X = 3 tabs
advertisement

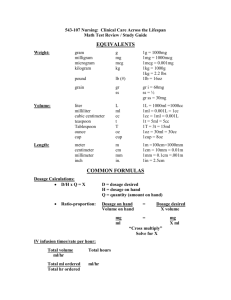
NURSING SKILLS – instructor sheet SUMMARY OF MATH PRESENTED IN MORRIS’S CALCULATE WITH CONFIDENCE AND PRACTICE PROBLEMS METHODS OF CONVERTING 1. Multiply or divide by the conversion factor (in metric system move the decimal point) – see conversion table on page 3 RULES: **smaller unit to larger unit – divide; **larger unit to smaller unit – multiply EXAMPLE #1: 10000 mg = X Gm? 10000 mg becomes 10.000 Gm (move decimal three spaces to left to divide) OR USE RATIO/PROPORTION METHOD IF CAN’T REMEMBER IF NEED TO DIVIDE OR MULTIPLE TO CHANGE METRIC UNITS 10000mg = 1000mg x 1 Gm RULE: Must have same units above the line and same units below the line eg mg above and Gms below (1000mg)(x) = (10000mg)(1 Gm) 1000mg x 1000mg x = = EXAMPLE #2: 10000mg/GM 1000mg 10Gm RULE: MUST ASK SELF IF ANSWER IS REASONABLE? 5 Gm = X mg? 5 Gm becomes 5000 mg (move decimal three spaces to right to multiply) OR USE RATIO/PROPORTION METHOD IF CAN’T REMEMBER IF NEED TO DIVIDE OR MULTIPLE TO CHANGE METRIC UNITS 1000mg 1Gm = x mg 5Gm REMEMBER ABOVE AND BELOW LINE RULE (1000mg)(5Gm) = (1Gm)(x) 5000mg/Gm = 1Gm x 5000mg = x MUST ASK SELF IF ANSWER IS REASONABLE? 1 2. Ratio-proportion method rule summary: RULES: state known equivalents put the incomplete ratio on the other side of the equal sign, KEEPING THE SAME UNITS ABOVE THE LINE AND THE SAME UNITS BELOW THE LINE ON EACH SIDE OF THE = SIGN label all terms but ignore them while doing the math solve for X PRACTICE: You do the following examples, using the ratio/proportion method a. 8 mg = X g 1000mg = 8mg 1 Gm x 1000x = 8 x =8 1000 x = .008 Gm b. 12Gm = X mg 12Gm = 1 Gm x 1000mg x = (12)(1000) x = 12000mg 2 DOSE CALCULATIONS (note: when different systems of measurement are involved, convert to the unit that is available(what you have on hand)before proceeding to calculate the dose) 1.Ratio – proportion method EXAMPLE #1: Ordered: Lanoxin 0.75 mg; Available supply: Lanoxin 0.25 mg tabs RULE: SETTING UP THE PROBLEM: What you Have OR Supply available = What you Want OR Doctor’s Order 0.25 mg = 0.75 mg 1 tab X tabs Have or Supply = Want or Doc. order (0.25) X = (0.75) (0.25) X = 0.75 (0.25) (0.25) X = 3 tabs HOUSEHOLD APOTHECARY dram i 1 T (tbs) gr 15 Gr 1 1oz 2.2 lb METRIC 4 or 5 ml (cc) 15 cc 1 G (1000 mg) 60 mg 30 ml (cc) 1 Kg (1000 g) Other metric: Kilo = 1000 Centi = one hundredth of (0.01) Milli – one thousandth of (0.001) Micro = one millionth of (0.000001) 1Gm = 1000mg 1kg = 1000Gms 3 Practice Math Calculations for Oral Medications Answer Key: Practice Math Calculations for Oral Medications 1. Order: Prednisone 60 mg p.o. every day. Available: 20 mg tablets. How many tablet(s) would you give? WANT = HAVE 60mg = 20mg X 1 tablet 20x = 60 x = 3 tablets answer Logical? 2. Order: Lasix 0.06Gm p.o. every day. Available: 40 mg tablets. How many tablets would you give? How many Gm to mg? 1G = 1000mg WANT = HAVE 0.06G X = 1G 1000mg Ratio (0.06G)(1000mg)= (x mg)(1G) 60.00mg = x DOC.ORDER 60mg x 40x = x = = SUPPLY 40mg = 1 tablet 60 1.5 tablets answer Logical? (can the tablets be split?) 