sample SA
advertisement
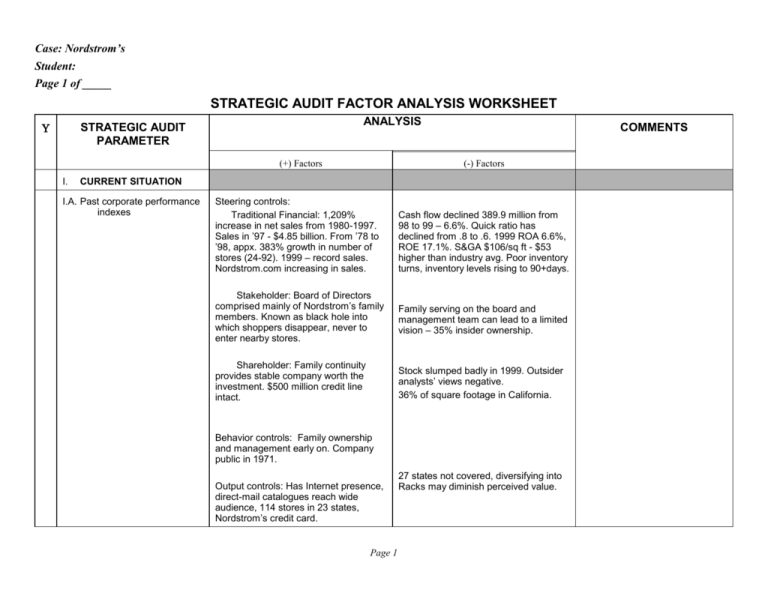
Case: Nordstrom’s Student: Page 1 of _____ STRATEGIC AUDIT FACTOR ANALYSIS WORKSHEET ANALYSIS STRATEGIC AUDIT PARAMETER (+) Factors I. COMMENTS (-) Factors CURRENT SITUATION I.A. Past corporate performance indexes Steering controls: Traditional Financial: 1,209% increase in net sales from 1980-1997. Sales in ’97 - $4.85 billion. From ’78 to ’98, appx. 383% growth in number of stores (24-92). 1999 – record sales. Nordstrom.com increasing in sales. Cash flow declined 389.9 million from 98 to 99 – 6.6%. Quick ratio has declined from .8 to .6. 1999 ROA 6.6%, ROE 17.1%. S&GA $106/sq ft - $53 higher than industry avg. Poor inventory turns, inventory levels rising to 90+days. Stakeholder: Board of Directors comprised mainly of Nordstrom’s family members. Known as black hole into which shoppers disappear, never to enter nearby stores. Family serving on the board and management team can lead to a limited vision – 35% insider ownership. Shareholder: Family continuity provides stable company worth the investment. $500 million credit line intact. Stock slumped badly in 1999. Outsider analysts’ views negative. 36% of square footage in California. Behavior controls: Family ownership and management early on. Company public in 1971. Output controls: Has Internet presence, direct-mail catalogues reach wide audience, 114 stores in 23 states, Nordstrom’s credit card. Page 1 27 states not covered, diversifying into Racks may diminish perceived value. I.B. Strategic Posture: Mission Objectives What, when, & quantified Strategies 2 philosophies: focus on customer – outstanding service, selection, quality, and value; select managers from among employees with sales floor experience. No real mission stated – could cause confusion and makes strategic planning very difficult. The what and when and how are answered. Steady growth increases stakeholder security. What does the top quartile mean in sales figures or in increases – does it pertain to stores – the amount of square footage – what? Total shareholder return sounds nice, and is the bottom line – but what does it mean for the company? Good marketing slogan – will they? Aggressive store expansion, new store layout. New buying structure will reduce costs. Emphasize merchandise and service tailored to appeal to affluent and fashion-conscious shoppers. Do not lose middle-class customers. Offered unparalleled attention to customers, guaranteed service, and wide & deep line of merchandise. Merchandise selection, local tastes, and customer preferences shaped what stores looked like inside. Focusing on goals provides superior service to customers. Chance of alienating existing customer base. Costs will be extremely high. Page 2 Time to implement this strategy not given. Chance of losing interest of middleclass shoppers – could take offense. Inventory costs and labor hours high, store frontage and square area extremely large. Some continuity from store to store is lost. Focus on attracting 25-30 year olds Move into top quartile Sustain growth of 3 to 5 new stores/yr, of 150k to 250k sq/ft. 15 new Rack stores by 2001. Distribution centers for new areas to Nordstrom’s. Reinvent yourself Shift from regional to national approach #1 in service in country. Goal orientation of employees. Carry a good percentage (30) of specialized inventory of r each store or region. Policies Control of marketing message allows them to tailor it according to desire. In-house advertising and marketing cut costs. Return policy improves customer satisfaction. Each Bus. Unit developed own planning strategy (buyers when applicable). Operational Mngmnt. Store Mngr duty. Idea generation and operat’l dec. making encouraged, expected and supported wherever employee had approp. Info. Units and indiv. Goaldriven and rewarded for achievements. Employee heroics provide behavior standard. Costs are high for large campaign. Also reduces the amount of people, and customer base, reached. Do they possess enough expertise to pull off a major campaign? RP also adds costs, as does the personalized services offered to the customers – is it worth it? Could cause conflict with overall strategies or objectives. Personal agendas often cause internal conflict in stores. Who determines what appropriate info is? Motivation is on ends not means. Stress is potential problem. Entertain customer, special services, return policy. No promotions – 3 major sales events, in-store advertising, inhouse marketing. Goal oriented - attention to customer is focus. S.W.O.T. Analysis Begins II. STRATEGIC MANAGERS II.A. Board of Directors Chairman has strategic management responsibility – sets strategic direction and major expansion decisions. Co-pres. Oversee nine business operating units. Sense of continuity with family presence in company management. Two women on board shows