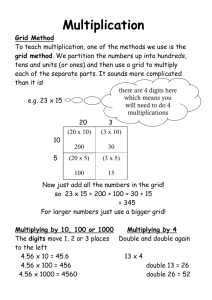
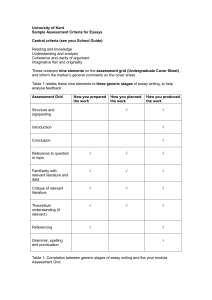
Book of Abstracts
advertisement

The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Table of Contents A Power System Operation and Management···································1 B Power System Analysis,Protection and Control·····························34 C High Voltage Transmission Technology······································79 D New Energy Power Generation and Microgrid Technology···············94 E Smart Grid Technology························································120 F Energy Internet and New Emerging Technologies·························130 I November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Associate Editor Bin li Bin Wang Can Huang Canbing Li Chongqing Kang Chuangxin Guo Chunming Tu Ci Tang Delin Wang Gang Li Gangui Yan Haijing Yang Haoyong Chen Hongjie Jia Hongming Yang Houhe Chen Hualiang Fang Huiming Xu Jianfei Ji Jianhua Zhang Jie Yu Jinghan He Jinyu Wen Jun Liang Junhui Zhao Kaigui Xie Li Ren Lina Wang Linquan Bai Mingchao Xia Qinran Hu Renjun Zhou Richeng Luo Rui Ma Sheng Lin Tianshu Bi Tianyuan Tan Wei Gu Wei Yao Wen Wang Tianjin University Tsinghua University The University of Tennessee Hunan University Tsinghua University Zhejiang University Hunan University Changsha University of Science and Technology Southwest Jiaotong University Jilin University North China Electric Power University State Grid Henan Electric Power Research Institute South China University of Technology Tianjin University Changsha University of Science and Technology Northeast Dianli University Wuhan University State Grid Information and Telecommunication Branch State Grid Corporation of China North China Electric Power University Beijing Southeast University Beijing Jiaotong University Huazhong University of Science and Technology Cardiff University University of New Haven Chongqing University Huazhong University of Science and Technology Beihang University University of Tennessee Beijing Jiaotong University The University of Tennessee Knoxville Changsha University of Science and Technology Changsha University of Science and Technology Changsha University of Science and Technology Southwest Jiaotong University North China Electric Power University Wuhan University Southeast University Huazhong University of Science and Technology Changsha University of Science and Technology The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Wenpeng Luan Xiangjun Zeng Xiangning Lin Xianyong Xu Xin Fang Xin Tang Yandong Chen Yao Xu Yigang He Yuanyuan Wang Yusheng Zhou Zaibin Jiao Zewen Li Zhikang Shuai Zhiliang Zhang Zhiqian Bo Zifa Liu China Electric Power Research Institute Changsha University of Science and Technology Huazhong University of Science and Technology Hunan Electric Power Research Institute University of Tennessee at Knoxville Changsha University of Science and Technology Hunan University Lamar University Hefei University of Technology Changsha University of Science and Technology Changsha University of Science and Technology Xi'an Jiaotong University Changsha University of Science and Technology Hunan University Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics XUJI Group of SGCC North China Electric Power University November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China II The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) method can estimate and compare the sensitivity of commonly-used primary equipments in power system directly, satisfying the needs for maintenance strategy better. A: Power System Operation and Management TuA02.2 TuA01.1 Analysis of the Impact of Voltage on the Loss Allocation Method Based on Circuit Theory pp. 12-16 Analysis Correlation Modeling of the O il Flow of Transformer and Temperature pp. 1-5 Dongri Yan Changsha University of Science and Technology Rui Ma Changsha University of Science and Technology Haijing Yang State Grid HAEPC Electric Power Research Institute Zeqian Mao Shandong University Li Zhang Shandong University Xueshan Han Shandong University Ji Feng Shandong University Effect of voltage hasn’t been considered reasonably in existing loss allocation methods. Aiming at the problem, the impact of voltage on the loss allocation method based on circuit theory is deeply discussed in this paper. Firstly, the two node equivalence modes and principles of the branch loss allocation method are investigated. Then the relationship between voltage and the loss under different node equivalence modes is analyzed on the premise that all nodes’ injection currents are fixed, so as to keep the influence of current on loss allocation constantly at different voltage levels. The analysis and simulations reveal that none of the methods can reflect the effect of voltage on loss allocation, and this is due to node equivalence rather than branch allocation principle. So a more reasonable node equivalence should be developed to reflect the influence of voltage on loss allocation. Yongchao Liang Human Electric Examine and Repair Company Transformer oil is the main insulation and heat dissipation medium of oil immersed transformer, its flow velocity, pressure and density distribution has a significant effect on transformer insulation and heat dissipation performance. Based on this, this paper has deduced the relationship between the oil flow velocity and the instantaneous temperature field of the transformer, and the mathematical model. The simulation results reveal the relationship between the fault of the transformer and the flow velocity of the oil, and provide the theoretical basis and simulation platform for the study of the digital gas protection based on the fault characteristics. In addition, analyze the relationship between the temperature of inlet oil flow and the load factor and the temperature rise in the transformer, providing a good base for studying the setting value of the transformer gas relay. TuA02.5 The Evolutionary Game of Electric Power Market Including Renewable Resource Generation pp. 17-22 TuA02.1 An Improved Algorithm for Power System Reliability Sensitivity Analysis pp. 6-11 Yan Zhao Electric Power Exchange Centers State Grid Shanghai Municipal Electric Power Company Zhihong Guo State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company School of Electrical Engineering and Information Hui Wang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company Sichuan University Yong Wang Shandong University Guojing Liu Shandong University Yeyong Li Jichun Liu School of Electrical Engineering and Information Sichuan University Shandong University The Future Renewable Electric Energy Delivery and Management (FREEDM) systems provide a promising solution to accommodate the high penetration of intermittent renewable energy resources by energy internet. As the intelligent power distribution system, the FREEDM systems allow users to use their own Distributed Generation (DG) and load to participate in the competitive electricity market. In this paper, we first assume the users have the DG and elastic load. Then we establish the three layers evolutionary game model including customer-side , supply–side and generation–side under the condition of incomplete information. Lastly, we realize the simulation of evolutionary game for eight-bus system by multi-agent The power system reliability sensitivity analysis can recognize weak parts of the system. It is significant for system reliability assessment and enhancement. Against deficiencies in conventional reliability sensitivity analysis, this paper proposes an improved method by analyzing graphical representations of sensitivity and practical engineering requirements. This method meets real needs better and keeps the calculating errors of reliability indices from impacting results of component sensitivity assessment effectively. What’s more, cooperating with the generalized power network reliability analysis, the suggested 1 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) technology and reinforcement learning algorithm. The results of simulation verify the validity of the proposed model and method. model in the wholesale market, while the renewable companies behave in accordance with supply function model in the TGC market. This model can be formulated as an equilibrium problem with equilibrium constraints (EPEC) and is solved by the nonlinear complementarity approach. The simulation results show that, when the RPS is relatively low, renewable companies tend to withhold some of TGCs to raise the TGC price. Nevertheless, when the RPS is relatively high, renewable companies have few TGCs to withhold, and they may choose to reduce their wholesale electricity output, so as to reduce the amount of TGCs and raise the TGC price. These strategic behaviors will raise the electricity market price, and have negative impacts on the market efficiency. TuA02.6 Power Losses Allocation for Bilateral Electricity Transactions based on Transaction Power Traci ng pp. 23-28 Jianhu Lv Nanjing Branch of China Electric Power Research Institute State Grid Corporation of China TuA02.8 Chunbo Huang Nanjing Branch of China Electric Power Research Institute State Grid Corporation of China Jun Xu Analysis of an Electricity Market Equilibrium Model with Penalties for W ind Power ’s Bidding Deviation pp. 35-40 Nanjing Branch of China Electric Power Research Institute State Grid Corporation of China Xiao Wang North China Electric Power University Ming Zhou North China Electric Power University Mengtao Huang To power loss allocation for bilateral electricity transaction, a novel transaction power tracing based allocation method is put forward. Based on the method, this paper firstly introduces a framework for explicitly modeling bilateral transactions and specified contract paths through transforming the meshed network into tree type network. With the proposed method, it is possible to trace transaction power in the physical network, then transmission losses is partitioned to each transaction reasonably. The simulation on 5-bus system validated the equity and validity of the proposed method. The result shows the proposed allocation method leads to a more accurate reflection of quantity and distance of each transaction, and considers parallel flow and loop flow simultaneously. Shanghai University Xian Wang Shanghai University Shaohua Zhang Shanghai University In an electricity market with strategic bidding of wind power, penalties are applied whenever the delivered wind power deviates from the bid. In order to investigate the impacts of bidding deviation penalties on wind firm’s bidding behaviors, a stochastic Cournot equilibrium model is presented. In this model, a scenario reduction technique is employed to describe the uncertainty of wind speed. We use nonlinear complementarity methods to solve this model. Then numerical examples are given to verify the reasonableness and effectiveness of the proposed model. It is shown that the penalty mechanism stimulates wind firms to reduce bidding error. This conduces to market regulators to mitigate wind firms’ bidding deviations through appropriate penalty. TuA02.7 Joint Equilibrium Analysis of Electricity Market with Tradable Green Certificates pp. 29-34 TuA02.9 Application of Robust Optimization Theory to Generation Asset Allocation pp. 41-46 Xuena An Shanghai University Chen Zhao Shanghai University Shaohua Zhang Shanghai University Jie Zhou Shanghai University Xue Li Shanghai University Chen Zhao Shanghai University Shaohua Zhang Shanghai University Xue Li Shanghai University Renewable portfolio standard (RPS) and tradable green certificate (TGC) schemes are important mechanisms to promote the development of renewable energy. In order to investigate the impacts of RPS and TGC schemes on the electricity wholesale market competition, a joint equilibrium model considering the oligopolistic TGC market is proposed in the paper based on the oligopoly competition equilibrium theory. Therein all generation companies behave in accordance with cournot November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China In the deregulated electricity market, the generation company (Genco) can sell energy through several trading choices such as the wholesale spot market, bilateral contracts and option contracts. These trading choices have different risk characteristics. To achieve a satisfactory risk-return target, the Genco should 2 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) allocate the electricity among these trading choices reasonably. A robust optimization based risk management model is proposed for Genco’s generation asset allocation under uncertain spot market prices. In this model, the robust profit (RP) and conditional robust profit (CRP) are used to describe Genco’s profit under a certain confidence level. The objective of the Genco’s generation asset allocation problem is to maximize Genco’s CRP. With this method, different allocation strategies can be made for Genco’s different attitudes toward risk. The Monte Carlo simulation-based numerical examples are presented to validate the reasonableness and effectiveness of proposed model. Power allocation into decision-making model plays a valuable role for the power supply company to mitigate price risks and improve their profitability in electricity market environment. In this paper, we develop a power allocation model based on the prospect theory, which considers the psychological factors of decision-making in reality, through calculating the value of electricity purchasing business function and weighting function retrieves the maximum number of prospects for the utility as the optimal allocation scheme. The results show that the risk preferences of the real decision makers will change along with the psychological expectations, the power allocation strategy is more conform to the actual decision model of decision makers compared with the traditional power allocation model. TuA02.10 TuA02.12 An Evaluation Method of Utilization Efficiency of Power Grid Equipment Based on Three Stage DEA Model pp. 47-53 Yuheng Guan South China University of Technology Wen Sun Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Yue Zhang Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Pricing Method for Cross-zone Electricity Trading Curve pp. 60-64 With the reform process of power system continuing to accelerate, the input-output efficiency of power grid enterprises is getting more and more attention. In order to get scientific, objective and accurate evaluation results of inputoutput efficiency, improve the economic and social benefits of power grid enterprises, the three stage DEA model is proposed to evaluate the utilization efficiency of power grid equipment in this paper. The first stage DEA evaluates the utilization efficiency of power grid equipment based on BCC-DEA and CCR-DEA model. The second stage DEA utilizes stochastic frontier analysis method to quantify the influence of environmental factors such as the total number of GDP, the resident population and the power supply area, and to modify input variables of DEA model. The third stage makes the DEA evaluation again with the adjusted input variables after SFA regression. This paper chooses 19 cities' power supply bureaus as the empirical sample of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation and the results verify the validity, effectiveness and reasonability of the model and method which can provide reference for power grid enterprises to evaluate the utilization efficiency of power grid equipment. Jingjie Ma Shanghai University Chen Zhao Shanghai University Shaohua Zhang Shanghai University Libing Yang State Grid Corporation of China Xiaogang Li State Grid Corporation of China Renewable energy develops rapidly around the world. In China, to achieve fully use of renewable energy, the scale of cross-zone renewable electricity trading increases constantly. In addition, the difference between peak and base load increases year by year. As a result, the base-load cycling problem is getting worse. This problem imposes negative impacts on the utilization of renewable energy during the base-load period. To mitigate the base-load cycling problem, it is crucial that mutual relief of base-load cycling capability should be achieved among provinces in the import zone and good cycling characteristics of the cross-zone electricity trading curve provided by the export zone. TuA02.13 Optimization of Cross-Regional Bilateral Power Transaction and Analysis of Transaction Path pp. 65-70 Jun Xu TuA02.11 China Electric Power Research Institute Jianhu Lv Allocation Strategy Based On Prospect Theory For Power Supplier pp. 54-59 Bing Lu Shanghai University Chen Zhao Shanghai University Shaohua Zhang Shanghai University China Electric Power Research Institute Minghui Zhu Xi’an Jiaotong University Jianxue Wang Xi’an Jiaotong University Xian Zhang State Grid Power Exchange Center Cross-regional bilateral power transaction is an effective way to solve the problem of energy distribution imbalance among regions. The amount of power transaction, the price and the transaction path is valuable for signing a power transaction 3 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) contract. The common method for practical use is based on the network flow approach which lacks the consideration of electrical property of power transaction. In this paper, a basic model that considers the electrical property with the objective of maximizing social welfare is introduced first. Then the basic model is elaborated into a synthesized model through considering the function of auxiliary adjustment and transmission cost. A practical method for settling power transaction path is also proposed. Finally, a case study based on IEEE 30 was performed to verify the applicability of the proposed model. Results show that auxiliary adjustment and the proposed model do have positive effects on promoting the cross-regional bilateral transaction of electrical power. Comparison on the similarities and differences in demand side of capacity markets in different countries pp. 71-75 Xi’an Jiaotong University Xiuli Wang Xi’an Jiaotong University Li Yao Xi’an Jiaotong University Xian Zhang China Electric Power Research Institute Jianhu Lv China Electric Power Research Institute A Risk Management Strategy for a W ind Power Producer Based on Bilateral Contracts pp. 82-86 Xi’an Jiaotong University Xiuli Wang Xi’an Jiaotong University Furui Hou Xi’an Jiaotong University Li Yao Xi’an Jiaotong University Zece Zhang Xi’an Jiaotong University Zhu Li China Electric Power Research Institute Electric Power Trade Center The integration of renewable energy is increasing rapidly in electric energy systems throughout the world. This paper presents a bilateral contract model for wind power and provides a risk management strategy for a wind power producer to trade energy in spot market and bilateral contract market. It uses long-term wind speed prediction to determine contract volume, and uses short-term wind speed prediction to determine offers submitted to spot market. Autoregressive moving average model and autoregressive model are used to simulate wind farm output and spot price series. Profit-at-Risk index is used as a risk management metric. Simulation results of a case study show that the purposed trading strategy can obviously reduce financial risk of a wind power producer with the expected profit unchanged. Probabilistic Assessment of Interregional Available Transfer Capability for Renewable Energy Transactions pp. 76-81 Xi’an Jiaotong University Xi’an Jiaotong University China Electric Power Research Institute November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Zechen Wu Chunbo Huang TuA02.15 Haihua Cheng Department of Power Exchange Center TuA02.16 The 3rd Electricity reform in UK has been implemented which includes capacity markets. Among many parts of capacity market, the demand side is the key part for government imposing their force on promoting the market into the planned direction which is to meet the reliability standard. This paper gives a brief overview on demand side of capacity markets in different countries, and compares creatively their similarities and differences from the combination of reliability and market perspective. The main similarities are the core of capacity market and the force of government. And the differences focus on the capacity mode, capacity requirement and the length of capacity agreement. Finally, combined with the new electricity reform in China, this paper gives some suggestions in demand side for the future creation of capacity market in China according to the results from comparisons. Jianxue Wang Xian Zhang Electric Power Trade Center Jun Xu Feng Li China Electric Power Research Institute This paper investigates a probabilistic assessment method for calculating interregional available transfer capability (ATC) in renewable energy transactions based on randomness and correlation of renewable energy. Firstly, the discrete joint probability model is established to consider wind power correlation based on wind speed data of multiple wind farms. Then the nonsequential Monte Carlo method is implemented to determine the evaluation state of numerous uncertainty factors such as load fluctuations, equipment availabilities. As the assessment of ATC is susceptible to adjustment strategy of generator output, the paper analyzes practical power adjustment strategies. An accelerated algorithm of mixed evaluation strategy is proposed based on sensitivity and optimization adjustment according to the changes of network configuration, which compromises the calculation speed and accuracy. The IEEE-RTS results verify the effectiveness of the improved model and the proposed method. TuA02.14 Furui Hou Yaxian Zheng 4 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) to participate in bidding electricity market by managing enormous quantity and dispersive air-conditioning load (AL), which not only reduces load peak-valley difference, but also provides the opportunity for AL to take part in power market bidding. This work adopts reference price effect from behaviour economics to depict electricity consumption preference. A bi-level optimization method is being established. The upper level problem aims to maximize the social welfare, while the lower level aims to maximize the ALA benefits based on consumers' preference. Karush–Kuhn–Tucker condition is being applied to transfer the complex bi-level problem to a solvable sing-level problem. Case studies are provided to verify the feasibility of proposed model. TuA02.17 A Model for Analyzing Transaction Price Volatility of Generation Rights Trade Market Based on Cellular Automata and Complex Network Theories pp. 87-92 Yang Wu Sichuan University Junyong Liu Sichuan University Jichun Liu Sichuan University Yuan Huang Sichuan University Zhanxin Yan Sichuan University Li Zhang Sichuan University Hongjun Gao Sichuan University TuA02.19 Design of the Reserve Ancillary Service Market Mechanism for the Micro-grid with Energy Storage pp. 98-102 For the researches on the relationship between the influence factors of the generation rights transaction price and the price volatility are very few, the effects of individual behavior on the price volatility of generation rights trade market are studied in this paper based on cellular automata (CA) and complex networks (CN) theories. Firstly, the CA model of generation rights trade market is proposed. Then, the behavior model of the generation rights trader forecasting the coal price trends is constructed based on CN theory. At last, depending on the above two models, combining the transformation rules of generation rights trade CA with the behavior model, the model for analyzing the price volatility of generation rights trade market is established. The simulation results show that the individual behavior is an important factor of causing price volatility of generation rights trade market. It is verified that the relationship between the individual behavior and the price volatility of generation rights trade market can be depicted clearly by the proposed model, and it provides a new method for constructing the model of influence factors of power generation rights trade market by complex system theories. Bo Yang China Electric Power Research Institute Jilei Ye China Electric Power Research Institute Jinhua Xue China Electric Power Research Institute Dan Lu Hohai University Haoming Liu Chunlai Li Hohai University Qinghai Electric Power Corporation In this paper, the foundation of the micro-grid ancillary service market is introduced and some basic assumptions are made. In view of the reserve ancillary service market, the market participants are analyzed, the benefits of energy storage providing reserve generation are modeled, including the reserve capacity benefit and reserve generation benefit, and the optimal clearing mechanism of the reserve ancillary service market is designed to minimize the customers’ total expense for reserve capacity. The example shows that the participation of energy storage and demand response in the ancillary service market is helpful to reduce the total costs of the ancillary service market. TuA02.18 TuA02.20 Bidding strategy analysis for air-conditional aggregator considering consumers' preference pp. 93-97 Sanhua Zhang Dynamic Restoration of the State of Charge for the Battery Participating in Mutiple Markets Using Market Price Signals pp. 103-107 Changsha University of Science and Technology Hongming Yang Changsha University of Science and Technology Yongxi Zhang Ming Li The University of Sydney Changsha University of Science and Qiwei Zhai The University of Sydney Jin Ma The University of Sydney ZhaoYang Dong The University of Sydney Chao Lu Tsinghua University Technology With the increasing use of Variable Renewable Energy (VRE) resources and the recent advance of battery technologies, battery would likely become a non-generation alternative to par- Considering the increment of air-conditional electricity consumption, air-conditioning load aggregators (ALA) are prone 5 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) ticipate in the deregulated electricity markets. This paper focuses on utilizing batteries for providing frequency regulation services and taking advantage of the short term price arbitrage(price spikes) in the spot market, because batteries have quick response time, and price spikes and frequency regulation services have similar time scales. Our experiment with real market data demonstrates that the proposed dynamic State of Charge (SoC) model makes much higher profits than a static SoC operation model. tomers participate in energy scheduling by providing load shift resources. Compared to basic DR models, the proposed models of LRDR and LTDR are extended with a refined description by adding various constraints in the offer package. The actual operation characteristics of DR resources are reflected in the models. Besides, the day-ahead scheduling mode with DR is studied. Finally, a co-optimized day-ahead energy/reserve scheduling model integrated with DR which simultaneously schedules energy and reserve is established. The effectiveness of the proposed day-ahead scheduling model is verified on a modified IEEE 118-bus system. TuA03.1 TuA03.3 Capacity Credit Assessment of Renewable Distributed Generation in Active Distribution Systems Considering Demand Response Impact pp. 108-113 A Comprehensive Decision Model for Optimal Demand Response Program pp. 121-126 Xiong Zheng North China Electric Power University Zhen Zhang North China Electric Power University Bo Zeng North China Electric Power University Yi Ren North China Electric Power University North China Electric Power University Ming Zhou North China Electric Power University Geng Wu Jianhua Zhang North China Electric Power University Ming Zeng North China Electric Power University Jinyue Shi North China Electric Power University In this paper, demand response (DR) is modeled based on price elasticity and customer benefit function. A comprehensive decision model for DR based on Multiple Attribute Decision Making (MADM) techniques is proposed to extract the priorities of DR programs and select the most effective program. The proposed model includes the determination of attribute set, calculation of attribute weight and comprehensive evaluation of the alternatives. As for the attribute set, two new attributes, namely the electricity consumption manner satisfaction index and electricity cost expenditure satisfaction index, are introduced to consider customer's satisfaction. Besides, a combination weighting method is adopted to determine the weights of attributes. To prioritize DR programs, a new sorting method which combines Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) with Gray Correlation Analysis (GCA) is proposed to overcome the decision bias due to the limited information in the decision approach. The performance of the proposed decision model is evaluated on a modified IEEE 118-bus system. The renewable distributed generation (RDG) has gained booming development in the past decade, thus its capability to displace conventional generation has become an urgent issue to be studied for future power system planning. In this paper, the capacity credit (CC) of RDG is investigated given an active distribution system (ADS) context, wherein the impact of demand response (DR) is highlighted. To achieve this, the CC index is first specified to cater for different operating modes of ADS. On this basis, a generalized possibilistic-probabilistic model is proposed for DR characterization. The CC is calculated using the sequential Monte-Carlo simulation (SMCS) method, embedded with an adaptation strategy developed to improve the computation efficiency. Numerical results on a real multi-voltage distribution network show that the CC of RDG varies with the energy mix in ADS and the presence of DR could substantially improve the CC of RDG. TuA03.4 A Calculation of Power Users’ Demand Response Potential under the Angle of Big Data pp. 127-134 TuA03.2 Joint Day-Ahead Energy and Reserve Scheduling Model with Demand Response pp. 114-120 Zhen Zhang Ming Zhou Tingting Lu Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Smart Grid Technology & Equipment North China Electric Power University Ciwei Gao Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Smart Grid North China Electric Power University Qian Xu State Grid Zhejiang Electric Power Company Liying Sun State Grid Zhejiang Electric Power Company Technology & Equipment Southeast University Lingling Sun Technology & Equipment Two demand response (DR) programs, namely, load reduction demand response (LRDR) program and load transfer demand response (LTDR) program are both incorporated into the day-ahead scheduling in this paper. The LRDR participants provide load curtailment in energy scheduling and reserve capacity in spinning reserve scheduling while the LTDR cus- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Smart Grid 6 Fuchao Liu State Grid Gansu Power Company Yongjun Han State Grid Gansu Power Company Jianhua Zhang State Grid Gansu Power Company The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) With the development of economic, China is facing the problem of the shortage of power supply; so it is necessary to implement interruptible load projects. Now when the interruptible load participating in the system peak optimization, the interruptible load potential is generally considered to be a constant and the acquisition the demand response potential lacks scientific and theoretical models. A calculation method of power users’ demand response potential is presented in this paper; cluster analysis is used to divide the users into several patterns on basis of load data and then the Bayes method is used to predict the users’ behavior patterns by temperature and day type, and ultimatelyusers’ demand response potential of prediction days can be known. Anexample is carried out to verify the feasibility of the method, which can effectively calculate the demand response potential of power users. tor is an effective measure to give play to demand response resources. This presents a new demand of ultra-short term (15min) load forecast for the aggregator and the affiliated users. Large scale Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) installation introduces huge real time electricity consumption information which makes it possible to forecast load in a small spatial and temporary scale. To single user or an aggregator with small electricity consumption but relatively large fluctuation, this paper firstly proposes a method to choose the historic similarity day based on fuzzy C-mean clustering. Then wavelet decomposition is adopted to resolve the similarity day load curve, low frequency series and high frequency series is modeled and used to forecast by time series method and neutral network method, respectively. Furthermore, a hierarchical coordination approach is presented to tune the aggregator load forecast and the affiliated individual user load forecast to ensure the whole forecast accuracy and feasibility. The forecasting result for a load aggregator with three users shows the proposed approach is effective and more accurate. TuA03.5 Comprehensive Evaluation on User Energy Efficiency Based on Improved Matter-Element Model pp. 135-140 Huan Liu Southeast University Ciwei Gao Southeast University TuA03.7 The research and application of Power Integrated Cyber-marketing pp. 147-151 Fuchao Liu State Grid Gansu Power Company Weiwei Lu Yongjun Han State Grid Gansu Power Company Lishi He Marketing Department HHBS Jianhua Zhang State Grid Gansu Power Company Hongpeng Wang Marketing Department HHBS Yue Li State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Company State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Research Institute According to the influence factors of energy efficiency digged from user energy data, this paper establishes a multilevel energy efficiency evaluation system considering equipment and users on the whole. Objective and subjective weighting method is adopted to balance the influence of subjective and objective factors. Matter-element extension model is used to build a hierarchy of energy efficiency indicators to form user’s electric energy efficiency grades. Analyzing assessment results based on this model can reflect the energy efficiency level of the user, and offer users help in energy management and tap the energy saving potential. Under the background of today's concept “Internet +”, the marketing of electric power enterprises develop a new trend and the reform of power marketing is in urgent need. In order to adapt to the development of times and meet the needs of business growth, this paper puts forward the concept of Power Integrated Cyber-marketing, and further constructs the Power Integrated Cyber-marketing application model to integrate the idea of power marketing information collection, processing and application during the whole process. Finally, an application example is used to make the empirical analysis. TuA03.6 TuA03.8 Hierarchically Coordinated Ultra-Short Term Load Forecasting for Load Aggregator pp. 141-146 Application of the Ward's Method with TABU-Search in the Classification of Load Characteristics pp. 152-155 Yi Ren North China Electric Power University Ming Zhou North China Electric Power University Gengyin Li North China Electric Power University Zhao Shen Shenzhen Power Supply Company Zhiwei Liao South China University of Technology Lingshu Zhong South China University of Technology Ward's method is an effective method for classification of power system load characteristics. In view of the limitations of the traditional Ward's method which can only reduce the number of clusters through amalgamating, an improved measure to optimize the cluster result based on TABU search is put forward along with a statistical method to guide the clus- The load aggregator is a collector, acting as a hub, to link the system control center and multiple electricity users, which integrates multiple end electricity users to participate in the market competition or the system dispatch. The load aggrega- 7 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) tering process and test results. In this paper, the daily load curve is used as the feature vector, while the traditional Ward's method is used to find a suitable number of clusters. The clustering results are optimized by means of the method of TABU search. A classification case of the load curves of 744 days in Guangzhou shows the advantage of those methods. In order to enhance the frequency response capability of the power systems, the EV (electric vehicle) clusters and AC (air conditioner) clusters are used as response resources to maintain the system frequency within an acceptable range. The frequency control strategies of the EV clusters and AC clusters are given respectively. A load assessment index is proposed to evaluate the available response capability of the EV/AC loads in real time. Then an EV-AC coordination frequency control strategy is developed. The control sequence of the two controllable loads is determined by their impacts on the comfort level of EV/AC users. In the case study, a simplified frequency regulation model is used to investigate the effectiveness of the proposed strategy under two frequency events, the simulation results show that utilizing the EV/AC loads to stabilize the system frequency can reduce the frequency deviation to some extent without serious impact on the comfort level of users. TuA03.9 An Interactive Operation Strategy for Microgrid Cooperated with Distribution System Based on Demand Response pp. 156-160 Feijin Peng Foshan Power Supply Bureau Hongzhi Su Tianjin University Peng Li Tianjin University Guanyu Song Tianjin University Jinli Zhao Tianjin University TuA03.11 Effect Evaluation and Compensation Scheme Design of Demand Response Based on Baseline Parameter Identification pp. 166-172 Microgrid is an autonomous system which can achieve self-control, self-protection and self-management. It will not only comprehensively exploit the advantages of renewable energy sources (RES) in environment protection and energy conservation, but also overcome its intermittency and volatility, reduce the impact to distribution system when the distributed energy resources (DERs) are connected to the distribution network as microgrids. Deployment of microgrids can facilitate efficient demand side management and integration of RESs at the distribution level. This paper proposed an interactive operation strategy for microgrid cooperated with distribution system based on demand response. In the present paper, a day-ahead operation optimization model of microgrid on account of electricity purchasing cost, electricity selling benefits, generation cost of distributed generations (DGs) is proposed. And then an interaction model in which the microgrid responds to the interaction demand through adjusting the scheduling plan aiming at dealing with the excessive peak load of distribution system is presented. We analyzed the relationship between interaction capacity and interaction cost via sensitivity analysis and finally achieved the interaction between the microgrid and the distribution system. The simulation results in a microgrid, which has a wind turbine (WT), photovoltaic (PV) system, energy storage system (ESS) and loads, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Liangjie Zhang Ciwei Gao Huan Liu Gaojie Xu Dezhi Li Calculation of baseline load is a prerequisite for the evaluation of the effect of demand response. This paper summarizes the commonly used method for calculating the baseline of the demand response, and put forward a new method using the harmony search algorithm to identify the baseline parameters. It combines the similar date algorithm and intelligent algorithm, which guarantees the accuracy and speed of calculation. This paper proposes the time compensation and step compensation scheme, encouraging users to implement demand response projects and improving operation economy of power network. TuA04.1 Modeling of Traveling Wave Protection Functions Based on IEC61850 Standard pp. 173-177 Ran Xu Shandong University Zhaoyong Meng Shandong University Ji Ma The University of New South Wales Considering the object-oriented modeling design of the IEC 61850 standard, this paper takes the traveling wave protection as a study case, and proposes the modeling and design method of traveling wave protection devices. To be specific, the data objects are clarified first to establish the entire information models and functional model services. According to IEC 61850, each of the traveling wave protection functions and the related functions is viewed as a logical node, and all the traveling wave protection functions are implemented through the information interaction between logical nodes. Also, considering the card pieces design principle, the hardware of a traveling wave protection device is divided into four cards, and each card is with the corresponding function. Further, ACSI service and device’s configuration file of GOOSE service are introduced. TuA03.10 A Coordination Frequency Control Strategy for Electric Vehicles and Air Conditioners based on the Load Assessment Index pp. 161-165 Xudong Wang Tianjin Electric Power Research Institute Ling Jiang Tianjin Electric Power Research Institute Xianjun Ge China Electric Power Research Institute Naishi Chen China Electric Power Research Institute Jian Meng Tianjin University November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Southeast University Southeast University Southeast University China Electric Power Research Institute China Electric Power Research Institute 8 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuA04.2 TuA04.4 Reactive Power Optimization in Distribution Network by Using Improved Gravitational Search Algorithm pp. 178-182 Simulation of wind power time series based on the MCMC method pp. 187-191 Siyuan Wang Ning Wang Qiaoqiao Wang Yi Yang Guihong Huang Kuan Zheng Jinan Power Supply Company State Grid Jinan Power Supply Company State Grid Jinan Power Supply Company State Grid Bazhong Power Supply Company State Grid Xihua University Dept. of Energy Strategy and Planning Research State Grid Energy Research Institute Jun Liu Dept. of Energy Strategy and Planning Research State Grid Energy Research Institute As it is a new challenge for reactive power optimization reactive power optimization to bring distributed generators (DGs) into electric distribution network, this paper researches the reactive power optimization in electric distribution network including DGs. The randomness of DG output results in the randomness of the node voltage in the electric distribution network including DGs, the DG’s incorporation into grid, therefore, becomes very significant to the uncertainty analysis of electric power system. Random power flow algorithm is adopted in this paper to figure out the probability distribution of each node, and the model, with the objective function of active network loss minimization based on the chance constraints, is established, under the condition of the secure voltage margin. Improved gravitational search algorithm (IGSA) is adopted to conduct the simulation analysis in the IEEE-33 node standard test system, and the result indicates that, compared with the routine gravitational search algorithm (GSA), IGSA can effectively solve the reactive power optimization problem in electric distributed network, avoiding the premature convergence. Songxu Xin Dept. of Energy Strategy and Planning Research TuA04.3 TuA04.5 Non-mechanism Equivalent Model of W ind Farm for Transient Stability Analysis pp. 183-186 Investigation on Fundamental Issues of Dynamic Equivalent Modeling of W ind Farms pp. 192-196 Feng Wu HoHai University Pupu Chao Harbin Institute of Technology YongXiang Chen HoHai University Jinling Qi Harbin Institute of Technology GuangJing Gong HoHai University Weixing Li Harbin Institute of Technology Linjun Shi HoHai University Xiaoming Jin State Grid Energy Research Institute Jinfang Zhang Dept. of Energy Strategy and Planning Research State Grid Energy Research Institute Building an accurate and reasonable time-series model of wind power is of great significance for the power system operation and planning. This paper proposes a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method to simulate the time series of the wind power. Taking into account the nonstationarity and stochastics of the wind power, this model constructs Markov chain for time series of the wind power to keep the stochastics and utilize the Gibbs sampling to realize the probability transition matrix. A numerical case study with one-year real measurement of the wind power from one large wind farm in Gansu province of China is applied to illustrate the validity the proposed model: the simulated wind-power time series of arbitrary length that accurately reproduce the statistical behavior of the original series. Electrical Power Research Institute China Southern Grid To study the transient stability of the power system with large scale wind farm, the equivalent model is necessary to represent the aggregated dynamics of the wind farm. Since the mechanical dynamics of the wind turbine is usually decoupled by the power electronic devices, and the inertia of the generation system can’t be seen from the power grid. A non-mechanism equivalent modelling method is proposed in this paper. The transfer function based equivalent model is employed to describe the output dynamics of the wind farm. The parameter estimation method is also introduced. The proposed equivalent method is applied on a wind farm consisting 9 wind turbines, and simulations are performed to test the effectiveness of the proposed equivalent modeling method. This paper takes the GE1.5MW DFIG wind turbine as an example, to simulate and analyze the transient response characteristics of the wind turbine under different wind velocities. Three critical issues related to dynamic equivalent modeling of wind farms are summarized by intensive investigations. Firstly, the wind turbines working on low wind speed are found to consume a large number of active power during the transient process, and their transient current and active power response curves sometimes are close to ones working on high wind speeds. Consequently, the wind turbines working on low wind speeds cannot be ignored casually for dynamic modeling of wind farms. Secondly, a counterintuitive phoneme, i.e. more 9 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) clusterings is not necessarily to have higher equivalent accuracy, is found, since the transient current and active power curves of the wind turbines working on various wind speeds show significant and nonlinear differences in amplitude, fluctuations and transient response time. Finally, for a large wind farm with long collector lines and complicated configurations, the equivalent network impedance, calculated by the equivalent power loss rule, is seen to be able to guarantee the consistency only during the steady-state process instead of the transient one between the detailed and equivalent models. Studies about the dynamic characteristics