______ _______ _____. 12. Place the second pad on the ______ _______ ___ ________. 13. Once pads are on the AED will ______ the hearts rhythm. Do not _____________ the victim during this time. 14. After a _________ is delivered or not, begin ______ cycles of CPR or ____ minutes. 15. After _____ ________ the AED will automatically advise you to stand ______ of the victim s it can _______ the hearts rhythm again. 16. Continue to follow prompts of the AED and _____________ ________. 17. If you notice an obvious sign of life such as __________ stop CPR, maintain an ________ ____________ and _______________ for any ____________ in condition. AED – Child and Infant 1. Use _________________________ pads if they are available. 2. Apply the pads the _____ way you would for an __________. 3. For a small child the pediatric pads may be too __________ to apply without _________________ each other. 4. One pad may need to be attached to the ________ and the other to the __________ between the ___________ _______________. AED – with 2 Responders 1. One responder continues with ____, the second responder prepares ________. 2. CPR and AED’s work ____________ in the links of __________ _______ ___ _________. 3. Responder number one continues _______ while responder number two operates the ______. Breathing Emergencies Conscious Choking Adult and Child 1. If a person is coughing forcefully, he is getting air, so encourage them to ______ _________________. 2. If a conscious adult or child, can no longer cough, speak or breathe, he may be choking. Have someone _________ for _______ and obtain _______________. 3. A combination of 5 _________ _________, followed by 5 ____________ __________________ is an effective way to clear the airway obstruction. 4. Bend the person forward at the ______________ and deliver ___________ _________________ with the heal of your hand and between the shoulder blades. 5. If the five back blows do not clear the airway, give 5 __________ __________. 6. Standing behind the person, use ________ or ______ fingers of one hand to find the ______________. 7. Make a ____________ with your other hand and place the _______ ________ of your fist just above the navel, in the middle of the person’s __________________. Grab that fist with your other hand. 8. Give _______ quick _________ _________. 9. Continue to give 5 back blows and 5 abdominal thrusts until: a. __________________________________________ b. __________________________________________ c. __________________________________________ 10. If the person becomes unconscious, gently ________________ them to the ground, _____________________ his head on the way down. 11. Do not use as much _______________ with a child. Conscious Choking – Infant 1. If an infant is coughing forcefully, ____________________________________. 2. If an conscious infant can not ______________, __________ or breath, assume the airway is ___________________. 3. Act quickly to clear the airway and have someone else _________ ___ _______. 4. Obtain ____________ from a parent or guardian. 5. Give a combination of ______ back blows and _______ chest thrusts to force the object out of the infant’s airway. 6. To give back blows, place the infant between your __________________, supporting their ___________, _______ and _________. 7. With your _________ and __________ supporting the infant’s jaw, position her _____________________ along your forearm, with her head ____________ than her chest. 8. With the heal of your other hand, give _______ firm back blows between the infant’s ____________________. 9. To give __________ __________, support the infant between your arms and carefully turn the infant over, so she is __________ ______ along your other forearm. 10. Place the pads of two or three ____________, in the center of the __________, just below the nipple line toward the infant’s ____________. 11. Give ______ chest thrusts, each about _________ inches deep. 12. You can give back blows and chest thrusts effectively whether you ________, ________ or _________, as long as the infant is supported on your ___________, and the infant’s ___________ is lower then the _____________. 13. Continue to give sets of ______ back blows and ______ chest thrusts, until: a. b. c. d. Unconscious Choking – Adult and Child 1. To care for an unconscious adult or child who is choking, use a _____________ CPR technique. 2. If the chest does not clearly rise with _______ ________, the __________ could be blocked. 3. Retilt the ____________, and give another _________ _________. 4. If the chest still does not clearly rise, assume the ______________ is blocked by a __________ __________. 5. Remove the CPR ______________ ___________, and give _______ chest compressions. 6. Open the person’s mouth, if you see an ____________ , remove it with your _____________. 7. If you have removed an object, or can’t see one, give ________ rescue breaths. 8. Repeat this __________, giving ______ _________ , looking for an object, and giving ______ rescue breaths, until the chest clearly rises with the rescue breaths. 9. If the breaths make the chest clearly rise, remove the ________ ________ _________, and check for _____________ for no more than _____ seconds. Unconscious Choking – Infant 1. To care for an unconscious infant who is choking, use a _________________ CPR technique. 2. If the chest does not clearly rise with _________ _________, the airway could be _________________. 3. Retilt the ____________ and give another _________ _________. 4. If the chest still does not clearly rise, assume the airway is blocked by a _____________ __________. 5. Remove the ___________ __________ _________, and give __________ chest compressions. 6. Open the infant’s ______________. If you see an ___________, remove it with your little _______________. 7. If you have removed an object or can’t see one, give ________ rescue breaths. 8. Repeat this __________, giving ______ _________ , looking for an object, and giving ______ rescue breaths, until the chest clearly rises with the rescue breaths. 9. If the breaths go in, remove the ________ __________ _________ and check for breathing for no more than _________ seconds.