desire to diversify Could become stagnant. All co-pres. in mid-thirties and white, chairman in mid-forties, ex. Committee all young old men. All of top management appears to be Caucasian – no diversity here. Less industry experience here. COB: 45yr old J. Whitacre 6 co-presidents – 4th gen Nordstroms 3 previous co-chairmen now serve as executive committee on board. Chairman – 66 (Male Nordstrom), President – 39 (MN), President of Nordstrom.com – 37(FN), Executive VP – 46 (MN In-Law), Exe. VP. – 48 (F). II.B. Top Management 43% of officers of vice-pres. And higher and 61% of store mngrs were women. Five of nine bus unit mngrs women, by 1997, and 22% managers were minorities. Inverted pyramid stresses sales, and department managers, while top management rests at the bottom, making strategic decisions. Fast becoming a female dominated orgz – this also holds threats of becoming stagnant, with only a feminine point of view (70% of workforce). General managers oversee nine business operating units, divisional merch. Mangrs, rgnl mngrs, corp. staff offcrs NW, CA, E Coast, MW, and Rack Clearance and Off-Price stores. Direct Sales, Faconnable Boutiques, Nordstrom Prod. Group, Nord Nat Credit Bank. Middle Management Page 3 . III. EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT: [Optional External Factor Analysis Summary, or EFAS] Page 4 III.A Societal Environment Socio-Cultural Political-Legal Economic Technology Baby Boomers cohort trends to spend. Value conscious shoppers see Nordstrom’s as providing higher value in services and return policies. NAFTA provides some new opportunities. Employ a majority of women in sales force. Income levels are increasing – Nordstrom’s could expand customer base. Internet presence is critical for growth into new regions and improves the customer information and knowledge for both Nordstrom’s and the consumer. Dual income families expand potential customer base. Higher standard of living equates to more customers. Page 5 Minority groups expanding in numbers – Nordstrom’s does not target them. Casual dress has become more prevalent, which leads to projected apparel sales decreases. Without advertising or promotions, Nordstrom’s could easily lose market share to competitors. Increased stressors on families – mean less time to shop. AIDS reaching epidemic proportions, people dying off, slowly. Employment laws address the concerns of discrimination at Nordstrom’s Diversity, as far as minorities, needs to be focused upon. Must stay on top of style changes and trends in apparel industry. Trade Agreements – NAFTA, etc., Employment laws, American w/ Disabilities Acts, Diversity. Average number of children decreasing. Poverty levels increasing Average income of devlpd and undevelpd nations increasing. World population growing to reach 7.32b by 2010. Number of nations increasing. Trade increasing $5tr to $16.6tr. World economy growing $26tr to $48tr, by 2010. Average life expectancy rising. AIDS cases increasing. Telecommunications computers and related technology increasing – Internet. Automobile production increasing rapidly in dvlpng nations. Entertainment industry burgeoning. Air travel, credit card transactions, McDonald’s restaurants (fast food industry), communications satellites,, golf courses, casinos, Int. value of US dollar all will increase tremendously in the next ten years, as consumer inflation will decline. III.B. Task/Industry Environment Shareholders Suppliers Customers Competitors Governments Trade Associations Labor Unions Committees Special Interest Groups Bricks and clicks – going to enhance customer value (perceived), and expand customer base. Overhauling their purchasing strategies should lead to reduced costs. Customers are fairly loyal to Nordstrom’s. Outgrew major competitors with aggressive growth. Well known for excellent sales staff. Federated, Nieman Marcus, and May stores all have increased the competitive advantage in different areas. Could alienate existing suppliers. Nordstrom’s needs an advertising or promotional effort to stem the tide of lower market share. Potential customers may be blocked by a mental picture of stodginess. Diversity still seen as a problem, many lawsuits and affirmative actions taken against Nordstrom’s. NAFTA, other Trade agreements. Too many catalogues and stores, along with discount stores. Cost management, and consolidation INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT IV.A. Corporate Structure Good decision to form divisions – may lead to higher profitability. Somewhat decentralized by operational decisions being passed to General Managers of stores. Too many family members controlling and making a majority of decisions. Store managers make many of the important decisions regarding their stores. Inverted pyramid: Store mngmnt level, the mid-level – 9 business unit managers, and the executive level. IV.B. Corporate