chapter19 - ahs-honorsbio2009-1
advertisement

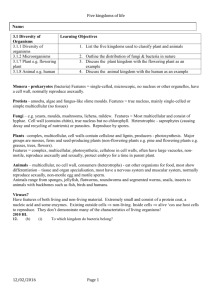
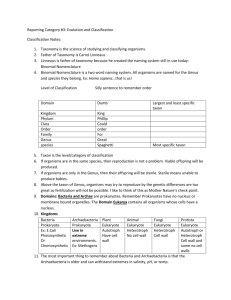
19.1-19.5 Questions & Answers 1. What evidence did the Galapagos Islands provide for evolution by means of natural selection? The tortoises of the islands had long necks in order to reach the edible leaves of the cactus. In areas where cacti were lower to the ground the tortoises had shorter necks because they did not need the height of the turtles in the Galapagos. Any turtles without the long neck adaptation would not be able to survive in the Galapagos thus proving evolution through natural selection. 2. How does evolution play a role in the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria? Many strains of bacteria that were once killed off by antibiotics are now resisting the drugs through evolution. The bacteria that resisted drugs survived long enough to reproduce creating more antibiotic-resistant bacteria; because the bacteria that are not resistant to the antibiotics get wiped out almost immediately the drugs are in fact reducing the competition of the drug resistant bacteria allowing more to reproduce. 3. What is the significance of a nearly universal genetic code with respect to evolution? The significance of a nearly universal genetic code is that it means we most like likely all evolved from one or two organisms. This shows how different evolution can make things like physical characteristics. 4.What are isolating mechanisms? How do they operate? Isolating mechanisms are things that separate population such as geographical landforms, and mating behavior that restricts the organisms from mating. They operate by preventing organisms from mating eventually evolving and resulting in different species. 5. What is polyploidy? What is its connection to speciation? A polyploidy is a duplication of chromosomes. Its connection to speciation is that it often forms new species by creating new organisms that can only reproduce asexually or with another polyploidy. Given that the definition of a species says that they can only reproduce with other organisms of that species a new species if formed through polyploidy.