3. Your patient is unable to swallow pills. You need to crush the medication. Can you crush: tablets? Coated tablets? Slow release capsules? Tablets: Yes – usually Coated Tablets: Usually no! Slow release capsules: No 4 4. Ordered: Proventil syrup 2mg/5ml. Give 3 ml p.o. TID. How many mg are you giving per dose? SUPPLY = ORDER 2mg = x 5ml 3ml (2)(3)= (5)(x) 6 = 5x 6 = 5x 5 5 1.2 = x Answer: 1.2 mg/3ml Logical? The PDR states that the maximum dose is 0.3mg/kg in 3 divided doses. The child in the above example weighs 56 pounds. Is this a safe dose for the patient? HAVE = WANT How many kg is 56 lbs? 2.2 pound = 56 pounds 1kg = x 2.2x = 56 2.2x = 56 2.2 2.2 x = 25kg Logical? What is the maximum dose for this child for the day? 25 kg x 0.3mg = 7.5 mg/day What is the maximum dose divided into 3 doses? 7.5mg 3 = 2.5mg per dose Your patient is receiving 1.2 mg per dose, which is below the maximum dose. 5. Order: Vicodin (2.5mg hydrocodone/500mg acetaminophen) i or ii tablets q 4-6 hrs prn pain. PDR states acetaminophen dose is not to exceed 4G/d. Your patient had: 2 tabs at 0030, 1 tab at 0500, 2 tabs at 0930, 2 tabs 1440, and 1 tab at 1850. It is now 2250, your patient is in pain. How many tablets could you give the patient? How many tablets can the pt have in a day? (500mg per tablet and the limit is 4 G) WANT = HAVE 4Gm = 1Gm x mg 1000mg (1)(x) = (1000)(4) x = 4000mg 5 So your patient can have 4000mg of acetaminophen a day, which is how many tablets? HAVE = WANT 500mg = 4000mg 1 tab = x tablets 500x = 4000 500x 500 x = 4000 500 = 8 tablets Logical? If your patient can have 8 tablets in one day, how many tablets has your patient had so far? 8 tablets - Your patient has reached the limit. 6. Order: Keflex 250mg p.o. TID. The label on the bottle states: Keflex 125mg/5ml. Directions: Add 36ml of water to dry mixture in the bottle. Shake well. Will make 40cc of Keflex. How many cc per dose? About how many doses will the bottle contain? How many cc per dose? SUPPLY 125mg 5ml (125)(x) 125x 125x 125 x = WANT = 250mg = x ml =(5)(250) = 1250 = 1250 125 = 10ml Answer = 10cc per dose Logical? How many doses per bottle? WANT = HAVE 40 cc = 10cc x 1 dose 10x = 40 10x = 40 10 10 x = 4 doses per bottle Logical? 7. Order: Darvocet-N (propoxphene 65mg /acetaminophen 650mg) i or ii tablets q 4-6 hours prn pain. PDR states acetaminophen dose is not to exceed 4g/d. How many tablets could the patient have in a 24 hour period? How many mg in 4G? WANT = SUPPLY/HAVE 1000mg = x 1G 4G (1)(x) = (1000)(4) x = 4000mg 6 So the patient could have 4000mg of acetaminophen per day. How many tablets is this? WANT = SUPPLY/HAVE 4000mg = 650 mg x 1tablet 650x = 4000 x = 4000 650 x = 6.1 tablets Answer = 6 tablets/day Logical? EXAMPLE FOR PARENTERAL MEDICATION MATH CALCULATIONS EXAMPLE #1: Ordered: heparin 1100 units / hour. Have available 25000 units in 500 ml. How many ml per hour would you run the IV? HAVE = WANT 25000 units = 1100 units 500 ml X ml after checking same units above line and same units below line, remove units for calculations 25000 = 1100 500 X 25000 X = (1100) x (500) 25000 X = 550,000 25000 X = 550,000 25000 25000 X = 22 ml Does this make logical sense? 