Culture Customer focus, do anything to retain customer. Extravagant stores. Promotions come from within and are based on outstanding sales and customer relations(rewards). Continuity with customer contact adds to Nordstrom’s mystique. Goal driven. Sometimes expectations can be set too high, leading to employee failure, in both customer service and sales goals. Goal orientation leads to high stress levels. Family controlled. IV.C. Corporate Resources Employs multiple channels to reach customer. Spends 2% less than competitors on advtsg. Great reputation for quality and service. Is Nordstrom’s capable of affording to reinvent themselves? Does their message reach enough potential customers in minority ranks and twoincome families? Main stores, Rack, Internet, email, and catalogue. Reinvent yourself MC1 Marketing Page 6 MC2 Finance Ratios and indicators suggest Nordstrom’s is stable. Not much debt utilization to fund growth. Share value improved from 88 ($7.86) to 97 ($19.34). Return on Equity and Return on Assets have both decreased steadily, over the years, but appear to be on the upswing again. Low returns, must realize some cost-cutting. Stock price low, currently. MC3 Research and Development Based on direct customer feedback – relative to their desires not trends. Ebusiness would provide better returns than interactive Nordstrom’s not quick enough in responding to recent trends through. TV. MC4 Operations (Manufacturing services) Very large inventory. Strong distribution system serves stores in geographical areas. Stores strategically located in affluent communities. Large base of suppliers (12k to 15k). Breakdown of 70% shared styles for all stores and 30% unique to each region assists in maintaining image. Cost is extremely high to maintain and labor intensive. Too much concentration in California. Human Resources Good rewards for attaining goals (compensation). Not a large amount of turnover, surprisingly. Strong values dictate younger sales force with degree. Sales mngr hires. Promotions happen from w/in the sales force. 31% of workforce is minority. High pressure sales lead to gigantic stress. 70% of sales force are women – reverse discrimination. Missed sales quotas, 3 months in a row leads to dismissal. MC6 Information Systems Information systems lead to improved inventory ordering and vendor services and relations. Web site promotes product lines and increases orders. Need for improved intranet system for internal transfer of data. An employee data base for customer information might also prove invaluable. (+) Factors (-) Factors Page 7 ROE .13 .10 .12 .15 .12 Some continuity lost from store to store. MC5 V. ANALYSIS OF STRATEGIC FACTORS (Optional: Strategic Factor Analysis Summary, or SFAS) 98 97 96 95 94 ROA .065 .055 .060 .085 .064 HANDBOOK: Use good judgement in all situations. . V.A S.W.O.T Key Internal and External Strategic Factors. STRENGTHS: WEAKNESSES: Public image has attained most goals – excellent reputation as a Herculean customer service retailer. Past financial troubles have some predicting a return to form. No International presence, minorities not targeted for apparel. One of the tops in fashion retailers. Lawsuits tarnished public image. Distribution channels Family stranglehold on company. Financial ratios on upswing Decentralized managerial approach leads to better decisions. Huge inventory lowers style change responsiveness and escalate costs. Too much California dependency. Sales per square foot solid. Community service projects helped to regain some of the public image. Lack of current effective strategic direction. Alienating current customer base. OPPORTUNITIES: VIII. Customer service expectations increase each year – IX. International and regional markets. X. Price-sensitive shoppers’ needs. XI. Global Economy: NAFTA, Asian Pacific Rim, European Economic Community, South American Union, etc., facilitate trade and therefor sales. Page 8 THREATS: Competition heightened among the main three rivals. Increased alienation of customer base through reinventing yourself – “Why am I not good enough?” Unions may cause problems Afro and ethnicity discrimination based lawsuits may continue. Markets are maturing in the US and elsewhere. Recession in California. Causal Fridays may cause decreased sales. Outlet stores and lower priced retailers. V.B. Review of Mission and Objectives STRENGTHS: WEAKNESSES: New inventory and purchasing systems implemented. Not targeting burgeoning minorities. Capturing more of the female market share, through the targeting of a younger age working woman, allows complimentary clothing designs. Does not specify how top quartile will be met. Growth is emphasized when financial situation does not reflect capacity. Cstmr service expectations exceeded. Quantifiable THREATS: This is a race between Nordstrom’s and its competitors to locate