of the collector network impedance should be emphasized. ence on the results of optimization. To solve this problem, a robust optimization operation method of power system risk-control is presented in this paper, considering the non-probabilistic uncertainty of parameters based on information gap decision theory (IGDT). In the method, loads are modeled as the non-probabilistic uncertainty parameters, and the model of robust optimization operation of risk-control is presented. By solving the model, the maximum fluctuation of the pre-specified target can be obtained, and the strategy of this situation can be obtained at the same time. The proposed model is applied to the IEEE-30 system of risk-control by simulation. The results can provide the valuable information for operating department to risk management. TuA04.6 TuA04.8 Study on Fault Characteristics of Jinsu UHVDC Based on the True-type Device of UHVDC Control and Protection pp. 197-199 Peng Wei Jiangsu Electric Power Research Institute Qian Zhou Jiangsu Electric Power Research Institute Jiankun Liu Jiangsu Electric Power Research Institute Chenggen Wang Jiangsu Electric Power Research Institute The OPF Model and Algorithm for “SourceGrid-Load” Interactive Optimal Regulation Participated with Flexible Load pp. 205-209 Qi Li Xueshen Cui Limin Jiang Bingqing Guo Xu Yang With deep study of UHVDC, pure electromagnetic or electromechanical-electromagnetic hybrid simulation cannot meet the need of analysis of transient characteristics of UHVDC. In this paper, take ±800 kV Jinsu UHVDC project as background, Jiangsu power grid with Jinsu UHVDC accessing was built in RTDS, true-type device of UHVDC control and protection was taken. To ensure that the size of the grid while guaranteeing the DC system transient characteristics of the protection and control. Take an AC fault occurred in history of direct near placement as background, the simulation results of using the true-type simulation systems built and traditionally electromechanical-electromagnetic hybrid system were compared with the real fault recorder. The results shows the true-type device of UHVDC control and protection performance remain highly consistent with actual UHVDC project in protection functions, behavior and trends of steady-state operating conditions. Flexible load has increasingly becoming an important means of regulating the power grid and consuming new energy, as well as an important part of “source-grid-load” coordination control. On the other hand, nowadays typical new energy resources such as wind and solar energy are being accessed to the power grid in a large scale, but the phenomenon of abandoning wind or solar energy is very serious since the effect of channel bottlenecks or little load consumption. Aiming at solving this problem, and combining with the possibility of adjusting load flexibly because of the loose electricity price in the new situation of Chinese electric power reform, this paper gives the DC OPF model for the "source-grid-load" interactive optimal regulation based on the traditional OPF model. To be precise, this model puts forward the goal of maximizing the system-wide social net marginal benefit, which is on the basic of any time section with balanced power flow in the system, and considers the marginal cost of the source and network side as well as the net marginal benefit of the load side, to research the optimization operation strategy of the large-scale new energy, conventional power and flexible load. Then linear program algorithm is deduced based on basic mathematics model foundation. The example is simulated under the goal of maximizing the social net marginal benefit with MATLAB/linprog, the results show the effectiveness of the model and algorithm. There is no convergence problems in the model and algorithm presented in this paper. In addition, the compute speed is fast. On the one hand, the scheduling decision can meet the security, economy, reliability and other operational requirements of the power system. On the other hand, the regulation value of the “source-grid-load” interaction which participated with flexible load can be fully reflected. In a word, this paper provides new ideas of OPF for future "relatively independent" power dispatching / trading platform. TuA04.7 Robust Optimization of Risk for Power System Based on Information Gap Decision Theory pp. 200-204 Xue Li Zhenchen He Shaohua Zhang Shanghai University Shanghai University Shanghai University Risk-control optimization has great significance for security of power system. Usually the probabilistic uncertainties of parameters are considered in the research of risk optimization of power system. However, the method of probabilistic uncertainty description will be insufficient in the case of lack of sample data. Thus non-probabilistic uncertainties of parameters should be considered, and will impose a significant influ- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China North China Electric Power University North China Electric Power University China Electric Power Research Institute China Electric Power Research Institute Beijing HUASHANG Energy Management Limited Company 10 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) head lines as equality constraint and temperature as an state variable in optimal power flow which maximizes the VSM index. The proposed approach is capable of improving evaluation accuracy and the evaluation results of consider and disregard HBR of transmission line are compared via simulation. TuA04.9 Power System Electromagnetic Transient and Electromechanical Transient Hybrid Simulation based on PSCAD pp. 210-215 Xiaowen Han Haibo Zhang TuA04.11 North China Electric Power University North China Electric Power University A Novel Congestion Management Method in High-voltage Distribution Network Based on Logic Constrains of Functional Units pp. 220-225 Due to the expanding scale of power system and the access of HVDC and FACTS devices, independent electromagnetic transient simulation and electromechanical transient simulation begin to show their limitations. However, the electromagnetic-electromechanical transient hybrid simulation can expand the simulation scale, and improve the simulation speed and accuracy, which has important theoretical value and practical engineering significance. In this paper, the electromechanical transient simulation program is completed by C programming language, and the electromechanical transient user-defined module is developed in PSCAD. The function calling of electromechanical transient simulation program by EMTDC is realized through interface program that is developed based on Fortran programming language. This paper expounded the interface equivalent circuits of electromagnetic and electromechanical side, and built a hybrid simulation system through connecting electromagnetic transient subsystem and the user-defined module of electromechanical side. Through the comparison between the simulation results of the proposed hybrid simulation and pure electromagnetic model, the correctness of hybrid simulation method based on PSCAD is verified. Yong Jin Junyong Liu Sichuan University Sichuan University Load transfer is an important method for congestion management in high-voltage distribution network. Functional units were proposed to express the topological structure of high-voltage distribution network (HVDN) in this paper. In addition, three types of logic constraints of functional units including sequence, mutual exclusion and orientation were established to facilitate minimal transfer, load curtailment and balancing with variables of transfer units instead of traditional switch status. The proposed model was verified using the practical HVDN of an urban power system in China. Simulation result shows that the proposed models can be efficiently solved by commercial software. TuA04.12 Research on Modeling and Simulation of Communication in Power SCADA System pp. 226-230 TuA04.10 Aijun Hou Chunchao Hu Kai Ma Zexiang Cai Chengqiao Huang Tianliang Pan An OPF Based Approach for Static Voltage Stability Evaluation Considering Heat Balance Rule of Overhead Line pp. 216-219 Youmin Li Shandong Electric Power Maintenance Company Jing Xiao Shandong Electric Power Maintenance Company Ronghua Yang Shandong Electric Power Maintenance Company Yingchun Feng Shandong Electric Power Maintenance Company Qiang Zhang Shandong Electric Power Dispatching and Control Center Mengxia Wang Shandong University Guangdong Power Grid co., LTD Guangdong Power Grid co., LTD Guangdong Power Grid co., LTD South China University of Technology South China University of Technology South China University of Technology In order to solve the problem of analyzing network performance of SCADA system communication of power grid in effective and practical way, this paper proposes a method based on OPNET Modeler, in which communication object models of SCADA system and variety simulation scenes are built properly. According to the actual situation of SCADA system communication, the paper analyzes the modeling demand of communication network, services information flow, communication protocol and studies the modeling method of the system. The networks for simulation were established and the networks performance was analyzed under variety simulation scenes. The paper provides an effective tool and useful material for accident drills, equipment selection and network planning of SCADA system communication. In this paper, overhead lines' heat balance rule (HBR) is integrated into static voltage stability evaluation and an optimal power flow (OPF) based approach for voltage stability margin (VSM) evaluation is proposed. It captures the coupling nature between current & temperature of overhead line and also considers the influence of temperature on series resistance of conductor by introducing heat balance equation (HBE) of over- 11 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) sign of coordinated control system of ultra-supercritical coal-fired (USC) power unit. This may serve as a reference for engineering analysis and simulator development of ultra-supercritical power units. TuA04.13 Arc Grounding Overvoltage Suppression Strategy by Using ZnO Nonliear Resistance Grounding Mode pp. 231-235 Wangjing Tan Qian Wang Jiandong Duan Zan Ye Shuaishuai Cui TuA04.15 Xi’an University of Technology Xi’an University of Technology Xi’an University of Technology Xi’an University of Technology Xi’an University of Technology Using the STATCOM with Energy Storage to Enhance the Stability of AC-DC Hybrid System pp. 242-247 Xu Zheng Wuhan University Jianyong Ding Wuhan University huang Zhao Huazhong University of Science and Technology Mei Li Huazhong University of Science and Technology Ni Zeng Huazhong University of Science and Technology Ruoxi Zhu Huazhong University of Science and Technology Buhan Zhang Huazhong University of Science and Technology With the development of power capacity, the arc grounding overvoltage has become increasingly prominent. Consider system capacity, the operation mode and so on, a new method to determine the current-voltage (V-I) characteristics of ZnO nonlinear resistance on the new grounding mode is put forward by analyzing the power system through symmetrical component method. Then the V-I characteristics of ZnO nonlinear resistance is obtained through the segmental linearization method. Finally, by using discrete wavelet, the multi-resolution analysis on zero sequence current is performed. According to the high frequency component energy ratio within the time window, the protection strategy based on ZnO nonlinear resistance is put forward. Results indicate that the designed ZnO nonlinear resistance parameters can suppress arc grounding overvoltage, and the proposed grounding mode is safe and reliable. UHVDC has been rapidly developed for its large conveying capacity, small net loss and easy power control, which can solve the problem of the uneven distribution of load and energy with great economy. However, with DC transmission access, the power system must have a strong ability of reactive power support to cope with the possibility of transient voltage problem. At the same time, regional power oscillation issue also can’t be ignored. Considering that the STATCOM, as a new type of the device, can only provide dynamic reactive power to support the system voltage and cannot undertake active regulation and control to damp system power oscillation problem, the STATCOM with energy storage is presented in this paper to solve both problem of transient voltage and power oscillation in AC/DC hybrid system. In view of the central China province power grid planning, possible serious faults of the system were analyzed. The simulation results show that the STATCOM with energy storage can not only effectively support the system transient voltage and promote voltage of DC inverter station to avoid DC block caused by commutation failure, but also significantly enhance the system damping and restrain the power oscillation of UHVAC lines in the case of system failure. TuA04.14 Improvement of a Non-linear Model of Ultra-supercritical Boiler-turbine Unit and Its Application pp. 236-241 Yanna Xi Yinsong Wang North China Electric Power University North China Electric Power University The characteristic of supercritical unit is not easily controlled, because the research on the coordinated control system of ultra-supercritical coal-fired (USC) power unit is usually based on a kind of mathematical model, which is used to test the correctness of the design concept and the effectiveness of the control strategy. If the mathematical model cannot reflect the intrinsic nature of the controlled object, the simulation results are difficult to explain that the control strategy designed is successful. In this paper, a simplified non-linear model which is suitable for the controller design in coordinated control system of a once-through boiler-turbine unit is analyzed at first. Then based on the study of the above model, features and improvement suggestions of the non-linear model are proposed. At last, step forced simulation test and comparison test with operation data were done to test the effectiveness and accuracies of the simplified non-linear once-through boiler model. Simulation results show that this model has same dynamic characteristics with the actual unit and can predict output changes with certain accuracy which means that it is fit for the controller de- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China TuA04.16 Reliability Modeling of W ind Farms Considering Weather Conditions pp. 248-254 Fan Chen Zhinong Wei Haitao Liu Jun Li Xiaolian Zhang College of Energy and Electrical Engineering College of Energy and Electrical Engineering School of Electric Power Engineering School of Electric Power Engineering School of Electric Power Engineering Wind speed correlation, time variation of wind turbine generator’s forced outage rate (WTG FOR), and dependent failure of WTGs in adverse weather are three factors that affect reliability evaluation of wind integrated power systems. These three factors are related to weather conditions, which can be divided 12 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) into normal and adverse weather conditions. Although wind speed correlation has been well studied by researchers, the other two factors are not addressed in the existing reliability models of wind farms. A new enhanced reliability model of wind farms is proposed in this paper to effectively incorporate all of these factors. In the proposed model, WTGs are assumed to fail dependently in adverse weather, but independently in normal weather and the dependency of WTG FOR value on weather conditions is considered. Nataf transformation method (NTM) is chosen to simulate correlated random variables for correlated weather conditions, correlated wind speeds, and WTG dependent outages. In order to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model, a series of studies have been carried out on the IEEE RTS with two wind farms added. The results validate the effectiveness of the proposed wind farm model. of the calculation as well. However, this paper shows that there are characteristics in common with all FACTS controlled by voltage source converters (VSCs). In power flow calculation, each VSC converter can be equivalent to a contr-ollable voltage source in series with transformer impedance, and thus the power flow model of each kind of VSC FACTS devices can be described by the equations of all the equivalent branches accompanied with the topology of those branches. Based on Newton-Raphson (NR) algorithm theory, a general algorithm framework designed for new power flow calculation considering of multiple types of VSC FACTS has been presented. An open source power system simulation package named InterPSS is extended to realize the generality of the power flow calculation, and automatic differential (AD) technology is utilized to develop a function module to automatically generate the Jacobian matrix so as to avoid manual deduction. The calculation of power flow with VSC FACTS is tested in several IEEE sample systems to validate the correctness and efficiency of the method proposed in this paper. TuA04.17 Comparison of Simulation Methods of Spatially Correlated W ind Speeds pp. 255-261 Fan Chen Haitao Liu Jun Li Xiaolian Zhang TuA04.19 Simulation and Modeling of Blended Constant-frequency and Variable-frequency Air-conditioner pp. 269-273 Nanjing Institute of Technology Nanjing Institute of Technology Nanjing Institute of Technology Nanjing Institute of Technology Rongling Zhou Zhengli Zhang Xiaobo Liu Ping Ju Chuan Qin Qian Chen With the rapid development of wind power generation technologies, increasing wind power has been integrated into power systems. In order to study the impact of wind power uncertainties on power systems, efficient wind speed modeling and simulation methods are demanded. In this paper, the stochastic characteristics and spatially correlation of wind speeds of wind sites are presented. Then, three common wind speed simulation methods to generate spatially correlated wind speeds are compared, including Cholesky decomposition, Nataf transformation and Copula method. Further, the historical wind speeds of two wind sites in Netherland are used, and the performances of the three simulation methods are analyzed by some numerical tests. This paper provides guidance for the choosing of wind speed simulation methods in power system analysis. The conventional constant frequency airconditione-r (CFAC) and the inverter based variable-frequency air-conditioner (VFAC) are increasingly used now. The study of air-conditioner based load and its impact on power system is greatly demanded. In this paper, the characteristics of CFAC and VFAC are investigated, respectively. Then, a modeling method of blend-ed air-conditioner (BAC) load is proposed, and parameters of CFAC and VFAC are studied in detail. Later, the proposed model is tested in real power system. It is found that the characteristics of blended air-conditioner model is strongly related to the composition proportion of CFAC and VFAC, and they apparently affect power grids especially on voltage/reactive power issues. TuA04.18 A General Power Flow Calculation Method for Power Systems with VSC FACTS Based on InterPSS and Automatic Differentiation pp. 262-268 Zibin Yu Zhigang Wu Zijian Huang Suyun Wang Hohai University Hohai University Hohai University Hohai University Hohai University Hohai University TuA04.20 Solution of Probabilistic Load Flow in Power System Based on Non-intrusive Arbitrary Polynomial Chaos Theory pp. 274-279 South China University of Technology South China University of Technology South China University of Technology South China University of Technology Xue Li Haitao Wang Shaohua Zhang This paper presents a general approach to solve the power flow with multiple kinds of VSC FACTS installed in the same power system. Traditional power flow model should be different for each type of VSC FACTS, which will increase the complexity Shanghai University Shanghai University Shanghai University Non-intrusive arbitrary polynomial chaos theory (NIAPC) can overcome the defects of traditional methods which need abun- 13 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) dant simulations and time. Meanwhile, NIAPC can deal with probabilistic load flow analysis with arbitrary distributed uncertainties precisely with a small quantity of simulations. The paper presents the probabilistic load flow based on non-intrusive arbitrary polynomial. Firstly, the probabilistic collocation points are chosen. Then, Hermite polynomial is solved , and the uncertain problems whose parameters obey to experienced probability distribution are solved. Finally, the paper simulated the process of probabilistic load flow (PLF) on the platform of Matlab. The results were compared between NIAPC and Monte Carlo (MC). Results indicate that the PLF calculation based on NIAPC is not only able to achieve a high accuracy compared to the MC, but also it does own high potential to relief the computation burden of traditional PLF calculation drastically. Yue Xia TuA04.21 TuA04.23 A Probabilistic Equivalent Method of DFIGbased W ind Farm Based on Offline Calculations and Online Match pp. 280-284 Influence on Transmission Line Relay Protection under DFIG-based wind farm intergration pp. 290-295 Haiqiang Zhou Kanghui Gu Jingdong Han A dq0-domain synchronous machine model that is aimed at accurate and efficient simulation of electromagnetic and electromechanical transients in power electric networks is developed. The electromagnetic part of the machine model is derived firstly in the dq0 reference frame. Then, imaginary parts for the dq quantities are constructed to ensure the compatibility with external multi-scale network model. Finally, a multiscale companion model of synchronous machine is established to simulate diverse transients. The first benchmark case for subsynchronous resonance studies is studied, and a comparison of the results with those obtained from EMTP-type simulator verifies the accuracy and efficiency of the proposed machine model. Gao Feng Guan Zhe Zhang Shuang Zhang Jun Dou Jingming Hohai University Hohai University Hohai University The equivalent model of wind farm was changing when randomness and intermittent were taken into consideration. A probabilistic equivalent method of the DFIG-based wind farm is proposed in this paper. It was based on offline calculations and online match. Firstly, the equivalent method of the wind farm was discussed. It was assumed that the equivalent model consists of three type of equivalent DFIG. The structure of the equivalent model keeps unvaried whereas the parameters keep changing with the drifting of scenarios. The historical recorded scenarios are analyzed to get samples of the equivalent model. The representative samples are extracted through statistics and combinations with the three kind of typical equivalent DFIGs. The probability distribution function of each representative sample was also got by investigation. Then, a BP neural network with two hidden layers and six inputs was used in the wind power prediction. It was used in online match. The output of next moment was used in calculating to which degree the scenarios in the sample set match with the next scenario. The matching degrees were sorted and the most matched scenarios were chosen. Finally, this method was applied in the augmented IEEE 3-generator and 9 bus test system with wind farm connected in. It was shown that the wind farm equivalent model can be predicted and its probability is also given. It can reduce computation tasks effectively and solve the difficulty of wind farm equivalent when working conditions are changing. TuA04.24 Research on the interface algorithm of power system electromechanical-electromagnetic hybrid simulation pp. 296-300 DQ-domain Modeling for Multi-scale Transients in a Synchronous Machine pp. 285-289 Hui Zhang Ran Li Yunting Song Wenzhuo Liu Chinese Academy of Sciences Chinese Academy of Sciences November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Xi’an Jiaotong University Xi’an Jiaotong University Xi’an Jiaotong University Xi’an Jiaotong University Xi’an Jiaotong University In conventional wind farm outgoing line protections, the fault characteristics of wind farms have been rarely considered and thus the protections may mal-operate or refusal-operation due to the integration of large-scale wind power. This paper analyzes fault characteristics of the outgoing transmission line from a DFIG-based wind farm with LVRT capability and indicates that the main frequency component of the wind farm side short-circuit current varies with the speed of wind turbine generators, while the main frequency component of the wind farm side bus voltage still maintains the power frequency during a non-bolted-three-phase fault in the outgoing transmission line. Performances of directional protection based on the positive sequence voltage and current power frequency ,the distance element using the power frequency voltage current ratio to measure fault distance, and the fault-type element which uses the sequence current or phase current differential mutation quantity are affected severely, while zero sequence current protection is affected to some degrees. Performances of those two algorithms are analyzed and compared on the PSCAD/EMTDC platform. TuA04.22 Hua Ye Yanan Tang Technische Universit¨at Berlin North China Electric Power University North China Electric Power University China Electric Power Research Institute China Electric Power Research Institute With the increase of the number and capacity of HVDC, the 14 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) influence of HVDC system on AC power network is more and more complex. Electromechanical transient simulation and electromagnetic transient simulation cannot meet the requirements of HVDC system study in large power grid. Therefore, research on power system electromechanical-electromagne-tic hybrid simulation has very important significance. In this paper, we improve the algorithm of the interface based on the PSD-PSModel hybrid simulation. The optimization curve fitting algorithm based on FFT is proposed to improve the accuracy of the algorithm. The test method of interface algorithm is proposed, and the practical conclusion of PSD-PSModel interface is obtained. tween paralleled lines. In order to analyze the reason of unbalanced current in a 220kV short line in Jiangxi Grid, the paper made equivalent grid network using PSASP and modeled the double-circuit transmission line by EMTP. Then unbalanced currents of different working conditions were simulated by EMTP. The results revealed that the adjustments of bundle spacing of each conductor, the reduction of the three-phase load imbalance, the rational arrangements of phase sequence and the reasonable choices of operation mode could constrain the unbalance current effectively. TuA04.27 TuA04.25 Fault Transient Simulation Analysis for HVDC Transmission Lines pp. 312-317 Modeling of Electric Vehicle Loads Applicable to Power System Quasi-Steady State Analysis pp. 301-305 Yingle Fan Hengxu Zhang Fang Shi Luhua Xing Dong Yang Dandan Zhang Wenbo Li Qing Chen Shandong University Shandong University Shandong University Fault transient analysis plays an important role in protection and fault location research for high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission lines. Fault transient simulation methods and analysis for HVDC transmission lines are detailed presented in this paper, to avoid repetitive tasks and waste of research efforts. Influences of the control system, operation modes and direct current (DC) filter links on the fault transient simulation analysis for HVDC transmission lines are discussed. Transient characteristics of voltages and currents on HVDC transmission lines for faults on HVDC transmission lines, lightning strokes and commutation failures are analyzed, and corresponding simulation methods are also given. Electric vehicles (EVs) are new power loads of power systems. It is important to model the charging process of EVs in power system numerical simulation. This paper proposes a methodology for modeling of EV loads applicable to power flow calculation and other quasi-steady state analysis. The numerical methodology of EV load modeling is expounded from the DC and the AC side of charging EVs. In the DC side, the constant current and the constant voltage charging processes are considered. In the AC side, the changes of the charging efficiency and power factor versus the AC frequency and voltage are analyzed. Based on the current EV market status and the development trends, four types of EV load models are calculated using this methodology. The EV load modeling methodology considers EV quantities, initial state-of-charge distributions, load change processes during charging and the effect of grid side parameters. TuA04.28 The Simulation of the Static Frequency Converter in Pumped Storage Power Plant pp. 318-323 TuA04.26 Tao Zheng Xue Jiang Shuo Yu Analysis of Unbalanced Current in a 220kV Short double-circuit Line pp. 306-311 Jiangyuan Zhou Dahai You Shuilin Lu Zhan Shu Shandong Electric Power Research Institute Shandong Electric Power Research Institute Shandong Electric Power Research Institute Shandong Electric Power Research Institute Shandong University North China Electric Power University North China Electric Power University North China Electric Power University In the field of modern network, the static frequency converter start–up of the pumped storage unit is one of the important issues of research. The paper has analyzed and studied on the intermittent commutation stage, the natural commutation stage and the convergence problem of the two stages. Based on the principle of static frequency converter start-up, in the natural commutation, the control method of the inverter has been simplified according to the rotor position. Combined with some engineering practices, it has proposed the improved control strategy that the double-loop control could be inputted directly when the motor starts. Finally, the Matlab/Simulink has been used to build control model to verify the correctness of the improved method proposed in the paper. Huazhong University of Science and Technology Huazhong University of Science and Technology Huazhong University of Science and Technology Jiangxi Electric Power Research Institute With the growing electricity demands of the grid, more and more new power plants and substations have been connected to long transmission line through short lines, which results in current imbalance since that short lines are generally erected without transpositions and the inherent parameter asymmetry of them leads to the unbalanced electromagnetic coupling be- 15 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuA04.31 TuA04.29 Deepen Research on Electric Load Modelling pp. 334-339 A General Test Scheme for Electrical Measurement and Control Unit and Its Application pp. 324-328 Fei Wang Kui Wang Rui Wang Yuanyuan Geng Jing Xiao Wang Qi Yi Jun Zhao Bing Liu Liping Tang Yong Ministry of Education Shandong University Ministry of Education Shandong University Ministry of Education Shandong University Ministry of Education Shandong University State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company Maintenance Company Detailed procedures for the modelling of synthesis load of practical power network are presented; then based on the detailed investigation and statistics of load composition at 220 kV and 330 kV substations, the distribution of different kinds of load in domestic power grids are analyzed and the necessity of establishing the parameters of synthesis load model (SLM) suitable to actual power networks is pointed out; finally, the influence of SLM parameters on stability of interconnected power grids is researched. Research results show that it is crucially important for accurate analysis on power grid stability to choose appropriate load model and parameters. To improve the generality and flexibility of test scheme, a general digital and analog mixed test scheme, which is based on a computerized model and signal generator has been designed in this paper, the test scheme applies simulation software to produce any kind of digital test signal, which is then transferred to analog signal by signal generator to meet input requirements of the device under test. The measurement value of device under test can be compared with original input value to analyze the measurement precision under all conditions. A test example for PMU Light is given to describe the test process, and the test result shows that the test scheme proposed in this paper can produce any kinds of test signals, it is a general and flexible test means for electrical measurement and control unit with high accuracy. TuA04.32 AVC Testing Platform Design and Implementation for the Regional Power Grid Based on Advanced Digital Power System Simulator pp. 340-345 Yonghong Tang TuA04.30 Lin Xu Consistency Analysis of DFIG W ind Generation Models in PSS/E and PSASP pp. 329-333 Zhenchao Jiang Junyong Liu Xiaodong Shen Lixiong Xu Xiaoyan Sun Tao Fu Shandong University Hengxu Zhang Shandong University Changgang Li Shandong University Qingwen Xu Shandong University of Technology Xiaoming Liu State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company Ji Zhang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company Chao Qi State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company State Grid Sichuan Electric Power Research Institute State Grid Sichuan Electric Power Research Institute State Grid Sichuan Electric Power Research Institute Sichuan University Sichuan University Sichuan University Sichuan University The automatic voltage control (AVC) system provides real-time automatic control for the on-load transformer tap changer (OLTC) and capacitor/inductor banks, which is widely used for power system voltage monitoring and control in the regional grid. An advanced digital power system simulator (ADPSS)-based testing platform of the AVC controller is designed in this paper. The circuit model of the regional power grid is established, as well as the OLTC and the reactive power compensation devices. The data conversion interface is utilized for bidirectional data exchange from the remote meter and control signals between the ADPSS and the AVC system. The principle of the AVC voltage regulation and the ADPSS-based AVC testing platform are also introduced, followed by the data flow process of the OLTC and capacitor/inductor banks, which formulates the foundation for closed-loop testing of the AVC control system. To evaluate its rationality and availability, especially the effect of voltage regulation and control, an index system is established. Furthermore, functional modules of the assessment system and their implementation are presented. With rapid increase of wind power installed capacity, the operation mode of power system has changed greatly, it is necessary to include modeling and simulation based on wind turbines and farms. Numerical simulation plays a unique role in power system operation and control, and its accuracy turns out to be the focus of electric industry. PSASP and PSS/E, as two main sorts of simulation analysis software at home and abroad respectively, both enable wind turbines electromechanical transient simulation. In this paper, Detailed comparisons are made between Doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) in PSS/E and PSASP. Finally,simulative results of power system including the models are compared and analyzed. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China China Electric Power Research Institute China Electric Power Research Institute China Electric Power Research Institute China Electric Power Research Institute China Electric Power Research Institute 16 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Test results show that all the modules in the assessment system possess good operational robustness and can perform automatic voltage control well on continually varying real-time simulated data of regional grid. TuA04.35 Arc Grounding Model and Simulation in Non-effectively Grounded System pp. 358-362 TuA04.33 Fei Wang Houlei Gao Yong Sun Research on the User-Defined Modeling of HVDC Converter F iring Control Based on ADPSS/ETSDAC pp. 346-351 Linli Zhang Arc grounding faults appears in distribution system quite frequently. But the study of simulation model of the arc grounding is quite little. This paper mainly focused on the analysis of arc grounding process and proposed a new method theoretically to judge when and whether the arc should be off or renewed. There are two successive processes in zero off period of the arc: thermal breakdown process and electrical breakdown process. A method was proposed that use Mayr and Cassie model to simulate this two progress. And a simulation of arc model was built using the transient simulation tool PSCAD. After that, the simulation results are compared with theoretical analysis to verify the correctness of the model. In the end, this model was used to analyze the role of the Petersen coil in reducing the over-voltage caused by arc grounding fault. Kun Chen State Grid Hubei Electric Power Research Institute Bo Wen State Grid Hubei Electric Power Research Institute Xujiang Chen China Electric Power Research Institute Shiyun Zhang HUST Xianggen Yin HUST This paper has carried out a research on the user-defined modeling of the trigger control module of HVDC converter based on ADPSS/ETSDAC simulation platform is carried out in this paper. A detailed digital simulation model is also constructed. Firstly, an electromagnetic transient simulation model of the HVDC primary system is put up on the ADPSS/ETSDAC simulation platform. On this basis, user-defined method is applied to build simulation models of the module centered on the converter firing control, as well as its surrounding independent functional modules. The key function modules of the simulation model are analyzed in detail and the response curves are given. Finally, taking Longquan-Zhengping HVDC project as an example, this paper has compared and analyzed the DC line voltage and current waveforms obtained from the user-defined model and the actual HVDC project when instantaneous grounding faults occur on the DC line to show the validity and effectiveness of the user-defined model. TuA04.36 Comprehensive Evaluation of Smart Grid Technology based on TRLs pp. 363-368 Lin Liu Han Huang Wenjin Qi Qiming Zhao Xiaojun Li Hongjie Jia Yuan Zeng Yanli Liu TuA04.34 Generalized Load Modeling Based on the Improved Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm pp. 352-357 Jiangwen Yi Jianquan Zhu Shandong University Shandong University State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Institute State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Institute State Grid Energy Research Institute State Grid Energy Research Institute Tianjin University Tianjin University Tianjin University Tianjin University Tianjin University Tianjin University The application of advanced technologies is one of the key differences between smart grid and traditional grid. Its development and application will be through various periods and field of the construction of smart grid. This paper establishes a comprehensive evaluation index system for smart grid technology. The whole index system has the general characteristics, which can evaluate the technology itself from three aspects including technology performance, economy value, and social & environmental impact. Technical performance is evaluated by dividing hierarchy, while economic value and social & environmental impact are evaluated by the use of traditional hierarchical type index system. Two kinds of evaluation approaches in this paper have been effectively combined. Meanwhile considering some indexes may exist uncertainty when they are collected, probability theory is applied to analysis the uncertainty of the final result. The case result shows that the proposed method can provide reference comments for the continued development of the technology. South China University of Technology South China University of Technology On the basis of a large number of documents, an improved artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm is proposed, and then is applied in the generalized electrical load modeling in this paper. Firstly, an update replacement strategy of the worst nectars is presented by integrating the main principle of shuffled frog-leaping algorithm (SFLA) and ABC algorithm. In this way, the overall fitness of bee colonies is improved effectively, providing better optimizing performance as a result. Secondly, the structure of the generalized load model is given according to the impact of the distributed power to the load characteristic. The key problems such as the dynamic and static ratios, the difference between the rated and system capacities, and the initialization of motor are also analyzed in detail. Finally, the improved ABC is implied to the parameter identification of general. 