Week 2
advertisement
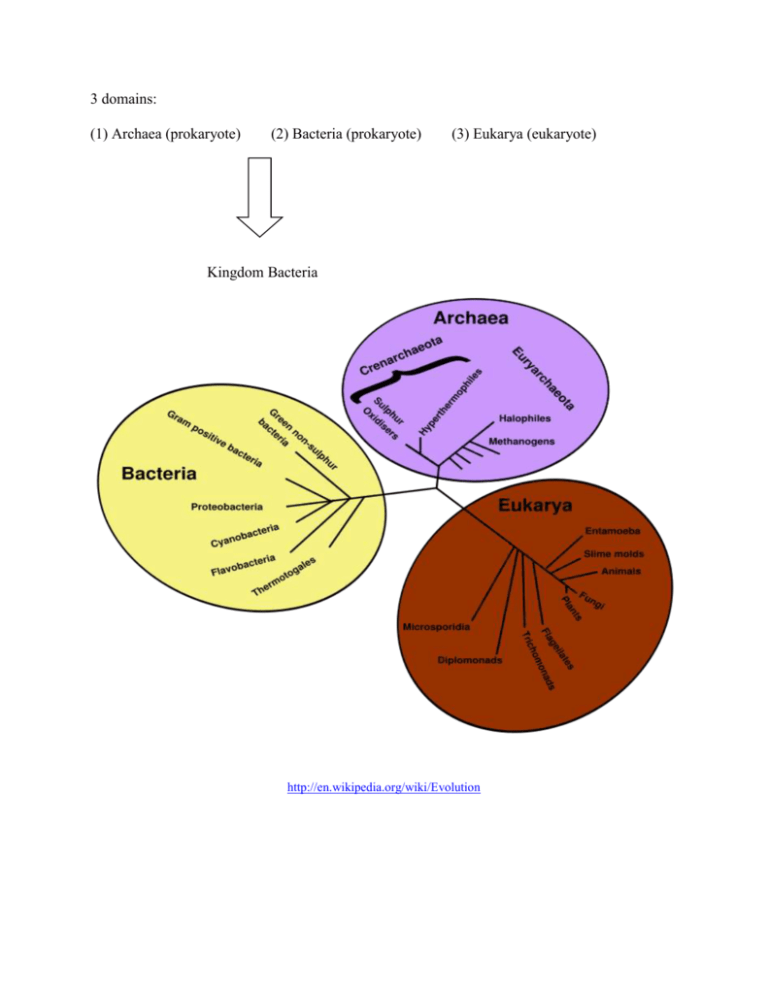
3 domains: (1) Archaea (prokaryote) (2) Bacteria (prokaryote) (3) Eukarya (eukaryote) Kingdom Bacteria http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evolution Domain Eukarya Kingdom Protista Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Plantae Archaea: - oldest form of life on Earth (date back to ~ 3.8 billion years ago) - live in extreme environments (salt, heat, alkaline/acid) extremophiles - unusual cell walls and distinct cell membranes Bacteria: - heterotrophic (get food from others) decomposers (feed on dead organic matter) - some are autotrophic (make their own food) - reproduce asexually (binary fission) or sexually (conjugation) - 3 shapes: (1) bacillus, (2) coccus and (3) spirillum Kingdom Animalia http://www.infections.bayer.com/images/diseases/bacteria1.gif http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit1/shape/images/coccus.gif and http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.mansfield.ohio-state.edu/~sabedon/003cocci.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.mansfield.ohiostate.edu/~sabedon/biol2010.htm&h=384&w=576&sz=4&hl=en&start=1&tbnid=2_9nGGpTGeXMUM:&tbnh=89&tbnw=134&prev=/images% 3Fq%3Darrangements%2Bof%2Bbacillus%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Den%26lr%3D Kingdom Protista: (1) Algae: - photosynthetic (autotrophs) - pigmented (chlorophylls, caretenoids and phycobulins) - unicellular, filamentous or colonial - Phlyum Chlorophyta, Phaeophyta, Rhodophyta,Chrysophyta, Pyrrhophyta & Euglenophyta Phylum Chlorophyta: (1) Chlamydomonas - unicellular - motile (flagella) - stigma – absorbs light - pyrenoid – production and storage of starch - asexual and sexual reproduction (syngamy) http://www.jochemnet.de/fiu/bot4404/Chl_chlamydomonas_draw.gif Chlamydomonas Life Cycle http://sps.k12.ar.us/massengale/images/chlamydomonasrepro.jpg (2) Spirogyra and Cladophora - filamentous - found in freshwater - sexual reproduction = conjugation (Spirogyra) http://www.lima.ohio-state.edu/academics/biology/images/spiro1.jpg - alternation of generation (Cladophora) http://www.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/image/47850/Cladophora.gif (3) Volvox - colonial (multicellular) - spherical in shape - 2 flagella protrude from each cell to spin the colony through the water - cells within the colony are functionally different - sexual reproduction (oogamy – one gamete is small and motile while the other is large and nonmotile) - daughter cells are initially held within the parent colony http://www.world-science.net/images/volvox.JPG (4) Volvocine Line (unicellular isogamous colonial isogamous colonial oogamous) http://www.unbf.ca/vip/photos/Cris's%20color%20volvocales_files/image002.jpg Phylum