Punnett Square Worksheet 1
advertisement

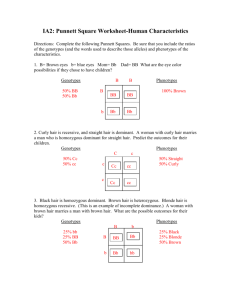
Name: ______________________ Date: __________ Period: ______ Punnett Squares Directions: Read each problem carefully. Make a “key” for the trait (what does each letter mean), identify the genotypes. Show the Punnett square and give the ratio of both genotype and phenotype. Before you begin….Define the following terms from your notes… Homozygous Heterozygous Phenotype Genotype Dominant Recessive 1. In rabbits, black fur is dominant over white fur. Show the cross of a heterozygous black male with a homozygous white female. Key: Genotypes: 2. Tall is dominant over short in pea plants. Show the cross of a homozygous short plant is crossed with a homozygous tall plant. Key: Genotypes: 3. In humans, free-ear lobes are dominant to attached. Two parented that are both heterozygous free are expecting a child. What are the chances that the child will have free ear lobes of attached? Key: Genotypes: 4. Wrinkled seed are recessive to smooth seeds. Show a plant that always produces wrinkled seeds crossed with a heterozygous smooth seeds producing plant. Key: Genotypes: 5. As in the previous problem… Show a heterozygous smooth plant crossed with another heterozygous smooth seed producing plant. Key: Genotypes: 6. Blue eyes are dominant to red eyes in rabbits. Show a heterozygous blue-eyed rabbit crossed with a red-eyed rabbit. Key: Genotypes: 7. In fruit flies, red eyes are dominant over white eyes. Show a cross between two whiteeye fruit flies. Key: Genotypes: Directions: Complete the following Punnett Squares. Be sure that you include the ratios of the genotypes (and the words used to describe those alleles) and phenotypes of the characteristics. 1. B= Brown eyes b= blue eyes Mom= Bb Dad= BB What are the eye color possibilities if they chose to have children? Genotypes Phenotypes 2. Curly hair is recessive, and straight hair is dominant. A woman with curly hair marries a man who is homozygous dominant for straight hair. Predict the outcomes for their children. Genotypes Phenotypes 3. Black hair is homozygous dominant. Brown hair is heterozygous. Blonde hair is homozygous recessive. (This is an example of incomplete dominance.) A woman with brown hair marries a man with brown hair. What are the possible outcomes for their kids? Genotypes Phenotypes 4. Attached earlobes are dominant over free hanging earlobes. Complete the Punnett Square for the following individuals: Mom=BB and Dad=bb Genotypes Phenotypes 5. Incomplete dominance problem: T=tall (5’11”-6’2”); Tt=medium height (5’4”-5’10”) t=short (5’3” or smaller) Mom= 5’5” Dad= 6’0” What are the possible height outcomes of their children? Genotypes Phenotypes 6. Freckles are recessive. No freckles are dominant. Mom= heterozygous Dad=homozygous recessive Possible outcomes for kids? Genotypes Phenotypes Type of Inheritance: Dominant/Recessive 1. Apples can have a long stem or a short stem. Long stem (L) is dominant. Use a Punnett Square for a cross between a Long stem apple (LL) and GENOTYPES PHENOTYPES a short stem apple (ll). Show all percentages or ratios of genotypes and phenotypes. 2. In humans, hitchhikers thumb (H) is dominant to straight (h) thumbs. Use a Punnett Square to show the possible offspring for a cross between a heterozygous parent (Hh) and a straight thumb parent (hh). Show all percentages or ratios of genotypes and phenotypes. GENOTYPES PHENOTYPES 3. The type of running gait of horses is inherited. Trotting is due to a dominant gene (T) and pacing is a recessive allele (t). If two hybrid trotters (Tt) are crossed, what are the possible outcomes? Use a Punnett Square to show all ratios of GENOTYPES PHENOTYPES genotypes and phenotypes. THE FOLLOWING PROBLEMS HAVE CERTAIN THINGS MISSING FROM THE QUESTION THAT YOU HAVE TO FIGURE OUT. BE CAREFUL THAT YOU ARE SETTING UP THE CROSS CAREFULLY. MAKE NOTES IN THE MARGINS IF YOU HAVE TO. 4. Tomatoes can be red (R) or yellow (r). If a homozygous dominant tomato plant is crossed with a homozygous recessive tomato plant, what GENOTYPES PHENOTYPES are the possible outcomes? Show all ratios of genotypes and phenotypes. 5. In fruit flies black eyes (B) is dominant to red eyes (b). If a hybrid black eyed fly is crossed with a red eyed fly, what are the possible outcomes? Show all ratios of genotypes and phenotypes. 6. Cleft chins (C) are dominant over smooth chins (c). What if two heterozygous parents were crossed? What would the possible outcomes be? Show all ratios of genotypes and phenotypes. GENOTYPES PHENOTYPES GENOTYPES PHENOTYPES TO FIGURE THE QUESTIONS OUT IN YOUR HEAD FIRST, AND THEN USE A PUNNETT SQUARE TO TEST YOUR ANSWER. 7. Huntington’s Disease is a dominant genetic disorder. If a hybrid person (Hh) is crossed with a normal person (hh), what is the probability that their offspring will have Huntington’s Disease? 8. Yapping is a trait controlled by a dominant allele (Y) and is uncommon in some populations. If two heterozygous parents (Yy) have children, what is the probability that their offspring will be a non-yapper? What percent will yap?