17 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) hidden failures of line protection. First the evolvement of cascading failures is investigated which reveals that power flow transferring and hidden failures of line protection are significant for cascading failures. Then this paper uses event tree approach to analyze the process of cascading failures with multiple hidden failures of line protection and the probability of each failure sequence during the cascading process is calculated by Bayesian network. Finally, the simulation case on IEEE 30-bus shows the validity of the proposed method. TuA04.37 Frequency Spectrum Characteristic Analysis of Single-Phase Ground Fault in a Petersen-coil Grounded System pp. 369-374 Shuai Zhang Houlei Gao Mengqian Hou Yong Sun Zhimin Shao Jianxiu Li Shandong University Shandong University Shandong University State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Institute State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Institute State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Institute TuA04.39 On Static Load Model of Variable Frequency based Motor Drive pp. 380-385 Fangzhao Yu Qian Chen Xiaoyi Che Ping Ju Chuan Qin Yuqing Jin Hongyu Li This paper theoretically analyzes the frequency spectrum characteristics of the single-phase ground fault in a Petersen-coil grounded distribution network. Different equivalent circuits are analyzed for faults with low transition resistances and with high transition resistances, separately. The analysis concludes that the system makes a transition from an underdamped state to a damping state, and finally to another underdamped state with the increase of transition resistances. A distribution network model is built with PSCAD/EMTDC. Simulations are performed for different fault locations, different fault initial angles, different transition resistances and different cable proportions. The analysis in time domain and frequency domain is performed. Results show that the use of cables enables the main frequency of the fault current move towards lower frequency. Meanwhile, the amplitude of the fault current obviously increases due to the high capacitance to ground of cables. The transition resistance makes the biggest influence on the characteristic frequency band. Fault location mainly affects the zero sequence current main frequency amplitude. The further the fault location is away from the Bus, the little the amplitude of high-frequency component is. The transient capacitive current component increases, the transient inductive current component decreases and the high-frequency component amplitude increases with the increase of fault initial angles. Power electronics based energy-saving technology has being developed rapidly in recent years. It is an inevitable trend for traditional load devices to be upgraded with power electronics technology. For example, more and more motor drives, which occupies a large proportion in total power load, change from asynchronous motors to Variable Frequency (VF) motor drives. Thus, the actual features of electrical loads, which plays an important role in power system analysis, will have obvious difference than that of before. Firstly, the operation theory of VF motor drive is studied in this paper, and its detailed model is also established in simulation software. Then, the curves of dynamic response curves under the disturbances of voltage and frequency in power grid are obtained. Finally the parameters of the static model of VF motor drive are identified. TuA04.40 A Study on HVDC User-Defined Modeling in PSS/E pp. 386-391 TuA04.38 Study on Risk Assessment of Cascading Failures with Event Tree Approach and Bayesian Network pp. 375-379 Lin Zhu Ping Liu Lei Feng Yingguo Yang Feng Qian Rui Chen Donghui Zhang Xiaoming Jin Baorong Zhou Hailin Su Yuchuan Chen Lin Zhu South China University of Technology South China University of Technology South China University of Technology Guangdong Power Grid Power Dispatching Control Centre Guangdong Power Grid Power Dispatching Control Centre Guangdong Power Grid Power Dispatching Control Centre Electric Power Research Institute, CSG Electric Power Research Institute, CSG Electric Power Research Institute, CSG South China University of Technology South China University of Technology South China University of Technology Power System Simulator for Engineering (PSS/E) is one of the most extensively used power system simulation software in the globe. In this paper, by modeling a high-voltage direct-current (HVDC) transmission system, an in-depth study of its user-defined function in PSS/E is illustrated. Furthermore, comparing the simulation curves of user-defined HVDC in PSS/E with those simulated by PSCAD/EMTDC and PSD-BPA, the This paper proposes a new method to evaluate the operational risk of cascading failure in power systems considering multiple November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Hohai University Hohai University Chengdu Engineering Corporation Limited Hohai University Hohai University Hohai University Hohai University 18 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) correctness of the HVDC user-defined model, the feasibility as well as the practicability of PSS/E’s user-defined function are validated. Similarly, the modeling method proposed in this paper provides guidance for modeling of other complex two-terminal and multiport components applied to power systems. The experimental results prove the accuracy of the HVDC user-defined model as well as the practicability of the method, by which the feasibility of two-terminal component modeling in PSS/E is also verified. and efficiently solved to global optimality by using the available commercial software. Finally, case studies on IEEE 33-node test feeder are conducted and the results demonstrate the validity as well as effectiveness of the proposed model. TuA04.43 A Real-time Transient Simulator of Grid- connected Photovoltaic/Battery System Based on FPGA pp. 402-406 TuA04.41 Zhiwen Xie High-precision W ind Power Generation Model based on Actual W ind Farm pp. 392-396 Zhiying Wang Peng Li Chengdi Ding Zhengjun Bi Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Jilin Electric Power Company Limited Changzheng Gao Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Jilin Electric Power Company Limited A grid-connected photovoltaic (PV)/battery simulation system based on FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) is designed in real-time in this paper. It provides a simulation platform for hardware-in-loop test of physical devices. The simulation framework is designed and functional modules are introduced. The modeling of PV and battery is realized in a single FPGA chip. A typical PV/battery system is simulated in real time. The time step for electrical and control system is 1.096μs and 1.696μs. The simulation results are compared with PSCAD to validate the correctness and effectiveness of the design. The large-scale integration of wind power plays an increasingly important role in power systems. Accurate and effective modeling and simulation methods of wind power are urgently demanded. This paper studies the actual wind power generation over time, and proposes an electromagnetic transient model of wind power generation. Also, the hybrid transient (electromagnetic transient and electromechanical transient) programs are implemented with the consideration of the electromagnetic networks of wind-farm sides and electromechanical networks of Jilin-Grid sides, respectively. The proposed wind power generation model is verified through real measurement data. The proposed work is promising for the electromagnetic transient wind power integration research. TuA04.44 Simulation analysis of low voltage control in rural areas based on PSCAD pp. 407-412 TuA04.42 Beibei Zhang A Fast Modeling Method of Distribution System Reconfiguration Based on Mixed-integer Second-order Cone Programming pp. 397-401 Xiaoyun Huang Haoran Ji Peng Li Guanyu Song Jinli Zhao Foshan Power Supply Bureau Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Tianjin Univ. Tianjin Univ. State Grid Tianjin Economic Research Inst. Wen Lu Yulin Zhang Hongwei Du Foshan Power Supply Bureau Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Tianjin Univ. Tianjin Univ. Tianjin Univ. Tianjin Univ. NARI Tech. Co., Ltd NARI Group Corporation NARI Tech. Co., Ltd NARI Group Corporation NARI Tech.Co., Ltd NARI Group Corporation NARI Tech.Co., Ltd NARI Group Corporation In order to study the causes and treatment measures of low voltage in countryside distribution network, this paper takes a district of Hubei distribution network as an example, using the electromagnetic transient simulation software PSCAD to carry out a three-phase model, by adopting the combination of theoretical analysis and simulation modeling method researchmethods, completed the quantitative analysis of the factors influencing about the quality of voltage, breakdown and comprehensive control measures was given. The results will help the region according to their own input costs and voltage requirements to take appropriate management strategies. Network reconfiguration is a primary means of changing the operation mode of the distribution system with distributed generation. A model for the distribution system reconfiguration problem based on mixed-integer second-order cone programming is presented in this paper. Firstly, the network reconfiguration model is built to minimize the active power losses of distribution system with distributed generation. Then, some equivalent conversion and relaxation are presented to cast the initial mixed-integer nonlinear model above into a mixed-integer second-order cone model, which can be reliably 19 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuA04.45 TuA04.47 LabVIEW FPGA based Electromagnetic Transient Simulator Using Nodal Analysis Methods and State-space Analysis Methods pp. 413-417 Research into Probabilistic Representation of Electric Vehicle’s Charging Load and Its Effect to The Load Characteristics of The Network pp. 426-430 Can Huang Yao Xu Chad Harley Drew Masters Fangxing Li Yanning Li Jinguo Zhang The Univ. of Tennessee at Knoxville Lamar Univ. The Univ. of Tennessee at Knoxville The Univ. of Tennessee at Knoxville The Univ. of Tennessee at Knoxville Tsinghua Univ. State Grid Jiangsu maintenance company The uncertainty in the temporal and spatial distribution of electric vehicle’s (EV) charging load will directly affect the network’s load pattern and other operational characteristics. This paper analyses the key factors which can affect the EV’s charging load. Based on the data obtained from the EV charging terminals of a technology park in Beijing, the EV charging’s starting time, duration and charging power are analyzed in terms of their probability distribution and probability density function. EV load’s temporal and spatial probability representation and the charging load’s expected model are then analyzed. Using Beijing area’s summer load as a case study, the EV’s unregulated charging and its effect to the distribution network’s load characteristic is analyzed under different EV penetration levels. In the community of electric power systems, it is always desired to perform accurate and fast simulation, especially for transient studies. This brings great challenges to electromagnetic transient program (EMTP), and demands electromagnetic transient simulators with larger scale, higher speed, lower cost, and better expansibility and functionality. This paper briefly reviews the modeling and computing methods of EMTP, and analyzes the ongoing challenges and opportunities of EMTP simulators. Later, a new electromagnetic transient simulator is designed using multiple LabVIEW FPGAs. This simulator efficiently performs electromagnetic transient simulation with nodal analysis methods or state-space analysis methods, and presents the low-cost, easily expandable, and user-friendly programing advantages. TuA05.1 TuA04.46 Optimal Scheduling of Active Distribution Systems for Transregional Utilization of Renewable Energy pp. 431-436 Research and Implementation of the Simulation Model and Algorithm of Multi-terminal VSC-HVDC Transmission System in DTS pp. 418-425 Jinyue Shi Bo Zeng Yiyao Zhou Jianhua Zhang Xiong Zheng Xu Yang Wenhui Wei Shujin Zhou Yunjun Zhao Jihong Xia Zhengping Chen Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Co. Ltd Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Co. Ltd Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Co. Ltd Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Co. Ltd State GridFujian Electric Power Co In this study, the optimal operation of active distribution system (ADS) is investigated considering renewable energy harvest in cross regions under a multi-objective optimization framework. For this end, we first deduce the active/reactive capability of renewable distributed generation(RDG) units under the decoupled state. On this basis, a multi-objective model for ADS scheduling is developed, which considers the minimization of operation cost, renewable energy curtailment and network losses simultaneously. In this model,various types of distributed energy resources, including RDG,energy storage and interruptible loads are incorporated collectively, and the inter-temporal constraints that associated are especially accounted for. The proposed optimization problem is solved by the Multi-objective Harmony Search (MOHS)algorithm. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified on a modified 33-bus distribution system, and the necessity for incorporating reactive capability of renewable-based DG units is also revealed. Based on the part of DTS in smart grid dispatch control system, we have a research on steady-state simulation model of multi-terminal VSC-HVDC (Voltage Source Conveter-High Voltage Direct Current) and hybrid solution algorithm of AC/DC system, and propose the alternating solution algorithm based on the Newton-Raphson method in this paper. Finally, a simulation example is given, and the correctness and effectiveness of the proposed model and algorithm in this paper are verified by the results of example. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. 20 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) always need additional backup to mitigate the fluctuating power. This additional backup results in increased investment and operational costs. The V2G storage in such a situation can act as energy buffer and can supply the microgrid with balancing services at low costs. However the availability of the power from the V2G storage is also intermittent in nature because of the random plug-in pattern of electric vehicles. In this paper a microgrid containing a wind, PV and diesel generation and energy storage (V2G/fixed) is connected to an external grid. The external grid has the problem of capacity shortage. Because of the intermittent energy sources, a novel multi-objective stochastic chance constrained programming model is developed for the operational-planning of microgrid. The multiple objectives include the minimization the total net present cost and the operating hours of the diesel generation subject to constraints. The time series data for wind speed, solar radiation, V2G plug-in pattern and load fluctuation is estimated by using the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm,which is a Markov chain Monte Carlo Method. Due to the conflicting objectives, the non-dominant solutions are sorted out and presented using the Pareto front. The simulation results show confidence levels of provision of power by V2G storage and renewable energy sources. The results further show substantial economic implications of V2G storage on microgrid operation in terms of minimization of the total net present cost. TuA05.2 Optimal Capacity Expansion-Planning of Distributed Generation in Microgrids considering Uncertainties pp. 437-442 Asad Waqar Shaorong Wang Samir M. Dawoud Tao Tao Yida Wang Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. State Grid Hangzhou Electric Power Supply Company State Grid Hangzhou Electric Power Supply Company Capacity shortage problem extensively occurs in the developing countries. Microgrids comprising of distributed generation provides a solution to this capacity shortage problem.However an optimal capacity expansion-planning of the distributed generation in a microgrid is necessary to satisfy the load demand most economically. In current research the capacity expansion-planning of distributed generation like wind, solar,diesel generation along with energy storage is carried out considering the uncertainties associated with wind speed, solar radiation and load fluctuation. The account of uncertainties is very important as it results in a more reliable and robust planning model. These uncertainties are estimated by using their expected values based on the probability distributions and the autoregressive model is used to generate the scenarios. A stochastic optimization approach is used for optimal capacity expansion planning with multiple objectives including the minimization of the total net present cost, emissions and non-renewable fraction in the presence of constraints. A microgrid in grid-connected mode is utilized for the example problem. Because of the conflicting objectives, the non-dominant and most near to the optimal solutions are presented using the Pareto fronts. The results from both stochastic and deterministic optimization approaches are compared.The results support the investment and hence the capacity expansion. TuA05.4 The Planning of Distribution Network Containing Distributed Generators Based on Mixed Integer Linear Programming pp. 449-453 Jinyue Shi Ying Qiao Yingrui Wang Junqiang Wen Jingjing Tong Jianhua Zhang TuA05.3 Currently, the methods for solving the planning of distribution network (DN) are meta-heuristic algorithms whose computational efficiency is low and the results are not accurate. Therefore, this paper uses the advanced mixed integer linear programming (MILP) technology to model the multi-conductor DN planning containing the allocation of distributed generator(DG). Firstly, replace power flow calculation with an equivalent cone programming, then remove the product terms of binary and continuous variables, and finally use polyhedral models which are linear to approximate the planning model. In addition, as the siting and sizing of DG are added to the network planning, the situation that part of the loads are supplied by the DG separately perhaps appear thus leading to the appearance of loops. So the spanning tree (ST) constraints are introduced to the model to ensure the radiation of the DN. Finally, 23-node distribution system is used to simulate the above-mentioned model, and the results show the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed model. Multi-objective Chance Constrained Programming Model for Operational-Planning of V2G Integrated Microgrid pp. 443-448 Asad Waqar Huazhong Shaorong Wang Muhammad S. Khalid Xiaohan Shi North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Shandong Univ. This paper presents a novel chance constrained programming model for the operational-planning of a microgrid containing renewable energy sources like wind and solar, and vehicle to grid (V2G) storage. The model investigates the economic implications of the V2G storage on the microgrid operation.The microgrids consisting of intermittent renewable energy sources 21 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Haozhong Cheng Qi Zuo TuA05.5 Electric power network planning based on multi-object optimization model pp. 454-458 Linhao Ye As its sampling frequency is independent of the scale of the system, Monte-Carlo simulation is widely applied to reliability evaluation of generation and transmission system,which is a complex large system. However, it takes a relatively long period to obtain a higher accurate reliability index. This paper points out that, the combination of Importance sampling method and Discrete Latin Hypercube sampling method is able to reduce the variance of the sample space and uniformly sample it simultaneously, which improves the convergence of MonteCarlo simulation. Besides, the combination of sensitivity analysis and linear programming in the process of overload correction is able to guarantee the solution optimality as well as improve the solving speed. Finally, the practicability of the proposed algorithm is verified with the case study in IEEE RTS79 and RTS96. South China Univ. of Tech. Guangdong Power Grid Foshan Power Supply Bureau Aiming at solving network planning problems brought by multi-stage and multi-objection, in this paper, a multi-objective optimization method of network planning is proposed. Considering taking economy and reliability into account,with the objective function of the minimum cost of investment, the minimum annual operating costs of the system and the minimum lack of electricity costs, a general optimized model of multi-objective electric power network planning is presented. The hierarchical optimization model and hybrid genetic-simulated annealing algorithm is used to solve the problems emerging in the process of multi-objective planning. Case proves the effectiveness and scientifically of the proposed method and algorithm. TuA05.8 Reliability Evaluation of W ind Integrated Composite Power System Based on Third-Order Polynomial Normal Transformation pp. 472-477 TuA05.6 Weighted Cloud Prediction Model for Distribution Network Reliability pp. 459-464 Biyun Chen Liwen Qin Qingyu Wang, Shaonan Chen Bo Zhao Shanghai JiaoTong Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. Qinyong Zhou Hailei He Pingliang Zeng Taishan Yan Haozhong Cheng Libo Zhang, Guangxi Univ. Guangxi Univ. Guangxi Univ. Guangxi Univ. Guangxi Univ. China Electric Power Research Insti. China Electric Power Research Insti. China Electric Power Research Insti. Shanghai Univ. of Electric Power Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. To overcome the drawback that wind speed distribution is assumed in the reliability evaluation of wind farms integrated power system, the third-order polynomial normal transformation (TPNT) based non-sequential Monte Carlo simulation method, is proposed to evaluate the reliability of generation and transmission system incorporating wind farms in this paper. When historical data or distribution functions of wind speed are given, the relationship between wind speed distribution and standard normal distribution can be established with the TPNT.Then correlated wind speed samples, which are employed in the process of reliability evaluation, can be produced through TPNT and correlated normally distributed samples. The accuracy of TPNT to simulate variables and applicability of the proposed method were verified by case study. Based on that, impacts of wind farms on composite power system are studied from four aspects, including wind speed correlation, location, rate capacity and wind source intensity. Aiming at the difficulty of determining the exact topology of distribution network during long-term reliability evaluation, a weighted cloud prediction model is proposed to predict the reliability of distribution network in long-term planning. Firstly, the digital features of cloud model of the influencing factors are obtained from the statistical historical data by an improved backward cloud generator. Secondly, based on the above digital features, the average weighted cloud prediction model are set up where the weight of each influencing factor is calculated by analytic hierarchy process according to the sensitivity of the influencing factors on reliability. Finally, the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed method is demonstrated by comparison with the traditional cloud prediction method and the least square support vector machine method from the indices of maximum, minimum and average error. TuA05.7 TuA05.9 Reliability Evaluation based on Modified Latin Hypercube Sampling and Minimum Load-Cutting Method pp. 465-471 A Comprehensive Energy Saving Potential Evaluation Method for the Distribution Networks pp. 478-481 Hailei He Qinyong Zhou Tengfei Sun Biyun Chen Tangshan Cui Lei Ye Cuizhen Li China Electric Power Search Inst. China Electric Power Search Inst. Shanghai JiaoTong Univ. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China 22 Guangxi Univ. Guangxi Univ. Guangxi Univ. Guangxi Univ. The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) The construction projects for distribution networks require good economy besides energy saving and voltage quality improvement. Thus the line loss rate and voltage qualification rate are the main assessment indices of construction projects for distribution networks. This paper proposes a comprehensive energy saving potential (ESP) evaluation system for distribution networks. The above basic indices and comprehensive ESP indices for each selected feeder are calculated under different improvement measures. Firstly, typical feeders are modeled using Power Factory software. Then power flow for distribution networks is calculated and weak networks can be found. Secondly,improvement measures for typical feeders can be chosen based on weak networks analysis to achieve the purpose of reducing the power loss rate. Thirdly, the paper gives the definition of loss reduction rate, voltage improvement rate and economic benefits.Furthermore, the implementation order of the measures is optimized according to the value of comprehensive ESP indices and the difficulty extent of implementation. The investment cost and the transformation effect are considered simultaneously for planning. Four measures which include replacing high-loss transformers and worn conductors, adding reactive power compensation devices and adjusting bus voltage are carried out on the IEEE 33-bus test system. The results of simulation calculation demonstrate the validity and superiority of the proposed system. TuA05.11 Reactive Power Optimization Based on Modified Membrane Computing for Distribution Network with Electric Vehicles And W ind Power Generat i on pp. 488-493 Siyuan Wang Yongjie Lv Shuying Ding Xiangyan Xie Zhuyun Li Hongjian Wu The rapid development of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles and renewable generation brings new challenges to the secure and economic operation of power systems. A reactive power optimization model based minimizing network loss is established, considering electric vehicle stochastic charging /discharging and uncertain outputs of wind turbines. To improve the accuracy and global searching capability, The modified membrane computing (MMC) based communication rule, cross transposition rule and mutation rewrite rule is proposed. Finally,the modified IEEE-33 nodes system is simulated through the proposed algorithm and general GA. The effectiveness and correctness of the proposed method and model are verified. TuA05.10 TuA05.12 The Whole-process Reliability Evaluation of Power System Including Generation, Transmission,Transformation and Distribution pp. 482-487 Biyun Chen Qianyi Chen Jinan Power Supply Company, State Grid Jinan Power Supply Company, State Grid inan Power Supply Company, State Grid Jinan Power Supply Company, State Grid Xihua University Xihua University A Method of Evaluating the Transfer Capacity for Power System Considering of the Power Injection and the Power Grid Topology pp. 494-499 Guangxi Univ. Guangxi Univ. Suyun Wang Zhigang Wu Zibin Yu Baorong Zhou Aiming at the problem that using current reliability evaluation indices, which can reflect only one segment of power system, for power system planning leads to partial planning results and is hard to achieve the goal of global programming,this paper proposes an approach to evaluate the reliability of the entire power system, considering the effect of generation, transmission, transformation and distribution system. The power supply reliability not only depends on the structure of the distribution system, but also on the main grid. In the proposed evaluation procedure electrical connection of substation is firstly equated to some equivalent branches based on minimal cut-set method. Then Monte Carlo Simulation (MCS) is used to assess the reliability of generation and transmission composite system and substation system simultaneously by sampling and to obtain hierarchical available capacities and probabilities. Finally, the hierarchical reliability indices of the main grid are used as multistate equivalent sources to assess the distribution system reliability. The proposed method is tested using a system constituted by the IEEE RTS 79 and feeder of IEEE RBTS-bus6. The results show that the main grid has obvious influence on the reliability of distribution system, and the proposed method can provide more details for system planning and operation. South China Univ. of Tech. South China Univ. of Tech. South China Univ. of Tech. Southern Power Grid The transfer capacity is a varying value for a certain power system, which may be changed with the evolution of the system. Although the topology of a power system is usually designed in an optimizing way to maximize the transfer capability, the capability itself will be inevitably weaken because of a time lag between the increasing load and the enhancement of grid topology. Due to the lack of qualification tools to deal with the varying transfer capability, related topics are seldom to be discussed. This paper proposes a new method to evaluate the transfer capacity, in which the mechanism describing the mismatch can be boiled down to a new index named Spatial Characteristic Length Ratio (SCLR) considering of both the power injection and the power grid topology. By calculating the index SCLR, the transfer capability as well as the factors affecting it can be analyzed, which has an important meaning for power grid planning personnel. The method is used to analyze the transfer capacity of IEEE 4-node system, IEEE 9-node system and IEEE 162-node system, each under different modes of operation. Calculation results has proved the validity of this concept, and the related method is effective. 23 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuA05.13 TuA05.15 Transmission Network Expansion Planning Based on Coordinated Economy and Security pp. 500-505 Research on the Topology of DC Distribution Network and the Influence of Distributed Generations Access to the Network pp. 512-517 Taishan Yan Libo Zhang Haozhong Cheng Hailei He Qinyong Zhou Pingliang Zeng Shanghai Univ. of Electric Power Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. China Electric Power Research Insti. China Electric Power Research Insti. China Electric Power Research Insti. Tianhao Liu Gengyin Li Bing Han Dongdong Zhang Singirankabo Youssouf Transmission network expansion planning (TNEP) is a key component of power system planning. Two important aspects to be considered in TNEP are economy and security factors, which are always contradictory and affect the benefits of both investment and power demand side, so the balance between these two factors needs to be focused. In this paper, a TNEP model based on coordinated economy and security is proposed so as to reconcile these two contradictory factors. The objective function of proposed TNEP model is to minimize the annual synthetic cost of transmission system, which contains investment cost,operation cost, maintenance cost and load shedding cost. The annual synthetic cost of transmission system is calculated with multistep load model established by load clustering using improved K-means algorithm. Then, an improved niche genetic algorithm is utilized to solve the TNEP model and an optimal scheme is obtained. Furthermore, the applicability and effectiveness of proposed TNEP model and algorithm are verified by case study on IEEE 24-bus system. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. Recent years the research of DC power distribution network is getting more and more attention which mainly focus on the technical and economic analysis, power conversion technology, control and protection technology aspects. In this paper we calculate the DC distribution network line loss and the voltage unbalanced distribution by DC flow calculation analysis under different topologies. According to the simulation results of steady state power flow of DC power distribution network, we analysis the influence of the distributed generations and network structure on the voltage distribution and network loss. The results show that the structure of the DC distribution network directly affects the network loss and the unbalance of voltage distribution, and the mesh structure can improve the absorptive capacity of the distributed generations. Access points’ numbers and capacity of DGs can also influence both of network loss and unbalance voltage distribution. TuA05.16 TuA05.14 The Coordinate Evaluation of Grid Based on Power Import and Export Capacity pp. 518-522 A Peak Load Regulation Scheme for Hubei Power Grid with UHVDC Integration pp. 506-511 Ni Zeng Mei Li Buhan Zhang Ruoxi Zhu Minwei Wang Shuang Zhao Chengxiong Mao Wangcheng Long Hui Li Jinyu Xiao Dong Peng Xiao Wang PengFei Zhang Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. The coordinate evaluation of grid is about the matching degree between capacity of power import and export for a level grid, it is important to power network planning. Considering the power transmission direct, the definition of equivalent import capacity and the equivalent export one are proposed,the import one includes generation, DC converter station, tie line,step-up substation and so on, uniformly, the export one includes direct load capacity, step-down substation and so on. The coordinate evaluation criterion is present based on Code about power system. Finally, a provincial power grid is used to demonstrate the calculation of equivalent import capacity and equivalent export one , and the coordinate of the provincial power grid is analyzed based on the evaluation criterion. Under the background of transmitting thermal power via UHV transmission line from Mengxi to Hubei in the long-term planning, this paper analyzed Hubei power grid’s peak load regulation scheme which Mengxi UHVDC involved in.Based on the energy-efficient power generation scheduling approach and multiple constraints of units, a peak load regulation scheme under the coordinated operation of thermal power, hydropower, pumped-storage and UHVDC power in a calculating level year was given. It is indicated that the peak regulation capacity shortage problem in Hubei is solved effectively with Mengxi UHVDC integration. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China State Power Economic Research Inst. State Power Economic Research Inst. State Power Economic Research Insti. State Power Economic Research Inst. State Power Economic Research Inst. State Grid Corporation of China 24 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) straint. The particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm and MonteCarlo simulation method is used to solve the optimization problem. Taking a regional power network as an example, Power System Analysis Software Package (PSASP ) is used to carry out transient and steady stability verification for the extreme scenario, and contingency plans for the accidents which is not satisfied with the verification requirement must be worked out to ensure the safe and stable operation of the network. TuA05.17 A Multi-Stage Generator Reconfiguration Method for Relieving Transmission Congestion pp. 523-526 Yudong Tan Zhisheng Xu Bing Huang Yong Li Yi Tan State Grid Hunan Economy & Tech. Research Inst. State Grid Hunan Economy & Tech. Research Inst. Hunan University. Hunan University Hunan University TuA05.19 Comprehensive Risk Assessment Method of Power Planning Scheme Considering Natural Disasters pp. 532-537 A reduced-voltage operation scheme of generator unit is proposed to relieve transmission congestion of 500 kV/220 kV power grids. First, the initial generator reconfiguration schemes are obtained according to voltage levels of generators connected to power grids and the matching degree between loads and generator capacity. Then, a comprehensive evaluation index is proposed by considering network loss, over-load rate, voltage deviation rate and static voltage margin. This index is used for the ranking of the above initial schemes. By N-1 analysis, the final scheme is determined. The case study on the eastern grid of Hunan province is used to validate the proposed method. Hailei He Qinyong Zhou Qi Zuo Jun Zhong In order to hedge the small-probability high-risk events which power system may face against, it is essential to consider the impact of natural disasters in the power system planning stage. First, this paper establishes the component damage probability model under natural disasters. Second, the system risk assessment based on analytical method is discussed, and the indicators and algorithm for rapid line risk identification are proposed to alleviate the computation burden of the analytical method. Finally, a comprehensive risk assessment method considering natural disaster is proposed based on PSD-BPA transient stability program. The case study performed in the actual systems verifies that the proposed indicators and method are accurate and effective. TuA05.18 A Planning Method for Siting and Sizing of Distributed Generation Based on Chance-constrainedProgramming pp. 527-531 Zhaoxia Sun Weiwei Li Jinfeng Zhu Qiangmin Liu Tianci Liu China Electric Power Research Insti. China Electric Power Research Insti. North China Electric Power Univ. Chongqing Univ. Suizhou Power Supply Company State Grid Hubei Electric Power Corporation Suizhou Power Supply Company State Grid Hubei Electric Power Corporation Suizhou Power Supply Company State Grid Hubei Electric Power Corporation Suizhou Power Supply Company State Grid Hubei Electric Power Corporation Suizhou Power Supply Company State Grid Hubei Electric Power Corporation TuA05.20 Risk-based Transmission Lines Importance Calculation under Ice Storm Weather pp. 538-542 Yushen Hou Xiuli Wang Zechen Wu Zece Zhang With the increasing of the new energy’s permeability in the regional power network, the inherent characteristics of new energy output bring new challenges to the power network planning. In order to solve the problem that the traditional distribution network planning is too conservative for the new energy planning, a planning method for siting and sizing of distributed generation (DG ) based on Chance-constrained programming is proposed in this paper. The method provides an approach to calculate the new energy’s maximum installation capability and the optimal installation site for regional power network Basing on the analysis of stochastic models of wind power, solar output and load, the planning model has the objective function of maximizing renewable energy utilization with the considering of several constraint conditions such as node voltage constraint and branch transmission power con- Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. A risk-based transmission lines importance calculation method is proposed under ice storm to identify the importance of icing lines to system operation in this paper. The model of forced outage rate of icing line is established by load-strength interference theory. Then risk functions of demand not supplied and power failures are established. The concept of transmission lines’ global sensitivity of risk functions is proposed to quantify the influence of icing lines to system operation by analysis of variance decomposition. The quasi-Monte Carlo method based on Sobol’ sequence is used to calculate global sensitivity of icing lines. The proposed method is tested on the system of IEEE RTS79. The results show that different lines have various importance to system risk and the importance sorting of icing lines could be a feasible tool to help arrange the deicing work. 25 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) single index and multiple weights respectively. Three comprehensive evaluation methods including Delphi, Entropy weight method,grey relational analysis (GRA), which will help decision makers master and deal with the sensitive indexes and weights more carefully in the decision-making process. Secondly, this paper takes comprehensive evaluation values of each alternative obtained by each comprehensive evaluation method with the change of index values and index weights as sample data respectively,and introduces cloud model to compare the robustness of decision-making results under each comprehensive evaluation method in order to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each comprehensive evaluation method, this will help decision makers choose the comprehensive evaluation method with better robustness of decision result. Finally the example analysis results verify the effectiveness of the method proposed in this paper, so as to gain insight into the sensitivity analysis of decision problem and relate it back to real engineering application. TuA05.21 Composite Power System Risk Assessment and Weak Links Identification Considering Cascading Failures pp. 543-548 Chunzheng Tian Yulong Zhou Yuanyuan Wang Jianxue Wang State Grid Henan Economic Research Insti. Xi'an Jiaotong Univ. State Grid Henan Economic Research Insti. Xi'an Jiaotong Univ. Blackouts generally stem from cascading failures in power system operation. Their diminution requires very much the development of approaches and algorithms that analyze cas-cading failure risk and identify weak links of power system. Different from optimal load shedding model widely used in conventional risk assessment, this paper considers the impact of cascading failures on power system, and adopts a practical re-dispatch model. A fault chain model is established to better describe the propagation process of cascading failures and to calculate the occurrence probability of cascading failures quantitatively. To better understand how cascading failures propagate and to effectively identify weak links that are crucial for cascading failure propagation, this paper proposes the index called “risk participation factor” to measure the effect of branches on the reliability level of power system. Besides, Monte Carlo simulation method is applied to assess these indices. The proposed cascading failures model and fault chain model are validated on the IEEE 39-bus system. Results show that the proposed model that considers the propagation of cascading failures can provide more weak links information for power system planning and operation. TuA05.23 The Stability Study and Simulation Analysis on Multi–infeed AC–DC Hybrid Power System pp. 557-562 Weiwei Zhao Shunxin Li Lihan Qin Yichen Huang It is planned that several ultra–large–scale multi–infeed AC–DC hybrid power systems would be built in China by 2018. In multi–infeed AC–DC hybrid power systems, since AC–DC transmission lines are in parallel operation and the electrical distances between many DC converters are very short, there will be interactions between AC–DC hybrid power systems. And this will bring new challenges to the operating characteristics analysis and stability control strategy of multi–infeed AC–DC hybrid power systems. This paper begins with discussing complicated the interactions between AC–DC systems and the interactions between DC systems in the multi–infeed DC transmission system,and outlining the studies on researches of commutation failure of multi–infeed AC–DC hybrid power system, DC system failure recovery, the power angle / voltage stability problems, and etc.This paper sets up two indicators, namely Multi–infeed Short Circuit Ratio and Multi–infeed Interaction Factor, to measure the interaction extent between the AC power systems and its connected DC power systems. Then, the paper introduces the principle of emergency DC power support and the support strategy of DC power increase and fallback. Next, the paper takes the Jibei Power Grid, which is planned for 2018, as an example, using PSD simulation program to simulate and calculate the stability conditions of Jibei Multi–infeed AC–DC hybrid power system. In the end, the paper proposes the technical solutions for the structure enhancement of AC systems and the additional stability control strategy of DC systems, and etc., according to the simulation results. TuA05.22 Sensitivity Analysis for Decision-making of UHV Long Distance Power Transmission Site Selection under Uncertainty Based on Cloud Model pp. 549-556 Weigang Jin Yong Li Xue Lin Xiaoyun Guo Xue Cui Huijin Liu Jiangpeng Fan Central China Branch of State Grid Corporation of China Central China Branch of State Grid Corporation of China Wuhan Univ. Wuhan Univ. Wuhan Univ. Wuhan Univ. Wuhan Univ. The selection of Ultra-High Voltage (UHV) substation site is a complex multi-objective decision-making problem.The randomness of wind power output and continuous adjustment of the grid structure will bring uncertain factors to the decision-making process, which will directly affect the stability of decision-making result. Therefore, the sensitivity analysis is necessary to be carried out to the uncertainty of index values and index weights in the decision-making process. Firstly, this paper carries out the sensitivity analysis under the change of November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China State Grid Jibei Electric Power Economic Research Inst. State Grid Jibei Electric Power Economic Research Inst. State Grid Jibei Electric Power Economic Research Inst. State Grid Jibei Electric Power Economic Research Inst. 26 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuA05.24 TuA05.26 Study on Renewable Energy Integration Influence and Accommodation Capability in Regional Power Grid pp. 563-568 A Risk Assessment Approach for Power System Based on a Comprehensive Fault Probabilistic Model pp. 574-577 Youjun Zhang Ting Zhao Dongxu Lu Dong Wang Yuan Zeng anli Liu Linjun Wei Jing Li State Nuclear Electric Power Planning Design & Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. State Nuclear Electric Power Planning Design & Research Inst. Wind power and photovoltaic (PV) power generation is currently scale developing with high speed in China. Due to the uncertainty of wind power and PV power output, more reserve and balance capacity is additional necessary caused by large scale wind power and PV power integration, which bring a challenge on the accommodation, accessing options, sending out channel of the large scale of renewable energy. Development scale renewable energy is studied in this paper based on considering government planning and preliminary progress. Evaluation method of renewable energy generation capability is submitted to analyze characteristic of wind and PV power. The method of sequential production simulation based on random unit commitment is presented to simulate daily operation of power system. Accommodation capability of renewable energy integrated into power grid is study based on considering the layout of flexible and traditional power resource. Traditional risk assessment methods focus on the power network side while ignoring the impacts of the information system. A risk assessment approach for power system based on a comprehensive fault probabilistic model is proposed. The risk factors of the information system are considered in the model.Overload and voltage violation risk indices are adopted. The risk indices thus gained can be used to help operators and the planners to monitor the system, and make a more credible plan. The correctness of the proposed approach is validated by IEEE-118 bus test system. TuA05.27 The Research on the Planning Model of Rural Distribution Network Containing Diversification Loads pp. 578-582 TuA05.25 Investment Allocation Model Based on Gini Coefficient and Its Application to Electric Power Subsidiaries pp. 569-573 Fuqiang Zhang Hui Luo Meizhao Liu Nana Li Dong Zhang State Grid Smart Grid Inst. Tianjin Univ. Tianjin Univ. Tianjin Univ. Tianjin Univ. Fuchun Zhang Kexue Liu Qi Zhang Bo Tian Wenjun Li Lihan Qin State Grid Energy Research Inst. JiangSu Electric Power Company JiangSu Electric Power Company State Grid Energy Research Inst. State Grid Energy Research Inst. Qinhuangdao power supply company Qinhuangdao power supply company Qinhuangdao power supply company Qinhuangdao power supply company Qinhuangdao power supply company Jibei Economic and Tech .Research Inst. The accession of diversification loads containing DG and electric vehicles charging stations into distribution network has an important impact on the distribution network planning and operation. This paper proposes a planning model of rural distribution network containing diversification loads, which can realize the integrated optimization planning including the location and sizing of DG, charging station location and capacity,distributed network frame construction and renovation. Taking the diversification loads into account, and selecting the minimum costs of investment, operation and environment as the objective,the paper establishes the planning model of rural distribution network containing diversification loads. The simulation results show the model can improve the economic and environmental benefits. In this paper, Gini coefficient is introduced into the allocation of investments in electric power subsidiaries. First,three indicators including the return on total assets, future forecasted electricity consumption and the investment to electricity sales ratio are used to determine the initial allocation scheme of future grid investment in subsidiaries. The initial scheme ensures benefits (efficiency) priority. Then, control indicators such as the capacity-load ratio, power grid reliability are used in designing investment allocation model based on the Gini coefficient. The proposed model optimizes the initial allocation scheme from the perspective of improving the fairness. Finally, a provincial electric power company in China is taken as an example to verify the feasibility of the proposed model. 27 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuA05.28 TuA05.30 Research on the Distribution Network Planning with Multiple Loads pp. 583-586 Optimal Planning of W ind and PV Capacity in Provincial Power Systems Based on Two-Stage Optimization Algorithm pp. 593-598 Xinghua Don Kexue Liu Bo Tian Zhongshu Hu Kai Zhang Youzhong Miao State Grid Qinhuangdao power supply company State Grid Qinhuangdao power supply company State Grid Qinhuangdao power supply company State Grid Qinhuangdao power supply company State Grid Qinhuangdao power supply company Jibei development and planning department Yue Yuan Yang Cao Jingjing Zhou Jiangmin Bao With the rapid development of wind power and photovoltaic (PV) power industry, the curtailment of wind power or PV power in ‘Three North’ areas is serious, due to their short planning and construction time period, as well as being disjoined with the regional generation and grid plan. A novel formulation based on two-stage optimization under low-carbon economy is proposed in present paper to optimize the proportion of wind and PV capacity for provincial power systems, in which, carbon emissions of generator units and features of renewable resources are all taken into account. In the lower-level formulation, a time-sequence production simulation (TSPS) model that is suitable for actual power system has been adopted. In order to maximize benefits of energy-saving and emissions reduction resulted from renewable power generation, General Algebraic Modeling System (GAMS), a commercial software, is employed to optimize the annual operation of the power system. In the upper-level formulation, a hybrid bacterial foraging algorithm and particle swarm optimization (BFAPSO) algorithm is utilized to optimize the proportion of wind and PV capacity. The objective of the upper-level formulation is to maximize benefits of energy conservation and carbon emissions reductions optimized in the lower-level problem. Simulation results in practical provincial power systems validate the proposed model and corresponding solving algorithms. The optimization results can provide support to policy makers to make renewable energy related policies. Based on the different demands of distribution network planning, the paper establishes the economic model of distribution network planning with multiple loads. In the paper,different factors, which include the expenses of line construction and operation, the generating expenses of multiple loads and the power purchase cost, are considered in the objective function.Then, by using the genetic algorithm (GA), the capacity and location of the multiple loads are analyzed. In the end, for an example of a real distribution network, the feasibility of the algorithm is verified. TuA05.29 Two-step Optimization and Decision Model for Opening Electromagnetic Loops pp. 587-592 Xue Xia North China Electric Power Research Insti. Co., Ltd State Grid Jibei Electric Power Company Limited Dong Yang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. TuA05.31 In order to improve the grid safety and stability, we put forward a two-step optimization and decision method for opening electromagnetic loop circuits. Firstly, several parts from the low voltage level network are separated in the electromagnetic loop circuit using the GN dividing algorithm and complex network theory according to the distribution of center stations and the characteristics of network structures. The scheme set for opening electromagnetic loop circuits is generated in accordance with the sequence that every part separated from the network in the dividing process. Then, aiming at the contradiction between improving the system stability and limiting the short circuit current, a comprehensive evaluation model based on the analytic hierarchy process is built. The systematic and quantitative assessments on opening electromagnetic loop circuits are realized by the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation algorithm. Case studies verify the effectiveness of the proposed strategy. