chapt40 - Strive Studios

Chapter 40
Student: _________________________________________________________
1. The sense of smell is directly connected with which nervous system structure for associations between smells and memory or emotion?
A. cerebellum
B. brain stem
C. hypothalamus
D. limbic system
2. A sense that would make a predator less likely to capture prey could be:
A. keen sense of smell
B. panoramic vision
C. sensitive hearing
D. all of the choices
3. Using corrective lenses will correct all but which of the following eye conditions?
A. farsightedness
B. cataracts
C. nearsightedness
D. astigmatism
4. Which of the following would be recognized by a chemoreceptor?
A. smell
B. balance
C. hearing
D. bladder expansion
E. vision
5. Which of the following is NOT a possible function of a sensory receptor?
A. monitor the internal environment of the body
B. interpret the information from the environment
C. respond to external stimuli from the environment
D. transduce energy from the environment into a nerve impulse
E. send information to the brain about changes in the body's homeostasis
6. Which statement is NOT true about smell receptors?
A. They are chemoreceptors.
B. They are located in the roof of the nasal cavity in humans.
C. They send information to the brain by way of the olfactory bulb.
D. They are capable of responding to pressure as well as chemical changes.
7. Which statement is NOT true about chemoreceptors?
A. They are universally found in animals.
B. They are found all over the body surface in humans.
C. They are concentrated on the auricles of the head in planaria.
D. They are found on antennae and mouthparts in insects and other arthropods.
E. They are thought to be the first kind of sensory receptor to have developed in animals.
8. The sense of smell is unique because it
A. can often be associated with vivid memories.
B. has direct connections to the limbic system and associated emotions.
C. uses a variety of olfactory cell types to permit a wide combination of smell perceptions.
D. may work in conjunction with the sense of taste to produce a combined smell-taste effect.
E. All of the choices are correct.
9. When you perceive a sense of taste, your brain
A. responds to the one taste sense (sweet, sour, etc.) that is sending the most signals.
B. takes an average of the taste messages being received.
C. uses memory to form a taste image after eliminating those signals (sweet, salty, etc.) not received.
D. identifies the chemical profile as a mix of sweet, sour, etc. and remembers the smell from previous experiences.
E. takes a near infinite variety of taste signals and generalizes them into one of the four primary tastes.
10. Which statement is NOT true about taste receptors?
A. They are chemoreceptors.
B. They are located within taste buds in humans.
C. They are found only on the tongue in animals.
D. They recognize the tastes sweet, sour, bitter, and salty.
E. They provide a sense that is not as acute as the sense of smell in humans.
11. The Greek root word meaning "eye" is the basis for the term
A. rhodopsin.
B. retina.
C. cochlea.
D. optic.
E. ommatidia.
12. Which statement is NOT true about photoreceptors?
A. A camera-type eye is found only in vertebrates.
B. They are different in complexity in different kinds of animals.
C. Eyespots in planaria allow the direction of light to be determined.
D. The simplest photoreceptors only recognize the presence and intensity of light.
E. A compound eye as seen in insects has many different visual units, each containing a lens.
13. The Greek root word meaning "hard" is the basis for the term
A. sclera.
B. optic.
C. chorion.
D. rhodopsin.
E. ommatidia.
14. The Greek root word meaning "membrane" is the basis for the term
A. sclera.
B. optic.
C. chorion.
D. rhodopsin.
E. ommatidia.
15. Which statement is NOT correct about the layers of the human eye?
A. The retina is closest to the vitreous humor.
B. The white portion of the eye's outer surface is called the sclera.
C. The innermost part of the layers of the eye contains rods and cones.
D. The cornea is part of the outermost layer of the front of the eye.
E. The choroid layer of the eye contains the light receptor cells and connects them with the optic nerve.
16. What is the aqueous humor?
A. one of the fluids in the inner ear
B. the fluid that surrounds the ossicles of the middle ear
C. the fluid in the eye between the cornea and the lens
D. the fluid in the eye between the retina and the lens
E. the gel-like material in a cupula of a mechanoreceptor
17. The vitreous humor is
A. one of the fluids in the inner ear.
B. the fluid that surrounds the ossicles of the middle ear.
C. the fluid in the eye between the cornea and the lens.
D. the fluid in the eye between the retina and the lens.
E. the gel-like material in a cupula of a mechanoreceptor.
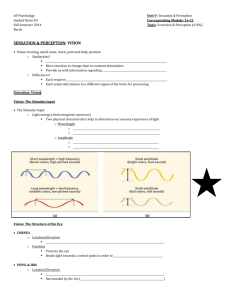
18. At night, we see primarily black and white and shades of gray, except near lights where some color is still evident. This is outward evidence of what internal anatomy?
