Unit 1 - Industrialization Urbanization and the Progressives
advertisement

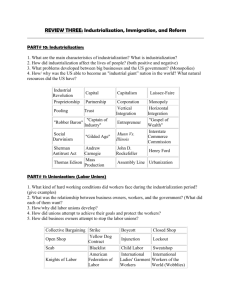
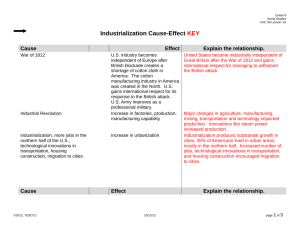
Connecticut Technical High School System Modern American History 6/28/11 Unit 1: Industrialization, Urbanization and Reform (1890-1920) Goal: Students will DEMONSTRATE an understanding of the significance and impact of industrialization and urbanization on the early 20th Century. Big Ideas: The new inventions and technologies during the early 20th Century affected peoples’ lives. Immigrants, African Americans, labor and industrialists played a significant role in the industrialization and urbanization of the United States. Industrialization and urbanization helped transform the United States into a global economic power. Immigration increased dramatically in the late 19th and early 20th Centuries. These immigrants were very different from immigrant groups of the past. These differences added to the cultural diversity of the country but were not always received with acceptance. Increased immigration was one component of the new urbanization. This rapid growth of cities was one factor that gave rise to the progressive movement. The growth of industry, inventions, and new means of production were key components of the second industrial revolution. The Progressive Movement attempted to address the problems (industrial capitalism, political corruption and immigration) caused by industrialization and urbanization. Progressives were a varied group of reformers, each with its own goals. Reforms focused on different political, social, economic, business, and moral goals. Discrimination based on gender, class, race, and ethnicity existed throughout the period. The Progressives and other individuals had varying degrees of success in combating discrimination. Essential Questions: How did the changes and innovations affect peoples’ lives? What problems were created by industrialization? How did industrialization and urbanization change American society? What are the conditions that create social reform? Does reform always promote progress? What role did immigrants, African Americans and labor play in the industrialization and urbanization of America? How did American society discriminate against minorities? Learning Outcomes Students will: Literacy 1. Define and apply key vocabulary/concepts: Industrialization, Urbanization, Immigration, Progressive Movement, Reform, Suffrage: Paraphrase/summarize Compare/contrast Classify Categorize Discuss/explain As evidenced by oral, written, and/or performance: Vocabulary journals Narrative descriptions 2-3 Column Notes (i.e. term/definition/illustrate/paraphrase/relat e) Lincs/Frayer Visual representation (i.e concept diagram/map, graph, chart, drawing, poster, comic strip, cartoon) (H) Honors: Honors students will complete assignments during the trade cycle. Connecticut Technical High School System Modern American History 6/28/11 Illustrate Demonstrate Reflect/relate Infer 11.1 Explain the causes and effects of industrialization and urbanization on American society. Role of Labor Working Conditions Inventions, scientific and technological innovations. Robber Barons/Captains of Industry Patterns of Urban Growth Immigration 11.2 Critique the importance and judge the success of the progressives and other reform movements in social, economic, moral and political reform. Discussion Oral presentation Short answer (H) Essay (H) Make judgments and inferences related to the historical novel. An explanation of the causes and effects of industrialization and urbanization. (H) Assess the impact of Robber Barons/Captain’s of Industry and the impact of business leaders of today. A critique of the success of the progressives. Goals of the Progressive Movement Accomplishments of the Progressive Movement Election of 1912 Muckrakers Suffrage Movement 11.3 Analyze the roots in segregation and discrimination and the responses of African American leaders. Segregation/Discrimination o Amendments: 16th 