Phaeophyta: - some of the largest algae - chlorophylls a and c - brown color due to fucoxanthin - marine and cool waters - store energy as laminarin - important as a food source (Laminaria) - alginic acid used as an emulsifier (1) Fucus - attached to rocks by a holdfast - sexual reproduction - no haploid stage like most protests http://www.euita.upv.es/varios/biologia/images/Figuras_tema1/fucus.jpg M = male conceptacle (contains antheridia F= female conceptacle (contains oogonia that produce sperm) that produce eggs) http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.lima.ohiostate.edu/academics/biology/images/spiro1.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.lima. ohiostate.edu/academics/biology/biodiv/webplant.htm&h=461&w=551&sz=80&hl=en&start=99&tbnid=cwRF2Ik_3aNhQM:&tbnh=111&t bnw=133&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dspirogyra%26start%3D80%26ndsp%3D20%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Den%26lr%3D%26sa%3DN Phylum Rhodophyta - red algae - chlorophylls a and d - red color due to red phycobulins (phycoerythrin) - marine species - attached or free floating - filamentous or fleshy http://ind.ntou.edu.tw/~b0232/porphyra.jpg Phylum Chrysophyta - golden algae - diatoms - free swimming - unicellular - chlorophylls a and c - get their yellow-brown color from carotenes and xanthophylls - autotrophs (primary link in food chain) - asexual or sexual reproduction - silica cell wall – accumulates as diatomaceous earth - paint additive for reflectivity - polish for silver and toothpaste - insulation (furnaces) http://www.zeiss.com/C12567BE00472A5C/GraphikTitelIntern/Discovery_Applications02/$File/Diatoms.jpg Phylum Pyrrhophyta - dinoflagellates - unicellular - 2 dissimilar flagella - marine or freshwater - cause red tides (Ptychodiscus bruvis) which kill many fish (toxins and decreased oxygen) - autotrophs (primary producers in food chain) - some are parasitic - some live symbiotically with corals http://serc.carleton.edu/images/microbelife/topics/red_tide.jpg Phylum Euglenophyta - euglenoids - unicelluar - freshwater - chlorophylls a and b - protein cell walls = pellicle (flexible for movement) - eyespot (stigma) for detection of light - autotrophic or heterotrophic (phagocytosis) - asexual reproduction (longitudinal fission) but no sexual reproduction - measure of pollution (increased numbers, increased pollution like Nitrogen) http://www.personal.psu.edu/dcw1/graphics/euglena.gif http://scienceblogs.com/clock/upload/2006/07/Euglena.JPG Evolution of Body Form (unbranched filamentous branched filamentous branched parenchymous) http://www.mtsu.edu/~rsb2b/Lab9Protists_files/frame.htm http://kentsimmons.uwinnipeg.ca/2152/Stigeoclonium1.jpg http://www.californiabiota.com/cabiota/ulva_lobata.jpg





