Ms. Mackey's 8th Grade Language Arts 1st Six Weeks Notes
advertisement

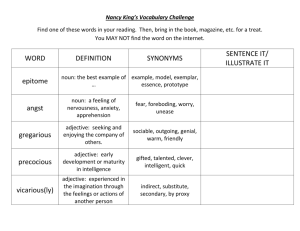
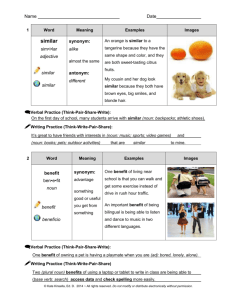
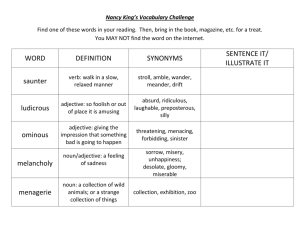
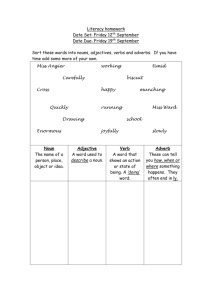
Ms. Mackey’s 8th Grade Language Arts 1st Six Weeks Notes & Vocabulary 5 Things Needed for Complete Sentence 1. Begin with a capital letter. 2. End with correct punctuation (Period. / Question mark? / Exclamation mark!) 3. Must have a subject (noun). 4. Must have a predicate (verb). 5. Must make sense. Synonym vs. Antonym Synonym: word that has the same or similar meaning. o EXAMPLES smart and intelligent sad and unhappy; Antonym: word that has the opposite meaning. o EXAMPLES cat and dog black and white fast and slow Noun vs. Adjective Noun: word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. o EXAMPLES Common Noun—teacher, student, school, street, country, love, desk, and jealousy Proper Noun—Mr. Brown, Shannon, Hopewell Middle School, Gulf Way, United States, and China Page 1 of 4 Adjective: word that describes a noun or another adjective. o EXAMPLES Tall, short, fat, skinny Black, white, blue, yellow Lazy, honest, hard-working, tricky Literary Elements Conflict: a problem or struggle that a character faces o Internal conflict: occurs when the character battles within himself (inside the head) o External conflict: occurs when the character battles with another character or outside force Plot: the series of events in a story (what happens in a story) o Linear Plot Development (Plot Diagram) Exposition-the characters and setting are introduced; reveals the conflict or sets the stage for it Rising Action-introduces obstacles that make the conflict more complicated; builds suspense as “ the plot thickens” (what leads up to the main problem of the conflict) Climax-when the problem or conflict reaches its highest point; the moment of greatest suspense (the turning point of the story) Falling Action-reveals the outcome of the story’s climax; shows how the main character resolves the conflict (when the problem or conflict is solved or over) Resolution-reveals the story’s final outcome (story is wrapped up and brought to a closing) Page 2 of 4 o Subplot- a second part of a story that supports or affects the main plot; a story within a story Internal vs. External Conflict Internal conflict means conflict within a given character: struggling against his fears, his doubts, his moral failings and similar emotional or intellectual conditions. External conflicts are outside the hero's own mind: fellow men, the natural world, or larger societal organizations. A well-written novel may contain multiple types of conflict, blending external and internal. o Types of EXTERNAL CONFLICTS Man vs. Man—the most basic type of external conflict is man vs. man. It pits the hero against another person or people bent on defeating him. Not every instance of man vs. man conflict is obvious. Sherlock Holmes, for example, is often fighting against a criminal mastermind: a struggle of intellect and will, rather than a physical fight. Man vs. Nature—Man vs. nature encompasses a human being's struggle against the weather, the wilderness or some manner of wild beast. It can also be a conflict against natural forces, such as the struggle to find a cure for a disease, or the fight to get crops to grow. Man vs. Society—A man vs. society conflict is an individual struggling against larger social forces, such as governments, cultures or societal trends. Tone vs. Mood Tone- the author’s ATTITUDE about the subject he’s writing about Mood- the reader’s feeling THEME- what the author is trying to tell us about the subject; author’s message or life lesson (moral) Point of View- the perspective from which the story is told Ist person—uses “I” or “me” 3rd person—uses “he” or “she” Figurative Language Definitions Imagery - Any word or group of words that create a picture Simile - A figure of speech that compares two things, and is usually introduced by the words like or as. Page 3 of 4 Repetition - When a word or phrase repeats itself in a piece of literature Metaphor - A comparison of two things without using like or as Alliteration - The repeating of the same sound at the beginning of two or more words that are next to or near each other. Symbolism - The creative use of symbols as representations of objects or concepts in a story Personification - Giving non-human things human characteristics Extended Metaphor - A detailed and complex metaphor that extends over a long section of literature Hyperbole – An extreme exaggeration used to make a point Onomatopoeia- A word whose sound suggests it meaning (sounds like the word itself) Oxymoron – A combination of contradictory words (words with opposite meanings) Idiom-An expression whose meaning is different from the meaning of its individual words SIFTT Method- things to look for when responding to literature S- Symbolism I- Imagery F- Figurative Language (simile, metaphor, personification, hyperbole, idiom) T-Tone (author’s attitude about the subject) T-Theme Page 4 of 4