17th 18th 19th Jim Crow Laws Booker T. Washington W.E.B. Dubois Marcus Garvey Ida B. Wells Great Migration Plessey v. Ferguson An explanation of the causes of segregation. Explain roots Identify relationships Make comparisons Draw logical inferences Present logical conclusions An assessment describing the responses of African Americans to segregation /discrimination. Resources: Bringing History Alive, TCI United States History Program (H) Honors: Honors students will complete assignments during the trade cycle. Connecticut Technical High School System Modern American History 6/28/11 Industrialization/Urbanization American Nation-Ch. 6 American History Political Cartoon 14, 15 Primary Source Reading 6 Literature Reading 6 America: Pathways Ch. 16, sec. 2 and 3 Comparing Primary Sources-On Cultural Ties *Honors-The Americans-Ch. 7 Guided Reading-Problems of Urbanization Primary Sources-How the Other Half Lives, Artifacts from Ellis Island, America 1900, PBS Video Ellis Island http://www.ellisisland.org Jacob Riis’ How the Other Half Lives http://www.cis.yale.edu/amstud/inforev/riis/contents.html Tenement.org http://www.tenement.org/ NY 1900-1920 http://www.albany.edu/mumford/1920/groups.html Progressives American Nation-Ch. 8, 9 Literature Reading 8, 9 Graphic Organizer Activity 8, 9 Primary Source Activity 9 America: Pathways-Ch. 16, sec. 4; Ch. 19 Literature Activity-Horrors of the Meat-packing Industry Primary Source Activity-The Shame of the People Decision-Making Activity-Marching for Child Labor Laws *Honors-The Americans-Ch. 9 Guided Reading-The Origins of Progressivism Literature Selections-The Jungle Primary Sources-Child Labor in the Coal Mines New York: A Doumentary, Episode 4, PBS Video. “The Hardest Struggle”, Women and Sweated Industrial Labor, A Unit of Study for Grades 7-12, by Eileen Boris and Rita Koman, NCHS and OAH. Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire http://www.ilr.cornell.edu/trianglefire/ Regents Prep Progressive Reforms (H) Honors: Honors students will complete assignments during the trade cycle. Connecticut Technical High School System Modern American History 6/28/11 http://regentsprep.org/Regents/ushisgov/themes/reform/progressive.htm Women and Social Movements http://history.sandiego.edu/gen/soc/reform-women.html Segregation American Nation-Ch. 3, Sec. 4 Literature Reading 3-The Cruelty of Jim Crow Laws America: Pathways-Ch. 17, sec. 3 Primary Source Activity-The Washington-Du Bois Debate, Lynchings and Mob Law Decision-Making Activity-Can Separate Be Equal *Honors-The Americans-Ch. 8, Sec. 3 Plessy v. Ferguson http://www.landmarkcases.org/plessy/home.html Jim Crow History http://www.jimcrowhistory.org/ Extension Activity: (H) Honors: Honors students will complete assignments during the trade cycle. Teacher(s) Designed Formative Assessments District-wide Trimester Assessment(s) http://sde-cthsi/DWTA/academic.html Concepts Skills Students need to know about: Students need to be able to do: Goal 11.1 Industrialization Urbanization Reform Goal 11.2 Progressive Movement Reform Suffrage Identify and explain (key concepts) Chart (causes and effects) Debate (role of robber barons) Take and support a position (on a significant invention Map (immigration movements) Develop a resume (on an industrialist) Critique and Judge (Reform Movements) Recreate (muckraker news story) Analyze (political cartoons) Take and support a position (on successes or failures of the Progressive Movement) Discuss (Election of 1912) (H) Honors: Honors students will complete assignments during the trade cycle. Connecticut Technical High School System Modern American History 6/28/11 Analyze (impact of Suffrage Movement) Goal 11.3 Discrimination Jim Crow Laws Great Migration “Separate but equal” Interpret (decision and impact of Plessey v. Ferguson) Chart (positions of and reactions to African American leaders on segregation) Map (Great Migration) Explain (impact of Great Migration) (H) Honors: Honors students will complete assignments during the trade cycle.