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Hohai Univ. Hohai Univ. Hohai Univ. Hohai Univ. Research on Probabilistic Load Flow Method based on Point Estimation and Dimension Reduction by Dominated Variables pp. 599-603 Yuanbing Xiao Haozhong Cheng Ting Lei Shenxi Zhang Weijie Luan Di Yang Shanghai Univ. of Electric Power Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. State Grid Shanghai Municipal Electric Power Company Shanghai JiaoTong Univ. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. There are many uncertain factors such as the random fluctuations of load, equipment failure out of operation and the outage of distributed generation changes with the climate in power system operation, probabilistic load Flow method gets more attention. Meanwhile, with the system scale increase, the computational efficiency limits the application of probabilistic load 28 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) flow (PLF). Therefore, in this paper, a dominated variables based point estimation method is proposed. A dimension reduction method is also depicted. And the point estimation samples are transformed into arbitrary correlated distribution by polynomial normal transformation and singular value decomposition. Then the calculation of PLF is transformed into several deterministic power flow calculation. Simulation on IEEE 118 bus system demonstrates the validity of the proposed method. The results show that proposed method can enhance the computational efficiency of point estimation evidently. And the utilization of singular value decomposition can easily handle the non-negative definite correlation matrix. simulate charging demand of the electric vehicle . the models are structured based on the bi-level programming, the upper level model which aims at minimizing the sum of investment costs of investment operators and charging costs of electric vehicle users, the lower level model which aims at maximum the captured traffic flow. Imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA) and integer programming algorithm are applied to solve the upper and lower level model of the bi-level programming model, respectively. The case study shows that the proposed model and method for the charging stations planning is reasonable and effective. TuA06.1 TuA05.32 A Reactive Power Compensation Method Based on Tracing the Power Flow and Loss Function of Power System Application of Cuckoo Search Algorithm in Power Network Planning pp. 604-608 Shuxin Tian Haozhong Cheng Libo Zhang Shaoyun Hong Tengfei Sun Lu Liu Pingliang Zeng pp. 615-619 Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. China Electric Power Research Inst. Ke nan Yang Yiyu Gong Pu Zhang Zhaoyan Liu Cuckoo Search algorithm is a new bio-inspired algorithm, which describes cuckoo’s foraging behavior based on parasitized breeding mechanism of cuckoo’s egg and Lévy flight search principle. Cuckoo Search algorithm can explore solution space as much as possible and jump out the local best flexibility. Combined with truncation and rounding theory, Cuckoo Search algorithm is improved to apply to power network planning, which is introduced to solve power network chance-constrained integer planning model and search the global optimal solution. The effectiveness and feasibility of the improved Cuckoo Search algorithm solving power network planning model are verified by taking 77-bus system as computational examples. Compared with particle swarm optimization algorithm and genetic algorithm, the proposed algorithm has less parameters and more powerful ability of global searching. This paper proposes a new method for locating and sizing of reactive power compensation of power system. The proposed method is based on the reactive power flow tracing. Defines the power loss distribution coefficient, which has direct response distribution of reactive power sources with clear physical concepts. Utilize this new factor to determine the points of compensation. Calculate the second order loss sensitivity, combined with the principle of most economical operation, to determine the optimal capacity. Application of proposed method is useful for the optimization of reactive power distribution and the reduction of power loss. The simulation result of the IEEE 39-bus system shows the correctness and effectiveness of the proposed method. TuA06.2 TuA05.33 A Generation-Reserve Co-optimization Approach Considering W ind Power Cross-regional Accommodation Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Layout Research Based on Bi-level Programming pp. 609-614 Gang Zhang Hongming Yang Jinjun Dong Beijing Maintenance Company Beijing Electric Power Corporation Beijing Power Economic Research Inst. Beijing Electric Power Corporation Beijing Power Economic Research Inst. Beijing Electric Power Corporation Beijing Power Economic Research Inst. Beijing Electric Power Corporation pp. 620-625 Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. Mu Wang Ming Zhou Hongkun Bai Jiangbo Wang As public service infrastructure of the city, the locating and sizing of electric vehicle charging stations should be based on actual charging demand. Obtaining the path traffic flow via introducing the stochastic user equilibrium (SUE) assignment model, the size configuration method of charging stations is proposed by combining with the user travel behavior rules to North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. State Grid Henan Economic Research Inst. State Grid Henan Economic Research Inst. In recent years, the wind power industry of China has a rapid development. However, because of the uncertainty, randomness and fluctuation nature of wind power, the problem of its integration and accommodation has become the bottleneck of its sustainable development. Cross-regional accommodation 29 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) has emerged as an attractive and challenging research area due to the fact that wind energy resource is usually far away from load center and hard to be used locally. Thus, a generation reserve co-optimization dispatch method for wind power integrated power system considering cross-regional accommodation is proposed in this paper. Considering the prediction errors of wind power and load demand and also equipment failures, the reserve requirement for each area is calculated based on the theory of conditional value-at-risk. Further, generating units are scheduled optimally, and the geographical allocation and levels of the required reserves are determined taking into account interregional transmission line constraints. The aim of this paper is to promote the wind power accommodation in a larger spatial scale and also the system efficiency from both the economic and security point of view. The reasonableness and effectiveness of the constructed model is validated by case study. bility index lost of load probability (LOLP) and reliability index expected energy not served (EENS) deviate eachother. In this paper, unit commitment (UC) formulation is revised to optimize day-ahead generation schedule for those systems with high wind power penetration level. In the revised UC formulation, conventional deterministic constraint on spinning reserve (SR) is replaced by a chance constraint on reliability index LOLP and minimum optimization objects is extended by expected interruption costs estimated by a product of EENS and the value of lost load (VOLL). With considerations of stochastic fluctuations of load/wind power together with random outages of generators, an analytic algorithm is presented to calculate reliability indices LOLP and EENS. Genetic algorithm (GA) is utilized to solving the revised UC formulation. In addition, an intelligent mutation operator (IMO) is specifically designed to improve the performances of the GA. Simulation results on certain 10-unit case system have proven the efficiency of the methodology proposed here. TuA06.3 TuA06.5 Research on a Two-stage Optimization Algorithm for Multi-objective Reactive Power Optimization of Distribution Network pp. 626-631 Fei Gao, Yu Zhang Jianfang Li Xueping Feng Xiaohui Song Research on Transmission Cost Allocation of MultiTerminal Transmission Line pp. 638-641 Fuqiang Zhang Junshu Feng Jianhua Bai Dong Zhang China Electric Power Research Inst., CEPRI China Electric Power Research Inst., CEPRI China Electric Power Research Inst., CEPRI China Electric Power Research Inst., CEPRl China Electric Power Research Inst., CEPRI This paper, on the basis of the existing literature, proposes a new allocation method combining MW-Mile method with post stamp method for transmission cost allocation of multiterminal transmission line, which can follow the principles of allocating by utilization and balance the payments. Besides, the methodologies of economic comparisons of coal transportation and power transmission have been expanded. Finally, an example based on the first UHVAC transmission line on JindongnanNanyang-Jinmen in China has been given and the comprehensive method is applied in this paper. This paper proposes a two-stage optimization algorithm for multi-objective reactive power optimization of distribution network. In the first stage, an approximate Pareto solution set is obtained using traditional multi-objective optimization algorithm. Then the preferred area for searching is calculated with the preference information of Decision Maker (DM) and the approximate Pareto solutions. In the second stage, an improved dominance relation is proposed to guide the particles of multiobjective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) to focus on a deep searching in preferred area, with a high calculation efficiency. The case in IEEE 33-node system verifies that compared with the traditional multi-objective reactive power optimization, the method proposed in this paper has a large improvement in generation distance(GD), spacing(SP), error ration(ER) and reduce the optimization time. TuA06.6 Optimal Scheduling of Active Distribution Networks with Energy Storage Systems Considering Environmental Cost pp. 642-647 TuA06.4 Rongrong Bao Wen Zhang On Day-ahead Scheduling Based on Chance Constrained with Significant W ind Power Penetrat i on pp. 632-637 Xinsong Zhang Jingfeng Mao Shandong Univ. Shandong Univ. Along with the increasingly serious environmental issues, besides economic efficiency, much attention is paid to the environmental aspects in the daily dispatch of active distribution networks (ADN). This paper presents a comprehensive optimal model to minimize the economic cost and environmental cost. The damage cost from gas emissions and the uncertainty of renewable generations are taken into consideration. The charging and discharging strategy of energy storage systems Nantong Univ. Nantong Univ. Large-scale integrations of wind power increase stochastic nature of generation schedule decision, and might make relia- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China State Grid Energy Research Inst. State Grid Energy Research Inst. State Grid Energy Research Inst. State Grid Energy Research Inst. 30 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Hongji Xiang Jie Ming Han Li Yu Zhuo Chaohua Dai Xintao Xie Mengjiao Li (ESS) is a focus of the model. The general algebraic modeling system (GAMS) is used to solve this mixed-integer nonlinear problem. A modified 33-bus distribution network including photovoltaic (PV) systems and ESSs is employed to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Simulation results under different scenarios, with and without PVs/ESSs, show that utilization of charging/discharging strategy of ESSs can decrease the economic cost through peak load shifting. Moreover, increasing the penetration of renewable generations leads to the decrease of total cost. The widely use of wind power generation in modern power system exerts much pressure on peak regulation, especially after the large-scale wind power plants was connected to the grid. Information of newest researches about wind power integration and peak regulation are introduced at the beginning of the paper. Although there are many methods and theory about increasing the peak regulation capacity proposed, it is hard to avoid wind curtailment totally. In this paper, the operation costs of wind power plants are calculated and it can be inferred that the output of wind power plants and the unit cost of electricity has a nonlinear inverse relationship. Therefore, an appropriate wind curtailment capacity can exert prominent effects on improving the peak regulation ability with low costs. According to the situation that there are many provinces affluent in both water and wind resources, the optimized wind and water combined curtailment strategy is proposed in this paper. It can make the capacity of wind curtailment stay in an appropriate range with the cooperative work of water curtailment. Wind castoff rate and peak adopting rate are calculated in the paper to provide criterion for optimizing the ratio between wind and water curtailment, in order to increase the peak regulation capacity with low cost, especially for the areas which affluent in water resource. In the second half of the paper, a calculate example come from Houlong area of Hunan province is processed by the optimized method. The results and analysis demonstrate that the optimized wind and water combined curtailment strategy is effective and adaptability. TuA06.7 Coordinated Optimization of Unit Commitment and DC Transmission Power Scheduling Using Benders Decomposition pp. 648-653 Bin Wang Ye Xia Haiwang Zhong Qing Xia Huiling Zhang Hongwei Han Tsinghua Univ. Tsinghua Univ. Tsinghua Univ. Tsinghua Univ. Ningxia Power Dispatching & Control Center State Grid Cooperation of China Ningxia Power Dispatching & Control Center State Grid Cooperation of China In response to the challenges brought by generation scheduling with hybrid AC/DC transmission system, this paper presents a hybrid scheduling mode for coordinated optimization of unit commitment and DC transmission power scheduling. Considering the characteristics of both units and DC transmission system, the optimal unit commitment and operation state of DC transmission system are acquired to achieve the best system economic profit, while AC/DC transmission constraints are also delicate formulated in the model to ensure the security of scheduling results. Since this coordinated optimization model is a large scale mixed integer nonlinear optimization problem, the Benders decomposition method is employed to tackle the computational difficulties. The coordinated optimization model is decomposed into a master problem to optimize unit commitment and DC transmission power without considering AC/DC transmission constraints, and hourly security check sub-problems which check the power flow violations caused by inappropriate results of unit commitment and DC transmission power schedule obtained by the master problem. Corresponding solution procedure and iteration algorithm are proposed to enhance convergence and computation efficiency, in which parallel computation technique is implemented to accelerate the convergence. Numerical results based on the CEPRI 22-bus system validate the effectiveness of our proposed method. TuA06.9 Reactive Power Optimization and Control Considering Penetration Reactive Power for UltraHigh Voltage Power System pp. 659-662 Di Yang Haozhong Cheng Shuxin Tian Tengfei Sun Zeliang Ma Pingliang Zeng Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. East China Grid Company Limited China Electric Power Research Inst. With the development of UHV (Ultra-High Voltage) transmission, great changes have occurred for the reactive power distribution. Especially the reactive power of UHV transmission varies with the different transmission power. Therefore, reactive power optimization considering penetration reactive power is presented in this paper. The estimation of the penetration reactive power is proposed in the paper. The optimization scheme can minimize the penetration reactive power of the UHV transmission and hence the voltage stability margin of the whole power system with UHV transmission. And the optimization is solved based on improved differential evolution algorithm. An example of Huadong power grid is discussed and analyzed. And it’s proved that the present optimization control is effective and practical. TuA06.8 Optimized W ind and Water Combined Curtailment Strategy for Peak Regulation of Power System pp. 654-658 Guodong Liao Boyuan Wei Southwest Jiaotong Univ. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. State Grid Hunan Electric Power Corporation State Grid Hunan Electric Power Corporation State Grid Hunan Electric Power Corporation Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 31 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuA06.10 TuA06.12 Reactive Power Optimization in Smart Distribution Network under Power Market pp. 663-666 A New Relaxation Method to Obtain Reactive Power Allocation in Regional Power Grid pp. 673-677 Kunpeng Zhou Haixia Tang Tian Liu Feng Xiong Lei Wang Qi Yin Jian Zhang Rui Ding Jiao Ming Junyong Liu Xiaodong Shen Lixiong Xu Yanlin Guo Hubei Electric Power Research Inst. Suizhou Power Supply Company Suizhou Power Supply Company Suizhou Power Supply Company Suizhou Power Supply Company The basic framework for reactive ancillary services under power market that views the reactive power as a compensatory consumption is investigated in this paper. In the given scenarios the Distributed Generators (DGs) are motivated and utilized as sources of reactive power and optimizing the overall distribution operation which takes into account the costs of reactive power delivery. The basic framework for reactive ancillary services under power market that views the reactive power as a compensatory consumption is investigated in this paper. In the given scenarios the Distributed Generators (DGs) are motivated and utilized as sources of reactive power and optimizing the overall distribution operation which takes into account the costs of reactive power delivery. The case indicated that the model proposed can reduce the loss of the lines and the cost of reactive power and improve the voltage profile in distribution network. State Grid DeYang Power Supply Company State Grid DeYang Power Supply Company State Grid DeYang Power Supply Company State Grid DeYang Power Supply Company Sichuan Univ. Sichuan Univ. Sichuan Univ. Sichuan Univ. This paper analyzes the problem of reactive power optimization (RPO) in regional power system thoroughly. Successively, we further discuss the problem caused by the mismatch of the configuration of reactive power compensation and the demand of the system. Eventually an extreme optimal power flow method (EOPF) is proposed to verify the validity of the existing reactive power compensation. By relaxing the control variables including the range of transformer taps and the capacity of capacitors, the proposed method enlarges the convergence region of the optimization algorithm and further provides the advice of optimal allocation of reactive power compensators for departments of system planning and operation. Case study on a regional power grid with load uncertainty in Sichuan Province, China demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed EOPF method. TuA06.11 TuA06.13 Optimal Operation of Complicated Distribution Networks pp. 667-672 Lanxiang Wang Changnian Lin Yukai Li Hong Zhang Beijing Kedong Electric Power tem Co., LTD Beijing Kedong Electric Power tem Co., LTD Beijing Kedong Electric Power tem Co., LTD Beijing Kedong Electric Power tem Co., LTD Day-ahead Generation Scheduling W ith W ind Power Based on the Coordination of Source and Load pp. 678-682 Control SysControl Sys- Jialong Li Shouya Kang Wenmeng Zhao Jianquan Zhu Mingbo Liu Control SysControl Sys- A new day-ahead generation scheduling with wind power based on the coordination of source and load is proposed in this paper. First, the effect of time of use (TOU) pricing on day-ahead economic scheduling program is analyzed. Secondly, to consume more wind power in the day-ahead generation scheduling, the TOU pricing problem is combined with the unit commitment (UC) problem. The problem of uncertainty of wind power is also dealt with by scenario method, which transforms the stochastic optimization problem to a deterministic one effectively. Finally, the proposed method is tested on a provincial grid. The simulation results indicated that the coordination of source and load can benefit to the consumption of wind power and consumers. The operation cost of power system is also decreases significantly. Economic operation of complicated distribution network is an important problem. A bilevel optimal operation model of complicated distribution networks with microgrids integration is built. In the model, the day-ahead optimal operation of complicated distribution networks is on the upper-level and the optimal operation of the microgrid is on the lowerlevel. Electricity exchange price constraints are considered in this model. Further, in order to overcome negative influences brought by the volatility of renewable distributed generators, electric vehicles are adopted to balance the volatility. The proposed bilevel optimal operation model is solved by particles swarm optimization based on bilevel iterative algorithm (BIAPSO). The demonstration is performed on a modified IEEE 33-node radial distribution network with microgird integration. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Guangdong power grid control center South China Univ. of Tech. South China Univ. of Tech. South China Univ. of Tech. South China Univ. of Tech. 32 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) poses an integrated operation optimization scheduling strategy considering the photovoltaic-wind-pumped storage hybrid power, which is based on coordinated operation of wind power and the pumped storage hydro power station. Through load shifting performance of pumped storage hydro unit, volatility of photovoltaic-wind power system can be alleviated. Based on this, this paper establishes a multi-objective optimization scheduling model which considers unit generation cost and pollutant emission. Non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II) is adopted to solve the model. Numerical results show comprehensive optimality of both economic and environmental benefits. The rationality and effectiveness of the proposed model and algorithm is verified. TuA06.14 The Research on an Optimal Dispatch Model of Micro-grid pp. 683-687 Kexue Liu Qi Zhang BoTian Wenjun Li Wenhua Xuan Fuchun Zhang Junyang Li Qinhuangdao power supply company Qinhuangdao power supply company Qinhuangdao power supply company Qinhuangdao power supply company Qinhuangdao power supply company Qinhuangdao power supply company Qinhuangdao power supply company With the gradual development of the micro-grid construction, the problem of micro-grid optimal dispatch has become the key of depth application. Based on the operating characteristics of Distributed generation (DG) and load changes, the paper establishes an optimal dispatch model of Micro-grid. The model is solved by particle swarms optimization. At last the control strategy of micro-grid island operation and network operation is developed. The simulations of examples prove the effectiveness of the model. TuA06.15 Satisfaction Evaluation of Power Customer Based on Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets pp. 688-692 Jie Wang Fan Peng Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. Satisfaction evaluation indexes of power customer are given in this paper according to the characteristics of power supply quality and customer satisfaction model. Because of the uncertainty of power customer satisfaction, this paper discusses a method for satisfaction evaluation and improvement model of power customer. Interval type-2 fuzzy sets and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method are used to analyze and evaluate power customer satisfaction and related indexes. Improvement objectives are set and improvement measures are determined. In addition, the feasibility and effectiveness of this method is validated by an example. TuA06.16 Multi-Objective Optimal Scheduling of Power System Considering the Coordinated Operation of Photovoltaic-W ind-Pumped Storage Hybrid Power pp. 693-698 Rui Ma Xuan Li Zhaoyu Wu Qiang Zhang Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. State Grid Linyi Power Company In order to improve the utilization of photovoltaicwind power system and reduce wind power curtailment, this paper pro- 33 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) With the development of science and technology, the security of power system is facing great challenge, and it is necessary to implement the analysis of electricity behavior characteristics based on big data technology. Today, in the big data environment of the smart grid, it is generally to analyze the performance from a single aspect of power grid, this analysis method lack of theoretical modeling of the system. In this paper, a load characteristic analysis and demand response assistant decision analyzer based on large data technology is proposed, which consists of three levels: data preprocessing layer, electricity behavior analysis layer, advanced application layer. The simulation of MATLAB is carried out to verify the feasibility of the method, which can provide the theoretical support for the operation of the power system. B: Power System Analysis, Protection and Control TuB01.1 Power Equipment Reliability Evaluation Based on Data Mining pp. 699-703 Sipeng Hao School of electrical power engineering Nanjing Inst. of technology Jitao Zhang School of electrical power engineering Nanjing Inst. of technology Shaofan Liu School of electrical power engineering Nanjing Inst. of technology Dong Wang School of electrical power engineering Nanjing Inst. of technology Can Huang School of electrical power engineering Nanjing Inst. of technology TuB01.3 Multi-objective Optimal Configuration for Traveling Wave Acquisition Unit in Distribution Network pp. 712-716 Electrical power equipment reliability is the basis of the stability operation of distribution network. Equipment reliability includes inherent reliability and operational reliability. Inherent reliability focus on familial defects. Operational reliability focus on meteorological, load rate and others. This paper evaluates power equipment reliability based on integration platform of Jiangsu province electric power company. The inherent reliability and operational reliability are researched separately. The quantitative relationship between fault and condition is researched based on data mining. Weighting coefficients is calculated to combine different factors. On this basis, the reliability evaluation model is constructed and develop the relative software. Operation shows that power equipment reliability evaluation system has engineer applicability and practicality. Feng Deng Changsha University of Science and Technology Ke Zheng Changsha University of Science and Technology Xiangjun Zeng Changsha University of Science and Technology Lan Yang Changsha University of Science and Technology Donghong Zhao China Wuzhou Engineering Group Co. According to the topology characteristic of distribution network, traveling wave acquisition units(TWU) installed at all the terminals of branch must be greatly increase one-off investment. Thus, an multi-objective optimal configuration method for TWU in distribution network was proposed in the paper. Firstly, based on the topology structure of complicated distribution network, initial configuration scheme was presented. And then network fully observability was analyzed. A mathematical model was built by considering network fully observability, and maximal number of TWU. Binary particle swarm optimization(BPSO) was proposed to solve the multi-objective optimization problem. MATLAB simulation results show that the optimal configuration method can be rapidly achieved by synthetically evaluated, which can greatly decrease one-off investment and guarantee fault location accuracy and reliability, which has greatly practical engineering significance. TuB01.2 Assistant Analyzer for the Characteristics of Electricity Behavior Based on Big Data Technology pp. 704-711 Dong Zhu Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Smart Grid Technology & Equipment Ciwei Gao Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Smart Grid Technology & Equipment Southeast University Chengxian College Southeast University Tingting Lu Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Smart Grid Technology & Equipment Fuchao Liu Electrical Power Research Inst. State Grid Gansu Power Company Yongjun Han Electrical Power Research Inst. State Grid Gansu Power Company Jianhua Zhang Electrical Power Research Inst. State Grid Gansu Power Company November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China TuB02.1 Online Calculating Method of Switchgear Circuit Resistance for 3/2 W iring Connection Substation Based on Optimal Planning Model pp. 717-721 Yang Hou Jing Bu Minghui Yi 34 School of Automation Nanjing Univ. of Science and Technology School of Automation Nanjing Univ. of Science and Technology School of Automation Nanjing Univ. of Science and Technology The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Aiming at the online calculation problem of the switchgear circuit resistance in 3/2 wiring connection substation and phase difference of the current through each switch, this paper proposed a kind of online calculation method based on optimal planning model. The optimal planning model is established on basis of the current through the switch and the circuit resistance, therefore the complex calculation problem of switch resistance is transformed into solving optimal planning model. Using genetic algorithm can avoid the complexity which brought by the conventional method to solve the problem of multidimensional space planning during the process of calculation. In the end, it proved the effectiveness of the proposed method through carrying out simulated operation based on the data from 500 kV substation using 3/2 wiring connection mode. Compared with the equation model, the optimal planning model is more accurate and the calculated result is closer to the actual value. out to get the power network model which is used to calculate the indicatrix on reliability of power system. The proposed method achieves a more realistic simulation of power system operation process and improves the accuracy of reliability assessment. Test on RBTS-BUS6 system proves that the method is correct and effective. Using this method in power grid reliability sensitivity analysis, the reliability sensitivity of primary equipments can be evaluated and compared directly to satisfy the demand for maintenance strategy better. TuB02.4 Analysis of Influencing Factors of Short Circuit Ratio of Multi-Infeed AC/DC Power Systems pp. 732-734 Weifang Lin TuB02.2 Yong Tang Adaptive DFT Algorithm for Measuring Synchrophasors Based on Shifting W indow Symmetrical pp. 722-726 Shiming Liu Tao Guo Jianhui Li Jukun Wu Power System Department China Electrical Power Research Inst. China Electrical Power Research Inst. With the development of power grid in China, multi-infeed HV AC/DC systems are embedded into South China power grid and East China power grid. Multi-infeed short circuit ratio (MSCR) can simultaneously reflect the strength degree of HVAC systems and interaction among HVDC systems, so it is an important reference index in the construction of multi-infeed HVDC power system. The factors influencing MSCR are analyzed in depth theoretically, the influences of such factors as the electrical distance between the positions where HVDC lines connect into HVAC system, namely the mutual impedance, and network structure including network topology, line impedance, distribution of power sources on MSCR are analyzed; the variation law of MSCR is given. The conclusions are verified by calculation results of an HV AC/DC hybrid grid containing two multi-infeed HVDC systems. Shandong University Shandong University Shandong University Shandong University In order to improve the measurement accuracy of synchronized phasor in the case of frequency offset, an adaptive DFT algorithm based on shifting window symmetrical was presented. First of all, sampling window length of DFT is determined by tracking the frequency of the power grid. Secondly, the composed phasor is calculated by utilizing three sampling windows which were away from a quarter sampling window length to each other. After compensating the fixed offset, the precise phasor measurement results can be computed. In addition, in order to quickly and accurately track the frequency, a zero-crossing algorithm based on three-phase signal for measuring frequency was proposed. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can meet the accuracy of synchronized phasor measurement, significantly decreases the computational complexity over the conventional method, and satisfies the requirements of real time applications for the smart grid. TuB02.5 Efficient Computation Model of du/dt for Travelling Wave Protections on HVDC Transmission Lines pp. 735-739 Dehui Zeng Jingmei Guo TuB02.3 School of Electric Power South China Univ. of Technology School of Electric Power South China Univ. of Technology Du/dt is one of the most important features for voltage travelling waves on occurrence of a dc-line fault, and it is often used to construct an action criterion for Travelling Wave Protection on HVDC transmission lines. In order to alleviate the sharp contradiction between the accuracy and efficiency in obtaining the trend of dt du/ by traditional simulations, this paper proposed a global-sensitivity-based efficient computation method. The global-sensitivity concept is proposed and derived first, then the detailed implementation scheme, which is based on Vector Fitting Method (VF) and Thiele-type continued fraction interpolation technique, is presented. Finally, numerical examples show that the high computation accuracy can be achieved, at the same time, the proposed method has a huge advantage in saving CPU time to obtain the trend of du/dt over traditional simulations. Reliability Assessment of Power System Based on Topology Logic Relation pp. 727-731 Ying Ding State Grid of China Technology Coll. Chao Li Shandong electric power maintenance company Yao Jin Shandong power economic and technological inst. Shuguang Qi Shandong electric power technology co., LTD A method for power system reliability evaluation based on topology logic relation is presented. Firstly, topology logic analysis for substation is made to get equivalent nodes and the connectedness, then system topology logic analysis is carried 35 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) variable—system frequency is added. And the loss is no longer undertook by balancing generator only but by all generators having speed controllers. In addition, this paper also considers the contingency set of power system by calculating the probability of each contingency happening and then obtaining the PDLF of each contingency. Thus, the overall PDLF considering contingency set can be obtained by combining the full probability theory and PDLF based on cumulants. The algorithm can provide valuable information for power system planning, reliability analysis and static security risk assessment. TuB02.6 A Research of D-FSC Technology for Improving Voltage Quality in Distribution Networks pp. 740-745 Yuanfang Zeng Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology Buhan Zhang Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology Mei Li Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology Pei Bie Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology Hang Li Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology Tuo Guo State Grid Hubei Electric Power Company Yunxian Power Supply Company Gang Yu State Grid Hubei Electric Power Company Yunxian Power Supply Company Xia Tu State Grid Hubei Electric Power Company Yunxian Power Supply Company TuB02.8 Energy Theft Detection via Integrated Distribution State Estimation Based on AMI and SCADA Measurements pp. 751-756 The series capacitor can improve the transmission capacity and voltage stability effectively. The fixed series capacitor (FSC) applied to the distribution networks can improve the voltage quality and reduce the system losses. This paper presents the analysis methods of D-FSC used to regulate the distribution network voltage. For a typical radial 110kV high voltage distribution grid, we selected the compensation position and calculated the compensation capacity of single-point and multi-point compensation methods, then do the research of the relationship between the compensation capacity and compensation effects. In the scheme proposed, the D-FSC can effectively improve the voltage quality and reduce system losses. Wenpeng Luan Guan Wang Yixin Yu Jiaying Lin Weixin Zhang Qing Liu Energy theft has been a serious and long existing problem facing by many power utilities. The implementation of Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) provides power companies with new means for energy theft detection. As fundamental equipment of AMI, smart meters collect interval measurements from customer sites and thus provide system wide visibility for power companies. Leveraging both AMI and SCADA measurements, this paper puts forward an integrated distribution state estimation method for medium-voltage and low-voltage distribution network. Numerical studies show that the proposed approach can achieve a higher accuracy level for estimation. Furthermore, an energy theft detection method is proposed based on “weight-dropped polling” integrated distribution state estimation. Simulations show that it can deliver promising results comparing with conventional state estimation methods. TuB02.7 Probabilistic Dynamic Load Flow Algorithm Considering Static Security Risk of the Power System pp. 746-750 Pei Bie Buhan Zhang Hang Li Yuanfang Zeng Mei Li Shuang Zhao Jiasi Wu Guojun Lu Yong Wang Guoyan Chen Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology Guangzhou Power Supply Co., Ltd Guangzhou Power Supply Co., Ltd Guangzhou Power Supply Co., Ltd TuB02.9 A Lower Sideband EMD and Its Application in Power Systems pp. 757-764 Chengxin Li School of Electrical Engineering and Information Sichuan Univ. Junyong Liu School of Electrical Engineering and Information Sichuan Univ. Zhaoyang Dong School of Electrical and Information Engineering Univ. of Sydney Guo Chen School of Electrical and Information Engineering Univ. of Sydney Nowadays, the stable and secure operation of power system has attach more and more attention. The traditional static security analysis is based on deterministic load flow, which cannot reflect the uncertainty of load and the probability of branch outage. In addition, the conventional load flow model does not consider the static power-frequency characteristic of generators and load, which is not in accordance with the real operating condition of power system. In order to provide comprehensive static security risk assessment for the power system, so that the potential dangerous and vulnerable part of power system can be recognized before serious outage happens, a Probabilistic Dynamic Load Flow considering Static Security Risk (PDLF-SSR) algorithm is proposed, in which a new state November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China China Electric Power Research Inst. Tianjin University Tianjin University Tianjin University Tianjin Electric Power Research Inst. Tianjin Electric Power Research Inst. Low frequency oscillation assessment methods based on measured data have attracted increasing attention from research and industry stakeholders in power systems engineering. Among those existing methods, empirical mode decomposition (EMD) is a multi-resolution signal processing method used for 36 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Xiaojun Tang Hongmei Luo Jinghua Jia analysis of non-stationary signals. In recent years, EMD has been a most widely used method in practice. However, it has some disadvantages such as end effect, mode mixing, etc. If a signal contains more than two individual components whose frequencies fall within an octave, it cannot be decomposed by standard and the frequency heterodyne EMD methods. To improve the frequency resolution, a lower sideband frequency shift EMD (LSB-EMD) is proposed in this paper. The method includes an advanced approach on how to select an appropriate modulation frequency so as to can enlarge the component frequency ratios and avoid frequencies turn over. The improved frequency shift EMD is integrated with the procedure of the standard EMD. Consequently, the complex signal can be decomposed by the method. This method can be applied for the analysis of lowfrequency oscillations, as well as other power-system signals such as power quality signals and inrush currents. The effectiveness of the method to separate closely spaced modal components is demonstrated by both numerical simulation and field measurements. Lun Cheng The probability of power system cascading failure is very small, but once happened, its influence is disastrous. There are a few key branches play an important role in the process of cascading failures in power system. The identification of these key branches is of great significance to the safe and stable operation of power system. Power system transmits active power and reactive power at the same time. Different from the full range of active power, the reactive power has the characteristic of regional decoupling. The impact is generally limited in the vicinity of fault branch, so this paper temporarily only considers active power. Firstly, in this paper, the only link line between two subsystems is detected. If the branch is the only link line, it is the key branch. If it is not, then make the power flow of the fault branch as the basic parameters, and reduce the active power flow in the relevant branch of the fault branch to the fault branch by the power grid topology. Then get the grid key branch identification evaluation indicator. Finally apply the evaluation indicator in practical example of IEEE 39 bus system, and the result conform to the actual operation characteristics of IEEE 39 bus system and prove the correctness and effectiveness of the method. TuB02.10 Temperature-Dependent Optimal Power Flow Based on Simplified Interior Point Method pp. 765-769 Qin Gao Zhinong Wei Guoqiang Sun Yonghui Sun Haixiang Zang Coll. of Energy and Electrical Engineering Hohai Univ. Coll. of Energy and Electrical Engineering Hohai Univ. Coll. of Energy and Electrical Engineering Hohai Univ. Coll. of Energy and Electrical Engineering Hohai Univ. Coll. of Energy and Electrical Engineering Hohai Univ. TuB02.12 Reactive Power Optimization Algorithm Containing Discrete Variables Based on Sensitivity Information pp. 775-780 In this paper, a novel temperature-dependent optimal power flow (TDOPF) is proposed to improve conventional optimal power flow (OPF). In conventional OPF, the resistance of branches is assumed to be constant and temperature effects on line resistance has been neglected, which will result in a great deviation with actual operation situation. Based on the weak coupling property of electrical and thermal variables, the decoupled TDOPF is proposed to improve the efficiency of TDOPF algorithm. All the OPF algorithms are sufficiently solved by a novel simplified primal-dual interior point method. Finally, it is shown by the numerical simulation results that the proposed TDOPF and its decoupling algorithm are available and effective. Wenbo Li Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. Zhe Jiang Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. Dandan Zhang Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. Si Yang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company Xin Su State Grid Shandong Electric Power Co.l Jinan Power Chao Zhang Shandong Zhongshi Yitong Group Corporation Ltd To solve the difficulties in the calculation of reactive power optimization caused by discrete variables, a reactive power optimization algorithm based on the in-depth analysis of the mathematical model of reactive power optimization and the solving principle of prima-dual interior point method is proposed, which makes the most of the sensitivity information of discrete variables. The algorithm makes full use of the optimization information embodied by the sensitivity, and adopts the approach of successively structuring discrete variables to improve the reliability of the sensitivity information and the feasibility of the optimal solution, with less calculation and easier operation. Finally, the rationality and effectiveness of the proposed method are verified by the analysis of examples. TuB02.11 Complex Network Theory Based Recognition of Power Grid Key Line pp. 770-774 Rui Liu Jiancheng Zhang Zhe Dong Yi-qiang Li China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. Hebei Electric Power Corporation State Grid Corporation of China Hebei Electric Power Corporation State Grid Corporation of China North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. 37 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Qianying Mou Shandong University Changgang Li Shandong University Liang Wang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company Bing Zhang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company TuB02.13 Reduced Order Modeling for Load Aggregation based on Empirical Covariance Matrices pp. 781-786 Gang Zhang Zhengchun Du Chongtao Li Yu Ni The accuracy of transformer parameters is critical for power system analysis and control decision. In practice, the parameters of a transformer may deviate from its factory values due to the influence of environment and equipment aging. An improved model is presented in this paper to identify transformer parameters based on WAMS and SCADA data. Relative errors are considered in the objective function. Cases with different objective functions are examined. The accuracy and convergence of the different method are compared. