Crayfish dissection answers
advertisement

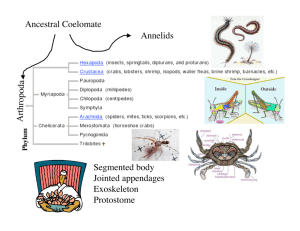
Name: ______________________________________________________________ Period:___________ EXTERNAL ANATOMY OF THE CRAYFISH PRE-LAB QUESTIONS: 1. Crayfish belong to the Kingdom _Animalia_, the Phylum _Arthropoda_ and the subphylum __Crustacea_. 2. List three characteristics that all arthropods share. a. _Exoskeleton_ b. ___Jointed Appendages___ c. __Segmented bodies___ d. Open circulatory system 3. Name two other animals in the same phylum as a crayfish. a. ___Shrimp, lobsters, barnacles, crabs____ b. _____________________ EXTERNAL ANATOMY: 4. Locate the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd MAXILLIPEDS. These appendages are used for manipulating food. (The 3rd maxilliped is the largest and topmost one, the 2nd is underneath, and the 1st is underneath the 2nd) 5. Locate the MANDIBLE (jaw) which lies underneath the maxillipeds. This structure should be hard and difficult to move. What difference do you notice between the crayfish and the human jaw? ___________________________________________________ 6. Locate the two large antennae and the smaller antennules that branch from the base. The ANTENNAE are sense organs (touch, taste, balance) 7. Locate the EYES, which extend from two stalks called pedicles. 8. The body of the crayfish consists of a cephalothorax (fused head and thorax). The cephalothorax is encased in an armor called a CARAPACE. 9. Remember that arthropods have a segmented body, bend the crayfish and notice it bend between the abdomen and the cephalothorax. 10. Locate the CHELIPEDS (the claws). Gently manipulate the cheliped to determine the direction in which the appendage can bend. How many joints are on a single cheliped? ____________ Name: ______________________________________________________________ Period:___________ 11. Cut the end of the cheliped off and use the forceps to find the connective tissue inside. Pulling on this tissue will make the claw open and close. TRY IT!! 12. Behind the cheliped are four pairs of WALKING LEGS. How many joints are on each leg? ____________ 13. Locate the SWIMMERETS (appendages attached to each segment of the abdomen). Are the swimmerets jointed? ____ How many pairs of swimmerets are there? ___ 14. The last segment of the abdomen (7th segment) is called the telson, and it is specialized for swimming. Locate the two UROPODS (on the outside of tail); these are two muscles that allow the crayfish to swim backwards. 15. Determine the gender of your crayfish by looking at the first pair of swimmerets. If these swimmerets are much larger and stiffer than the other swimmerets, than CONGRATULATIONS, you have a MALE. If the swimmerets are about the same size as the others, CONGRATULATIONS, you have a FEMALE. Gender:_____ Label the external structures on the crayfish below: WORD BANK: ABDOMEN MAXILLIPED SWIMMERETS UROPOD WALKING LEGS CEPHALOTHORAX EYES ANTENNAE CEPHALOTHORAX ABDOMEN EYES SWIMMERETS MAXILLEPEDS UROPOD CHELIPED ANTENNAE WALKING LEGS CHELIPED Name: ______________________________________________________________ Period:___________ INTERNAL ANATOMY OF THE CRAYFISH 1. Place the crayfish in the dissecting pan on its belly (dorsal side up – back is up). 2. Insert the point of the scissors under the top of the carapace at the back of the cephalothorax and cut up towards the eyes, stopping when you are between the eyes. 3. Cut across the carapace behind the eyes, and remove the two pieces of carapace. 4. Look at the feathery structures. These are the GILLS. The gills remove oxygen from the water and put it in the crayfish bloodstream, through the process of DIFFUSION. 5. Remove the gills and legs attached to the thorax. Carefully separate the dorsal layer of muscles in the thorax and look at the light colored HEART. 6. Remove the heart, and notice the two light colored masses on each side of the body. These are the DIGESTIVE GLANDS. 7. Between the digestive glands are the reproductive organs (usually white in color). If you have a female, you may notice a large dark mass of eggs. 8. Locate the INTESTINE by taking your scissors and cutting the shell of the abdomen back toward the telson (tail). Spread the shell, and the intestine will be found as a tube on the top side of the muscles of the abdomen. Follow the intestine down to the end of the crayfish (towards the telson and uropods) and you will find the ANUS. 9. Trace the intestine forward to the point where it joins a large thin walled organ, the STOMACH. This should be in the front of the cephalothorax. 10. Cut out the stomach and open it up with your scissors, you will find the GASTRIC MILL. 3 ‘teeth’ that aid in digesting the food. 11. Once the stomach is removed, you should be able to see the GREEN GLANDS (kidneys) located in the head of the crayfish. 12. If you cut between the eyes, you will notice a small mass of white tissue, the BRAIN. Name: ______________________________________________________________ Period:___________ LABEL THE INTERNAL STRUCTURES OF THE CRAYFISH WORD BANK: HEART BRAIN GREEN GLANDS INTESTINE STOMACH ANUS REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS 6. STOMACH 5. BRAIN 1. HEART 2. INTESTINE 7. REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS 4. GREEN GLANDS 3. ANUS Name: ______________________________________________________________ Period:___________ Crayfish Anatomy & Function “How do crayfish move/protect themselves?” Carapace ________ A. Organs which help crayfish visualize food and escape predators. Walking legs ________ B. Large bumpy covering over the thorax used for protection. Abdomen ________ C. Help the crayfish touch and taste. Swimmerets ________ D. Broad flat plates which form a paddle to move crayfish backward quickly . Eye ________ E. Appendages with small pinchers which allow crayfish to walk/move around. Antennae ________ G. The muscular posterior end which propels the crayfish backward. Uropod ________ H. Small appendages on abdomen which aid in the reproduction & development of crayfish “How do crayfish eat/digest?” Cheliped ________ A. Sturdy jaws around the mouth used for chewing Mandible ________ B. Second set of internal ‘teeth’ used to grind food in stomach Mouth ________ C. Large claws used to catch and break apart food and fight other crayfish. Stomach ________ D. Pumps body fluid around inside of crayfish to circulate oxygen and nutrients. Gastric Mill ________ E. Large organ which stores and digests food. Gills ________ F. Opening which allows crayfish to ingest food. Heart ________ G. Organ which helps crayfish breathe. “How do crayfish excrete their waste?” Green gland ________ A. Long tube which absorbs nutrients from food passed from stomach. Intestine ________ B. Small opening used to excrete solid waste. C. Organ which produces bile (digestion) and filters out waste from body fluids. D. Functions as a crayfish bladder/kidney used to excrete liquid waste. Name: ______________________________________________________________ Period:___________ Anus ________ Liver ________