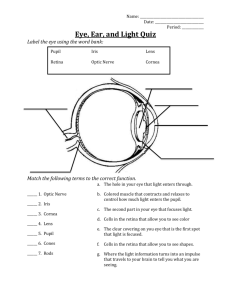
A. There are more rods than cones, and rods amplify the stimulus.
B. There are more cones than rods, and cones amplify the stimulus.
C. The retina has a circadian rhythm.
D. The lens filters differentially the many wavelengths of light.
E. The vitreous humor filters much light, and daytime intensity is necessary to get colored light through to the retina.
19. The order in which light reaches the lens of a human eye is
A. pupil–cornea–aqueous humor–lens.
B. lens–aqueous humor–pupil, cornea.
C. cornea–aqueous humor–pupil–lens.
D. cornea–pupil–aqueous humor–lens.
E. cornea–vitreous humor–pupil–lens.
20. The correct order in which a light ray reaches the retina is
A. cornea-vitreous humor-lens-aqueous humor-retina
B. lens-vitreous humor-cornea-aqueous humor-retina
C. lens-cornea-aqueous humor-vitreous humor-retina
D. cornea-aqueous humor-lens-vitreous humor-retina
E. lens-aqueous humor-cornea-vitreous humor-retina
21. The sclera is continuous with the
A. cornea.
B. iris.
C. retina.
D. choroid coat.
E. fovea centralis.
22. The outermost layer of the eyeball is the
A. choroid layer.
B. sclera layer.
C. retinal layer.
D. fovea.
E. iris.
23. Which of the following is FALSE?
A. The iris regulates the amount of light reaching the retina.
B. The rods are involved in black and white vision.
C. There is a blind spot where the optic nerve joins the retina.
D. The sclera is the outer coat of the eye.
E. The malleus attaches to the oval window.
24. The ____ controls the change in shape of the lens needed for near and far vision.
A. optic nerve
B. fovea
C. cornea
D. ciliary muscle
E. suspensory ligaments
25. What is the ciliary body?
A. the point of the eye at which color vision is most acute
B. the part of the eye that contains rods, cones, and bipolar cells
C. part of the choroid coat of the eye that is attached to the lens and the iris
D. the part of the inner ear that recognizes dynamic equilibrium and movement
E. the internal part of the cochlea with hair cells that are stimulated by sound waves
26. What are the semicircular canals?
A. the point of the eye at which color vision is most acute
B. the part of the eye that contains rods, cones, and bipolar cells
C. the part of the choroid coat of the eye that is attached to the lens and the iris
D. the part of the inner ear that recognizes rotational equilibrium and movement
E. the internal part of the cochlea with hair cells that are stimulated by sound waves
27. On the retina there is an oval, yellowish area with a depression in which vision for color is most acute. This area is called the
A. tectorial membrane.
B. otolith.
C. fovea centralis.
D. blind spot.
E. ampulla.
28. The structure that regulates the size of the opening for light in the eye and is similar to a camera diaphragm, is the
A. pupil.
B. retina.
C. iris.
D. ciliary muscle.
E. lens.
29. When you look at an image, it is inverted on the back of the retina and yet appears right-side-up when perceived in the brain. If a person constantly wore glasses that inverted the image before it entered the eyes, the perceived image is originally inverted but eventually is perceived correct-side-up. This change has occurred in
A. the retina which integrates the visual image.
B. the ganglionic cells.
C. the rods and cones themselves.
D. the visual regions of the brain.
E. the lens.
30. The change in the shape of the lens that allows the eye to focus on nearby objects after focusing on distant objects is
A. activation.
B. rotation.
C. accommodation.
D. interpretation.
E. maximization.
31. As people age, they often can read at a distance but not close up. This farsightedness is treated by
A. radial keratotomy.
B. an unevenly ground lens to compensate for an uneven cornea.
C. cataract surgery.
D. wearing concave lenses to refocus the image on the retina.
E. wearing convex lenses to refocus the image on the retina.
32. The photoreceptors of the eye are located in the
A. retina.
B. optic nerve.
C. choroid layer.
D. sclera.
E. organ of Corti.
33. Retinal is a pigment that is derived from vitamin
A. A.
B. B
2
.