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Load model contributes a lot in power system stability analysis. Induction motors aggregation is one of the most important parts in load modeling. This paper presents a new method for aggregating induction motors based on nonlinear model reduction. Firstly, the induction motors were seen as a nonlinear input-output system with bus voltage as input and equivalent impedance as output. Secondly, nonlinear model reduction technique was applied on the system to calculate the empirical covariance and transformation matrix of the system. Then the reduced-order system was obtained by performing Galerkin projection on the original system. Lastly, an adaptive genetic algorithm was used to get more accurate result. Simulations and analysis were carried out in IEEE 39-bus system. The simulation results show that the new method could attain high accuracy to simulate all the individual induction motors under different operating states and improve the precision of simulation. TuB02.16 Distribution Network Energy Loss Calculation Method Considering W ind Power Integration pp. 797-801 Jiasi Wu Huazhong University of Science and Technology Mei Li Huazhong University of Science and Technology Bu-han Zhang Huazhong University of Science and Technology Bo Ruan State Grid Hubei Economic Research Inst. Dehua Yu State Grid Hubei Electric Power Company Grid energy loss is one of the key factors affecting the economic operation of power systems. Accurate calculation of electric energy consumption, will have a great positive effect on the planning, operation and management of all aspects of the grid. Due to the randomness of wind power resources, wind power is likely to increase access or may reduce power system losses. Therefore, study on grid energy loss calculation method containing wind integration has very important practical significance. Currently there are many grid theoretical line loss calculation method, but these methods have some limitation such as, less considering the load curve changes. This paper presents an improved method of equivalent power to calculate energy loss of wind power integration, through considering the impact of the load curve, and the random fluctuations of wind power, making use of load shape coefficient to correct the average power, computing power flow calculation by using equivalent power, calculate the energy loss more accurately. TuB02.14 A Risk Assessment Method for Cascading Failure Caused by Electric Cyber-Physical System (ECPS) pp. 787-791 Ting Zhao Dong Wang Dongxu Lu Yuan Zeng Yanli Liu State Grid Smart Grid Inst. Tianjin University Tianjin University Tianjin University Tianjin University This paper presents a new risk assessment method for cascading failure caused by electric cyber-physical system (ECPS). The development of a trustworthy smart grid requires a deeper and more specific analysis of potential impacts resulting from failures of ECPS. A probability model is presented to calculate the reliability of ECPS which controls the security and stability control system. Cascading failure due to failures of ECPS is being investigated by risk assessment method in this paper. Two scenes including signal lost and signal transmission error which may lead to cascading failure in power system is considered. IEEE 118-bus system is used as a test system and the simulation results verifies the effectiveness of proposed failure model and risk assessment method. TuB02.17 A Quantitative Evaluation Method for Dynamic Equivalence Based on Prony Algorithm pp. 802-806 Lin Zhu Qiliang Sheng Ping Liu TuB02.15 An Improved Method of Transformer Parameter Identification Based on Measurement Data pp. 792-796 Yaping Zhang Hengxu Zhang A quantitative evaluation method for dynamic equivalence in power System using prony algorithm is presented, and an equivalence error index calculated by the prony analysis result of transient response in original and equivalent system is defined to quantitatively describe the accuracy of dynamic equivalence. Before that, a practical method to aggregate gen- Shandong University Shandong University November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China South China University of Technology South China University of Technology South China University of Technology 38 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) erators which involves selecting the largest capacity one as the dominant generator of a group and modifying the reactance parameters using single variable optimization is presented to prove the effectiveness of proposed quantitative evaluation method on account of the apparent difference before and after modifying. Choosing IEEE39 power system as the original system to be reduced, transient simulation results verify the accuracy and reliability of the quantitative evaluation method proposed in this paper. that mainly affect system stability are given using the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. Finally, the optimal scheme can be determined from maximum priority. The rapidity of the proposed method is verified by the simulation of short-circuit current exceeding limit of 220 kV buses of Area Power Grid. TuB02.20 The Disturbance Propagation Model of Power Grid Considering Induction-Motor Load pp. 817-821 TuB02.18 A Power Flow Algorithm for Distribution Networks Based on the Equivalent Nodal Injection-current Transformation pp. 807-812 Yuehao Yan Wei Bao Di Su Yang Zuo Lu Xin Xiong Yang Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst. Qiang Li Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst. Xiaodong Yuan Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst. Zhinong Wei Hohai Univ. Guoqiang Sun Hohai Univ. With the development of power grid interconnection, once a disturbance occurs, the propagation of the disturbance take form of electromehcanical waves. Therefore, the reveal of disturbance propagation mechanism is of great importance for the power system security. In this paper, the electromechanical transient process of induction-motor load is taken into consideration for the model of power grid in the electromechanical wave study. The consistence between generator and induction-motor load during disturbance propagation is proved. Then, the structural frame model of power networks considering induction-motor load for disturbance propagation is proposed based on structural frame model. Furthermore, the propagation equation of electromechanical wave in the basic unit of the proposed model is derived. Simulation results in IEEE 14 buses system are given to show the validity of the proposed model. A distribution network power flow algorithm based on the equivalent nodal injection-current transformation is presented. According to the basic principles of the traditional Newton-Raphson method, the nonlinear power flow equations of the PQ nodes are converted into the linear equations by using the equivalent nodal injection-current transformation. It simplifies the Jacobian matrix of the iterative formula, and most of its elements are constant. The nonzero elements of the Jacobian matrix are calculated by making full use of the sparse technique, it greatly saves the memory space, and improves the calculating speed and efficiency of the proposed algorithm. Finally, the simulation results verify that the proposed algorithm is effective and successful, and has better calculating speed and efficiency, stable convergence, and strong ability of processing loops. TuB02.21 Unbalanced Three-Phase Distribution System Power Flow with Distributed Generation using Affine Arithmetic pp. 822-829 TuB02.19 Research on Optimal Scheme of Decreasing Short Circuit Level for Local Power Network pp. 813-816 Guanglei Li Chunlin Wang Xianzhen Zeng Yuyao Qu Shuai Yuan Deshun Han State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Zhengzhou Xinli Electric Power Co.,Ltd. Feng Xue Weilun Xie Peicheng Xie Zhengning Pan Jiayi Ren Yinghui Nie Xuchong Wang Ming Chen Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Linyi Power Supply Company State Grid Heze Power Supply Company State Grid Dongying Power Supply Company State Grid Shandong Power Supply Company State Grid Shandong Power Supply Company Guangdong Power Grid Company Limited Guangdong Power Grid Company Limited Guangdong Power Grid Company Limited Southeast University Southeast University Southeast University Southeast University Southeast University Due to the high penetration of the uncertain distributed generations (DGs), including wind power generators (WTG), photovoltaic (PV) power generation and plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV), the power flow of the distribution system has become asymmetry and uncertain. Based on the combination of interval and affine arithmetic, this paper establishes the model of three-phase load with uncertain DGs, and proposes a threephase forward-backward sweep power flow algorithm for the distribution system. Compared with the deterministic Since breaking transmission lines has thousands of combinations for large power grid, it's difficult to find the best combination to decrease short circuit level in a short time. Sensitivity relationship between transmission line outage and impedance change is aquatinted firstly in this paper, then preliminary combination schemes of transmission line outage is selected according to the sensitivity. Index values of factors including constraint condition, power supply reliability and other factors 39 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) power flow, the proposed algorithm can not only analyze the impact of the uncertain load and DGs on the power flow, but also reduce the overestimation of bounds yielded by correlation of variables in interval arithmetic (IA). IEEE 33-bus test systems are used to analyze the influence of the penetration of distributed generations on the distribution system. ployed in numerical experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The results indicate that the proposed SADMM-based algorithm possesses a high computational efficiency and accuracy, and applies to large-scale power system problems. TuB02.24 TuB02.22 Distribution System Fast Decoupled State Estimation Based on Complex pu Normalization pp. 840-845 Study on the T ime Variability of Load Characteristics based on Markov Chain Monte Carlo Simulation pp. 830-834 Zhinong Wei Xing Chen Guoqiang Sun Haixiang Zang Guangyao Zhou Shandong Univ. Zhenshu Wang Shandong Univ. Xueli Wang Shandong Electric Power Maintenance Company Considering the high R/X ratios on distribution systems, the conventional fast decoupled state estimation (FDSE) algorithm can-not be applied to emerging distribution systems. To improve the performance of FDSE methods, this paper proposes the complex per unit (cpu) normalization method. The cpu concept is aimed to overcome the numerical problems raised by the high R/X ratios of distribution systems. Results and comparative analysis have been presented and illustrated using the 33-bus distribution test systems. The accurate degree of the load model in the whole time period has important influence on the decision of the system and the stability of the system. But the load is time-varying. Current algorithms can identify the load model with certain accuracy at the time points when the voltage is instable. In the moment with stable voltage, due to the difficulty of identifying the load model, they use a constant load model. This paper tries to find out the regularity of the time variation and solve the problem of the uncertainty of the load, and then put forward the corresponding method. TuB03.1 Zero-Sequence Voltages of UHV Untransposed Double-Circuit Lines and Their Influence on Pilot Protection pp. 846-851 TuB02.23 Solution of Optimal Power Flow Problems by Operator Splitting Method pp. 835-839 Wuneng Ling Tingting Wang Naishan Hang Deshui Chen Jinglong Dai Huiqin Liao Bin Li Zhongqing Li Dingxiang Du Xianguo Jiang Guangxi University Guangxi University Guangxi University Guangxi University Guangxi University Tianjin University Tianjin University China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. For untransposed double-circuit transmission lines on the same tower, there are zero-sequence voltages exerting on both ends of double-circuit transmission lines under normal operation and external phase-to-phase fault conditions. The amplitude and phase of the zero-sequence voltages are affected by wire parameters, wire orientations, the types of external phase to phase fault and system parameters. The zero sequence voltage may reach threshold value of zero-sequence power direction component, causing zero sequence power direction component maloperation with high zero sequence current. This paper analyzes the cause of zero-sequence voltages and their influence on pilot protection. Theoretical analysis and simulation results prove that system zero sequence impedance has influence on zero sequence voltage and zero sequence current. This paper will has great meaning to fault analysis of double-circuit transmission lines and protection configuration. In recent years, interior point method combined with linear conic programming (LCP) has become a hot topic of solving optimal power flow (OPF) problem in power system. However, interior point method has been proved to be inefficient for a large-scale LCP problem as it can’t take advantage of the sparse characteristics in the original data matrix while solving the Schur complement equation. To this end, an operator splitting method, simplified alternating direction method of multipliers (SADMM) which is high-efficiency of solving LCP problems, is presented in this paper. In order to acquire the solvable form of SADMM, based on semidefinite-quadraticlinear programming (SQLP), the original OPF problem is transformed into an intermediate model called SQLP-OPF which consists of two semidefinite matrix variables and a non-negative conic variable. After forming the constraint coefficient matrix and the objective function coefficient of SADMM through the dual problem of SQLP-OPF, the solvable SADMM-based OPF could be formed. Four IEEE benchmark systems (IEEE 30, 57, 118, 300) and a 703 buses power system from Asia are em- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Hohai Univ. Hohai Univ. Hohai Univ. Hohai Univ. 40 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuB03.2 TuB03.4 The Structure for the Fault Diagnosis System Aided for the Power System Operating pp. 852-857 Assessing the Aging Status of the Silicone Rubber Insulator using Unilateral NMR Technology pp. 864-868 Bin Li State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Yajuan Guo State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Jinming Chen State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Haibin Zhu State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Company Xiaoyi Zhang State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Liping Ye Jianhua Lin Yunfeng Xia Huagan Chen Haikun Wei Kaikai Meng Jiamin Wu Xianjun Cui Traditional strategy about the fault diagnosis always puts all thoughts on the identification of the fault location and its accuracy. Few systems associate the fault with the cause of fault occurring. This paper presents a structure of the fault diagnosis system aided for the power system operating, which diagnoses whether the lightning strokes the fault or the surrounding circumstances affect the grid operation. The system structure not only has extensibility for the intelligent algorithms, but also meets the requirements of information security. Validation demonstrates that the system with the environment monitoring is effective for the fault diagnosis and analysis. The aging of silicone rubber insulator threatens the safety of the power grid. An accurate estimation of the insulator aging status is necessary for taking precautions against insulation failure. In this study, we propose a novel unilateral nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) method to quantify insulator degradation attributed to aging. The CPMG sequence was employed to record the 1H NMR transverse relaxation curves of the silicone rubber insulators with different service years. The decay curves were fitted to the bi-exponential functions. Further data processing of the decay curves was performed with the inverse Laplace transformation for one dimensional T2 distribution analysis, and the mean life time of the long T2 component (T2long mean) was obtained. The result demonstrates that an increase in the aging level of the insulator clearly results in a decrease of T2long mean. To compare with the results of NMR measurement, the relative permittivity of the insulator was measured. It shows a same changing trend as that of T2long mean. It indicates that T2long mean relaxation time obtained from our portable NMR sensor can be used as an index to reflect the aging status of the silicone rubber insulator. TuB03.3 A Novel Sufficient Differential Protection For Distribution Network W ith DGs Based On Fault Synchronous Information pp. 858-863 Hanlin Li Yuping Lu Guangdong Power Grid Co., LTD Guangdong Power Grid Co., LTD Guangdong Power Grid Co., LTD Guangdong Power Grid Co., LTD Guangdong Power Grid Co., LTD Chongqing University Chongqing University Chongqing University Coll. of Electrical Engineering Southeast Univ. Coll. of Electrical Engineering Southeast Univ. The differential protection scheme is the most effective way to solve the protection problem of distribution network with DGs. Limited to the level of distribution network communication automation, traditional differential protection scheme can’t be applied in distribution network with DGs. To solve the problem above, this paper proposes a fault synchronous identification technology. As the moment of fault is the same time for both ends of line, the technology uses the moment of fault as a time reference. The measurement about the interval between the first zero point of fundamental frequency current wave rising edge (or falling edge) after fault and the moment of fault will be carried out, and then intervals will be used to calculate phase change, which can effectively overcome the difficulty of high precision synchronous sampling. Based on fault synchronous identification technology, this paper proposes sufficient differential protection compound criterion. Only amplitude of fundamental current wave and time information after the failure are used to structure braking equation. Besides the sufficient current amplitude comparison criterion is lead up. New criterion overcomes contradiction between improving phase shift restraint capacity and sensitivity at the same time. Simulation verified the accuracy of the synchronous identification technology, the new criterion based on which has good action features too. TuB03.5 T ime Synchronization Based on Multiplexing RPR Channel and IRIG-B T ime Code pp. 869-872 Haozhi Wang School of Electrical Engineering Shandong Univ. Guofang Zhu School of Electrical Engineering Shandong Univ. Meiyi Hou School of Electrical Engineering Shandong Univ. Shunpu Wang Shandong Electric Power Company State Grid For the time synchronization in smart grid, the paper proposes a solution that transmitting IRIG-B time code by multiplexing RPR channel. In the method, we multiplex RPR channel, using the control code in the coding of Ethernet physical layer to represent the rising and falling edges of the pulse signal, to transmit IRIG-B message. The RPR nodes are divided into master nodes and slave nodes. The master nodes are responsible for accessing precise time information and the output of IRIG-B time code, and slave nodes are responsible for receiving the IRIG-B time code and the output of precise time information calculated by using the recovery algorithm. This paper offer the design method based on Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA), and simulating test is proceeded by the 41 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Modelsim simulation software. The experimental results show that the synchronization scheme achieves the low cost and high precision time synchronization, laying a good foundation for the establishment of wide area measurement and control system in smart grid. tion. Simulation verification of the proposed method has been carried out by MATLAB/Simulink, the simulation results indicate that fault in low voltage active distribution network can be located and recognized accurately by the proposed method with fast speed and self-adaption. TuB03.6 TuB03.8 The Novel Cryptographic Key Generation and Distribution Scheme for Smart Grid pp. 873-875 Dynamic Pressure Analysis and Protection of Transformer in Internal Arcing Fault by FEM pp. 882-887 Zhidong Wang Piao Liu Peixia Lin Zhibin Yang Mei Liang Hanmu Zuo Xian Yang South China University of Technology South China University of Technology South China University of Technology South China University of Technology South China University of Technology South China University of Technology Jun Guan Chunyao Lin Dan Zhou Chunjun Ke Secret key generation and distribution is crucial to the information security of smart girds. The paper firstly analyzes the merit and vulnerable essence of the key distribution scheme proposed by Xia and Wang. Deliberate analysis reveals the essential weakness of Xia and Wang’s scheme is the failure of integrating the initiator’s identity with an explicit authenticated code, resulting in possible tampering by man-in-the-middle attacks. Then several improved methods are proposed according to different security requirements. These methods keep the high-efficiency of Xia and Wang’s method while avoiding its impersonation attack weakness. Whenzhe Chen Zhiguo Hao In view of the transformer internal fault would lead to the tank cracking, fire, explosion and other serious accidents, power transformers are usually equipped with pressure relief valve and gas relay. However, due to the lack of theoretical innovation and reliability remain in the existing protections. This paper proposes a numerical method to research the pressure behaviors of transformer tank under internal overpressure caused by the high-energy arcing faults and develops protection principles based on pressure characteristics. According to the real full-scale 100MVA/110kV oil-immersed transformer parameters, a transformer model has been set up. Then, the 4.4MJ and 3.1MJ arcing faults have been provoked as the simulation examples by employing 3D FEM. The transient pressure characteristics such as pressure rise curves and effective pressure indexes at different positions have been studied. Moreover, this paper develops new protection principles for heavy gas protection and light gas protection based on pressure characteristics. In addition, both the theoretical model and the simulation method proposed in this paper can be extended to study tank structure and overpressure in other types of transformers instead of dangerous and costly tests. TuB03.7 A Novel Fault Location and Recognition Method for Low Voltage Active Distribution Network pp. 876-881 Geng Niu Long Zhou Wei Pei Zhiping Qi Chinese Academy of Sciences Chinese Academy of Sciences Chinese Academy of Sciences Chinese Academy of Sciences As more and more DGs plugged into low voltage side of the distribution network, the low voltage distribution network has been changed to active distribution network. Bidirectional power flow and uncertainty of DGs’ output cause the conventional fault location methods to be inapplicable in active distribution network for malfunction and miss trip, which makes the fault location in low voltage active distribution network an urgent problem. In order to solve this problem, a novel fault location and recognition method for low voltage active distribution network which needs 3-phase currents measurement only is proposed in this paper. In the proposed method, a low voltage active distribution network is installed with the measurement and data process units for current measurement and data process at nodes and a control center for fault location and recognition. By the division of the low voltage active distribution network into several two-terminal sections without branch, the fault location (inside/outside the section) with fault-phase selection can be determined by the calculation of A, B and C phase current phaseangle differences of each section and the fault type can be identified by judging the amplitudes of zero-sequence node currents at both ends of every fault sec- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Electric Power Research Inst of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Xi’an Jiaotong University Electric Power Research Inst of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Electric Power Research Inst of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Electric Power Research Inst of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Xi’an Jiaotong University Xi’an Jiaotong University TuB03.9 Analysis of Pilot Zero-Sequence Directional Protection Mal-function in Double-circuit Lines Break-conductor Fault and Solutions pp. 888-893 Wenzhe Chen Zhiguo Hao Jun Guan Baohui Zhang Dingxiang Du Xianguo Jiang Xi’an Jiaotong University Xi’an Jiaotong University Xi’an Jiaotong University Xi’an Jiaotong University China Electric Power Research Inst China Electric Power Research Inst When asymmetric break-conductor faults occur in double-circuit transmission lines, the shift of load may produce large unbalance current in healthy line, leading to the mal- 42 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) function of pilot zero-sequence directional protection with voltage compensation. This paper discusses the zero-sequence character of double-circuit lines in break-conductor fault, presents the mal-function mechanism of pilot zero-sequence directional protection with voltage compensation in healthy line after singlephase grounding fault tripping. The theoretical analysis was confirmed through simulation model. Moreover, preventive measures based on one-end single line or double lines electrical information was proposed. matically collect current information of all adjacent substation interstation lines at other side. By comparing one current phase with the phase of all other current phasor sum respectively and sorting the difference value, the fault can be located according to the rank. The algorithm uses the current phase comparison principle, which can locate the fault quickly and accurately, the principle is simple and less information is needed. Finally PSCAD simulation is used to verify the feasibility of the algorithm. TuB03.10 TuB03.12 A New Concept Intelligent Integrated Protection System for Distribution Network pp. 894-898 Hierarchy of Distribution Centralized Substation Area Protection System Based on All-in-One Devices pp. 903-906 Zhiqian Bo Qingping Wang Yingke Zhao Lin Wang Le Chen Fanrong Wei XUJI Group XUJI Group XUJI Group XUJI Group Huazhong University of Science and Tech Huazhong University of Science and Tech Lin Wang Zhiqian Bo Yingke Zhao Xiaowei Ma Mengqi Yu Fanrong Wei Smart substation and communication technology have a tremendous development, making the grid to coordinate and optimize a wide range of data possible, thus providing a higher level of centralization foundation for the protection and control functions. Therefore, the direction of future’s protection is based on the high-performance computer technology and advanced communication networks. To this end, this thesis proposes the concept of "Protection Intelligent Center". The center in the distribution network can take over the main functions of protection of several substations. Protection Intelligent Center of distribution network side aims at high voltage distribution network, bases on the high-speed and reliable communication networks and international standards of the time synchronization. This paper based on distribution network Protection Intelligent Center of Liaoning Electric Power Supply CO, LTD. Through integration of panoramic information of regional power grid, and exploration and practice of centralized protection and control system, which is a bold attempt for the development of new generation intelligent substation. With the rapid development of communication technology and the widely constructing of smart substations, wide-area protection and substation area protection have become hot research topics. As an important part of network protection, substation protection at present only realized the centralization of the information transmission, but the comprehensive utilization of information has not been an in-depth digging, on the other hand, protect devices still been placed centralized in the master control room, the regulation that primary equipment and secondary equipment must be set aside a safe distance results in the Large occupation of land ,seldom play out the advantages of information protection which can make the devices highly integrated and miniaturized. In response to those questions, a novel distribution centralized substation area protection system based on All-in-One device is proposed in this paper, and the configuration and function of All-in-One device are also described in detail. Then introduces the VPN scheme of the proposed system. On this basis, considering the features of proposed system structure and networking schemes, this paper brings out a time-sharing cooperation work strategy. The example proves that the strategy is reasonable and effective, while shows the superiority of the distribution centralized substation area protection system compared to the traditional protection system. TuB03.11 Dealing W ith the Information-missing of the Entire Station by W ide Area Protection Online Adaptive Technology pp. 899-902 Yingke Zhao Zhiqian Bo Qingping Wang Xiaowei Ma Neng Jin Fanrong Wei XUJI Group XUJI Group XUJI Group XUJI Group Huazhong University of Science and Tech Huazhong University of Science and Tech TuB03.13 The Protection Cooperation of Distribution Network Based on Protection Intelligent Center and the Validation of its Reliability pp.907-912 XUJI Group XUJI Group XUJI Group XUJI Group Huazhong University of Science and Tech Huazhong University of Science and Tech Zhiqian Bo Yingke Zhao Lin Wang Xiaowei Ma Suyang Ding Fanrong Wei There are more and more studies on centralized protection, but the effective protection scheme dealing with the information-missing of entire substation is scarce. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a wide area protection online adaptive algorithm. When the information of entire substation is missing and inter-station line fails, the algorithm will auto- XUJI Group XUJI Group XUJI Group XUJI Group Huazhong University of Science and Tech Huazhong University of Science and Tech With the development of communication technology and arti- 43 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) ficial intelligence, the study of protection intelligent center is becoming the research focus. To make full use of the technology advance, the concept of protection intelligent center is proposed. The protection intelligent center is a remote center which can gather the electrical information of the whole network and give out tripping signals on the basis of analysis. In distribution network, the protection intelligent center could provide multiple protection with its local layer and center layer. This paper focuses on the cooperation method of different types of protection which protection intelligent center can participate in, and proposes a practical scheme which combines the protection deployed in local layer and central layer to reach an optimal protection performance. The protection method of the system proposed in this paper is complicated to achieve multi-space and multi-layer protection, so the verification of the protection cooperation is also provided in this paper. For extra-high voltage mixed line, the parameters of cable segment and overhead line segment are different, so the fault location method of uniform line cannot be used. Based on the characteristics of mixed line parameters, a fault location method for extra-high voltage mixed lines based on variation of sequence voltage is proposed. A precision, fast calculation method of voltage along the line is researched by using linear equivalent. Through simulation tests the precision of method is high. In terms of frequency domain transfer equations, sequence of the amplitude attenuation and phase delay along fault lines are calculated. Extra-high mixed line fault types can be divided into two categories: the asymmetric fault and the symmetric fault. For the asymmetric fault, before fault happened, the negative sequence voltage along mixed lines is 0. So the fault negative sequence voltage variation is the current time negative sequence voltage. Negative sequence voltage amplitudes along mixed line are calculated by using two-terminal electric parameters of line and compared for asymmetric fault. The fault location is the point with equal negative sequence voltage amplitudes. For the symmetric fault, the line will not appear negative sequence voltage. There is positive sequence voltage only. But, for three phase fault with transition resistance, the fault point voltage is not the lowest. The calculated voltage amplitudes along the line have two intersections: fault point and false point. The intersections have almost equal amplitude, so using numerical magnitude of point amplitude to false identification is hard. To solve the problem what has mentioned above, this paper uses the positive sequence voltage variation for fault location. Before fault happened, the positive sequence voltage along the line is not 0, so the positive sequence voltage variation is the difference of current and previous positive sequence voltage amplitude. Then, for three-phase symmetry fault, the fault location is the point with equal voltage amplitudes variation of positive sequence. Finally, the simulation is carried out to verify the algorithm. The proposed algorithm is computationally efficient with high precision. It is not affected by transition resistance, and no false identification problem. TuB03.14 The Study of Area Protection Principle Optimization Based on Protection Intelligent Center in Distribution Network pp. 913-915 Qingping Wang Zhiqian Bo Lin Wang Xiaowei Ma Neng Jin Fanrong Wei XUJI Group XUJI Group XUJI Group XUJI Group Huazhong University of Science and Tech Huazhong University of Science and Tech With the development of communication technology, a large number of intelligent substation has been constructed, substation area protection and wide area protection technology has been widely used. Then Protection Intelligent Center (PIC) taking over the main functions of multiple substations protection in the distribution network comes into being, making large-scale information centralized processed becomes possible. Against to the problem that traditional local information-based protection is difficult to set and coordinate brought by increasingly complex distribution network, this paper redefines the partition to protection are and its search strategy, gives a fault criterion based on multi-terminal current differential protection. Finally we propose the scheme of current differential protection based on partition principle. TuB03.16 The Simulation Research of Transverse Differential Protection Based on Impedance Ratio for Double Circuit Lines on the Same Tower pp. 922-926 Shilong Li Wei Chen Youjie Tao Deshu Chen TuB03.15 A Fault Location Method for Extra-high Voltage Mixed Line Based on Variation of Sequence Voltage pp. 916-921 Yunke Zhang Botong Li Xianguo Jiang Zhongqing Li Conventional current transverse differential protection has shortages when being applied to high-voltage and asymmetry power systems, such as low sensitivity and long successive operating zone. A new transverse differential protection scheme based on the measurement impedance ratio is proposed. The proposed scheme is unaffected by system impedance to a large extent, using the ratio of the sum and difference impedance of respective transmission line can build the criterion of the protection. PSCAD/EMTDC simulation shows that the fault re- Tianjin University Tianjin University China Electric Power Research Inst China Electric Power Research Inst November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Huazhong University of Science and Tech Huazhong University of Science and Tech Huazhong University of Science and Tech Huazhong University of Science and Tech 44 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) sistance almost does not affect the proposed protection. Compared with traditional current transverse differential protection the suggested protection can decrease the successive operating zone obviously. And the proposed integrated protection scheme is simple, reliable, and easy to realize. and equals the equivalent capacitance after that, proving that the proposed method is accurate in identifying the traveling wave head. In addition, the method is immune to the change of fault location and transition resistance and is applicable in AC systems and other DC systems. TuB03.17 TuB03.19 W ide-area Protection Scheme for Active Distribution Networks Based on Phase Comparison pp. 927-932 Description of Protection Intelligent Center using IEC61850 defined SCL pp. 938-942 Fan Zhang Longhua Mu Xiaowei Ma XUJI Group Zhiqian Bo XUJI Group Tongji University Tongji University The massive penetration of distributed generations (DGs) into electric distribution networks may reshape it from a passive system to an active network with bi-directional power flows, and have a serious impact on the system contribution to fault current. These effects may cause severe troubles for the coordination of existing current protection system. Phase comparison differential protection serves as a better option for active distribution networks (ADNs) due to its simplicity, sensitivity and selectivity. This paper proposes a new wide-area protection scheme for ADNs based on phase comparison. Wide area measurement system (WAMS) is used for time synchronous measurement and communication. An active distribution network model with high amount of DGs is established in PSCAD/EMTDC. Theoretical analysis and system simulation results validate the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed method. Le Chen Huazhong University of Science and Tech Fanrong Wei Huazhong University of Science and Tech Introduce the Protection Intelligent Center that suit the evolution tendency of the substation form, but the new form of substation is lack of corresponding description of information model, Based on IEC61850 defined SCL language, according to the characteristics of the Protection Intelligent Center, the paper put forward the structure of Protection Intelligent Center information model description. Then, based on the description of Protection Intelligent Center, a software application is brought out that can acquire the real-time topology of the grid within the range of Protection Intelligent Center, and the flow chart of software is given. Description of Protection Intelligent Center using IEC61850 defined SCL. TuB03.18 TuB03.20 A Novel Traveling Wave Head Identification Method in VSC-HVDC Based on Parameter Identification pp. 933-937 Influence on the Performance of Multi-terminal differential Protection Caused by Communication T ime Desynchronizing pp. 943-946 Haiyang Xu Guobing Song Xi’an Jiaotong University Xi’an Jiaotong University In the voltage source converter based high voltage direct current (VSC-HVDC) transmission system, traveling wave heads of currents and voltages are affected by fault location and transition resistance, thus are difficult to be recognized. To solve this problem and improve the accuracy of traveling wave head identification, parameter identification method is adopted in the present paper. In the zero-mode network of VSC-HVDC system, dorsal systems at both ends of DC lines are equivalent to parallel capacitors. When an internal fault occurs on the DC transmission lines, identified parameters computed with measured voltages and currents reach the value of equivalent capacitance after a sudden change at both ends, indicating the arriving time of the traveling wave heads. Through identifying the sudden changing time of the identified parameter, the arriving time of the traveling wave head is then recognized. Theoretical analyses and simulation results show that the identified parameter changes suddenly when the traveling wave head arrives at the end of DC transmission lines Qingping Wang XUJI Group Zhiqian Bo XUJI Group Yingke Zhao XUJI Group Lin Wang XUJI Group Suyang Ding Huazhong University of Science and Tech Fanrong Wei Huazhong University of Science and Tech As the “12th Five year development plan” of China is in progress, the new energy industry and tertiary industry has been developing rapidly, which sets a higher requirement for the power distribution network. In the foreseeable future, the connecting topology of civilian distribution network would become too complicated to the current protection method based on local information. Therefore, the multi-terminal differential protection which has a great operating experience in the main power network can be utilized to improve the performance of distribution network protection. However, attributed to financial affair, the communication system deployed on distribution network may not be as good as that on 45 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) main network, which may lead to a time desynchronizing that would heavily influence the accuracy of multi-terminal differential protection. This paper introduced method that utilizes the optimal algorithm to calculate the possible error brought up by time desynchronizing, and verify it through computation examples of different kinds of conditions. tailed expatiated at first, and the fault location process based on direction, overcurrent and distance is analyzed. According to the fault location, the tripping sequence of local protection and breaker failure protection, which have a good adaptability to different main connection and operation modes, are discussed. The proposed protection system not only provides the local protection and breaker failure protection for all the equipments in the substation but also shortens the operation time and avoids the complicated cooperation. TuB03.21 The Mechanism of Fault Searching for New Energy Distribution Network Based on Variation of Cutting Current pp. 947-950 TuB03.23 Yingke Zhao XUJI Group Zhiqian Bo XUJI Group Qingping Wang XUJI Group Compensation Scheme for Secondary Arc Current on Four Circuit Perfect Transported Parallel Transmission Lines pp. 956-961 Xiaowei Ma XUJI Group Z.Y. Xu North China Electric Power University Neng Jin Huazhong University of Science and Tech B. Gao North China Electric Power University Fanrong Wei Huazhong University of Science and Tech A new compensation scheme for four circuit perfect transposed parallel transmission line is proposed in this paper. The new scheme utilizes a neutral reactor to decrease the secondary arc current and limit the recovery voltage. The results by PSCAD show that the secondary arc current and recovery voltage can be limited to a low level. Hence, the application of the proposed compensation scheme can increase power system stability. With the increase of demand in power supply demand, increased strength of connection complexity and access of renewable energy, traditional current protection has been unable to meet the needs of the safe and reliable operation of distribution system. To prevent this, the cutting-current-based fault location searching algorithm is put forward in this paper using the single-end current vector. Firstly, the feeders are divided into several stages to determine the searching section. Secondly, search the whole line lengthways for the faulted stage, and the accurate fault location is carried out by the breadthwise search, and the fault can be cleared with the help of the existing method and the proposed method. For larger distribution network, dichotomy algorithm is utilized in lengthways search to minimize the time cost. PSCAD/EMTDC simulation results indicate that such a method can play a complementary role for existing protection equipped for the double end new energy distribution network. TuB03.24 Complete Observation against Attack Vulnerability for Cyber-Physical Systems with Application to Power Grids pp. 962-967 Xiaoyuan Luo Yanshan University Jianjin Li Yanshan University Zhongping Jiang TuB03.22 Xinping Guan Scheme Design and Algorithm of Substation Centralized Backup Protection System pp. 951-955 Lu Zhang Xi’an Jiaotong University Baohui Zhang Xi’an Jiaotong University Ye Li Xi’an Jiaotong University Zhiqian Bo Shanghai Jiaotong University This paper presents a novel framework based on system observability to solve the structural vulnerability of cyber-physical systems (CPSs) under attack with application to power grids. The adding power measurement point method is applied to detect the angle and voltage of the bus by adding detection points between two bus lines in the power grid. Then the generator dynamic equations are built to analyze the rotor angles and angular velocities of generators, and the system is simplified by the Power Management Units (PMUs) to observe the status on the generators. According to the impact of a series of attacks on the grid, we make use of grid measurements detection and state estimation to achieve observation status on the grid, enabling the monitor of the entire grid. Finally it is shown that the structural vulnerability against attacks can be solved by combining with the above-mentioned observations. Finally, some simulations are used to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. It is shown that some attacks can be effectively monitored to improve CPS security. XUJI Group With the enlargement of the power grid, the setting and cooperation of traditional backup protection become more difficult. Based on advanced communication network and computer technology, a new substation backup protection configuration using substation area information is introduced in this paper. The structure and function of protection configuration is de- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China New York University 46 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) non-fault reliably before three-phase reclosing, which is helpful to avoid blind reclosing and identify the fault phase for the arcing faults especially serious permanent faults. Moreover, simulations verify the correctness and effectiveness of this nonfault detection method, which is helpful to improve successful reclosing rate for three-phase reclosure. TuB03.25 Study on Line Protection of Distribution Network with DFIG Based on Current Decay Factor pp. 968-973 Jiandong Duan Xi'an University of Technology Lei Sun Xi'an University of Technology Shuaishuai Cui Xi'an University of Technology Wuji Liu Xi'an University of Technology Wangjing Tan Xi'an University of Technology TuB03.27 A Directional Comparison Pilot Protection Scheme for Hybrid HVDC Transmission Lines pp. 978-983 Because of the high permeability integration of the dispersed wind power to the distribution network, the fault current direction, amplitude and phase angle have significant changes, and it is difficult for the traditional three-current protection to adapt these changes. The transient characteristics of the