Lesson 3
advertisement

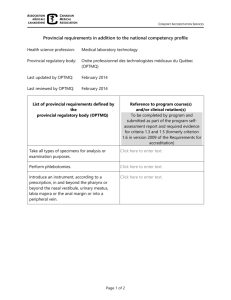
Lesson 3 & 4 - Federalism, the 3 Levels of Government & Passing a Bill Outcomes Students will identify federalism and apply it to the structure of government at its different levels Students will compare and contrast the positions and roles at the federal, provincial and municipal government levels Students will identify the stages that bills must go through to become passed as law and then work cooperatively to draft a bill in a party that will go through this process next class. Activities 1. 2. 3. 4. Lecture Notes – “Comparison of Federal and Provincial Governments”. Student assignment – “On the Right Level”. Using their thoughts, prior knowledge and partner, students have to come up with the appropriate level of government for each service or issue. Go over this as a group. How a Bill Becomes a Law – students are to refer to page 237 and go over the lengthy process of passing a bill. Address the “Thinking Critically” question at the top. Go through PPT for note-taking here. Passing a Bill Activity. Use the attached guide to get students to develop a bill. Next class we will take it through its 7 stages. Materials 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Lecture Notes – “Comparison of Federal and Provincial Governments” Student Assignment – “On the Right Level” Counterpoints page 237 How a Bill Becomes a Law Activity Guide PPT – Bills in Parliament Comparison of Federal & Provincial Governments Federal Provincial Branch _____ Branch ______ Monarch – Governor General Lieutenant Governor Prime Minister / Cabinet Premier / Cabinet --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Branch ______ ( Branch ) ( ) Composition: Party _____ ( ) Composition: # of seats Gov’t ______________ ( ) ___ Official Opposition ______________ ___ Opposition ______________ ______________ ___ ___ Party # of seats Gov’t _________ ( ) Official Opposition ______________ ___ ___ Each level of government (federal and provincial) also has a judicial branch, but we will examine that separately! Comparison of Federal & Provincial Government - KEY Federal Branch Provincial Executive Branch Monarch – Governor General Executive Lieutenant Governor Steven L. Point David Johnston Prime Minister / Cabinet Premier / Cabinet Stephen Harper – Cons. Christy Clark – Lib. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Branch Legislative Branch House of Commons & Senate (308) Legislative Provincial Legislature (105) Composition: Party # of seats Gov’t Conservatives (Harper) Official Opposition NDP 165 102 (85) Composition: Party Gov’t Liberals (Clark) Official Opposition NDP Independent Vacant Opposition Liberals Bloc Quebecois Green Independent Vacant 34 4 1 1 1 VOTERS! VOTERS! # of seats 48 34 2 1 Socials 11 Name ___________________________ Block ______ ON THE RIGHT LEVEL Using any prior knowledge you have, and given some thought to each service or issue, identify at which level(s) of government power is given: Area: Agriculture Armed Forces Copyright Correctional Facilities Education Elections Energy Fire Department Hospitals Human Rights Immigration International trade Internet Labour Libraries Liquor Licenses Marriage Permits Parks Passports Pensions Police Recycling Water and Sewers Social Insurance Numbers Taxes Telecommunications Tourism / Travel Traffic / Parking Signs Transportation Level(s) of Government Responsible: Federal Provincial/Territorial Municipal Socials 11 Name ___________________________ Block ______ ON THE RIGHT LEVEL - KEY Using any prior knowledge you have, and given some thought to each service or issue, identify at which level(s) of government power is given: Area: Agriculture Armed Forces Copyright Correctional Facilities Education Elections Energy Fire Department Hospitals Human Rights Immigration International trade Internet Labour Libraries Liquor Licenses Marriage Permits Parks Passports Pensions Police Recycling Water and Sewers Social Insurance Numbers Taxes Telecommunications Tourism / Travel Traffic / Parking Signs Transportation Level(s) of Government Responsible: Federal Provincial/Territorial Municipal LIMITED LIMITED LIMITED QUEBEC LIMITED Passing a Bill – Student Activity Students are divided into two parties Liberal & Conservative. Within each party, one is the Cabinet Minister introducing a bill. Students are to use page 237 of their textbook to follow the steps of introducing, reading, amending, debating and finally passing or rejecting a bill. Teacher is the Senate. Teacher can choose to pass or reject the bill if it gets to that stage. Leftist Party’s Bill legalization of all drugs in Canada Rightist Party’s Bill capital punishment to be enforced as law for capital crimes Step 1 give each party their bill. The chosen Cabinet Minister introduces it to their party. Step 2 the Cabinet must draft the bill so that it meets with majority approval Step 3 Cabinet Minister introduces the Bill in the “House of Commons”. Step 4 After a few minutes of discussion amongst the party, the bill is reread Step 5 10 minute debate of the bill Step 6 House can choose to amend the bill and send it to a third reading and vote Step 7 if the bill passes the house, Senate (teacher) then approves/rejects it Repeat this for the other party’s bill.