Estimating the size of the treatment effect
advertisement

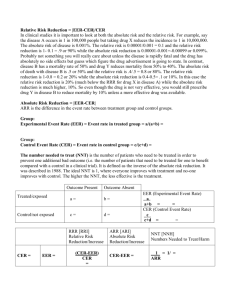
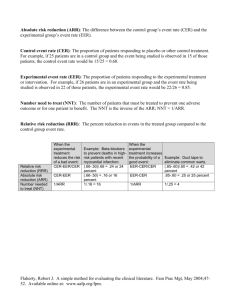
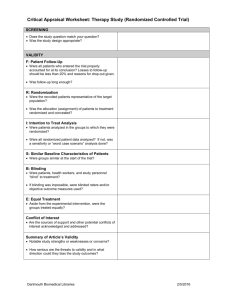
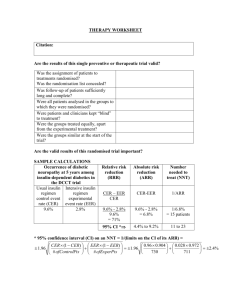
Estimating the size of the treatment effect Outcome Outcome risk of does not occurs outcome occur a b Y = a/(a + b) EER (experimental event rate) Control Unexposed c (X) d X = c/(c + d) CER (control event rate) Treatment Exposed (Y) Clinical Significance calculator Relative Risk (RR) is the risk of the outcome in the exposed (treatment) group divided by the risk of the outcome in the unexposed (control) group. RR = Y / X Relative Risk Reduction (RRR) is the percent reduction in risk in the treated group compared to the control group. RRR = [ ( X - Y ) / X ] x 100% Absolute Risk Reduction (AAR) is the difference in risk between the control group and the treatment group. AAR = X - Y Number Needed to Treat (NNT) is the number of patients that must be treated over a given period of time to prevent one adverse outcome. NNT = 1/ARR = 1 / ( X - Y ) "An NNT of 15 means that 15 patients must be treated over a given period of time to prevent one adverse outcome." Reference: Sackett, D. Evidence-Based Medicine: How to Practice and Teach EBM. 2nd ed. (CD-ROM) Churchill Livingstone, 2000. ACP Journal Club 1994 Jul-Aug:A10-A12.