wind turbine are not the same as the system power, leading to the protection scheme can’t adapt to such characteristics. By theoretical derivation the transient characteristics of the doublyfed induction wind generator (DFIG), the decay characteristics of DFIG is got in this paper. According to the analysis, a line protection scheme based on the current decay factor difference is proposed. The fault region is identified by the difference of the current decay factor between the two ends of the fault line. Referring to the parameters of the first exemplary project in which the dispersed wind power is integrated into the 10kV local power grid. The active distribution network simulation model is built in PSCAD/EMTDC, the simulation results show that the proposed scheme can operate correctly with different fault type, fault position and wind field output, and it can adapt to various operating conditions sensitively and effectively. Yanting Wang Xi’an Jiaotong University Baohui Zhang Xi’an Jiaotong University Fei Kong Xi’an Jiaotong University The hybrid high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission system comprising a line commutated converter (LCC) at the sending end and a voltage source converter (VSC) at the receiving end combines the advantages of both LCC and VSC and compensates their drawbacks. In order to guarantee the safe operation of the hybrid HVDC system, a directional comparison pilot protection for hybrid HVDC transmission lines is proposed in this paper. Fault direction is discriminated based on the different characteristics of current fault component under forward fault and backward fault. The faulty pole is identified based on the different variation trends of voltages at faulty pole and non-faulty pole. Simulation results show that the proposed protection is able to distinguish the internal faults from the external faults, identify the faulty pole, and has enough sensitivity to high transition resistance fault as well. TuB03.28 TuB03.26 A Method to Detect Inrush Currents in Power Transformer Using Current Derivation Characteristics pp. 984-987 Nonfault Detection for Three-phase Reclosure in Reactor-compensated Transmission Lines Based on Fault Location pp. 974-977 Wenquan Shao Xi’an Polytechnic University Yue Liu Xi’an Polytechnic University Wangni Zhang Xi’an Polytechnic University Wenquan Shao Ni Qiao Shu Wu Zaibin Jiao Xi’an Polytechnic University Xi’an Polytechnic University Xi’an Polytechnic University Xi’an Jiaotong University To further improve the performance of differential protection for power transformers, this paper presents a new method for distinguishing inrush currents from internal faults using the extreme value of current derivation rate. In the condition of internal faults, its derivation rate curve is close to sine waveform and the time span between the maximum value and the minimum one of the derivation rate is approximately near to half a cycle. While in case of inrush currents, due to the dead angle, the time span between the maximum value and the minimum one is less than half a cycle. Therefore ,the difference of the time span determined by the extreme value within a period is used to detect inrush currents. Thus, a criterion using the current derivation rate feature is developed and the corresponding realization flow is presented. At last, the dynamic tests under different conditions verified that the developed A novel nonfault detection method using fault location to calculate the differential currents at fault point is proposed for three-phase reclosure in transmission lines with shunt reactors. In the case of a transient fault with the extinction arcnamely nonfault, the differential currents of three-phase at fault point are all zeros. But in the case of an arcing transient fault or a permanent fault, the differential currents in the fault phases are non-zero because of the fault branch, and the differential currents of the healthy phases are close to zero as that of an arc extinction transient fault. Meanwhile, the fault phase can be confirmed as well based on the differential currents in the fault phases. It is noted that the presented non-fault detection is independent on fault phase selection and is able to detect 47 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) algorithm is of favorable performance for identifying accurately inrush currents from internal faults within a period, which provides helpful theoretical basis for improving the performance of differential protection for power transformers. rithms for promoted single ended location and automatic fault locating in teed circuit are proposed in this paper, comparatively there is no module for teed circuit in traditional systems generally. This system has been tested by an experimental system composed of traveling wave generator and high speed data acquisition system. The experimental results show that this system had improved the accuracy and reliability of fault location results significantly. TuB03.29 Research on Capacitive Current Compensation of Differential Protection on Segment Parallel Lines for Different Voltage Levels pp. 988-992 Yan Yang Huazhong University of Science and Tech Xianggen Yin Huazhong University of Science and Tech Cui Tang Huazhong University of Science and Tech Zhe Zhang Huazhong University of Science and Tech Xiongwei Wang Huazhong University of Science and Tech TuB03.31 Advanced Fault Location System for EHV Transmission Lines pp. 9991003 Current differential protection is the main protection of transmission lines including multi-circuit lines, whose sensitivity and reliability is mainly affected by the distributed capacitive current, especially with the widespread application of segment parallel transmission lines, the relationship of the electrostatic coupling between the circuits is more complicated, which makes the distributed capacitive current compensation more difficult. However, in the paper both the interphase capacitive current and the capacitive current between lines are compensated for the segment parallel transmission lines on the lumped parameter ∏ equivalent circuit model, and by using PSACD and matlab simulation software, it has further study of the relationship between the differential current and the length of segment parallel lines for different voltage levels, and some suggestions of capacitive current compensation schemes are proposed for segment parallel transmission lines under different voltage levels. Hongwei Li State Grid Of China Tech Coll Yanli Gan State Grid Of China Tech Coll Haike Liu State Grid Of China Tech Coll Zhuangzhuang Zheng State Grid Of China Tech Coll Ying Zhang Shandong University Feng Zhang Shandong University In this paper, an advanced fault location system for extra high voltage (EHV) transmission lines is proposed. This system is based on traveling waves, and contains the promoted single ended location method, automatic fault locating in teed circuit and location method under strong noise background. The presented system can significantly improve the location precision and reliability for EHV transmission line fault. This system is verified by an experimental system developed in the laboratory composed of a traveling wave generator and high speed data acquisition system. The experimental results show that this system had improved the accuracy and reliability of fault location results significantly. TuB03.32 TuB03.30 Singularity Point Detection of High Frequency Signal for Fault Location pp. 1004-1009 Improved Traveling Wave based Fault Location Scheme for Transmission Lines pp. 993-998 Hongwei Li State Grid Of China Tech Coll Haike Liu State Grid Of China Tech Coll Haike Liu State Grid Of China Tech Coll Tao Jia State Grid Of China Tech Coll Li Mou State Grid Of China Tech Coll Li Mou State Grid Of China Tech Coll Tao Jia State Grid Of China Tech Coll Xin Zheng State Grid Of China Tech Coll Yanbo Wang North China Electric Power University Ying Zhang Shandong University Feng Zhang Shandong University Feng Zhang Shandong University Yuling Gao State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company Traditionally the singularity point in extreme scenarios such as weak traveling waves may not be detected accurately as a result of their small amplitudes and naturally-existing attenuation. In this paper, a novel method based on curve fitting theory for singularity detection for extreme scenarios (weak traveling waves) is proposed, which considers both the characteristic of traveling waves and the influence of distributed capacitance at the bus bar. Mathematical equation of rising edge of In this paper, an improved fault location system based on traveling waves, which contains several innovative algorithms, has been proposed. In this improved system, the maininfluential factors such as the uncertainty of wave speed and the accuracy of transmission line length, which could affect the fault location results and generally are not of concern comprehensively in traditional systems, have been considered, and corresponding algorithms have been presented. Besides, innovative algo- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China 48 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) the initial traveling wave is deduced in this paper. Furthermore, the indirect mathematical equation based on Maclaurin expansion theory is derived to improve its feasibility in the real application. Combining the indirect equation and the measured traveling wave data, the least-square algorithm-based fitting curve can be obtained to determine the singularity point. The proposed method ’s efficiency in detecting the singularity point in weak traveling waves has been verified. The simulation results show that the proposed method had improved the accuracy and robustness of singularity point detection for weak waves significantly. portance to the reliable operation of the power system. This paper proposed a method of high-speed fault location based on circuit breaker reclosing transients. When a fault occurs in distributed system, faulted sections can be selected by contional methods. The circuit breaker reclosing transients is used for exact fault distance estimation in case of an unfounded permanent fault. As a result, it takes advantage of efficiency and practicality by reducing the time for positioning and ensuring the accuracy of location at the same time, and it doesn’t require the introduction of additional equipment or signal path. The performance of the proposed method is verified through Matlab/Simulink simulation. TuB03.33 Parameters-setting Method for Synchronization of Pumped Storage Units under Pumping Condit i on pp. 1010-1015 Zhiming Zhang Shandong University Wei Cong Shandong University Fei Wang Shandong University TuB03.35 Identification and Coping Approaches of Sympathetic Inrush Current Based on the Station-area Information of Smart Substation pp. 1020-1024 Yi Wang Electric Power Research Inst of Guangdong Guowen Hao State Grid Xinyuan Company Ltd Jianguang Li State Grid Xinyuan Company Ltd Xuanwei Qi* Huazhong University of Science and Tech Shandong Taishan Pumped Storage Power Xianggen Yin Huazhong University of Science and Tech Zhe Zhang Huazhong University of Science and Tech Yanping Yang Power Grid Corporation Station Co. Ltd Li Gan This paper presents a parameters-setting method for the synchronization of pumped-storage units under the pumping condition. The synchronizing process of the units is analyzed and the synchronizing parameters-setting principle of generating units is referred. Finally, the method is educed through mathematical formula derivation. Under the pumping condition, the setting value of the closing pulse leading time and the synchronizing process are both different from those of the generating condition, so the changes of voltage and frequency of pumping condition during closing pulse leading time are deduced. Then, the setting method of the allowable voltage difference, frequency difference and closing angular phase difference could be obtained. The parameters-setting method in this paper provides the theoretical foundation for synchronizing parameters setting of pumped storage unit. It is significant for decreasing the synchronizing impact current and heightening success rate of synchronization. search Co., Ltd Due to the absence of the effective identification and coping approaches of the sympathetic inrush current, the mal-operation of differential protection may be occasionally caused by sympathetic inrush current. In order to address this issue, the features of the sympathetic inrush current and the influence of the sympathetic inrush current on the differential protection are analyzed in detail in this paper. It is discovered that the second harmonic phase angle difference between the inrush current and the sympathetic inrush current are nearly 180°. Based on this, an identification and coping approaches for the sympathetic inrush current utilizing the information sharing between the smart substations is proposed in this paper. The effectiveness of this method is validated by the digital simulation and dynamic model experiment. TuB03.34 A Fault Location Method Based on Reclosing in Distribution Systems pp. 1016-1019 Ke Jia Zhefeng Ren Tianshu Bi Bohan Liu Changjiang Survey, Planning, Design and Re- TuB03.36 Fault transient analysis in Microgrid using discrete wavelet transform pp. 1025-1029 North China Electric Power University North China Electric Power University North China Electric Power University State Grid AC Engineering Construction Company Long Zhou Geng Niu Zhiping Qi Guohua Gao Yonggang Xu Fast and accurate fault location is crucial for the rapid recovery of power supply in distribution network and also vital im- 49 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences University of Chinese Academy of Sciences University of Chinese Academy of Sciences Beijing University of Technology Beijing University of Technology November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Microgrid is an effective means to integrate distributed generations and manage their power flows. Since the high penetration rate of DGs in microgrid and its capability to operate in grid-connected mode or islanded mode, the fault patterns of microgrid are not that obvious as those shown in the traditional low voltage distributed networks. Thus an extensive knowledge of fault transient characteristics is beneficial to design effective protection schemes for microgrid. Since conventional methods have difficulties in analyzing transient signals, discrete wavelet transform is employed in this paper to identify fault patterns from fault current/voltage signals. Aiming to provide a solution to the problems arise from applying wavelet in microgrid with short line segments, this paper proposed an improved wavelet transform method that using Daubechies complex wavelet with cubic spline interpolation. A modified benchmark microgrid network is modeled in Matlab/Simulink to verify the proposed method. Four types of fault cases in bus-bar and feeder are investigated respectively, and the simulation results indicate the unique fault patterns in the form of modulus maxima and wavelet energy. TuB03.38 A Distance Local Backup Protection Scheme Based on Regional Pilot Principle pp. 1036-1042 Jun Guan Xi’an Jiaotong University Wenzhe Chen Xi’an Jiaotong University Feng Dai Jiangsu Electric Power Company Jieqing Deng Jiangsu Electric Power Company Yidan Liu Jiangsu Electric Power Company Xiaohui Jia Jiangsu Electric Power Company Wei Cong Shandong University Jing Xiao State Grid Shandong Electric Power Com- Yingchun Feng State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company Maintaince Company Anning Wang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company This paper presents a new scheme for distance local backup protection. In this scheme, two main points are included: The first is the distance component that could reliably detect all the faults occurring in protection area; the second is the pilot comparison strategy which is based on the results of distance components. The former employs the setting principle that could meet the requirement of sensitivity when the fault occurs at the end of line where the protection installed. The later could confirm the fault location through the comparison between results of distance components, and then the operating delay time would be flexibly determined depending on fault location. Regional pilot distance local backup protection could make sure that the speed and the selectivity would meet the requirement. Meanwhile, the cooperation between different kinds of protections would be simplified and the improved protection performance of the backup protection could be realized. Through the simulation sample, it can be seen that the protection scheme proposed in this paper could reliably judge the fault, and then the speed and the selectivity of the local backup protection would be guaranteed, meanwhile this scheme partially possesses the ability of fault tolerance. Anti-saturation Algorithm in Differential Protection Based on the Phaselet pp. 1030-1035 Xi’an Jiaotong University Shandong University pany Maintaince Company TuB03.37 Zhiguo Hao Zhiming Zhang Current-transformer (CT) is prone to get into transient saturated during the fault in the power system. The transient saturation of CTs will cause serious distortion in the secondary side, operation performance of differential protection based on the traditional algorithm is seriously influenced. The phaselet algorithm can accurately obtain the basic frequency component of the fault current with the unsaturated data segment of CTs’ distorted secondary current in a relatively short time window. This paper researches the principle and features of the phaselet algorithm, eliminates the influence of the decaying DC component with the first order difference compensation, gives out the calculation process of the phaselet algorithm, proposes the scheme for the CT’s anti-saturation of the differential protection based on the phaselet algorithm. Finally, the accuracy of the phaselet algorithm is verified by CTs’ transient experiment data, and the validity of the scheme applying in the line differential protection is tested by the simulation in PACAD. TuB03.39 Analysis on Single-phase Line Break Fault of 10kV Non-grounded Distribution Network pp. 1043-1049 Rui Wang Shandong University Wei Cong Shandong University Qibao Kang Shandong University Guoqiang Liu Binzhou Power Company of State Grid Shandong Corporation Hui Wang Binzhou Power Company of State Grid Shan- Ruipeng Yi Binzhou Power Company of State Grid Shan- dong Corporation dong Corporation November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China 50 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Line break fault is becoming more and more frequent in 10kV neutral point non-grounded distribution system. This paper takes 10kV distribution line single-phase line break fault as the research object, analyzes the characteristics of electrical quantities when single-phase line break fault occurs, including single-phase line break without grounding point, single-phase line break with grounding at power supply side and single-phase line break with grounding at load side. Electrical quantities during single-phase line break fault are analyzed using symmetrical component method with sequence network and vector diagram, the variation of electrical quantities are summarized, and protection criterion for single-phase line break fault is proposed. Simulation results by PSCAD/EMTDC ensure the correctness of the analysis results and line break protection criterion. TuB03.41 Failure Mechanism Study of Conventional Active Methods Based on Inverter Disturbances and A Novel Islanding Detection Method pp. 1056-1062 Ke Jia North China Electric Power University Kaixiang Huan North China Electric Power University Hongsheng Wei North China Electric Power University Dongfang Wang State Grid Qinghai Electric Power Company Chunlai Li State Grid Qinghai Electric Power Company TuB03.40 Fault component comprehensive impedance based back-up protection algorithm for intelligent substation pp. 1050-1055 Zhongqing Li China Electric Power Research Inst Wei Li China Electric Power Research Inst Hong Cao Guoqing He China Electric Power Research Inst Guanghui Li China Electric Power Research Inst This paper analyzes the failure mechanism of the typical active islanding detection method (f-Q feedback islanding detection method) under multi-inverter distributed generation (DG) system circumstances. When disturbances produced by each inverter almost counteract each other or the reactive power variation of local load matches the reactive power disturbance, the f-Q feedback detection method will be malfunction. A novel active islanding detection method suitable for both single-DG and multi-DG system is put forward in this paper. It is based on impedance estimation and applies an external centralized disturbance algorithm to avoid mutual interferences of multi-supply disturbance signals. The method has high accuracy of detection and a high detection speed. North China Electric Power University A novel back-up protection algorithm for intelligent substation based on fault component comprehensive impedance is proposed in this paper. Calculation analyses of fault component comprehensive impedances of bus-line region, transformer-bus region and combination region are completed. The fault component comprehensive impedance of each zone reflects the positive-sequence impedance of the external system when an internal fault occurs. In a situation of external fault, it reflects positive-sequence magnetizing impedance or line positive-sequence capacitive reactance. In a situation of magnetizing inrush current, the fault component comprehensive impedance of the region which contains transformer reflects line positive-sequence capacitive reactance or decreasing positive-sequence magnetizing impedance. Fault location is implemented accurately according to the magnitude of fault component comprehensive impedance of each zone which in external fault situation is much larger than that in an internal fault situation. Then back up protection sends out trip signals after a time delay on the condition that failure still exists and the main protection of the fault element refuses to act. This algorithm is immune to transformer inrush current and high resistance fault, which has higher sensitivity than substation-area differential backup protection. Simulation tests based on PSCAD simulation model verify the proposed algorithm’s validity and superiority. TuB03.42 Compensation of Saturation in Current Transformer using Modified Prony Method pp. 1063-1067 Jieqing Deng Maintenance Branch of State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Company Zhi Yang Hao Xi’an Jiaotong University Zhiguo Hao Xi’an Jiaotong University Feng Dai Maintenance Branch of State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Company Xiujin Li Maintenance Branch of State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Company Xiaohui Jia Maintenance Branch of State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Company Peng Li Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Institute A novel scheme is proposed to fit and recover the primary current of the current transformer when transmission line fault occurs. Based on an iterative form of Prony method, the whole process require less than 1/4 of a cycle of base frequen- 51 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) cy.Due to the inconsistence of Prony method when embedded with noise and error, effective saturation detection and noise filtering algorithm using mathematical morphology transform are also applied in the scheme. Data obtained in a test system build by PSCAD software and practical experiments are both used to evaluate the performance of the proposed scheme. In order to solve the problem how to detect the wave head for traveling-wave based fault location when fault occurs, a new kind of wave head detecting algorithm for precise positioning which based on Kalman filtering is proposed.Model of voltage traveling wave is set up according to the actual characteristics of traveling wave signal. Recursion method of Kalman filtering is used to process the signal which contains fundamental component and harmonic component in the model. Getting the filter results and wave head signal can be achieved by subtracting the result from the original signal. The single-phase grounding model is established, then use this method to extract the wave head signal from the transient travelling wave signal in this model. Simulation results show that, the method proposed can effectively detect the wave head, so it has promoted value. TuB03.43 Simulation of Transformer W indings Mechanical Characteristics During the External Short-Circuit Fault pp. 1068-1073 Dan Zhou Electric Power Research Institute of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Zhengyuan Li Tu B03.45 School of Electrical Engineering Xi’an Jiaotong University Chunjun Ke The Influence Research of Large-scale W ind Power on Out-of-step Oscillation of The Northwest China Power Grid pp. 1080-1084 Electric Power Research Institute of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Xian Yang Electric Power Research Institute of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Zhiguo Hao Qi Liu School of Electrical Engineering Xi’an Jiaotong University Jiong-cong Chen Guangdong Electric Power Research Institute Wen-jie Zheng Guangdong Electric Power Research Institute Zhi Li North China Electric Power University Jian-xiong Lin North China Electric Power University November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China HeFei University of Technology State Grid Lianyungang Power Supply Company Shuanbao Niu Northwest China Grid Company Xianbo Ke Northwest China Grid Company China Electric Power Research Institute State Grid Based on theoretical research of the influence of Doubly Fed Induction Generator (DFIG) on equivalent system, it is offered that the oscillation is affected by the characteristic of wind turbine. The qualitative analysis shows that the influence of reactive power voltage control mode and protection mode of wind turbine to oscillation mode are unignorable. It is studied that the influence of DFIG active power output to oscillation splitting strategies. Grid simulation result shows that the wind turbine is likely to drop out from the grid if the wind turbines without Low Voltage Ride Through (LVRT) feature. As a result, oscillation will become more obvious, or even new out-of-step oscillation will emerge after wind turbines generator tripping. Reactive power and voltage control has little effect on the oscillation. It is found that the splitting strategies will be affected by the variation of DFIG active power output during a relative long time period compared to the transient oscillation process. The reason behind is that the power flow distribution and voltage level of the system will change due to the variation of DFIG active power output which will finally influence the splitting strategies in some extent. Guangdong Electric Power Research Institute Guangdong Electric Power Research Institute Ming Sun Corporation Research on the wave head detecting algorithm based on Kalman filtering pp. 1074-1079 Shu Huang China Electric Power Research Institute Yunting Song Tu B03.44 Chuan-jian Li Jian Ding Jiantao Gao With the development of voltage level and capacity in recent years, the impact of external short circuit has a growing threat to the stability of transformer windings than ever before. Because of the weakness of anti-short-circuit capacity, around 40% of the transformer faults are caused by the huge impact of short circuit every year. In view of this, it is of great significance to study the mechanical behavior of transformer winding structures during external short-circuit faults. This paper represents investigations of short-circuit current, the transient leakage magnetic field, electromagnetic forces and the von Mises stress of a real full-scale 500kV single-phase two windings transformer during the external short-circuit transient process. HeFei University of Technology 52 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Tu B03.46 Tu B03.48 Analysis on the Effects of 500kV Main Transformer Single-phase Replacement on Differential Protection pp. 1085-1088 Meng Li South China University of Technology The Warning Strategy Research on Safety Measures of Smart Substation According to Correlation Model pp.1095-1098 Chengjun Xia South China University of Technology Haihua Sheng State Grid Zhejiang electric power company Jianli Shi State Grid Zhejiang electric power company Guihua Qiu Foshan Electric Power Bureau Combined with the project which studies the feasibility of replacing a 500kV substation No.2 main transformer and based on PSCAD/EMTDC, this paper introduces a special autotransformer model to study the effects of percentages of threephase winding short circuit voltage on the transformer differential protection under normal operation and fault conditions after replacing the B-phase transformer for No.2 main transformer with original A-phase transformer for No.1 main transformer. It is preliminarily concluded that the replacement has little effect on differential protection and a certain degree of asymmetry of the percentage of three-phase winding short circuit voltage is allowed, which provides new ideas and references for further study on three-phase transformer single-phase replacement. Qunhui Qiu State Grid Zhejiang electric power company Weijian Jiang State Grid Zhejiang electric power company Juntao Niu Wuhan Kemov Electric Co.,Ltd. For the problem of safety measures in maintaining work of smart substation’s secondary system, this paper proposes a warning strategy according to correlation model. The strategy revolves around maintained IED, searches for relationship with other IEDs and establishes correlation model according to SCD file. The safety measures can be built automatically based on the correlation model, and can also be used to check if the work ticket and operation ticket are correct and comprehensive before they are executed. In addition, the setting of safety measures at substation site can be online read through MMS message. The warning strategy compares the read results with the given safety measures step by step, and maintaining work can be carried out only when all steps are passed. Tu B03.47 Performance of ROCOF Protection in Microgrid pp. 1089-1094 Tu B03.49 Bohan Liu State Grid AC Project Construction Co.,Ltd. Application of High Sampling Rate Data in Guozeng Yan State Grid AC Project Construction Co.,Ltd. Ke Jia State Grid AC Project Construction Co.,Ltd. Feng Yuan State Grid Yingkou Electric Power Company Merging Unit for Relay Protection pp. 1099-1104 Kaibo Liu China Electric Power Research Institute Hang Lv Accompanying the fast development of DG system and more DGs connecting to the distribution system, some new problems appear in protection technique area about grid-connected DG system, among which islanding is a typical and major one. Unplanned islanding will bring many problems to the grid: It threatens the life safety of power line maintaining staff and consumers; influence normal operation of equipment in the islanding system as well as reclosing action. This paper investigates the performance of rate of change of frequency (ROCOF) as used in embedded generation islanding detection of DFIG wind turbines. The impedance measurement based inter-lock algorithm was proposed to prevent the ROCOF from false tripping during a non-islanding situation. The simulation results show that the proposed inter- lock function can effectively distinguish the islanding and non-islanding situations. NR Electric Co., LTD. Zhongqing Li China Electric Power Research Institute This paper proposed a scheme of high sampling rate data in merging unit for relay protection. The data synchronization method based on the basic concepts of SMV, the low pass filter (LPF) algorithm and interpolation principle are studied, and then the protection scheme is proposed. The conclusion of the study showed that low pass filtering and interpolation synchronization scheme is simple and efficient for high rate sampling. That changing sampling data interface to enable the arithmetic and logical constant of protection can effectively reduce the risk of operation. This paper then tested the application in real time digital simulation (RTDS) system. 53 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Dingxiang Du China Electric Power Research Institute Xingguo Wang China Electric Power Research Institute AC Transmission Line Fault Current Analysis in Zhongqing Li China Electric Power Research Institute 220kV AC/DC Hybrid System A maloperation prevention method of zero se-quence direction longitudinal protection was presented in this paper directing at broken-line faults of double-circuit transmis-sion lines on a same tower. Firstly, the maloperation reasons were analyzed in detail. Then, the zero sequence direction amplitude-comparison criterion and the negative sequence direction ampli-tude-comparison criterion were constructed. The zero sequence criterion is used to detect earth faults sensitively and the negative sequence criterion is used to avoid maloperation of zero sequence criterion resulting from electrical and magnetic coupling during broken-line period. Meanwhile, the zero sequence current threshold and negative sequence current and voltage threshold were set for insuring the reliability of the whole protection scheme. The interior fault logic is that the zero sequence direc-tion criterions of the two sides of lines both reveal forward direc-tion. If that occurs, the zero sequence longitudinal protection acts and the fault line is removed. Otherwise, the protection will not act. Finally, the simulation results demonstrated the availability of the presented protection method. Tu B03.50 pp.1105-1109 Wenyuan Zhao Shenxing Shi Zhenghao Wang Xinzhou Dong Northeast Dianli University Tsinghua University Northeast Dianli University Tsinghua University This paper analyzes AC transmission line fault current in 220kV AC/DC hybrid system due to DC fast adjustment features. To illustrate the effect of DC response on AC fault current, a back-to-back HVDC system in 220kV hybrid system is exampled in the paper. After introducing basic principle and control method of HVDC system, the paper establishes simulation models of 220KV AC transmission system and 220KV AC/DC hybrid transmission system based on electromagnetic simulation software SIMULINK. Simulation results show that fault current in AC/DC hybrid system is different from the AC system, which will make AC transmission line protection misoperate or mal-operate. Tu B03.51 An Adaptive Fault Line Selection Method Based on Wavelet Packet Comprehensive Singular Value for Small Current Grounding System pp. 1110-1114 Xiangxiang Wei China Agricultural University Dechang Yang China Agricultural University Tu B03.53 A Logic Protection Program Design of Urban Distribution Network pp. 1120-1124 In this paper, an adaptive fault line selection method based on the wavelet packet comprehensive singular value for small current grounding system is presented. First of all, wavelet packet decomposition is utilized to decompose transient zero sequence current (TZSC) of 2 cycles, then the comprehensive singular values are introduced to describe the fault information. Secondly, normalize the comprehensive singular values to compute the fault membership values. At last, according to the difference between the maximum membership value and the second maximum membership value, the selected fault line can be output. The simulation results show that the proposed method cannot be affected by fault line type, fault resistance and fault initial phase angle, and also has good anti-noise capability. Maloperation prevention study of zero sequence direction protection to broken-line faults of parallel circuits on same tower pp. 1115-1119 China Electric Power Research Institute November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Qinhuangdao power supply company Ruijun Bu Qinhuangdao power supply company Kexue Liu Qinhuangdao power supply company Kai Zhou Qinhuangdao power supply company Tianshun Ma Qinhuangdao power supply company WenJun Li Qinhuangdao power supply company The traditional protection of urban distribution network has series of shortcomings such as the difficulty of coordination between protections, the large scope of blackout area and a long time for fault removing. Considering above situation, the paper presents a logic protection of urban distribution network. Based the location in the distribution network, the switches are classified with which the protection action criterion is given. Combined with the actual characteristics of urban distribution network, the logic protection program is designed. The analysis of example verifies the effectiveness of the program. Tu B03.52 Xianguo Jiang Fuchun Zhang 54 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Transient Temperature F ield simulation based on ANSYS for oil-immersed smoothing reactor when repeatedly Commutation Failure pp. 1137-1141 Tu B03.54 Research and Application of Network Load Stress Test for Smart Substation pp. 1125-1130 Ming Cai State Grid Jiangxi Electric Power Company Qi Xiao State Grid Jiangxi Electric Power Company Yuyun Chen State Grid Jiangxi Electric Power Company Wenxing Cheng State Grid Jiangxi Electric Power Company Xiaobing Zhou State Grid Jiangxi Electric Power Company Kai Zeng Changsha University of Science and Technology Rui Ma Changsha University of Science and Technology Haijing Yang State Grid HAEPC Electric Power Research Institute Yongchao Liang Human Electric Examine and Repair Company Gas relay takes the oil velocity in its installation location as the action criterion, and the gas and oil inflation which affect the oil velocity are caused by the fault fever. This paper researched the fact that flat wave reactor’s repeatedly commutation failures cause flat wave reactor gas relay’s malfunction, and proposed a transient temperature field simulation method of flat wave reactor under fault. The current situation of flat wave reactor when commutation fails is determined firstly. ANSYS is used to establish the geometric model of flat wave reactor. Normal temperature field is taken as initial value, and fault current is added, then transient temperature field of flat wave reactor under repeatedly commutation failures is calculated. This method can effectively simulate the temperature field of different time from the fault starts, and provide the basis for further calculation of oil velocity and analysis on gas relay operation. Load stress test of secondary equipment network is important for the large-scale construction of smart substations. In this article, several secondary equipment network schemes and their influence on relays related IEDs are discussed, and then stress test objects, principles for smart substation are proposed. Based on embedded CPU and large-scale FPGA, load stress testing device for secondary equipment network in smart substation is implemented with characteristic of supplying multi-type stress data stream along with IEDs’ necessary working stream, and field test practice is introduced in the end. Tu B03.55 Tu B03.57 A Simulation Platform for the Analysis of the Current Transformer Transient Characteristic pp. 1131-1136 Xuanwei Qi The Substation Fault Diagnosis Method Based on the T ime Constraint Probability Petri Net pp. 1142-1146 Huazhong University of Science and Technology Xianggen Yin Huazhong University of Science and Technology Zhe Zhang Huazhong University of Science and Technology Li Gan Changjiang Survey, Planning, Design and Re- Liang Gong Changsha University of Science and Technology Rui Ma Changsha University of Science and Technology Hai-jing Yang State Grid HAEPC Electric Power Re- search Co., Ltd search Institute The analysis of the current transformer transient saturation characteristic and its impact on differential current protection is an urgent problem to be solved. A simulation platform for analyzing the transient characteristic of the current transformer is introduced in this paper. The actual operating scene can be constructed in this platform in order to perform the complex transient process of power system. A variety of complex transient process in the power system can be simulated. The class P, PR and TPY current transformer model can be selected for analyzing the transient characteristic of the current transformer. This platform can achievement the analysis on the current transformer transient characteristic and its impact on the differential protection. The dynamic test and practical application prove the accuracy and the effectiveness of this platform. Yinghong He Hunan Ryan electrical engineering Company There exist some difficulties in existing substation fault diagnosis when dealing with the alarm information misstatement, omission, relay protection, breaker malfunction and tripping and such uncertain information. Therefore, the author put forward a kind of Petri net based on time constraint possibility of substation equipment fault diagnosis method to solve the problem of the uncertainty of substation fault diagnosis. First, time interval back model is constructed to represent the time constraints in the process of failure, to modify the alarm information, and delete the alarm information which is not in conformity with the temporal constraints. Then use probability indicates protection and circuit breaker movement situation and further processing uncertain information in case to increase the rate of fault tolerance. Finally, the correctness and effectiveness of the method is verified by the example analysis. Tu B03.58 Tu B03.56 55 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) pp. 1157-1161 Research on Traveling Wave Fault Location System based on High Accuracy Synchronous Clock pp.1147-1151 Zhiyuan Pan State Grid of China Technology College Hongwei Li State Grid of China Technology College Feng Deng Jing Wang State Grid of China Technology College Xinran Li Changsha University of Science and Technology Hunan University Xinyue Si Xiangjun Zeng Changsha University of Science and Technology Shandong University With increasing integration of distributed generation (DG) to the active distribution systems, the existing grid structure and protection configuration cannot meet the requirements of reliability. Adopting closed-loop configuration and reasonable protection schemes, it is possible to reduce the range of power outage and ensure continuous supply of DG. Firstly, an IED (intelligent electronic device) based complete protection structure consisting of several protection functions is proposed, including line protection, load protection and node protection. The protection principles of each protection function is described. The paper also studies the single-terminal weak-infeed issue of closed-loop distribution system by theoretical and simulation analysis. It is proved that the current phase variation based line protection function is not affected by the magnitude of fault current. It could correctly identify the fault under single-terminal weak-infeed condition. Nowadays, the reliability and accuracy of synchronous clock in the power system protection and location is hardly realized. High accuracy synchronous clock based on GPS and BEIDOU navigation satellite system was presented in the paper. Firstly, the accumulating error produced by crystal oscillator can be eliminated by reference of GPS 1PPS based on digital phase lock principle, and then GPS and BEIDOU mutual backup scheme can guarantee the reliability of synchronous clock when GPS worked under abnormal status or random error was too large. And then on the basis of high accuracy synchronous clock technology, a network-based traveling wave fault location system was proposed. The presented system operated in Hunan Changsha and Zhuzhou power system, and the results showed that it had great reliability, stability and accuracy. Tu B03.59 Tu B03.61 Operation Behavior of Converter Bridge Differential Protection in Converter Station of HVDC System pp. 1152-1156 A Novel Protection Scheme for Turn-to-turn Fault of Thyristor Controlled Transformer Controllable Shunt Reactor pp. 1162-1165 Hanli Weng China Three Gorges University Xuehua Li China Three Gorges University Guowen Yang China Three Gorges University Tao Zheng Ying Jin Fenfen Zhang Lianguang Liu Thyristor controlled transformer controllable shunt reactor (TCTCSR) with advantages of rapid response and continuously adjustable capacity is the preferable choice for reactive power control in EHV/UHV power system. But the protection scheme of TCTCSR is rarely studied. This paper addresses a problem in the application of traditional current differential protection against turn-to-turn faults where the traditional protection scheme may have less sensitivity or even refuse to operate in certain fault cases. Theoretical analysis is presented in this paper and three-phase fundamental zero-sequence component of CtrW as criteria to detect turn-to-turn faults is proposed to overcome the problem in traditional protection scheme. Finally, the setting value of the proposed method and its impact factors are discussed. Aiming at the abnormal operations of converter bridge differential protection of high voltage direct current(HVDC) transmission project, the operation behavior simulation of converter bridge differential protection under various fault conditions is carried out and the reason of the abnormal operations of converter bridge differential protection are explained and analyzed on the basis of PSCAD/EMTDC model. The simulation results indicate that, the converter bridge differential protection can operate correctly when a fault current difference exists between the sampled values of current transformers (CTs) on the △ bridge and Y bridge of the valve side. If the fault current flows or does not flows simultaneously into the CTs on the △ bridge and Y bridge of the valve side, the refusal- operation of converter bridge differential protection will occur. Tu B03.62 Tu B03.60 Complete Protection Scheme Closed-loop Distribution Systems North China Electric Power University North China Electric Power University North China Electric Power University North China Electric Power University for November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Identification Method for Internal and External Faults Based on Amplitude Feature of Backward Active 56 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Networks Traveling Wave for HVDC Transmission Line pp. 1166-1169 Xiaopeng Li State Grid Sichuan Electric Power Research Institute Sheng Lin Southwest Jiaotong University Shuai Jiang Xi’an Jiaotong University The theoretical analyses about the traveling wave transmission process for internal and external faults at HVDC transmission lines show that, in a short time, for internal faults, the backward traveling waves can be detected at both line terminals. For external faults, the backward