and occupy the most affluent neighborhoods, within the major cities across the nation. Competitors are in an average of ten States more than Nordstrom’s. Union, labor, minority and other concerns must be overcome. Becoming too female dominated in the workforce – 70% is a form of reverse discrimination. OPPORTUNITIES: Expand shoe stores Internationally. Expand Internationally. Regional expansion of main stores and shoe stores and Rack stores are possible, providing enough revenue can be generated. Minorities, especially Hispanics, Asians, and African-Americans provide a huge potential market. S.W.O.T. Analysis Ends VI. STRATEGIC ALTERNATIVES & RECOMMENDED STRATEGY VI.A. Strategic Alternatives ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES Page 9 Alt.1 Growth Strategy: Related Diversification Explore all Cities within the US, with major markets likely to support a store, and which type: a Racks or Nordstrom’s. Already have two different stores, covering the extremes of high-end and low-end retailing. Growing larger will increase debts and possible problems with stakeholders. Push with both into appropriate markets, pre-anticipating the competition’s moves. Will increase the Nordstrom image, and reach a larger customer base. Will mandate a task force or committee be formed to examine issues concerning minorities; clothing, shoes, and store layout. Utilizes Nordstrom’s perceived customer service excellence advantage. Expansion may diminish the Nordstrom mystique. Expansion can also threaten the normal transfer of culture to new Nordstrom’s. Low risk. Low returns. Less resources committed. Less cost and expenses. New investigative committees must be formed. Debt not increased dramatically. Potential to lose market share to competitors is great. Might lose competitive growth advantage. Might lose whole target market segments to competition – ie: FUBU. Stakeholders’ and Shareholders’ relations may become strained. Net assets will be reduced. Public image may be negatively affected – ‘wishy-washy.’ Reinvent yourself campaign may be construed as revert to your old self. Alt.2 Stability Strategy: Pause/Proceed with Caution Must gather all the facts concerning International markets and Minority markets penetration. Alt.3 Retrenchment Strategy: Divestment Sell off Racks stores and anything else that gets away from original culture of affluence. Overhead greatly reduced. Less inventory. Consolidation will hone focus and reinvent themselves simultaneously. Will allow focus on Minority target markets and International pursuits. Page 10 VI.B. Recommended Strategy Growth Strategy: Related Diversification coupled with Stability Strategy of Pause/Proceed with Caution and Retrenchment Strategy of Divestment of all things not affluent. VII. IMPLEMENTATION Strong footholds in Affluent Apparel and Shoes will require minimal attention and energies to maintain. Requires long-term commitment to task forces and committees dedicated to research. Diversification into untapped minority markets will lead to exponentially increasing sales and growing markets. Requires more R&D funds be diverted to researching potential markets. Examining minority markets will lead to a better understanding of them – more sales, and an enhanced public image. Public may see Nordstrom’s as elitist. Customer service will be compromised due to changes, unavailable merchandise, etc. Marketing should be divided into national and International branches. Web site will have to be expanded to contain an International section which will require translation software and International operators. Ethnic focus will require new thinking and planning for store layout and design. Less inventory initially, will lead to more inventory, but of many standard items. Will provide more focus for Nordstrom’s in-house marketing – affluent customer base, regardless of ethnicity. Can focus on expanding revenue through catalogues and the Internet versus building. Must restructure the existing business units to accommodate an International branch. Fully integrated Intranets will allow better information transferal between units and Management. Page 11 XII. E VALUATION AND CONTROL (ASSESSMENT) Sales and revenue. Marketing must be evaluated through measures beyond sales and generated revenue – surveys, etc. R&D, task forces, and committees must comprehend what it takes to sell to affluent peoples of all races. Intranets must be expanded to include new focus and exclude divested ones. New management team must be hired for International unit(s). Monitor major competitors. Transportation costs will increase and warehousing overseas. Marketing costs will increase. Manufacturing costs will increase and inventory. Distribution Channel Management is critical for smooth integration. Cultural and national differences must be accounted for. Payroll will increase. NOTES: Page 12