C. C.
D. K.
E. E.
34. Which of the following is NOT a true statement about the rod photoreceptors?
A. They contain the pigment rhodopsin.
B. They are functional only in dim light.
C. They detect even the slightest motion.
D. They detect fine detail.
35. Which of the following function to bend light rays?
A. choroid
B. rods and cones
C. ciliary body
D. lens and cornea
E. iris and vitreous humor
36. Glaucoma is caused by inadequate drainage of the
A. vitreous humor.
B. aqueous humor.
C. venous blood.
D. cochlear duct.
E. ampulla.
37. Which type(s) of receptor is found in the retina?
A. rods and cones
B. organ of Corti
C. muscle spindles
D. olfactory cells
E. hair cells in ampullae
38. Color vision depends on three types of cones that contain pigments sensitive to either
A. red, green, or blue light.
B. red, green, or orange light.
C. red, yellow, or blue light.
D. red, white, or blue light.
E. green, blue, or yellow light.
39. The molecules rhodopsin and retinal are involved in the sensory system that detects
A. hot and cold.
B. hearing.
C. smell.
D. sight.
E. balance.
40. Which of the following is NOT true about cones?
A. They detect color of an object.
B. They detect detail of an object.
C. They require high intensity light.
D. They are absent from the fovea centralis.
41. There are more rods than cones but many rods may synapse with one ganglion cell while only one cone does. Therefore, when light intensity drops at nighttime, we can expect a lit city street scene to be
A. intense in color and very sharp.
B. more black-and-white but very sharp.
C. intense in color but grainy.
D. more black-and-white and grainy.
E. identical to the image formed of the street in daytime.
42. Retinal cells that send signals to the bipolar cells and then to the ganglion cells result in an integrated nerve impulse to the brain. If each cell forwards a signal but also inhibits its immediate neighbor cells when stimulated by light, what is the total consequence of this integration?
A. Viewing the brightest field will always result in the strongest signals.
B. Viewing total darkness will result in signals since there will be no inhibition.
C. Viewing an "edge"–a half white, half dark region–will result in more integrated signal and focus attention on the edge.
