RS 5.5
advertisement

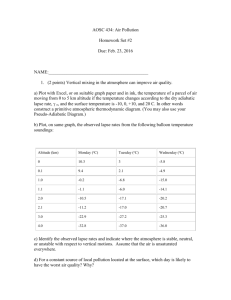
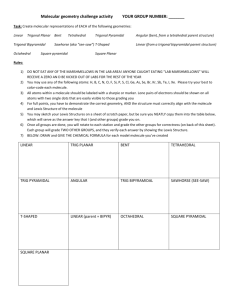
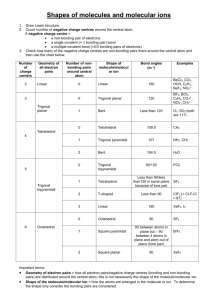
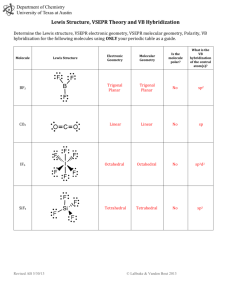
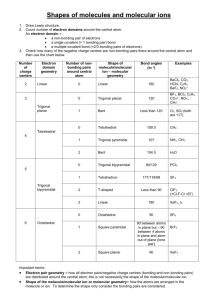
Week 6 Recitation Section 1. Lewis Dot: Write the Lewis dot structures, show formal charge and resonance structures: a. N2, SF4, NO, SF6, CO, NO-, BF4b. SH2, BF4-, NO3-, NO3c. SO3, ICl3, SeF6, OF2, AsO43-, NCS-, SCO–, N3– d. CH3COO–, SCN-,, SO2, SO42–, C6H6, e. H2C2, H4C2, H2CO2H, H2COH f. H8C4, H12C6 , C5H5-, C7H12 2. Write Resonance and Lewis Dot structures for: NO2-, NO3-, SO2, SO3 3. VSEPR: 4. Define Steric number: 5. Fill in the table below: Steric # 6 5 4 3 2 geometry example SF6 PF5 CH4, SO42SO3 BeH2, CO2 linear 6. Predict the shapes of: CH4, NH3, H2O, why does the angle change H4C2 SO3, SO2, O3 7. Fill in the table: Steric # Geometry 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 6 Oh 6 6 6 6 8. What is the shape of: a. IF4-, Lone Pairs 0 1 0 1 2 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 4 PF3, Shape Oh XeF2, SO2, example SO3 SO2 CH4, SO42NH3 H2 O PF5 SF4 CLF3 XeF2 SF6 IF5 XeF4 b. c. d. e. f. SO42-, SO3, CS2 ClO2 SF2, PF5, ICl3, SiH 4 H3CCO2H SeF6, BF3, CS2, CBr4, SiH4, SF2 H2CCCH2 PF3 9. What is the shape around each of the C atoms in H3CCOOH, H2CCH2, HCCCH3 10. Draw the Bonding and antibonding orbitals for H2 11. Why is the bond in Li2 weaker then H2 12. Draw the MO diagram for B2, C2 N2 O2 F2 13. What is the MO for O2 different than N2 14. 15. What orbitals participate in the bonding in HF and HCl. Why is the HCl bond weaker. 16. Is H2- magnetic? 1. Lewis Dot: Write the Lewis dot structures, show formal charge and resonance structures: a. N2, SF4, NO, SF6, CO, NO-, BF4F F Si B– F F F F :N:::N:, b. SH2, BF4-, NO3-, N , :–C-::O:+, –N=O, O F F F H S F H B- -O F N+ O O- F 3- - – c. SO3, ICl3, SeF6, OF2, PO4 , NCS , SCO , N3 S2+ O S+ O O- N+ O O- O- S O- N2– -, -S O- + 2– C d. CH3COO , SCN , SO2, SO4 , C6H6 e. H2C2, H4C2, H2CO2H, H2COH Cl -O O As O , N S C -O As O O- O- 5 more 3 more C I Cl O- +S O- O O-O N+ O 2 more S O O Cl 2 more - O- – O O O- N- C C C C C C C C C C f. , c C C- C C , (only C shown) 2. Write Resonance and Lewis Dot structures for: NO2-, NO3-, SO2, SO3 3. VSEPR: 4. Define Steric number: 5. Fill in the table below: Steric # 6 5 4 3 2 geometry Oh Sq pyramidal Td Trigonal planar linear example SF6 PF5 CH4, SO42SO3 BeH2, CO2 6. Predict the shapes of: CH4, NH3, H2O, why does the angle change Td, trigonal pyramidal, bent; angle 109.5, 107, 104 H4C2 SO3, SO2, O3 7. Fill in the table: Steric # Geometry 3 trigonal planar 3 trigonal planar 4 Td 4 Td 4 Td 5 trigonal bipyrimidal Lone Pairs 0 1 0 1 2 0 Shape trigonal planar bent angle<120 Td sq pyrimide bent angle <107 trigonal bipyrimidal example SO3 SO2 CH4, SO42NH3 H2 O PF5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6 6 trigonal bipyrimidal trigonal bipyrimidal trigonal bipyrimidal Oh Oh Oh Oh Oh 1 saw horse SF4 2 T shape CLF3 3 linear XeF2 0 1 2 3 4 Oh sq pyrimide sq planar T shape linear SF6 IF5 XeF4 8. What is the shape of: g. IF4-, sq planar PF3, trig. Pyr. XeF2, linear SO2 bent angle 115, 2h. SO4 , Td PF5,trig. bipyr BF3, trig plan CS2, linear i. SO3, trig planar ICl3, trig plan CBr4, Td SiH4 Td j. SiH 4 Td SF2 bent k. ClO2 bent H3CCO2H Td (left C) trig plan (right C) H2CCCH2 trig planar, linear, trig planar l. SF2, bent SeF6, Oh PF3 trig pyr 9. What is the shape around each of the C atoms in H3CCOOH, H2CCH2, HCCCH3 10. Draw the Bonding and antibonding orbitals for H2 - H bonding - - H - H antibonding 11. Why is the bond in Li2 weaker then H2 2s more diffuse than 1s so overlap is worse 12. What orbitals participate in the bonding in HF and HCl. Why is the HCl bond weaker. In HF it is 1s and 2p orbitals while in HCl it is 1s and 3p the over lap of 3p with 1s worse 13. Is H2- magnetic? No spins are paired.