7 Practice Math Calculations for Parenteral Medications Answer Key: Math Calculations for Parenteral Medications 8. Order: Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B12) 200mcg IM q month. Available: 100mcg/ml multi dose vial and 1000mcg/ml multi dose vial. Which one would you use? How many ml would you give? Use: 100mcg/ml vial because wasting less medication How much would you give? WANT = HAVE 200mcg = 100mcg x 1 ml (100)x x x = 200 = 200 100 = 2ml You would give 2 cc. Logical? 9. Order: Heparin 15,000 units SQ now. Available: 20,000 u/ml. How many ml would you give? ORDER = HAVE 15,000 u = 20,000 u x 1 ml 15,000 = 20,000x 15,000 20,000 = 20,000x 20,000 O.75 = x You would give 0.75cc. Logical? 10. Order: Penicillin G 30,000 u/kg q 12 hrs. Child weighs 8.8 lbs. How many units would you give? How many kg is the child? (2.2 lbs. per kg) HAVE/RATIO 2.2 lbs 1 kg = = 2.2x x = = x = WANT 8.8 lbs x 8.8 8.8 2.2 4kg Logical? 8 How many units would you give? HAVE 30,000u 1 kg = = = WANT x 4 kg x = (30000) (4) x = 120,000 u Logical? Available vial reads: Add diluent 9.6ml 100,000 u/ml 4.6ml 200,000 u/ml 1.6ml 500,000 u/ml How much diluent would you use? Since you need 120,000Units, select 4.6 ml to make 200,000 u/ml. (smaller injection and wasting less medication) How much (ml) medication would you give? HAVE = WANT 200,000 u = 120,000 u 1 ml x ml 200,000x = 120,000 200,000x = 120,000 200,000 200,000 x = 0.6cc Give 0.6 cc of medication Logical? 11. Order: Rocephin 1 gram IM now. Rocephin I gram vial reads: Add 2.7cc of sterile water or lidocaine to yield 3 cc of solution. How many ml of medication would you give? Yield 3cc of solution means 1 gram of Rocephin in 3cc. WANT = HAVE 1G = 1G x = 3 cc x = 3 cc Give 3cc Logical? 9 12. Order: Rocephin 1.5 grams IM now. Available: Rocephin 2 gram vial and the label reads: Add 2.7cc of sterile water to yield 3 cc of solution. How many cc would you give? HAVE = WANT 2 g = 1.5 g 3cc x 2x = (1.5)(3) 2x = 4.5 2x 2 x = = 4.5 2 2.25 Give 2.25 or 2.3 cc of Rocephin. Logical? 13. Order: Demerol 50 mg IM and Vistaril 25 mg IM now. Available: Vistaril 50mg/ml and Demerol 50mg/ml. You know: They can be mixed. The Demerol comes in a tubex syringe and the Vistaril is a multi dose vial. How many ml of Vistaril would you give? HAVE = WANT 50mg = 25mg 1 ml x 50x = 25 50x = 25 50 50 x = 0.5 Give 0.5 ml of Vistaril Logical? How many ml of Demerol will you give? HAVE = WANT 50mg = 50mg 1 ml x x = 1ml of Demerol Logical? How many ml of medication will you give? Demerol 1 ml Vistaril 0.5ml Total volume: 1.5 ml Is the volume a safe amount to give? Yes, for IM you can give 1-3 cc in all sites except the Deltoid 10 IV Calculations Terminology/Misc information: Drop factor – number of drops (gtts) per ml. Administration sets are labeled. Macro drop tubing – Large drops. Come in 10, 15, 20 gtts per 1 ml Microdrip tubing – Small drops. Comes in 60 gtts per 1 ml Standard IV bags come in 50cc, 100cc, 250cc, 500cc, 1000cc Rate – flow of IV over 1 hour. (Usually written ____ ml or cc/hr) Description of word problems: 1L D5W.45 NS with 1 amp MVI (multivitamin) infuse over 8 hours. Volume to infuse Description Infusion Rate/hr Total Infusion Time of fluid / 2 grams Rocephin in 100 cc NS @ 200 cc/hr medication Calculating Hourly Rate or Infusion Rate (ml/hr) Example: Scenario: You need to set the rate on an IV pump—always use cc/hr Order: Infuse D5W 1000 cc over 8 hours. Answer Volume Infusion time 1000cc 8 hours = 125cc/hr Practice – Find infusion rate when setting rate on an IV pump 1. Infuse 0.25% NS 500cc over 6 hours. 