D. All signals are averaged and the field is seen as uniform.
43. What is the physiological function of the iris?
A. gives color to the eye
B. determines what colors you can see
C. regulates the amount of light that can enter the eye through the pupil
D. focuses the rays of light on the proper area of the retina so that vision will be sharp
E. rotates the rays of light entering the eye so that the image is upside down on the retina
44. Which of the following is NOT necessary to "see" an object?
A. retina
B. optic nerve
C. frontal lobe of the cerebrum
D. nerve impulse
E. bipolar cells
45. A person who is farsighted cannot see close objects because
A. the lens is too small.
B. the optic nerve is damaged.
C. the eyeball is too short.
D. the eyeball is too long.
E. of a lack of rod receptors.
46. If light rays are not focused evenly on the retina, a fuzzy image is formed. This condition is called
A. nearsightedness.
B. farsightedness.
C. astigmatism.
D. cataracts.
E. conduction deafness.
47. In nearsightedness , light rays are brought into focus
A. in front of the retina.
B. in back of the retina.
C. on the retina.
D. on the hair cells of the ampulla.
E. unevenly across the retina.
48. Which is NOT a correct association of sensory problems?
A. color blindness–lack of red or green cones
B. eyestrain–muscle fatigue from constant contraction of the ciliary muscle
C. cataracts–lens becomes opaque with aging and sun exposure
D. nearsighted–unable to see near objects in detail
E. conduction deafness–new bones overgrow the stirrup requiring surgery
49. Which correctly traces the path of a sound vibration until the signal is sent to the brain?
A. auditory canal-tympanic membrane-malleus-incus-stapes-oval window-cochlea-cochlear nerve
B. auditory canal-malleus-incus-stapes-tympanic membrane-oval window-cochlea-cochlear nerve
C. auditory canal-tympanic membrane-malleus-incus-stapes-cochlea-oval window-cochlear nerve
D. auditory canal-tympanic membrane-oval window-cochlea-malleus-incus-stapes-cochlear nerve
E. auditory canal-malleus-incus-stapes-oval window-tympanic membrane-cochlea-cochlear nerve
50. The tympanic membrane, organ of Corti, and ossicles all participate in the sense of
A. vision.
B. balance.
C. olfaction.
D. gustation.
E. hearing.
51. The bones of the middle ear
A. respond to a change in the position of the head.
B. transmit sound waves.
C. are sense receptors connected to the auditory nerve.
D. are named the malleus, incus, and otolith.
E. are connected to the tectorial membrane and oval window.
52. Which of the following statements is true?
A. Hearing is not dependent on the inner ear.
B. All parts of the organ of Corti hear all ranges of sound.
C. Loud music cannot damage your ears.
D. Hearing is dependent on mechanical pressure.
E. Sound is similar to light insofar as it is transmitted through the vacuum of space.
53. The hammer, anvil, and stirrup are
A. located in the inner ear.
B. equivalent terms for the saccule, utricle, and the otolith.
C. surrounded by fluid in a bony cavity.
D. located between the tympanic membrane and the oval window.
54. Mail-order catalogs often advertise a device for repelling irritating insects. One device has a frequency range from 30,000 to 65,000 cycles per second (Hz). Humans hear from roughly 50 to 15,000 cycles per second. In designing an experiment to determine if this device actually does repel a certain insect, what questions should you ask?
A. Is the target insect able to perceive a sound between these frequencies?
B. Does the insect approach this sound device at a rate higher than random chance?
C. Does the insect move away from this sound device at a rate higher than random chance?
D. Does the insect produce any sounds within this range that would lead to a biological function to perceiving such frequencies?
E. All of the choices are correct.
55. Since the ear relies on the transmission of vibrations, under which conditions would you NOT hear anything, although you were in the presence of a vibrating surface with a frequency within the human hearing range?
A. The vibrating surface and you are both underwater.
B. The vibrating surface is in the air and you are nearby.
C. The vibrating surface is in outer space and you are in a space suit.
D. The vibrating surface is in a solid, such as the ground, and you place your ear to the ground.
E. All of the choices would generate perceptible sound.
56. Theoretically, if we take the nerves leading from the eye and from the ear and cross them over before they reach the appropriate region of the brain, what would happen?
A. Nerves would send vision at the speed of light, and hearing at the speed of sound.
B. Nothing, because the code sent along the nerves from vision is a different "dot-and-dash" from the impulses from hearing.
C. Nothing, because they are completely different types of nerve cells and each operates differently from other sensory nerve systems.
D. The main difference is in the origin and destination of the nerves involved, so the organism would "see" flashes of loud noises and "hear" bright light.
57. How does the stimulus for smell compare with the stimuli for the senses of vision and hearing?
A. All require direct contact of the sensory nerves with molecules of matter.
B. None requires contact but are triggered by light, sound, and smell energy from afar.
C. Smell requires the presence of molecules against the surfaces of the taste buds or nasal passages; sound and light are pure energy that can be transmitted in a vacuum.
D. Smell requires the presence of odor molecules, sound requires the vibrations of air molecules, but light is pure energy that does not need a medium to travel to us.