traveling wave can be detected only at one line terminal. The backward traveling wave in the other terminal is zero in theory. Taking the calculation error and noise into account, the amplitude of the backward traveling wave is still very small. Thus, the identification method for internal and external faults for HVDC lines can be proposed by comparing the amplitude of the backward traveling waves at both ends of line. For internal faults, the ratio of the integral results is relatively small. However, for external faults, the ratio of the integral results is relatively large. Plenty of simulation results based on PSCAD/EMTDC indicate that the proposed protection method can discriminate internal faults from external faults under various fault conditions including faults with high fault resistances. To solve the problem of precise location for long-standing single-phase grounding fault in complex treetype distribution network, a novel single-phase grounding fault location method with traveling wave has been proposed. This paper studied transmission characteristics of traveling wave modulus, and presented a new fault location method combining the two traveling wave principles. First, the multi-terminal location algorithm was established to find out fault trunk line and narrow fault location scope. Second, a double-terminal fault location algorithm based on the time gap between zero mode and aerial mode traveling has been put forward to calculate the fault distance. Finally, according to the information of multi-terminal and double-terminal fault location, the fault point was located. Simulation results indicated that the location method can carry out accurate fault location with traveling wave location device mounted on only part of the ends in the distribution network. Therefore, it can save investment effectively, and has advantages of little data load and simple algorithm implementation. Tu B03.63 Tu B03.65 Reliability Evaluation of Distribution Network Based on Sequential Monte Carlo Simulation pp. 1170-1174 Qi Lu Insulation Faults Detection and Location System with Traveling Wave for Transmission Lines pp. 1180-1183 Nari Technology Development Limited Company Yujie Hua Nanjing University of Science and Technology Ye Shen Nanjing University of Science and Technology Qi Kang New York Institute of Technology Rong Zhang pp. 1175-1179 Huan Ye Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Kexin Rui Changsha University of Science and Technology Zi-kun Zhu Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Xiangjun Zeng Changsha University of Science and Technology Dong-mei Yang Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Yan-zhao CAO Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Xiangjun Zeng Changsha University of Science and Technology Ke Zheng Changsha University of Science and Technology This paper designed an insulation faults detection and location system with traveling wave for transmission lines, to solve the problem of precise detection. A special traveling wave sensor was developed based on the two order differential principle,which enhanced the wave head steepness, then to improve the the detection accuracy. On this basis, combined with GPS satellite synchronous precision timing and GPRS wireless communication technology, the insulation faults detection and location system with traveling wave was proposed. And the initial fault point is located by a double-terminal fault location algorithm. The testing results showed that the detection sensitivity of partial discharge flashover current is 2.134A, which verified the performance of the proposed system for the insulation faults. Shanxi University of Technology In this paper, the reliability evaluation of distribution network is studied by using the sequential Monte Carlo simulation based on dual sampling. A reliability evaluation model of distribution network is established. The range influenced by fault is determined by the analysis method of node fault. And then, all kinds of reliability index are calculated. With matlab programming, IEEE RBTS Bus 6 test system is evaluated to prove that the method in this paper is effective. Then the simulation analysis is carried out for the cases that whether there is a standby transformer in power distribution network, whether the circuit breaker is reliable and whether there is a contact switch between the two feeders. The results show that the reliability of distribution network system can be enhanced by adding the standby transformer and the contact switch and improving the reliability of the circuit breaker. Tu B03.66 Tu B03.64 Household distribution protection device with fault pre-detecting A Novel Single-phase Grounding Fault Location Method with Traveling Wave for Distribution 57 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) pp. 1184-1189 Tu B03.68 Xiangjun Zeng Changsha University of Science and Technology Weiming Zhang Changsha University of Science and A new method for fault line selection based on Technology Shun Xu correlation between zero-sequence voltage in bus and zero-sequence current in feeders pp. 1196-1199 Hunan Hydro & Power Design Institute Yingke Gu Changsha University of Science and Technology Bin Zhang Hunan Province Planet Intelligent Electricity De- Yunkun Xiang Changsha University of Science and Technology velopment Company Yun Jiang This The development of human’s living condition and the corresponding technology application in low-voltage distribution system have currently caused lots of power consumption. Thus, it is important to find out the fault location and switch off the device before fault occurring. This paper analyzes the principle of leakage current &short-circuit current fault detection, applies fault pre-detecting theory to preclude the hidden fault, provides the measure of isolating force electricity from weak electricity, designs a novel household distribution protection device with fault pre-detecting. Its performance meets relevant low-voltage distribution system standards. Simulation and practical application show that the device has a bigger advantage of troubleshooting, correct malfunction for relays. Therefore the device is more smart and practical than traditional protection device and has more value for popularization. Yuanzhi Ning Changsha University of Science and Technology Dual-loop Control Strategy of Three-phase Unbalance Overvoltage Active Suppression Device in Distribution System pp. 1190-1195 Yancun Cai Changsha University of Science and Technology Changsha University of Science and Technology Based on Distance Proportion and T ime Difference for Distribution Network pp. 1200-1205 The three-phase unbalanced overvoltage exists normally in arc suppression coil grounded distribution network. Excessive unbalanced voltage threatens the proper operation of electric equipment and affects the quality of power supply. In this paper, a suppression method by injecting zero-sequence current to the neutral point through an active inverter device was proposed to inhibit overvoltage in distribution network which was caused by single-phase overload or the asymmetry of three-phase line-to-ground parameters. Then, a dual-loop control strategy consists of a proportional resonant controller and a dead-beat controller was designed, it makes it easy to suppress the unbalanced voltage quickly and precisely without measuring the grounding parameters of the network. Finally, a 10kV distribution system model was built in MATLAB for analysis. Simulation and prototype testing results showed that the suppression system has good steady-state and transient response. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Bohan Liu A Novel Traveling Wave Fault Location Method Xiangjun Zeng Changsha University of Science and Technology Changsha University of Science and Technology Changsha University of Science and Technology Tu B03.69 Changsha University of Science and Technology Wen Wang Fang Tao It is difficult to select the fault line due to the weak current when the single-phase grounding fault occurs in the resonant grounding system. A new method based on correlation between zero-sequence voltage in bus and zero-sequence current in feeders is proposed in this paper. The correlation coefficient is less than zero because the polarity of zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current is opposite in fault line, and correlation coefficient is large than zero because the polarity in sound line is same. Therefore, the feeder what corresponding to the minimum correlation coefficient is the fault line. Most simulation results show that in resonant grounding system, compared with the integrated correlation coefficient analysis between pure fault components of zero-sequence current from every line, this method can be applied to select fault line more better, and misjudgment will not be caused. Tu B03.67 Feng Zhou Changsha University of Science and Technology Jun Cai Changsha University of Science and Technology Xiangjun Zeng Changsha University of Science and Technology Yi Yang Changsha University of Science and Technology Shuguang Deng Hunan City University In order to solve the problem that the accuracy of fault location is influenced by traveling wave speed and conductor sag, a new method of traveling wave fault location based on the distance proportion and time difference presented in this paper. Firstly, installed traveling wave acquisition device at the end of each line and substation bus in distribution network, a standard array of the arrival time difference of traveling wave is constructed based on the time difference between simulating faults and the head/end of fault line. And then, comparing the actual array of the arrival time difference of traveling wave with the standard array, the fault section can be distinguished. Calculating the distance ratio between the fault point to the head of fault section and the whole length of the fault line, then 58 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) the fault position is determined on the basis of the location of each tower and cable connector. Finally, the ATP/EMTP simulation results show that this method is not affected by the wave velocity and the change of line length, and with high fault location precision compared with traditional method. By setting appropriate proportional and integral coefficient of PR controller, the controllability of injecting current and the static performance of system were improved. Simulation analysis and prototype test results verified that the control method has high precision and low steady-state error, and is able to suppress three phase unbalanced voltage quickly and accurately. Tu B03.70 IMF Energy Moments and LS-SVM Based Fault Section Location Method for Distribution Network pp.1206-1213 Tu B03.72 A Novel Three-phase Unbalanced Voltage Flexible Restraining Method for Distribution Systems pp. 1220-1223 Yingke Gu Changsha University of Science and Technology Xiangjun Zeng Changsha University of Science and Technology Shun Xu Hunan Hydro & Power Design Institute Shuguang Deng Hunan City University Rui Chen Electric Power Research Institute of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Hongjie Weng Electric Power Research Institute of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Leisisi He Changsha University of Science and Technology Yancun Cai Changsha University of Science and Technology Wen Wang Changsha University of Science and Technology In China, the method of neutral resonant grounding and neutral ungrounded are widely used in distribution networks. When grounding fault occurred in distribution network, the fault current is small, and vulnerable to the outside interferences, so the fault features are difficult to be detected. To solve this problem, a new method of fault section location based on intrinsic mode function (IMF) energy moments and least squares support vector machines (LS-SVM) was proposed. Firstly, the fault current signals were decomposed into several IMFs based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition(EEMD), then the fault feature vectors of IMF energy moments were obtained by integrating the IMF components with time. Secondly, the IMF energy moments with high correlation coefficients were taken as learning samples, then they were inputted to LS-SVM classifier to obtain fault selection location model. Finally, the unknown fault samples were inputted to the LS-SVM classifier trained before to achieve fault section location results. The simulation results show that this method can recognize features of fault signals accurately and identify the fault sections correctly. Three-phase voltage unbalance is frequently encountered in neutral ineffectively grounded distribution systems, which affects the normal operation and power quality of power system. This paper proposed a novel method to restrict the unbalance by means of injecting a current to the neutral point. The injecting current is used to compensate the grounding 1current and then force neutral voltage to zero and three-phase voltage to balance as well. An inverter is connected between the neutral point and the earth through a transformer to produce the injecting current. By controlling the inverter, the amplitude, phase and frequency of injecting current can be controlledflexibly. A 10kV distribution system model was built in MATLAB for analysis. The simulation results indicate that theproposed method can restrain the three-phase unbalance voltage efficiently and rapidly. Tu B03.73 Tu B03.71 Application of Beidou Satellite T iming and Injecting current control method for 3-phase unbalanced voltage suppression in distribution system pp. 1214-1219 Communication Technology in Power System Fault Location pp. 1224-1230 Leisisi He Changsha University of Science and Technology Feng Zhou Changsha University of Science and Technology Wen Wang Changsha University of Science and Technology Xiangjun Zeng Changsha University of Science and Technology Qingling Wang Maoming Power Supply Bureau of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Limited Lei Shu Changsha University of Science and Technology Honghui Chen The asymmetry of system parameters and electric loads lead to three-phase voltage unbalance in neutral resonance grounded distribution networks, which causes damages to the electrical equipment and power system. This paper proposed an unbalanced voltage limiting method by injecting a zero-sequence current to the neutral point of distribution network through an active inverter, and studied the controlling strategy of the injecting current with a proportional resonant (PR) controller. Maoming Power Supply Bureau of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Limited Xiangjun Zeng Changsha University of Science and Technology Huan Ye Maoming Power Supply Bureau of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation Limited Juntao Zhou 59 Maoming Power Supply Bureau of Guang- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) coil has been studied. dong Power Grid Corporation Limited Feng Deng Changsha University of Science and Technology Tu B03.75 In order to improve the accuracy of time synchronization and the reliability of data communication in power system fault location, a new Beidou satellite based timing and communication technology applied to power fault location system using traveling wave is designed in this paper. Principle1of Beidou timing was firstly analyzed. Considering the disadvantages and advantages of one-way and two-way timing style in Beidou, a new combinational timing scheme based on Beidou satellite system was proposed. Then, through the deep analysis of basic principle of communication, two-way short message communication of Beidou Satellite was proposed and the corresponding communication protocol was made. Eventually, traveling wave based fault location system using the technology of Beidou satellite timing and communication in transmission lines is preliminarily designed. Simulation and test results show that the presented scheme can be applied to fault location system absolutely, which can provide high accuracy of time synchronization for the system, and improve the location accuracy. It also could ensure the high reliability in Beidousystem using short message communication, which no longer need other data transmission access. in that case, it would save the construction cost of power grid communication greatly. Realization and Performance Analysis of Travelling Wave Based Directional Protection Prototype pp.1236-1239 Xinzhou Dong Tsinghua University Shenxing Shi Tsinghua University Bin Wang Tsinghua University Beijing Electric Power Company Travelling wave based protection is becoming attractive in ultra-high voltage (UHV) transmission systems due to the requirement for high-speed protection. However, the poor transfer characteristics of coupling capacitor voltage transformers (CCVTs) for high-frequency voltage have strictly limited its application. A travelling wave based protection prototype considering the characteristics of CCVTs is developed in this paper. Extensive laboratory tests are performed to assess the performance of the developed prototype. Further, the prototype has been applied in the 750 kV substations in China and an external fault was recorded during the operation period, validating the effectiveness and reliability of the proposed prototype. Traveling Wave Detection Principle Based On PCB Traveling Wave Sensor pp. 1231-1235 TuB04.1 A Novel Control Strategy for Static Excitation Electric Power Research Institute of Guang- System Based On Three-phase Current Source dong Power Grid Co., Ltd. Yuan Zhang Shuxin Luo Shiyong Wang Tu B03.74 Yi Wang Tsinghua University Converter Electric Power Research Institute of pp.1240-1245 Guangdong Power Grid Co., Ltd. Kexin Rui Yuhao Zhou Changsha University of Science and Technology Chengxiong Mao Xiangjun Zeng Changsha University of Science and Technology Yiran Jiang Jian Zhang Huazhong University of Science and Technology Huazhong University of Science and Technology Changsha University of Science and Technology Electric Power Research Institute of Guang- Zhu Chen Huazhong University of Science and Technology dong Power Grid Co., Ltd. Jiming Lu Huazhong University of Science and Technology Dan Wang Huazhong University of Science and Technology Traveling Wave Detection is the core problem in traveling wave fault location. Existing traveling wave detection methods could be mainly divided into current traveling wave detection and voltage traveling wave detection. Considering the existing current traveling wave detection is complex and costly, the existing voltage traveling wave detection is inconvenient to install, a PCB traveling wave sensor based on Rogowski coil has been proposed in this paper which could detect faults of the power system by abstracting substation secondary signal directly. The structure of PCB traveling wave sensor was analyzed, the transfer function and frequency characteristics of the high-frequency transient signal extracted from Rogowski November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China In modern power system, increasing pressures of system stability have become more and more serious. Because excitation systems are one of the most effective and economical ways contribute to effective control of voltage, increasing attention has been focused on the effects of excitation control. To satisfythe needs of modern power system, excitation system based on full-controlled devices is proposed to be used in synchronous generator excitation, and a new decoupled control technique is adopted to design a controller for current source converter based excitation system in this paper. Then, the modified Heffron-Phllips mathematical model of synchronous gen- 60 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) erator based on this new type of excitation system is discussed, which helps to explicate the principle of reactive power injector in the new excitation system and its design strategy. Also, the crucial function of reactive power injector that could provide more damping to the system is explained. The simulation results are presented to demonstrate the correctness and effectiveness of the proposed approaches, and its advantage over the conventional excitation system. proposed model and method. The simulation results show that voltage regulation is proved to be a good solution to increase the maximum penetration of DG, but a compromise must be made between higher penetrations of DG and fewer adjustments of voltage regulation devices. This will have major implications for the development of DG in SDG. TuB04.4 TuB04.2 AC/ DC Hybrid Micro Grid Voltage Recovery Control pp. 1256-1260 Hybrid PV-VSDG and stabilizing DC-Voltage bus Using SMES pp.1246-1250 Bashar Sakeen Farhan Huazhong University of Science and Technology Shaorong Wang Huazhong University of Science and Jinxiang Liang China Electric Power Research Institute Yu Ji China Electric Power Research Institute Wenhua Wu China Electric Power Research Institute Jing Cao China Electric Power Research Institute Jing Li China Tianchen Engineering Corporation Technology Hasan Wahhab Salih AC/DC hybrid is a kind of structure forms of mi- cro grid, to supply AC load and DC load. In order to realize the uniform distribution of DC power between AC converters, im- prove the DC bus voltage quality; this paper introduces a hierarchical AC converter control strategy. The first layer is the DC voltage-active power droop control method to realize the uniform load distribution; considering that droop control will lead to fall of the DC bus voltage, the second layer control method compen- sate voltage reference value of DC bus, to realize the recovery of bus voltage, and ensure the quality of the DC bus voltage. In this paper, control methods are analyzed by the root locus method, and the micro grid model is built based on the simulation of soft-ware DIgSILENT, to validate the control strategy. Huazhong University of Science and Technology In this paper an energy system topology consisting of a variable speed diesel generator (VSDG), PV using MPPT and single inverter is presented and considered to provide energy to an isolated load at constant frequency and voltage. SMES is utilized to maintain DC-voltage bus steady during the unbalanced power between generating power of (PV-VSDG) and load demand by releasing (or absorbing) the power difference until the system delivered the required power to the load. The PVVSDG and SMES is modeled in MATLAB/SIMULINK and simulation tests are carried out to verify the function and performance of the system. TuB04.5 TuB04.3 Study of Out-of-step Oscillation Characteristics forEast China Grid and Applicability Analysis of SystemSeparation Scheme upon the Operation of UHVBinjin DC Transmission Project Increasing Maximum Penetration of Distributed Generation by Voltage Regulation in Smart Distribution Grid pp. 1251-1255 Shanshan Zhao pp. 1261-1266 China Electric Power Research Institute Xiaoli Meng China Electric Power Research Institute Yun Su State Grid Electric Power Research Institute Xiaohui Song China Electric Power Research Institute Naiwang Guo State Grid Electric Power Research Institute Yinghui Yu State Grid Electric Power Research Institute Lei Huang State Grid Electric Power Research Institute Hao Chen State Grid Electric Power Research Institute With the increasing pressures on energy conservation and emission reduction, the urgent need arises to increase the maximum penetration of distributed generation (DG) without violating the voltage limits. This paper proposes a twodimensional multi-resolution model of smart distribution grid (SDG) to analyse dynamic changes of DG and load at first. And then based on the model, an analytical methodology is presented to determine and increase the maximum DG penetration without voltage violations by voltage regulation. IEEE Comprehensive Test Feeder is used to prove the feasibility and validity of the Fujian provincial grid was connected into East China grid through two parallel tie lines of 500kV in 2002. Out- of-step oscillation may occur between Fujian Province Grid and East China grid under the critical contingencies. System separation devices have been installed on 500kV tie-lines between Fujian grid and East China grid to maintain system stability. As 61 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) the newly built UHV Binjin DC transmission system was projected to come in service in 2014, power injected into East China grid through the system was gradually increased to its full capacity in accordance with the implementation of the project by three stages. The characteristics of out-of-step oscillation between Fujian grid and East China grid may be altered due to the significant changes involving tie lines, reinforcement and reconfiguration of local system as well as the scale of power injection. To investigate the characteristics of out-of-step oscillation, extreme contingencies contributing to out-of-step oscillation are identified based on the analysis of the practical grid operation. For each stage of Binjin transmission project, the center of out-of-step oscillation is determined through the simulation analysis of the oscillation characteristics for East China grid. The applicability of the existing system separation devices is evaluated, and system separation strategy is then reviewed for East China grid to accommodate the operation of UHV Binjin DC transmission project. on Displacement Voltage Method pp. 1273-1277 Jie Zhou State Grid Jiangsu Economic Research Institute In order to make sure the best compensation for the grounding fault current, neutral resonant grounding mode via the arc suppression coil is widely used in medium and low voltage distribution network in our country. The key problem is measuring the phase-to-ground capacitance accurately online. Displacement voltage is a method of measuring the phase-to-ground capacitance indirectly. Choosing the suitable inductive reactance is very important to calculation accuracy. The model of neutral resonant grounding is established with the simulation software in this paper. The inductive reactance and the displacement voltage corresponding to reactance are recorded. This paper used non-linear regression method to fit the multinomial between displacement voltage and the reactance. The resonance point can be determined to get the suitable reactance for capacitance calculation. It can improve the calculation accuracy and reduce the error. TuB04.6 Mechanism Analysis on Instability caused by Multiple HVDC Power Drop of Multiple Sending HVDC Systems TuB04.8 Jingzhe Tu China Electric Power Research Institute Jian Zhang China Electric Power Research Institute Condition Assessment of Gas-Insulated Switchgear Based on Multiple Information pp. 1278-1282 Junchuan Jia China Electric Power Research Institute Honghua Xu Jiangsu Nanjing Power Supply Company Qiang Yu China Electric Power Research Institute Chunning Wang Jiangsu Nanjing Power Supply Company pp. 1267-1272 As the high-voltage direct current (HVDC)s with large capacity are continually being commissioned, the “strong DC and weak AC” characteristic of the power gird is furtherly being presented, the influence of the multiple sending HVDC system on the stability of the interconnected power system is becoming significant. In this paper, the HVDC power drop characteristic caused by contingencies of the sending-side system is analyzed, on the base of the three-area AC/DC equivalent model, the impact of the multiple HVDC power drop on the stability of the interconnected system under different power flow directions is analyzed, and the single HVDC blocking is taken to be compared. Finally, the results are verified by the “North China-Central China-East China” power grid case system. The results show that the instability mode of the sending-side system caused by the multiple HVDC power drop is the first/second angle instability, the severity of the impact of which on the sending-side system stability is close to that of the single HVDC blocking, and further study on the effective counter-measures is quite necessary. Taoyun Wang Hohai University Lanying Yang Hohai University Hongzhong Ma Hohai University Condition assessment of gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) is an important approach to provide decision-making for condition maintenance which improves the operation reliability of power systems. Indices system of operation condition assessment for GIS is established according to its operation condition which is related to quite a few factors. A part of the factors is vague. Constant weight is determined by the interval analytic hierarchy process while variable weights are obtained by using entropy method to correct constant weight, which improving the accuracy of the condition assessment. The correlation function of each index is constructed by using extension theory. The status level and the corresponding GIS’s maintenance strategies based on the relationship between function values, the note value and warning value are specified by the procedures. Example analysis shows that condition assessment of GIS based on a variety of information is more rational and effective. TuB04.7 TuB04.9 Measuring Phase-to-ground Capacitance Based Identification of Critical Lines in Power Grid Based on Active Power Flow Betweenness November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China 62 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) pp. 1283-1287 pp. 1294-1298 Xiaowei Sun Three Gorges University Yichang Yude Yang Tao Zhang Three Gorges University Yichang Xiujun Qin Bin Zhang Three Gorges University Yichang Wentai Liu Guangxi University Jian Yang Guangxi University It is an important part for the power system operation risk control to identify the critical lines. To improve the iden-tification accuracy, the indicator of active power flow betweenness is proposed in this paper. The actual distribution of the power flow and the capacity of each transmission line are involved in the model which is more comprehensible to the physical backgrounds of power system. At the same time, the effectiveness of the identification results is verified by the changes of system transmission efficiency that proposed in the paper with the out- age simulation and cascading failure of the critical lines. The experiment on IEEE-118 bus system shows that a few lines with high active power flow betweenness play a vital role in the power grid. Continuous attacks on these lines lead to a sharp decline in the level of the power transmission efficiency. Thus, it is effective to identify the critical lines in power grid by using the active power flow betweenness. A Novel GA-PI Optimized Controller for MPPT Based PV in a Hybrid PV-Diesel Power System pp. 1288-1293 Shaorong Wang Shaorong Wang Guangxi University Modern power system is getting larger and complicated. Once it comes an accident, engineers need to make decision in a very short time which is a huge challenge for them. Thanks to the development of computer network and electrical equipment, nowadays power system has been achieved the goal of information resources sharing. The small-signal stability problem has been getting attention because of the occasional oscillation. Though numbers of measures are taken into account to enhance the small-signal stability, sometimes it would not help. Based on this actuality, this paper prospect a new method that can increase small-signal stability by adjusting power flow. The model considered small-signal stability constrained-optimal power flow(SSSC-OPF) by adding small-signal stability index into the OPF model. In fact, it does not substitute any other existing controller actions, but rather provides limited generator adjustment to obtain the required stability margin. By getting the real-time operation data from database, analyzing and forming into the specific format we need. Then calculating the power flow and smallsignal stability of the current point. If the stability index is not met, the algorithm will optimize the active power output until the damping ratio is high enough. Numerical simulations for two systems confirm the validity of the method and the robustness of the algorithm, so that can be widely used in practical system. TuB04.10 Hasan Wahhab Salih Department of Electrical Engineering Nanning Huazhong university of Science and Technology Huazhong university of Science and Technology Huazhong university of Science and Technology TuB04.12 Quantitative Analysis and Optimization of Primary Frequency Characteristic in Isolated Power Gr i d Because of the intermittency of output PV power, the authors have developed and implemented the Perturb and Observe (P&O) MPPT technique using genetic algorithm (GA) to tune and obtain the optimum parameters of the PI controller for the standalone PV-diesel hybrid power system. This PI controller regulates the output of boost converter for PV system. The results of this control technique are compared with the conventional P&O MPPT technique that is based on PI trial and error method for the same system. The proposed novel controller has improved the dynamic response of PV system output power and the voltage oscillation damping. Another reason to design this proposed controller is because the fluctuating power causes frequency deviation in the power system, so the controller also reduces the frequency deviation of the standalone PV-Diesel hybrid power system in term of rise time and maximum overshooting during any fluctuation of PV insolation. The whole system is implemented by using MATLAB/Simulink Environment using actual solar radiation data. The simulation results show the effectiveness of the proposed controller. pp. 1299-1304 Zhiyuan Qi North China Electric Power University Shiwu Xiao North China Electric Power University Fei Li North China Electric Power University Primary frequency regulation of isolated power grid is significantly different with large power system. In this paper, based on the frequency change of isolated power grid, mathematical expressions of a dynamic process of primary frequency regulation are derived. And then mathematical expressions of the maximum frequency deviation, maximum rate of frequency change and static frequency deviation are got. The influence on the primary frequency regulation by generator frequency coefficient, the ratio of generator participating in primary frequency regulation, the generator inertia time constant, and the governor time constant is analyzed. Optimization method of primary frequency regulation by adding the acceleration feed forward is proposed. The method, which equals to increasing the system inertial time, reduces the maximum frequency change rate and the maximum frequency deviation. At last, the TuB04.11 Small-signal Stability Constrained Optimal Power Flow Based on Real-time Data 63 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) validity of this method is verified by the simulation of an isolated power grid. measures are used up to obtain the optimized voltage. It proves the typical heterogeneous scale-free network features of power grid and uses electric coupling degree to identify the key substations which own the closest connections with other buses in the network, according to the results, changing corresponding backup lines from hot-spare into cold standby mode. Compared with circuit break depend on experiences in actual production, the proposed method has obvious advantage of improving the net-wide voltage with the least cut of backup lines, which is physical well-defined and convenient. The simulation results of practical grid validate the proposed strategy and show the effectiveness of optimizing the net-wide voltage profile which possess of good application prospects. TuB04.13 New Passivity Design for the Excitation and Steam-Valving Control of Synchronous Generators pp. 1305-1310 Tianbai Deng North China Electric Power Univ. Yinsong Wang North China Electric Power Univ. Xiaohe Qu North China Electric Power Univ. TuB04.15 This paper presents a new passivity design for the excitation and steam-valving control of synchronous generators. Different from conventional control method, the proposed control considers the steady-state error of active power and reactive power supporting capability of the generator. Based on the five-order nonlinear model with two inputs, steam-valving control is designed by backstepping method at first to ensure the angle stability, and then excitation control is achieved by using the passivity approach incorporating the high side voltage control technique. When design the controller, two integrators are added in the differential equations to reduce the steady-state error. And the step up transformer reactance is compensated in design, so the excitation control is optimized to sustain a high level voltage.The simulation shows the approach has strong positive impact on the performance of active and reactive power of the generator. An Emergency Load Shedding Algorithm pp. 1316-1320 TuB04.14 TuB04.16 State Grid Electric Power Research Inst. Ming Tang State Grid Electric Power Research Inst. Hua Zhang State Grid Electric Power Research Inst. Wenbin Hao State Grid Electric Power Research Inst. Min Liu State Grid Electric Power Research Inst. Kun Li Baohui Zhang Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. China Electric Power Research Inst. A new emergency load shedding algorithm is proposed in this paper based on the state plane representation of generator speed and power angle. When the trajectory of the power system stays in concave regions, the system is stable. When the trajectory crosses though the convex regions, the system is detected as unstable state. Based on the characteristic of the trajectory, a load shedding algorithm is proposed in this paper when active power is insufficient in receiving end. The proposed method was successfully tested in a single machine infinite bus system. Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis and ZnO-based Suppression of Ferroresonance Overvoltage in Distribution Network pp. 1321-1325 Ye Zan Wang Qian Jiandong Duan Wangjing Tan Xi’an Univ. of Tech. Xi’an Univ. of Tech. Xi’an Univ. of Tech. Xi’an Univ. of Tech. Ferroresonance overvoltage that is caused by saturation in electromagnetic type voltage transformers occurs frequently. In order to avoid interference from ferroresonance overvoltage in the safe operation of a power system, it is a to study a reliable and stable resonance elimination measure.Firstly, different types of ferromagnetic resonances are obtained with the different ratio of capacitive reactance and inductive reactance. Thereafter, nonlinear dynamics research method is used to analysis the effect of inhibiting ferroresonance in ZnO nonlinear resistance grounding mode. Finally, the method is verified by ATP-EMTP. The results show that the voltage amplitude of the neutral point through nonlinear resistance falls under State Grid East Inner Mongolia Electric Power Company Hohhot To avoid 110kV distribution network bus voltage conducting above the over-limit during holidays especially in the Spring Festival, a new voltage regulation method based on electriccoupling degree is introduced. The strategy takes example by circuit breaks in practical operation and accordingly alters key backup lines’ connection modes under the restraint of line thermal stability, transformer capacity and switching power flow on boundary when traditional voltage regulation November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Dezhi Chen A New Approach to 110kV HV Distribution Grid Voltage Control Based on Coupling Numerical Analysis pp. 1311-1315 Xiaoxu Wang Huaiyuan Wang 64 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) multi-objective model which considers the difference of the objectives’ importance is proposed. To get the most preferred alternatives, a non-r-dominance sorting genetic algorithm II (r-NSGA-II) is used to solve the model. The reference point determination method and solution set scale controlling method are proposed to improve the algorithm, which makes the solution set scale controllable and the preference to be better expressed. Simulation results show that the proposed method has practical value when solving the generator start-up problem for network reconfiguration. normal circumstances and chaotic phenomena is eliminated. The results imply that the suppression measure can well inhibit ferroresonance overvoltage. TuB04.17 A General Adaptive Multi-Segment Strategy for Transient Stability Constrained Optimal Power Fl o w pp. 1326-1331 Jian Yang Guangxi Univ. Hua Wei Guangxi Univ. Xiujun Qin Guangxi Univ. Chunmei Lin Guangxi Univ. TuB04.19 The Load Oscillation Energy and Its Effect on Low-Frequency Oscillation in Power System pp. 1336-1341 In view of the low computational efficiency and large memory occupancy in conventional numerical discretization algorithms for transient stability constrained optimal power flow (TSCOPF), this paper presents a general adaptive multisegment strategy, which could be applied to various numerical discretization algorithms. Based on the error analysis with implicit trapezoidal method (ITM) as an example, a multi-segment simultaneous strategy is put forward in light of the discontinuity of power network parameters before and after fault clearing; Furthermore, in view of the fact that excessively high accuracy of swing angle is unnecessary in engineering practice, an adaptive accuracy control strategy is put forward. The strategy proposed above could not only improve the accuracy of the conventional method, but simply need to calculate once to obtain the desired integration step within any accuracy limitation, thus avoiding large number of unnecessary computation burden by using adaptive rather than unified integration step size for different problems. The results of 5 test systems, such as 703-bus system, indicate that compared with the conventional ITM, the proposed strategy could limit the deviation between control accuracy and actual accuracy within the range of ±1 degree, and improve the computation speed by 2-20 times, which shows promising application prospects. A r-NSGA-II Algorithm Based Generator Start-up for Network Reconfiguration pp. 1332-1335 Shandong Univ. Hainan Zhu Shandong Univ. Yutian Liu Shandong Univ. Hohai Univ. Yaling Shen Hohai Univ. Xiang Zhang Hohai Univ. Jiyun Zhu Hohai Univ. Jiajia Du Hohai Univ. Low frequency oscillation is a potentially dangerous phenomenon in power systems involving exchange of power among generators and loads in different areas. The study of the low frequency oscillation mainly concentrated on the analysis and control of generator in the past. As important parts of power system, loads have a significant effect on the low frequency oscillation of the interconnected power system. In this paper, we study the effect of load to the low frequency oscillation by analyzing the characteristic and distribution of the load oscillation energy. Firstly, the equations of the load oscillation energy are introduced, which derived from the linearization of system dynamic equations. Then, based on the load oscillation energy, the distribution of the oscillation energy in a variety of static loads and internal induction motors is analyzed in a single-machine infinite-bus system. Different kinds of load have different effects on low frequency oscillation. Moreover, in the interconnected 4-generator 2-area system with weakly damped free oscillation, the oscillation energy distributions of the different kinds of load at different locations, as well as different induction motor load capacity ratio are analyzed. Finally, the effect of load characteristics on the low frequency oscillation is summarized from the perspective of oscillation energy. TuB04.18 Runjia Sun Yiping Yu The objective of power system restoration is to restore the load as soon as possible , while the successful start-up of generator is the precondition of load recovery and the emphasis of power system restoration. In this paper, both the generator start-up sequence and the restoration path are considered. A preference TuB04.20 Dynamic Stability Analysis of the Interconnected Power System with Mengxi UHVDC Integration 65 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) tions of resonant oscillation and beat frequency oscillation. Lastly, differences in frequencies and damping ratios of components forced power oscillation are analyzed and used for criteria for discriminating forced power oscillation from free power oscillations. Simulation results of the New England test system demonstrate the effectiveness of the forced power oscillation response analysis. pp. 1342-1345 Mei Li Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Ni Zeng Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Yuanfang Zeng Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Shuang Zhao Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Pei Bie Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Jiasi Wu Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Hang Li Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Ruoxi Zhu Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Buhan Zhang Xu Zheng TuB04.22 Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. State Grid Hubei EconomicResearch Inst. Real-time Transient Instability Monitoring and Determination for Large-scale AC/DC Interconnected Power System Using Synchronized Phasor Measurements pp. 1351-1357 Due to the mismatch between power supply and demand, in addition with the increasingly prominent problem of environmental pollution, UHV AC/DC power transmission overlong distance obtains rapid development in our country. With the expansion of the power grid, regional low frequency oscillation has become one of the major problems that endanger safe and stable operation of power system. In this paper, taking a large-area interconnected system integrated with Mengxi UHVDC transmission line as the background, dynamic stability of the system is analyzed using small signal analysis method and time-domain simulation based on PSASP under different load and UHVDC operating conditions. The results show that when DC out of running, weak damping will appear in the interconnected power grid. PSS is the most economical and effective equipment for damping low frequency oscillation, which can perform well to both the local mode and the inter-area one. In view of the existing weak damping mode, PSS parameters are optimized which effectively improve the system damping, thus insuring the safe and stable operation of the system after the UHVDC line access. Wei Wu Electric Power Research Inst. China Southern Power Grid Hong Rao Electric Power Research Inst. China Southern Power Grid Chao Hong Electric Power Research Inst. China Southern Power Grid Yongjun Liu Electric Power Research Inst. China Southern Power Grid In this paper, a real-time transient instability detection system is proposed to determine the transient instability using wide-area phasor measurements. The proposed system incorporates determination of oscillation tie lines and real-time transient instability detection. Oscillation tie lines can be identified immediately after the system