500ml = x 6hr 83.3ml/hr = x Logical? 2. Infuse D5W 1000cc over 12 hours. 1000cc = x 12hr 83.3cc/hr = x Logical? 11 Calculating Drip Rate or gtts/min using the shortcut chart 1. Figure out the infusion rate 2. Knowing the size of the administration set and the hourly rate, use the chart below to figure out the gtts/min. If drop factor is Then divide hourly fluid infusion amount by___ to get gtts/mins 10 gtts = 1 ml 6 15 gtts = 1 ml 4 20 gtts = 1 ml 3 60 gtts = 1 ml 1 (Notice that you can multiple the number in the first column by the number in the second column and always get 60!) Example: Scenario: You don’t have an IV pump and you need to figure out the drip rate. You have to count the number of gtts per minute to set the rate. Order: Infuse D5W 1000 cc over 8 hours. Administration set 20 gtts/ml. Answer 1. Figure out the infusion rate. Volume 1000cc Infusion time 8 hours = 125cc/hr 2. Now figure out the gtts/min. Use the chart above. 125cc/hr 3 = 41.6 = 42 gtts /min Practice – gtts per min when not using a pump 3. Infuse 0.45% NS 1000cc over 12 hours. Administration set 20 gtts/ml. Step one- find infusion rate: 1000cc =83 cc/hr 12hrs Step two – find the gtts/minute using: 83 cc/hr = 27.6 or 28 gtts/min 3 12 4. Infuse D5W 1000cc with 1 amp MVI over 8 hours. Administration set 15gtts/ml. Step one – find infusion rate: 1000cc = 125 cc/hr 8 hrs Step two – find the gtts/minute 125cc/hr =31.2 or 31 gtts/min 4 CALCULATING IV DRIP RATES 1. FORMULA: Volume to be infused X drop factor = gtts/min Time in minutes EXAMPLE #1: Ordered: 100 ml/hour; drop factor = 10 gtt / ml. At what rate do you set the IV for gravity flow to drip? (100 ml) x (10 drops/ml factor) 60 minutes = X (gtts/min) 100 x (10) 60 1000 60 or 100 6 17 gtt/min = X EXAMPLE #2: Ordered: Rocephin 50 ml/over 30 minutes; drop factor = 20 gtt/ml. At what drip rate should the IV be set for gravity flow? 50ml x 20 gtts/ml factor 30 min =X (50) x (20) = X 30 1000 = X 30 33.3 gtts/min = X 13 Calculating the Amount of Drug in a Specific Amount of Solution Example: Order: 0.45%NS 500cc with 80 U of Regular Insulin added. Give 8 U per hour. What is the infusion rate? Answer 500cc 80U 80x 80x x x = x 8U = (8)(500) = 4000 = 4000 80 = 50cc/hr Practice Calculating the Amount of Drug in a Specific Amount of Solution 5. 0.45% NS 500cc with 120 U Regular Insulin added. Give 10 U/hr. What is the infusion rate? 120U = 10U 500ml x 120x = 5000 120x 120 x = 5000 120 = 41.6 or 42ml/hr 6. Order: Heparin 600 U/hr. When the bag arrives from the Pharmacy, the label reads: D5W 1000ml with 20,000 U Heparin added. What is the infusion time? 20000U = 600U 1000ml x 20000x = (600)(1000) 20000x = 600,000 20000x 20000 x = = 600,000 20000 30cc/hr 14 7. You want to know how many units of Heparin a client is receiving. The label on the bag reads: D5W 500 ml mixed with 2,000 U of Heparin. The infusion rate is 15ml/hr. 500ml = 15ml 2000U x 500x 500x = (15)(2000) = 30,000 500x 500 = 30,000 500 x = 60U of Heparin per hour 15