Optical Comms 2008 (Winter)
advertisement

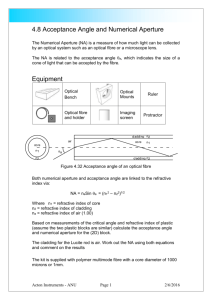
(2) W086/085/904 1 (a) Explain with the aid of a diagram what is meant by the terms acceptance angle and numerical aperture for an optical fibre. Hence derive an expression for the numerical aperture of a step index fibre with a core refractive index of n1 and a cladding refractive index of n2. [16 Marks] (b) Based on the fact that the worst case pulse spreading caused by modal dispersion only, 2 LNA can be described by t and based on the result in 1(a) discuss the trade-off 2cn1 between numerical aperture and fibre bandwidth and comment on the impact of this trade-off in an actual optical fibre system. [10 Marks] (c) Describe an experiment to measure the numerical apertures of a range of different core sized fibres using a HeNe laser. (i) How does the fibre core diameter influence the NA? (ii) Comment on the different factors influencing any inaccuracies in your results. [14 Marks] (d) (i) Describe what type of fibre cable structures (loose tube or tight jacket) would usually be used in a building cabling installation stating a reason why. (ii) An outdoor fibre cable is to be used to connect two buildings on a campus and is to be directly buried, what types of protection would you expect the cable to have? [10 Marks] (3) W086/085/904 2 (a) What is meant by the term “refractive index profile” for an optical fibre? Sketch each of the four refractive index profiles below and in each case state concisely a typical application were such a profile would be encountered: (i) Step index; (ii) Graded index; (iii) Depressed cladding; (iv) Triangular profile. [10 Marks] (b) Distinguish between fibre core misalignment and fibre parameter mismatch as potential loss mechanisms in a fibre-to-fibre joint. In each case state concisely two examples of each loss mechanism to illustrate your answer. Hence for the fibre-to-fibre jointing techniques listed below comment briefly on the three most likely causes of significant loss. (i) Demountable connectors involving an air-gap; (ii) A fusion splice using 3-axis fibre positioning; (iii) A mechanical splice. [12 Marks] (c) A multimode optical fibre is to be fusion spliced. From the fibre specifications the nominal core diameter is 50 µm 0.5 µm and the numerical aperture is 0.24. Assuming that no fibre misalignment occurs what is the worst case splice loss in dB? If lateral misalignment does occur (in addition to the core diameter mismatch) what is the tolerable misalignment in µm for a splice if the worst case loss is to be less than 0.25 dB? State all assumptions clearly. The loss due to lateral misalignment is given the approximate formula: 2d 10 Log 1 a [14 Marks] W086/085/904 (4) (d) The table below gives approximate bandwidths for various combinations of optical fibre and optical source. (i) Discuss and compare the factors that influence the bandwidth for the combinations marked “a” and “b”. (ii) “The symbol * indicates an unlikely choice” Discuss why this statement is true. b a [14 Marks] W086/085/904 (5) 3 (a) Explain clearly the terms below when used in reference to a coupler. (i) split ratio (ii) insertion loss (iii) excess loss (iv) crosstalk or directivity [8 Marks] (b) A four port multimode FBT coupler under test has 60 µW of optical power launched into port 1. The measured optical powers at the remaining ports are: Port 2: 0.005 µW Port 3: 21.8 µW Port 4: 32.7 µW Determine the excess loss, insertion losses, crosstalk and split ratio for this coupler. [12 Marks] (c) The theoretical strength of fibre is never achieved in real fibres. Explain briefly why this is so. Hence with the aid of an appropriate sketch explain how proof-testing is carried out after fibre manufacture and how it improves long-term fibre reliability. [10 Marks] (d) A fibre is proof tested for 1 second to a stress of 0.45 GPa. Show that with a maximum in-service stress of 0.14 GPa the predicted lifetime is in excess of 47.4 years, assuming the fatigue susceptibility parameter for the fibre is known to be 18.1. State any assumptions made clearly. The time-to-failure tf in a fibre is normally assumed to be given by: n t = A s f [10 Marks] (e) Explain how contact with moisture and elevated temperatures reduce the lifetime of an optical fibre. [10 Marks]