Text Reference: Brown, LeMay, Bursten, and Murphy, The Central
advertisement

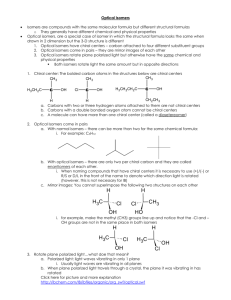
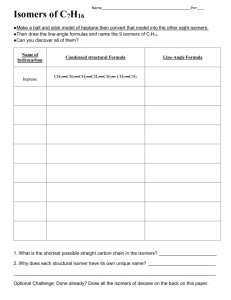
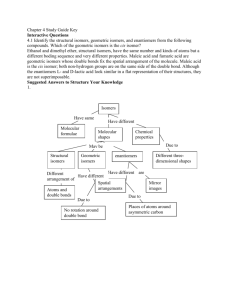
AP Chemistry Organic Chemistry Lab Text Reference: Brown, LeMay, Bursten, and Murphy, The Central Science Chapter 25 This molecular model-building lab is designed to help you develop a mental model that gives a three-dimensional image to two-dimensional Lewis structures that you draw on paper. It will also help you get a better picture of the different kinds of isomers that are possible with some molecular formulas. Prelab Assignment: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Distinguish between molecular and structural formulas. What is the meaning of the term isomer? Why should the properties of structural isomers differ? Distinguish between geometric and structural isomers? When is a carbon chiral? What hybridization does a chiral carbon have? What effect does being chiral have on the molecule? Procedure: 1. Sketch the Lewis structure, then build the model of the molecules. Indicate if they are 3-dimensional, 2-dimensional or 1-dimensional in shape. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. methane ethane ethene ethyne cyclopentene 1-propanol 2-propanol NH3 2. Name each of the following organic compounds, then draw the structural formulas. Show how many different isomers are possible with each one and name them. a. C6H12 & C6H14 b. C4H9OH & C5H11OH c. C2H4(OH)2 & C3H5(OH)3 d. C2H6O & C3H6O 3. Draw the Lewis structure, then build the model of the molecules. If they are chiral label which carbon is chiral. a. b. c. d. e. CHBrClF 2-butanol 2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid 2-(2-Propyl)-5-methyl-1-cyclohexanol 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (lactic acid) 4. Functional groups are a combination of atoms that behave as a unit and change the character of an alkane, alkene, or benzene ring. For the following compounds: (1) list 1 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry the functional group(s) and class of the compound, (2) use the model kit to determine the structure of the molecule, and (3) draw the structure/isomers of each compound. a. Formaldehyde b. Dimethyl amine c. Ethyl acetate d. Butanol (butyl alcohol), C4H10O e. Thymol, C10H14O f. Diethyl ether, C4H10O g. Diethyl amine, C4H11N h. Acetone, C3H6O i. Acetic Acid, C2H4O2 j. Ethanal 2 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry Teacher Notes: Have model kits for each student and extra parts for the more complicated molecules. Prelab Assignment: 1. Distinguish between molecular and structural formulas. Molecular formulas show the number and type of atoms that form a compound. The Structural formula shows how the atoms are bonded to one another. A molecular formula may have multiple structural formulas. 2. What is the meaning of the term isomer? Isomers have the same molecular formula, but different structural formulas. Two or more compounds that have the same composition, but a different arrangement of atoms. 3. Why should the properties of structural isomers differ? The properties will be different because the different arrangement of atoms gives the compounds different molecular interactions so they do not behave in the same manner. 4. Distinguish between geometric and structural isomers? Geometric isomers have the same molecular formula and the same groups bonded to one another, but differ in the spatial arrangement of these groups. Structural isomers have the same molecular formula, but not the same groups or spatial arrangement. 5. When is a carbon chiral? What hybridization does a chiral carbon have? What effect does being chiral have on the molecule? A chiral carbon is one where the molecule if not superimposable on their mirror image. A chiral carbon has four different groups attached. The hybridization of a chiral carbon must be sp3. The molecule is an optical isomer, it rotates polarized light. The chiral molecules may have different biological behaviors. Procedure: 1. Sketch the Lewis structure, then build the model of the molecules. Indicate if they are 3-dimensional, 2-dimensional or 1-dimensional in shape. a. Methane 3-Dimensional 3 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry b. Ethane 3-Dimensional c. Ethene 2-Dimensional d. Ethyne 1-Dimensional e. Cyclopentene (C5H8) 3-Dimensional f. 1-propanol 3-Dimensional 4 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry g. 2-propanol 3-Dimensional h. NH3 3-Dimensional 2. Name each of the following organic compounds, then draw the structural formulas. Show how many different isomers are possible with each one and name them. a. C6H12 & C6H14 C6H12 Isomers cyclohexane 5 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry C6H14 Isomers 6 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry b. C4H9OH & C5H11OH C4H9OH Isomers 1-butanol 2-butanol 2-methyl-1-propanol 2-methy-2-propanol C5H11OH Isomers 1-pentanol 7 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry 2-pentanol 3-pentanol 2-methyl-1-butanol 3-methyl-1-butanol 2-methyl-2-butanol 8 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry 3-methyl-2-butanol or 2-methyl-3-butanol 2,2-dimethyl-1-propanol c. C2H4(OH)2 & C3H5(OH)3 C2H4(OH)2 (ethylene glycol) C3H5(OH)3 (glycerin) d. C2H6O & C3H6O C2H6O Isomers ethanol 9 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry Dimethyl ether C3H6O Isomers 1. Draw the Lewis structure, then build the model of the molecules. If they are chiral label which carbon is chiral. a. CHBrClF b. 2-butanol 10 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry 2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic acid (Ibuprofen) c. d. 2-(2-Propyl)-5-methyl-1-cyclohexanol (menthol) e. 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (lactic acid) 2. Functional groups are a combination of atoms that behave as a unit and change the character of an alkane, alkene, or benzene ring. For the following compounds: (1) list the functional group(s) and class of the compound, (2) use the model kit to determine the structure of the molecule, and (3) draw the structure/isomers of each compound. a. Formaldehyde CH2O i. ii. Functional Groups – R-CHO Class of compound - aldehyde 11 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry iii. Structure/Isomers b. Dimethyl amine i. Functional Groups – amine, methyl ii. Class of compound - amine iii. Structure/Isomers c. Ethyl acetate i. Functional Groups – carbonyl, methyl, ethyl, ester ii. Class of compound - ester iii. Structure/Isomers d. Butanol (butyl alcohol), C4H10O i. Functional Groups - hydroxyl ii. Class of compound - alcohol iii. Structure/Isomers 1-butanol (isobutanol) 2methyl 1-butanol 2-butanol (isobutanol) (sec-butanol) 12 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry 2 methyl propan-2-ol (tertbuanol) e. Thymol, C10H14O i. Functional Groups – hydroxyl (phenol), methyl, propyl ii. Class of compound - phenol iii. Structure/Isomers f. Diethyl ether, C4H10O i. Functional Groups - ether ii. Class of compound - ether iii. Structure/Isomers g. Diethyl amine, C4H11N i. Functional Groups - amine ii. Class of compound - amine iii. Structure/Isomers h. Acetone, C3H6O i. Functional Groups - carbonyl ii. Class of compound - ketone iii. Structure/Isomers 13 Rev: 25 Oct 2010 AP Chemistry i. Acetic Acid, C2H4O2 i. Functional Groups - carboxyl ii. Class of compound – organic acid iii. Structure/Isomers j. Ethanal i. Functional Groups - carbonyl ii. Class of compound - ketone iii. Structure/Isomers 14 Rev: 25 Oct 2010