File
advertisement
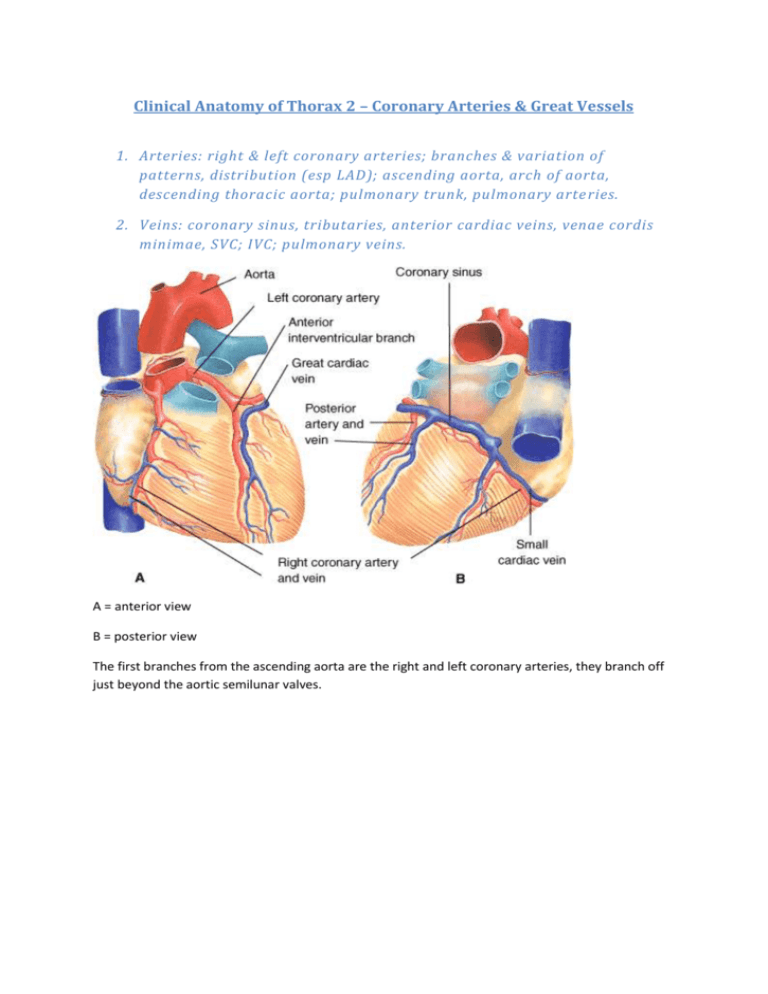
Clinical Anatomy of Thorax 2 – Coronary Arteries & Great Vessels 1. Arteries: right & left coronary arteries; branches & variation of patterns, distribution (esp LAD); ascending aorta, arch of aorta, descending thoracic aorta; pulmonary trunk, pulmonary arte ries. 2. Veins: coronary sinus, tributaries, anterior cardiac veins, venae cordis minimae, SVC; IVC; pulmonary veins. A = anterior view B = posterior view The first branches from the ascending aorta are the right and left coronary arteries, they branch off just beyond the aortic semilunar valves. Artery/Branch Origin Course Distribution Anastomoses Right Coronary Right aortic sinus Follows coronary (AV) groove between the atria and ventricles Right atrium, SA and AV nodes, posterior part of IV septum Circumflex and anterior IV branches of left coronary artery SA Nodal Right coronary artery near its origin Ascends to SA node Pulmonary trunk and SA node Right marginal Right coronary artery Passes to inferior margin of heart and apex Right ventricle and apex of heart Posterior IV Right coronary artery Runs from posterior IV groove to apex of heart Right and left Circumflex and ventricles and IV anterior IV septum branches of left coronary artery AV nodal Right coronary artery near Passes to AV AV node IV branches origin of posterior IV artery node Left Coronary Left aortic sinus Runs in AV groove and gives off anterior interventricular and circumflex branches Most of left atrium and ventricle, IV septum and AV bundles; may supply AV node SA nodal Circumflex branch Ascends on posterior surface of left atrium to SA node Left atrium and SA node Anterior interventricular (LAD, left anterior descending) Left coronary artery Passes along anterior IV groove to apex of heart Right and left ventricular and IV septum Posterior IV branch of right coronary artery Circumflex Left coronary artery Passes to left in AV groove and runs to posterior surface of heart Left atrium and left ventricle Right coronary artery Left marginal Circumflex branch Follows left border of heart Left ventricle IV branches Right coronary artery <> Variations of pattern of coronary arteries Most people (80%) are RCA dominant, 10% are LCA dominant and 10% have codominance. Some people have only a single coronary artery (rare), in some people, the circumflex branch arises from the right aortic sinus and rarely some people have an accessory coronary artery. Aorta The ascending aorta (approx 2.5cm in diameter) begins at the aortic orifice. The aortic valve, obliquely placed is located posterior to the left side of the sternum at the level of the 3rd intercostals space. The arch of the aorta begins posterior to the 2nd right sternocostal joint at the level of the sterna angle, it arches superoposteriorly and to the left. It ascends anterior to the right pulmonary artery and the bifurcation of the trachea and reaches its apex at the left side of the trachea and oesophagus as it passes over the root of the left lung. The arch descends on the left side of the body of T4 veterbra. The arch becomes the thoracic aorta posterior to the 2nd left sternocostal joint. Pulmonary Trunk This is approximately 5cm long and 3cm wide, it’s the arterial continuation of the right ventricle and divides into left and right pulmonary arteries. The pulmonary arteries take deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation. Venous drainage of the heart The coronary sinus is the main vein of the heart. It is wide and runs from left to right in the posterior part of the coronary groove. The coronary sinus receives the anterior interventricular vein (great cardiac vein) at its left end, the posterior interventricular or middle cardiac vein and small cardiac veins to its right. The left posterior ventricular vein and left marginal vein also open into the coronary sinus. The great cardiac vein (anterior interventricular) is the main tributary of the coronary sinus, it begins near the apex of the heart and ascends with the LAD of the LCA. It drains the areas of the heart supplied by the left coronary artery. The middle and small cardiac veins drain most of the areas supplied by the RCA. Several smaller anterior cardiac veins begin over the anterior surface of the right ventricle, cross over the coronary groove and usually end directly in the right atrium, sometimes entering the small cardiac vein. The venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins) are minute vessels that begin in the capillary beds of the myocardium and open directly into the chambers of the heart, chiefly the atria. They are valveless communications with the capillary beds of the myocardium and may carry blood from the heart chambers to the myocardium. They may also provide collateral circulation for parts of the heart musculature. The SVC and IVC enters the heart through the oblique pericardial sinus. The pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood to the left atrium.