58. What kind of receptors are involved in hearing?
A. chemoreceptors
B. photoreceptors
C. pain receptors
D. mechanoreceptors
E. interoceptors
59. Puncturing the eardrum so that it is inoperative would
A. not affect your sense of hearing.
B. prevent the normal transmission of sound vibration.
C. destroy the sense receptors for hearing.
D. account for why some people who hear still cannot sing a tune.
E. account for night blindness.
60. Which of the following groups are all membranous structures?
A. ossicles, tympanic membrane, oval window, otoliths
B. cochlea, ampulla
C. tympanic membrane, oval window, round window
D. malleus, incus, stapes
E. tympanic membrane, oval window, stapes
61. Which is/are found in the middle ear?
A. semicircular canals
B. auditory canal
C. hair cells
D. ossicles
E. glands for earwax production
62. Which is/are involved in balance and equilibrium?
A. semicircular canals
B. otoliths
C. saccule and utricle
D. vestibule
E. all of the choices are involved
63. Which is NOT associated with the middle ear?
A. cochlea
B. auditory tube
C. stapes
D. tympanic membrane
E. incus
64. The crayfish has a cavity or "statocyst" lined with sensory seta or hairs. A grain in the cavity is pulled downward by gravity; the pressure against the bottom hairs of the cavity gives the crayfish a perception of being upright and, when it changes orientation, the grain touches side hairs that make it realize it is not upright. Thus the crayfish "knows" which way is up in the dark. This sense is most closely related in function to the human sense of
A. hot and cold.
B. hearing.
C. smell.
D. sight.
E. balance.
65. What is the organ of Corti?
A. the point of the eye at which color vision is most acute
B. the part of the eye that contains rods, cones, and bipolar cells
C. the part of the choroid coat of the eye that is attached to the lens and the iris
D. the part of the inner ear that recognizes dynamic equilibrium and movement
E. the internal part of the cochlea with hair cells that are stimulated by sound waves
66. Which pair is mismatched?
A. semicircular canals–inner ear
B. ampulla–outer ear
C. auditory canal–outer ear
D. ossicles–middle ear
E. stapes–oval window
67. The cochlear nerve (auditory nerve) originates from the
A. pinna.
B. hammer.
C. organ of Corti.
D. hair cells of the ampullae.
E. rods and cones.
68. The cochlea
A. is a coiled structure found in the middle ear.
B. contains two fluid-filled canals.
C. contains the organ of Corti.
D. is used for equilibrium.
E. contains otoliths.
69. The organ of Corti consists of the
A. hammer, anvil, stirrup.
B. eardrum, round window, oval window.
C. hair cells and tectorial membrane.
D. saccule, utricle, and cochlea.
E. cochlea and auditory nerve.
70. That impulses from the eye result in sight perception and impulses from the ear are perceived as sound are due to
A. the neurons of these systems use different ions to send signals to the brain.
B. the neurons send signals at different frequencies.
C. the signals from the eye travel to the visual perception region of the brain; auditory signals go to the hearing section.
D. nerve signals form a visual pattern or a sound pattern as they travel through the nerves.
E. the different neurons (chemoreceptors, mechanoreceptors) are completely different types of cells.
71. The sense of equilibrium is accomplished by hair cells found in the
A. cochlear duct.
B. outer ear.
C. middle ear.
D. ampulla.
E. organ of Corti.
72. Rotational equilibrium is dependent on
A. the inner ear.
B. semicircular canals.
C. utricle and saccule.
D. the inner ear and semicircular canals.
E. coordination of eyesight with sense of balance.
73. From what you currently know, in a spacecraft at a point of weightlessness, which effect is most likely?
A. Rotational equilibrium would be lacking and you could not detect head movement.
B. Gravitational equilibrium would be altered since the otoliths would not be pulled down by gravity.
C. Without gravity, there would be no vertigo.
D. All balance systems would work similar to being on earth with normal gravity.
E. There would be absolutely no sense of balance signals without gravity.
74. The actual physiological mechanism that allows fish to school involves both the lateral line and eyesight.
Therefore, the stimuli that fish use to school are light and
A. pressure.
B. temperature.
C. sound waves.
D. gravitational pull.
E. molecules for taste.
75. Which of the following is NOT a correct association with respect to chemoreceptors?
A. planarians–entire body surface; auricles at the side of the head
B. flies–feet
C. crustaceans–appendages; antennae
D. amphibians–feet
76. Color vision occurs in all of the following EXCEPT
A. insects.
B. fish.
C. primates.
D. cattle.
77. Cataracts may be associated with which of the following?
A. aging
B. exposure to the sun
C. inability of the lens to transmit light rays
D. All of the choices are associated with cataracts.
78. Which of the following vitamins is most closely associated with good night vision?
A. Vitamin C
B. Vitamin B
C. Vitamin A
D. Vitamin E
79. Hearing loss can be due to which of the following?
A. anticancer drugs
B. untreated middle ear infections
C. excessive noise
D. All of the choices can be causes of hearing loss.
80. Which of the following is miss-matched?
A. inner ear–rotational and gravitational equilibrium
B. middle ear–amplifies soundwaves and equalizes air pressure
C. outer ear–equalizes ear internal and external temperature
D. All of the choices are properly matched.
81. Integration in sight
A. occurs in the retina.
B. occurs in the visual areas of the cerebral cortex.
C. involves the retina, which is composed of 3 layers: the rod and cone layer, the bipolar cell layer, and the ganglion cell layer.
