WH10 SAQ26 Chapter 14_2 Totalitarianism in Russia Questions
advertisement
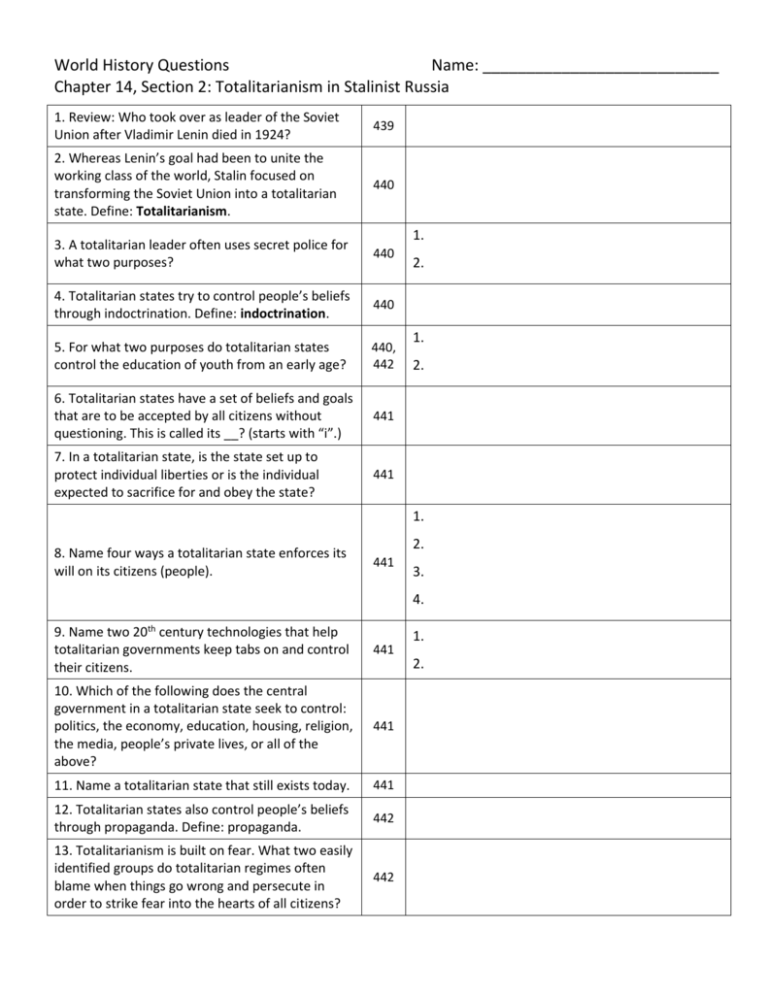
World History Questions Name: ___________________________ Chapter 14, Section 2: Totalitarianism in Stalinist Russia 1. Review: Who took over as leader of the Soviet Union after Vladimir Lenin died in 1924? 439 2. Whereas Lenin’s goal had been to unite the working class of the world, Stalin focused on transforming the Soviet Union into a totalitarian state. Define: Totalitarianism. 440 1. 3. A totalitarian leader often uses secret police for what two purposes? 440 4. Totalitarian states try to control people’s beliefs through indoctrination. Define: indoctrination. 440 5. For what two purposes do totalitarian states control the education of youth from an early age? 440, 442 6. Totalitarian states have a set of beliefs and goals that are to be accepted by all citizens without questioning. This is called its __? (starts with “i”.) 441 7. In a totalitarian state, is the state set up to protect individual liberties or is the individual expected to sacrifice for and obey the state? 441 2. 1. 2. 1. 8. Name four ways a totalitarian state enforces its will on its citizens (people). 2. 441 3. 4. 9. Name two 20th century technologies that help totalitarian governments keep tabs on and control their citizens. 441 10. Which of the following does the central government in a totalitarian state seek to control: politics, the economy, education, housing, religion, the media, people’s private lives, or all of the above? 441 11. Name a totalitarian state that still exists today. 441 12. Totalitarian states also control people’s beliefs through propaganda. Define: propaganda. 442 13. Totalitarianism is built on fear. What two easily identified groups do totalitarian regimes often blame when things go wrong and persecute in order to strike fear into the hearts of all citizens? 442 1. 2. 1. 14. Name three ways Stalin’s secret police controlled the population. 442 15. Why do you think children turned their own parents into the secret police? 442 An 16. What was the goal of Stalin’s Great Purge, during which up to 13 million Russians died? 442 17. What could happen to teachers or students who questioned official Communist party interpretations of history or science? 443 18. What did the Communist’s attitude toward religion and religious beliefs? 443 19. Why do you think the Communists tried to wipe out religious belief? (hint: read box on 443) 443 20. Stalin instituted (put into place) a command economy. Define: command economy. 443 21. What was the goal of Stalin’s Five Year Plans: increase the output of consumer goods or increase the output of industrial goods? Did they work? 443 22. What methods did Stalin use to bring agriculture under state control? How did the peasants react to these measures? 444 23. The Kulaks were wealthy peasants who fiercely resisted collectivization (combining small farms into big state run collective farms). What did Stalin’s soldiers do with the Kulaks? 445 box 2. 3. 1. 24. In what three ways did change under Stalin come “at a great cost” to Soviet citizens? (How was daily life under Soviet rule hard?) 444 25. What profession in Russia was dominated by women by the mid 20th century? 445 26. Which of the posters on page 446 would have been the most effective propaganda (=best at advancing the government’s beliefs) Why? 446 27. Why were the people standing next to Stalin in the first photograph on page 447 removed from later versions of the picture? 447 2. 3.