D. All of the choices are involved in the integration of sight.
82. Both the sense of smell and taste involve receptors that end in microvilli that are used to detect chemicals.
True False
83. The eyes are involved with rotational equilibrium.
True False
84. Chemoreceptors underlie sight, hearing, and touch.
True False
85. The sense of smell is due to a mechanoreceptor response.
True False
86. Molecules interacting with receptors on cilia of olfactory cells give the sense of hearing.
True False
87. The senses of smell and taste are chemical senses that are complementary to each other.
True False
88. Insects can see part of the ultraviolet spectrum that is invisible to humans.
True False
89. Certain mollusks such as the octopus have camera-type eyes similar to those of vertebrates.
True False
90. The rods are the cells of the eye that see very distinct images and colors.
True False
91. All photoreceptors contain lenses for focusing the light entering them.
True False
92. Color vision in humans depends on the pigment rhodopsin.
True False
93. The blind spot contains no rods or cones, and it is the point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye.
True False
94. Nerve impulses generated by the rods and cones are passed to the ganglionic cells and then to the bipolar cells in the retina.
True False
95. Nerve impulses are sent to the brain from the ear by way of the cochlear (or auditory) nerve.
True False
96. The auditory (eustachian) tube connects the outer ear to the middle ear.
True False
97. The sense of dynamic balance is dependent in part on clusters of hair cells that are displaced by the motion of otoliths.
True False
98. Hair cells are found only in the mechanoreceptors of the lateral line organs of fishes and amphibians.
True False
99. The most common injury to the eye is due to careless use of contact lenses.
True False
100. Humans taste only bitter, sour, and salt. All other flavors are combinations of these flavors.
True False
101. Describe and give an example in humans and in an animal of each of the following kinds of receptors: mechanoreceptors, chemoreceptors, and photoreceptors.
102. Name and describe each of the three coats of the eye in the human.
103. Even though the insect, the squid, and the human all have eyes, biologists do not believe that they arose from one common ancestor. Describe at least three lines of evidence and/or logic that would lead biologists to suspect this is a case of independent or convergent evolution of this complex structure.
104. Name and describe the parts of the inner ear in the human, telling what each part does.
105. Name and describe the parts of the outer and middle ear in the human, describing what each part does.
106. Explain the mechanisms by which a human can tell directions and maintain equilibrium using the receptors of the ear.
28. C
29. D
30. C
31. E
32. A
33. A
34. D
35. D
36. B
37. A
38. A
39. D
40. D
41. D
42. C
43. C
44. C
45. C
46. C
47. A
48. D
49. A
1. D
2. B
3. B
4. A
5. B
6. D
7. B
8. E
9. B
10. C
11. E
12. A
13. A
14. C
15. E
16. C
17. D
18. A
19. C
20. D
21. A
22. B
23. E
24. D
25. C
26. D
27. C
Chapter 40 KEY
68. C
69. C
70. C
71. D
72. D
73. B
74. A
75. D
76. D
77. D
78. C
79. D
80. C
81. D
82. FALSE
83. TRUE
84. FALSE
85. FALSE
86. FALSE
87. TRUE
88. TRUE
89. TRUE
90. FALSE
58. D
59. B
60. C
61. D
62. E
63. A
64. E
65. E
66. B
67. C
50. E
51. B
52. D
53. D
54. E
55. C
56. D
57. D
91. FALSE
92. FALSE
93. TRUE
94. FALSE
95. TRUE
96. FALSE
97. FALSE
98. FALSE
99. TRUE
100. FALSE
101. Answers will vary.
102. Answers will vary.
103. Answers will vary.
104. Answers will vary.
105. Answers will vary.
106. Answers will vary.