being subjected to a large disturbance according to the coherent groups of generators and system network topology. Then, system transient state is evaluated by a novel criterion in real-time with the crucial measurements. The used measurements during the post-disturbance are extracted from the huge number of PMUs data updated timely and can represent the transient status of a system. The proposed approach is examined on a practical AC/DC interconnection power system. The obtained results indicate the efficiency of the transient instability detection system for determining the transient unstable status. TuB04.21 Response Analysis and Type Discrimination of Power System Forced Oscillation pp. 1346-1350 Dong Yang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. Luhua Xing State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. Liang Wang Shandong Electric Power Dispatching and Control Center Hua Ye Shandong Univ. Yutian Liu Shandong Univ. TuB04.23 Mechanism and countermeasures for free power oscillation and forced power oscillation are different. The key to suppress them is to locate, discriminate, and then take effective measures. In this paper, an explicit expression for forced power oscillation response of a multi-machine power system is firstly obtained. Simplifications are then made by using the condi- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Nonlinear Oscillation Description by Swing Energy Sequence of the Controlling Mode pp. 1358-1362 66 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Qinglong Liu Nanjing Univ. of Science and Tech. Yusheng Xue State Grid Electric Power Research Inst. Qi Tao Zhen Wang Zhejiang Univ. Xin Xu Shandong Univ. Hengxu Zhang Shandong Univ. Yun Chai Zhejiang Univ. Shandong Univ. Fang Shi Shandong Univ. Zijun Bin Shandong Univ. Zhaowei Li NARI Group Corporation Tiangang Huang Southeast Univ. Wei Li NARI Group Corporation This paper presents a method to describe nonlinear oscillation of power system. Specifically, this paper uses the controlling mode which is identified by the extended equal-area criterion (EEAC). The energy of center equal point (CEP) or far end point (FEP) in each swing is used to express the oscillation energy of the controlling mode, so the trend of swing energy variations can be used to show the behavior of the nonlinear oscillation. In addition, the rationality of the method is analyzed and proved by the simulation results. Huge power transmitted over long distance through some crucial lines increases the probability of a sudden loss of bulk power in the power-receiving system. To prevent such emergency from deteriorating the security of the system, an emergency load shedding model, whose objective is to minimize the total load shedding cost, is built, and then an efficient algorithm is proposed based on trajectory sensitivity. The constraints of the model include transient voltage security, transient frequency security and available load that can be shed. This problem is a large scale, nonlinear programming problem with constraints considering time-varied parameters. The mathematical model is simplified by linearizing the security constraints through trajectory sensitivity, and the consistency of the solution is guaranteed by iterative calculation. The trajectory sensitivity is utilized in guiding the search direction and accelerating the solving process. A provincial power system is used to test the validity of this algorithm. TuB04.24 Dynamic Performance Comparison of Different Controlled Islanding Methods pp. 1363-1367 Tongxiao Wang Shandong Univ. Lei Ding Shandong Univ. Shanyao Yin Shandong Univ. Jingli Liu Shandong Univ. Yingzhe Jia Shandong Univ. Daonong Zhang TuB04.26 WAMS Light and Its Deployment in China pp. 1373-1376 North China Power Engineering Co.LTD Controlled islanding can be used as an efficient emergency action to prevent blackouts. Steps of controlled islanding methods implementing include graph modelling, objective function establishing, and the splitting solution finding. Researchers now concern about static constraints such as reactive power compensation and restoration capability when solving the objective function, but few papers have analyzed dynamic performance of splitting algorithms comprehensively.This paper investigates detailed dynamic responses with three typical methods: a) Ordered Binary Decision Diagram (OBDD), b) Weak Connection and c) Spectral Clustering islanding. To compare their differences, this paper separates the responses creatively into two phases from the perspective of time. In the first phase, characteristics of oscillations among generators and duration of transient process are taken into consideration. Maximum frequency shift and steady frequency shift in the second phase are compared then. Feasibility of different splitting solutions are also analyzed to compare the three methods. Time domain simulation of IEEE 118 case is carried out with PSS\E. Zongshuai Jin Shandong Univ. Hengxu Zhang Shandong Univ. Changgang Li Shandong Univ. It is determined by the nature of AC power grid that the disturbance in high voltage power grid can be reflected in low voltage power grid to some extent. The idea of the light synchronized phasor measurement unit (PMU Light) and that of the light wide-area measurement system (WAMS Light) was proposed and implemented in low voltage grid. Comparing the data recorded by WAMS and that recorded by WAMS Light, it is clear that the dynamic responses in high voltage power grid and low voltage power grid are strongly correlated. WAMS Light has already recorded several typical large disturbances. So WAMS Light has a broad application prospect in many fields. It also enlightens scholars to dig the value of the dynamic behavior of low voltage grid, the grid measurement theory, and even the way of the decentralized control of the power system. TuB04.27 TuB04.25 Analysis on the Influence of Rotational Inertia Level of Sending System on Transmission Capability Trajectory Sensitivity-Based Emergency Load Shedding Optimal Algorithm pp. 1368-1372 67 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) ing on the mid-long term voltage stability problem. The prediction horizon and the evaluation target node are firstly determined based on the predicted system trajectory. Considering the control rate constraint, the maximum voltage recovery amount with the current optimization steps is evaluated according the voltage response feature, based on which the voltage regulation limit index is formulated. The control horizon parameter is then determined according to the voltage regulation limit index, which is able to adjust itself according to the system operating state during the optimization process. The validation and effectiveness of the proposed method are verified by the simulation results of the New England 39-node system. pp. 1377-1380 Chao Zheng China Electric Power Research Inst. Huiling Li China Electric Power Research Inst. Tian Miao North China Electric Power Univ. Jingmin Zhou North China Electric Power Univ. It is an effective approach to improve utilization efficiency of primary energy source, to enhance security and stability margin of power grid and to lift overall operational efficiency of power grid via increasing transmission capability of power grid. During the initial period and the transitional period of power grid construction, in view of the impacts of techno-economy, implementation scheduling of the project, difference of seasonal power generation capacities, generally, there exists a circumstance that the outward transmission capability of power source is restricted by transmitting capacity of power grid. At first, it is analyzed that the influences of rotational inertia level of generators at sending end on both accelerating energy accumulation of rotors during fault period and the maximum decelerating energy that provide by power grid after cleaning up the fault, which is based on equal area criterion, and the mechanism of enhancing outward power transmission capacity by increasing rotational inertia of generators is revealed. On this basis, it is researched that the impacts of generation scheduling of Laohuzui main power plant in Tibet’s Nyingchi power network which transmits power outwards on disturbed trajectory of tie line and outward transmission capability, and it is pointed out that with the weak interconnection of Nyingchi power network with Tibet power grid via single circuit transmission line , it is an effective technical measure to improve outward power transmission capability and enhance security and stability margin by optimizing generation scheduling and increasing rotational inertial. TuB04.29 Index System and Methods for Subtransmission Grid AVC Assessment pp. 1387-1393 Li Min Zhang Bei State Grid Sichuan Electric Power Company Lu Yi State Grid Sichuan Electric Power Company Junyong Liu Sichuan Univ. Xiaodong Shen Sichuan Univ. Lixiong Xu Sichuan Univ. Zhenghua Jiang Sichuan Univ. Given the lack of a quantitative evaluation method, the paper presents a hierarchically structured method on the evaluation of sub-transmission grid AVC. The evaluation method and implementation steps are proposed, including the performance indices and the evaluation method. For index, some of it including voltage qualified rate, network loss rate and voltage stability has long been familiar to all. When it comes to method, AHP(analytic hierarchy process) and weighted evaluation has been developed and used for years. The current AVC system in DeYang city, China is evaluated using a set of comprehensive evaluation index and the application of fuzzy synthetic evaluation method. The result of the evaluating system including single strategy result and AVC operation result, in specified ratings. The numerical example indicates the reliability of this evaluation system. TuB04.28 Adaptive Model Prediction based Optimal Coordinated Voltage Control pp. 1381-1386 Yan Zhang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. Wen Zhang Shandong Univ. Gaofeng Zhang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. Qingyu Wang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. Qingqing Zhang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. Maolin Li State Grid Jinan Licheng Power Supply Company In traditional model prediction based optimal voltage control method, the control horizon and prediction horizon parameters need to be determined offline using experience or enumeration, and keep constant during the whole optimization process, which may cause negative influence to the control performance. Aiming at this problem, an adaptive model prediction based optimal coordinated voltage control scheme is proposed focus- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China State Grid Sichuan Electric Power Company TuB04.30 Multi-objective Optimization of Current Limiting Scheme Considering Constraint Conditions pp. 1394-1399 68 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Lines Yahui Chen Shandong Univ. Bo Zhang Shandong Univ. Zhiyuan Pan State Grid of China Tech. Coll. Hong Zhang Renfei Che The multi-objective optimization of current limiting scheme for power system is a complex, nonconvex and nonlinear problem and it is more complex when considering constraint conditions. Aiming to minimize total investments and short-circuit capacity margin under constraint conditions, a multi-objective optimization model of current limiting scheme based on the fast and elitist non-dominated sorting in genetic algorithms is presented. In order to increase the iterative rate, penalty coefficient is changed from zero to the maximum during the iterative process. Moreover, the influence on impedance matrix caused by common current limiting measure is analyzed, and the sensitivity relation between current limiting measure and node self-impedance is proposed. The conditions when the algorithm is used in multi-objective optimization of current limiting scheme are discussed. Then, case studies performed on IEEE 39-node network indicate the effectiveness of the proposed model and method in simulation results. An Evaluation Method of Maximum Urban Power Supply Capability Based on Dynamic Voltage Stability Margin pp. 1400-1404 TuB04.33 New Oscillation Emergence in Three-group Oscillation Mode and Its Control Measure Research After Islanding pp. 1410-1415 Xin China Electric Power Research Inst. Huiling LI China Electric Power Research Inst. Hongmei Luo China Electric Power Research Inst. Xin Zhang Huazhong Univ. of Science and Technology. Xiuyue Yu State Grid Fujian Electric Power Company. Feng Chen State Grid Fujian Electric Power Company. Shu Liu Shandong Univ. Shandong Univ. Affected by the bad operating conditions, the transmission line faults often occur. Thus timely fault cause identification is needed to make reasonable plan for power restoration so that to reduce the outage time. From the analysis of the fault mechanism, we know the most essential difference between all kinds of faults, is the distinction of transition resistances in the grounding channel. The transition resistances of each fault have two properties: resistance magnitude and volt-ampere characteristics, which can be reflected by the average value and standard deviation of the calculated transition resistance instantaneous value respectively. Therefore, a algorithm by combining the two characteristics of transition resistances for fault cause identification has been proposed in this paper. Use the electrical information during fault period to calculate the transition resistances instantaneous value. In order to obtain a high accuracy, this paper use Richardson extrapolation to slove the discrete numericaldifferential problem involved in the calculation. According to the comparison analysis of several typical actual faults, the paper set a criterion to identify the cause of transmission line faults. Eventually, a number of actual sample tests show that the proposed algorithm works well. TuB04.31 Zhang pp. 1405-1409 Beijing Sifang Automation CO., LTD. A method based on the dynamic voltage stability margin (DVSM) is proposed for calculating the maximum urban power supply capacity (MUPSC). In this method, the objective is to maximize the power load while observing N-1 security constraint. The constraints are system stability limit, thermal stability limit, excitation current limit of generators, voltage limit of load, etc. Considering dynamic response of the electric power devices, this method overcomes the limitations of traditional methods which is based on static power flow calculation and load model and dynamic response are ignored. A real urban grid is simulated, the result shows that by this method, MUPSC is calculated effectively, limiting factors of MUPSC is located as well as the weak points of the power grid. Jian Ding China Electric Power Research Inst. Lihua Wu China Electric Power Research Inst. Yunting Song China Electric Power Research Inst. Dong Li North China Electric Power Univ. Zongchuan Zhou State Grid Ningxia Electric Power Economic Research Inst. Dajiang Ren State Grid Ningxia Electric Power Economic Research Inst. Mengmeng Jia State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Meng Wang Materials Company of Henan Electric Power Company. Jiantao Gao State Grid Lianyungang Power Supply Company. Based on an equivalent system model, new oscillation emergence phenomena of three-group oscillation mode are focused after the traditional separation measure in which new oscillation center distribution character and regularity, its impact on separation measure are studied. The simulation results of Northeast Grid, Northwest Grid, East China and North China Grid of China validated the presented new oscillation center TuB04.32 Fault Cause Identification Based on Characteristics of Transition Resistances for Transmission 69 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) distribution character and regularity. The impact of all kinds of three-group oscillation modes on isolation measure and corresponding counter-measure are discussed in which the traditional oscillation mode of three main out-of-step generator groups, the mode of two main out-of-step generator groups with one minor counter-part and the mode of one main out-of-step generator group with two minor counter-parts are included. Simulation result shows that the major out-of-step interface should be the priority of the three-group oscillation mode islanding strategy. Analysis Based on Phase-plane Trajectory Geometrical Characteristic pp. 1422-1426 Fu Su The Influence of Wind Farm Containing DFIG on Power System Stability pp. 1416-1421 Electric Power Research Inst. of Guizhou Power Grid Co., Ltd. Zuyi Ren Meimei Xu Baohui Zhang Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Songhao Yang Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Huaiyuan Wang Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Time-domain simulation (TDS) for power system transient stability is less efficient and tedious, and there is no uniform standard to determine the transient stability based on empirically observation of the disturbed trajectories, which make the efficiency and reliability cannot be satisfied at the same time. A novel termination algorithm of time-domain simulation for transient stability analysis based on phase-plane trajectory geometrical characteristic is proposed in this paper. The output of time-domain simulation is used to analysis the transient stability, and once the system is judged to be stable or unstable, the time-domain simulation program is terminated. First, the transient instability can be detected quickly based on the convexity and concavity of phase trajectory; and if the phase trajectory is convergent and the oscillation is damped, the system can be detected to be stable early. The proposed method is easy to achieve, the efficiency and validity is verified by simulations on IEEE 39-bus 10-unit system. TuB04.34 Chenghui Lin Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. NR Electric Co., Ltd. Electric Power Research Inst. of Guizhou Power Grid Co., Ltd. Liang Wang Yong Xiao NR Electric Co., Ltd. TuB04.36 Electric Power Research Inst. of Guizhou Power Grid Co., Ltd. Mingcai Kang Zhiqian Bo Study of Considering the Interruptible Load to Improve the Limit Tranimission Power of Section Under the Constraints of N-1 Static Security pp. 1427-1430 Nanjing Univ. of Science and Technology. XUJI Group of SGCC. Access of wind farm will not only change the distribution of power flow but also have an impact on the power grid security and stability. With the proportion increase of wind farm capacity in power system, it is necessary to study power system stability containing a large number of doubly fed induction generator (DFIG). In this paper, the mathematical model of wind turbine generator based on DFIG was established. Analysis and simulation of actual system containing DFIG had been completed, from the two aspects of reactive power change after wind farm acessed and the influence of wind speed on wind farm. At the same time, it has been analyzed that the influence of wind farm containing DFIG on power system stability when external AC power grid fault happened. Simulation results show that the wind power generator based on the double fed induction machine can make positive contribution for power system to return to the normal operation when fault happens. Zixia Pei North China Electric Power Univ. Lanlan Chen North China Electric Power Univ. Anjia Mao North China Electric Power Univ. Yan Liu Economy & Technology Research Inst.of SGCC Liaoning. Zhuohang Wu Economy & Technology Research Inst.of SGCC Liaoning. Yuzheng Hou Economy & Technology Research Inst.of SGCC Liaoning. Introduce the viewpoint of interruptible load into N-1 static security analysis of transmission capacity of transmission section;broaden the conditions of traditional N-1 analysis through using the interrupt load management in receiving areas.A detailed mathematical model of the power flow constraints of transmission section considering the interruptible load is established and the solving methods based on sensitivity analysis is also given,and the relationship between the increments of limit tranimission power of section and the interruptible load quantities is obtained on this basis. The IEEE39 nodes numerical example in BPA running environment shows that the application of interruptible load to improve limit tranimission power of section can improve the operation economy while guaranteeing the security of the power system. TuB04.35 A Novel Termination Algorithm ofTime-domain Simulation for Power System Transient Stability November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China 70 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) narios and requirements for self-healing control system of smart distribution network were analyzed. Then, the static and dynamic models of the control system were built based on UML. Three types of self-healing control are realized through four self-healing stages in three scenarios. Finally, based on the modeling results, the system architecture and key applications for the self-healing control system were implemented. The results in this paper are useful for investigation on the conceptions and key technologies, increasing the normalization and reusability of self-healing control system as well as guidance for real self-healing applications. TuB04.37 Research on Automatic Testing Method of Antimaloperation Blocking in Smart Substation Bay Level pp. 1431-1434 Jian Qin State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Company. Zhanyang Wang State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Company. Xiaoyu Liu Hua zhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Xianggen Yin Hua zhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Hui Shi TuB04.39 A Quantitative Assessment Method for Degree of Transient Stability Coupling of DC and AC Transmission Sections pp. 1440-1445 State Grid Jiangsu Yangzhou Electric Power Company. Jingchao Yang Wuhan Kemov Electric Company Ltd. Substation anti-maloperation blocking system plays a key role in safe operation of power grids. Anti-maloperation blocking test is necessary before commissioning of the substation to ensure the correct blocking when mal-operated. The development of the smart substation puts forward higher requirements and provides more advanced technology. The common test methods are complex and inefficient, and possible of missed operation. On the basis of analysis of smart substation anti-maloperation blocking test principle, this paper researches on automatically testing method based on IEC61850 in substation bay level. In addition, an automatic test system with built in logic rules has been designed to complete the test efficiently, accurately and comprehensively. Hongli Zhang Xiaodan Cui Haijun Chang Zhou Xia Li Wei Huo Chao Niu Shuanbao Ke Xianbo NARI Technology Development Co.,Ltd. NARI Technology Development Co.,Ltd. NARI Technology Development Co.,Ltd. NARI Technology Development Co.,Ltd. NARI Technology Development Co.,Ltd. Northwest China Power System Dispatching & Control. Northwest China Power System Dispatching & Control. Northwest China Power System Dispatching & Control. Along with increasing operation of DC, the coupling degree between DC and AC power systems is more tightly and the influence with each other is more closely. It has great significance on improving the level of coordinated optimization control of power system security and stability and online auxiliary decision-making for evaluating the degree of transient stability coupling between DC and AC transmission sections quantitatively, and then searching automatically and identify the more closely related AC transmission sections with the transient stability coupling between DC and AC transmission sections. The transient stability coupling mechanism between DC and AC transmission sections is revealed by the theory of Extended Equal Area Criterion. On this basis, the matrix of transient stability margin of the dominant generators image of AC transmission sections is established through different DC power disturbances, and then the curves can be fitted with least square method. The curve slopes reflect quantitatively the transient stability coupling between DC and AC transmission sections. Finally the example demonstrated the effectiveness of the method. TuB04.38 The modeling of self-healing control system for distribution network based on UML pp. 1435-1439 Wei Liu The Production and Technology Department Guangdong Power Grid Corporation. Taifeng Kang Business Department of Distribution Network Beijing Sifang Automation CO., LTD. Wenxin Cheng Business Department of Distribution Network Beijing Sifang Automation CO., LTD. Fengqing Zhao Business Department of Distribution Network Beijing Sifang Automation CO., LTD. Self-healing for smart distribution network which is based on Distribution Automation(DA) and Advanced Distribution Automation(ADA), is one of the key characters and core functions for smart distribution network to deal with the inside and outside threatens of the network as well as to increase system operation security and efficiency. In this paper, we focus on the modeling of self-healing control system for distribution network based on UML. Firstly, the background, application sce- 71 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) and fuel cost included in the objective function. Thus the ra- TuB04.40 tional spinning reserve is optimized to prevent wind power ramp events. Monte Carlo method is adopted to simulate the Study on Electromechanical Dynamic of Power Systems Based on Trajectory Eigenvalue Sensitivity pp. 1446-1451 wind power ramp in each time interval. Conventional units’ Teng Wang Delin Wang Ningning Ma You Yuan of the proposed method. output and spinning reserve at 15-min time-scale are optimized based on the determined unit commitment. The analysis of the numerical examples are carried out to verify the effectiveness Southwest Jiaotong Univ. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. Traditional small disturbance analysis method and eigenvalue sensitivity (ES) are unable to accurately analyze the electromechanical dynamic characteristics of power systems. Based on trajectory eigenvalue method, the power system models are TuB04.42 linearized at non-equilibrium points (NEPs) and the trajecto-ry eigenvalues are calculated. With the changes of trajectory Study on the Calculation Model of Maximum Allowable Time and Ampacity for Overload Operation of Overhead Transmission Line in a Short Time pp. 1458-1461 eigenvalues, the factors affecting oscillating amplitude and oscil-lating period are studied. Combined trajectory sensitivity (TS) with ES at equilibrium points (EPs), the trajectory eigenvalue sensitivity (TES) is proposed and calculated by numerical per-turbation method. Based on the WECC 3-machine 9-bus system, the influence of disturbance size, disturbance duration, the gen-erator’s inertial and damping upon trajec- Ziqing Xia tory eigenvalues are analyzed. The TES to system parameters Yunfeng Xia are calculated and the trajectory eigenvalues of different pa- Central Soutlth Univ. Dongguan Power Supply Bureau of Guangdong Power Grid Corporation. rameters are analyzed on different time sections. Finally, the advantages for TES than ES at EPs are verified in terms of Zheng Xu Chongqing Univ. research electromechanical dy-namic characteristics. Jiamin Wu Chongqing Univ. At variance with the development of society economy, electricity transmission capacity is utilized insufficiently. It is of importance to research on the operation capability for transmis- TuB04.41 sion line under the condition of overload in a short time. Based Spinning Reserve Model in Response to Wind Power Ramp Events at Sub-Hourly Time-scale pp. 1452-1457 ble time of overload operation in different temperatures can be on the dynamic heat balance equations, the maximum allowaobtained. Take the typical meteorological condition of Guangdong district for example, the maximum permissible temperature, maximum allowable time of overload operation, and increment of current carrying capacity for different types of Xinyuan Tong Shan Dong Univ. Hongtao Wang Shan Dong Univ. aluminum conductor steel reinforced (ACSR) are analyzed. Wind power ramp events, driven by extreme weather conditions, will bring huge operational risk to the system. Considering the difficulty for hourly dispatch to respond to wind power ramp events within 1h, sub-hourly dispatch are scheduled in this paper. Loss of load expectation and expectation of wind TuB04.43 power curtailment caused by wind power ramp are set to satisfy the limit value. The expense of load loss and wind power Research on the Security Risk Assessment Sys- curtailment is converted into the risk cost, with reserve cost November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China 72 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) equipment maintenance model and system condition-based maintenance model is proposed. The modified imperfect maintenance model-Kijima II model is selected for equipment maintenance model comparing with minimal repair and perfect maintenance through optimizing imperfect maintenance effect factor. In addition, a genetic algorithm is used to find the optimal maintenance strategies from possible maintenance scenarios. These optimal maintenance strategies have been tested on a HVDC link which is simplified into an equivalent serial and parallel system and an IEEE-RTS79 system. The results demonstrate the feasibility and validity of the proposed model. tem for Regional Complex Power Grid pp. 1462-1465 Faqi Yan Central China Electric Power Dispatching and Control Sub-center of State Grid Yang Wang Central China Electric Power Dispatching and Control Sub-center of State Grid Xianggen Yin Huazhong University of Science and Technology Jinhui Li Huazhong University of Science and Technology Wen Yang Huazhong University of Science and Technology Biao Xu Huazhong University of Science and Technology Cheng Jian Huazhong University of Science and Technology TuB05.2 In order to guarantee the safe and stable operation of the complex power grid and prevent wide-area blackouts, safety and risk assessment of power grid, which is carried out by charge of the third party independent evaluation agency, is an important means of safety risk management and conducive to satisfy the respective requirements and interests of government, power enterprise and power user. Besides, it will promote the progress of deregulation of power grid under the present electric power system. Considering the current situation of regional power grids of China and the requirement of power grid security risk control, this paper introduces the framework and methods of safety and risk assessment for large power grid and analyzes one case of the application in a trans-provincial regional power grid of China. The Comprehensive Assessment of Composite Insulator Aging Condition pp. 1472-1477 Miaofu Ning Southern Power Grid uhv Transmission Company. Qisheng Liu Wuhan Univ. Xueping Yu Hunan power grid provincial maintenance company. Yan Chen Jian Wang Wuhan Univ. Chang Jiang inst. of survey, design and research. TuB05.1 Silicone rubber composite insulator with its excellent performance is being in a wide range of applications in our country instead of the traditional insulator. Most of the statistical results show that the composite insulator aging is the main reason of the failure. Composite insulator becomes one of the weakest link, constitutes a great threat to the safe operation of high voltage transmission line. So to carry out the research on the aging of composite insulators, build a complete aging evaluation model, timely grasp the insulator aging status is of important significance to the safe and stable operation of power system. In this paper, the variable weight theory is combined with the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process, and a multi-level and multiindex aging assessment model of composite insulators is constructed. The main work of the aging assessment includes: the determination of the weight of the index, the construction of the aging assessment model, and the verification of the model. First of all, we construct two layers of evaluation index system-the project layer and the index layer. Second obtain the constant weights, and introduce the variable weight model based on equilibrium function to obtain the variable weight. Then we chose the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process to build the insulator aging state comprehensive evaluation model. In the end, the aging model is verified by the experimental data of the composite insulators of the transmission line. The results show that the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model based on the variable weight theory can objectively reflect the aging state of A Condition-based Maintenance Approach to an Optimal Maintenance Strategy Considering Equipment Imperfect Maintenance Model pp. 1466-1471 Yeyong Li Shandong Univ. Xueshan Han Shandong Univ. Bo Xu Shandong Univ. Yunpeng Wang Shandong Univ. Power grid tries to maximize its profit by reducing generation cost, supply costs and operation costs while sustaining its required reliability. Developing maintenance strategies is one of the most effective methods. The condition-based maintenance approach is a key method in providing optimal maintenance strategies in theory. It considers the tradeoffs between the system maintenance risk and the potential system failure risk of system reliability losses. Since power grid contains a group of different kinds of equipments and the reliability of the electric equipments varies with time. One type of electrical equipment has different maintenance models because of their different failure modes and deterioration processes. A union method for 73 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) insulators objectively. The model has a reference for the maintenance and replacement of insulators. the type and the location of the accelerator is taken into consideration, the signal processing circuit is designed, the data acquisition (DAQ) card is chosen, at the same time, the software is developed by VC++, LabVIEW and MATLAB, which can acquire data and denoise the signal with user friendly interface. TuB05.3 Simulation of Electric Field Around Insulators in High Voltage Line pp. 1478-1482 TuB05.5 Application of Accelerometers in V ibration Test of High Voltage Circuit Breaker pp. 1488-1491 Zhangang Yang State Grid Chongqing Electric Power Company. Hongbing Li State Grid Chongqing Electric Power Company. Huaxing Yu State Grid Chongqing Electric Power Company. Yu Liang State Grid Chongqing Electric Power Company. Jixiang Wu State Grid Chongqing Electric Power Company. Jiamin Wu Chongqing Univ. Xianjun Cui Chongqing Univ. Bin Wu State Grid Chongqing Electric Power Company. Jing Zhang State Grid Chongqing Electric Power Company. Yan Liu Li-an Chen MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical System) piezoresistive accelerometer is proposed for the vibration measurement in the vicinity of vibration source inside high-voltage circuit breaker for mechanical fault diagnosis, which is verified from the theory as well as comparative test with piezoelectric accelerometer. The high voltage circuit breaker vibration test scheme based on MEMS piezoresistive acceleration sensor is presented in the paper. Insulators are important parts in power system, the property of insulator is good or bad will directly influence the operation of power system. Under the action of natural environment and electric field with high strength, electrical property and mechanical property of the insulators will decrease, as the service year of the insulator increasing. So how to find the insulator with defect and replace it with a good insulator is important to ensure security operation of the power system. In this paper, electrical porcelain insulators used in 110kV power transmission line were analyzed, electric field around insulators with different states through Maxwell software. The results show that: Through the regularities of electric field distributed around the insulators, we can estimate the properties of them. TuB05.6 Research on Condition Assessment for Distribution Vacuum Switch Cabinets Based on Multi-source Information Fusion pp. 1492-1497 Chaoqun Kang Jianhua Zhang Wanxing Sheng Erxia Li Fangyuan Chang Design and Development of Condition Monitoring System for Circuit Breaker Based on Vibration Signal pp. 1483-1487 North China Electric Power Univ. Middle voltage circuit breakers (MVCB) are important in power system. Applying condition monitoring on a MVCB is beneficial to detect potential hazards. Vibration analysis is a noninvasive method for condition monitoring of mechanism. Furthermore the vibration signal on framework of a MVCB carries abundant information of its operating mechanism. Thus developing a condition monitoring system for a MVCB is necessary and meaningful. During the building of the system, November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China North China electric power univ. North China electric power univ. China electric power research inst. China electric power research inst. China electric power research inst. Serve as one of the most important equipments in power distribution system, conditions of switch cabinets are closely connected with safety and stability of distribution network and exert great influence on power quality used by customers. But the information applied in the current research of distribution switch cabinet is not comprehensive enough, and the assessment model is not dynamic enough, because of this, a distribution vacuum switch cabinet dynamic condition assessment model based on multi-source information fusion is proposed in this paper. The vacuum switch cabinet is divided into three parts—vacuum circuit breaker, buses and cable outlets. The information used to assess these three parts’ conditions concludes ultrasonic results, TEV results, infrared temperature measurement results, vacuum degree, insulation resistance and mechanic parameters. Moreover, environment information, operation information and position information of the switch cabinet are also taken into consideration. Membership functions and scale models are used in the condition assessment. Thus, the historical conditions of the switch cabinet in the past 5 years can be obtained, and Bayes conditional probability model is used to fuse these condition assessment results. In the TuB05.4 Zhirui Liang Xiamen Univ. of Technology Xiamen Univ. of Technology 74 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) meantime, the corresponding examples are given to prove the validity of the models proposed in this paper. TuB05.9 Based on WAMS Generator Primary Frequency Regulation Calculation Methods and Its Comprehensive Evaluation Methods pp. 1511-1516 TuB05.7 Risk Assessment for Distribution Transformer Burning-out Based on D-S Evidence Theory pp. 1498-1503 Yu Zhang Fei Gao Jianfang Li Xueping Feng Xiaohui Song Caixiu Li Li Dai Dahai You Xianggen Yin Kai Wang Yan Yang Zhe He Cheng Long Gang Wang Meilin Dong Jin Hu China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. Jiamusi Suburb Electric Power Company Distribution transformer is one of the most important components of distribution power system, and its normal operation plays a very important role in power system. It is significant for operator to assess the risk of distribution transformer burn-out by fusing kinds of information of different automation systems in power system. The risk factors and their weights of distribution transformer burn-out are analyzed in the paper. A risk assessment method for distribution transformer burn-out based on the Dempster-Shafer evidence theory and expert experience knowledge is prevented in this paper, which regards the severity of distribution transformer burn-out caused by different risk factors scored by expert as evidence of distribution transformer burn-out. All the evidence is combined according to the Dempster’s combination rule, inferring the probability of distribution transformer burn-out. The example of distribution transformer burn-out risk testifies the feasibility and effectiveness of proposed approach, which can accurately identify the transformer burn-out risk. This article use adjustment dead zone, difference coefficient, lag time, stable time and contribution rate to construct the primary frequency index system and use WAMS data to analyze the generator primary frequency index calculation methods. At last, this paper uses the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and entropy weight comprehensive evaluation methods to evaluate the generator primary frequency performance. The effectiveness and correctness of proposed indices calculation methods and comprehensive evaluation methods are validated by the province actual WAMS data. TuB05.10 Design of Integrated Supervisory Control System for 110 kV Dry-type Transformer pp. 1517-1521 TuB05.8 Guangming Zhang Consensus Clustering Algorithms for Asset Management in Power Systems pp. 1504-1510 Qiang Gao Long Yan Yanli Xin Wenhu Tang Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Maojun Wang Qi Liu Univ. of Liverpool South China Univ. of Tech. South China Univ. of Tech. Dantian Zhong Hongkai Li This paper aims to present an intelligent approach to the Asset Management (AM) in power systems. Three existing consensus functions (i.e., Non-negative matrix Factorisation based, Weighted Partition via Kernel and Information Theorybased) have been compared and applied to analyse a power system document depository (PSD). In addition, ontology is employed in this research to implement a document dataset modification, which shows a significant improvement for the single consensus clustering algorithm. Moreover, Genetic Algorithm (GA) is utilised to solve the weighted kernel-based consensus function. The influences of different settings of GA are analysed. Relevant improvements of GA are also presented. Rongyu Du State Grid Liaoning Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Liaoning Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Liaoning Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Liaoning Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Liaoning Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Chaoyang Electric Power Supply Company State Grid Chaoyang Electric Power Supply Company The paper proposes a design scheme of integrated supervisory control system which is suitable for both 110kV drytype transformer and intelligent substation. Some special problems such as how to measure temperature in the high voltage winding is discussed in the paper. Fiber grating sensor is used in the system because of its strong anti-interference ability and accuracy for temperature. The installation method, quantity and trace of fiber are also discussed. The grounded current of core and working current could be monitored through the high precision current transformer. The supervisory and control intelligent electronic device (IED) is used the modular design method 75 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) based on high-performance ARM processor in order to improve the hardware and software efficiency. It receives the value of winding and core temperature, ambient temperature, grounded current, and analyzes the status of transformer. According to the data the IED could control the cooling fan to reduce the temperature. The IED also can deliver the data to substation control layer using IEC 61850. The comprehensive application server could display the panoramic data such as monitoring and warning data of transformer. high-voltage electric power equipment. Thus, it is an urgent issue to monitoring these gases. However, existing inspection methods still fail to conduct on-line monitoring of SF6 decomposed gases. Aimed to solve this problem, this paper proposes an On-line SF6 decomposed gases monitoring approach based on the Quantum-Cascade Laser Absorption Spectroscopy. In this system, the composition and the concentration of each kind of gas can be obtained by testing the absorption peak value and absorption intensity of the wavelength. Experiment results show that the proposed system is able to perform on-line monitoring of SF6 decomposed gases with high accuracy. TuB05.11 An Equipment Energy Efficiency Evaluation Method for Industrial and Commercial Use pp. 1522-1526 Ciwei Gao Haiming Luo Lulu Zhu Fuchao Liu Yongjun Han TuA05.13 Prediction of Dissolved Gas in Power Transformer O il Based on Random Forests Algorithm pp. 1531-1534 Southeast Univ. Chengxian Coll. State Grid Huaian Power Supply Company Jiangsu Electric Power Maintenance Branch Company Huaian Division Electrical Power Research Inst. of State Grid Gansu Power Company Electrical Power Research Inst. of State Grid Gansu Power Company Ke Deng Weihong Xiong Liming Zhu Hongzhi Zhang Zhengtian Li State Grid Hubei Electric Power Company Overhaul Branch Center China Grid Company Limited HUST HUST HUST With electrical energy conservation and emissions reduction promotes in China, the research on electrical energy efficiency evaluation has become one of the hot topics in the studies on power system. Meanwhile, with customers’ requirement on accurate assessment increases, it’s a trend to change from energy measurement to efficiency measurement of equipment in industrial and commercial scenes. An equipment energy efficiency on-line monitoring method was introduced for industrial and commercial use and an equipment energy efficiency evaluation model with probability was described in detail. The simulation on three-phase asynchronous motor with MATLAB indicated the feasibility of the evaluating model and method, which could effectively promote the appliance of energy efficiency on-line monitoring and reduce economic investment for monitoring. In order to adopt reasonable measures to anticipate and avoid possible internal failures in power transformers, accurate prediction of power transformer oil dissolved gas trends is useful. It is necessary to realize the condition based maintenance of power transformers, and the prediction of dissolved gas in the oil is solid foundation. The gas concentration is affected by many factors, so prediction model built by reasonable selection of the larger correlation factors will help to improve prediction accuracy. Random forests algorithm is used to predict the gas trends and the prediction performance evaluation is realized by appropriate evaluation indexes. By comparison with support vector machine prediction, the advantage of random forests method for power transformer oil dissolved gas prediction is proved. TuB05.12 TuB05.14 A Novel On-line SF6 Decomposed Gases Monitoring Approach Based on Quantum-Cascade Laser Absorption Spectroscopy pp. 1527-1530 Research on the Modification Methods for the Failure Rate Curve of Electric Equipment pp. 1535-1540 Yongquan Mao Ziguan Zhou Yanbin Song Yong Wang Guoyan Chen Jie Ji Zhe Zhang Xu Chen Xianggen Yin State Grid Info. &Telecommunication Group CO.,LTD State Grid Info. &Telecommunication Group CO.,LTD State Grid Info. &Telecommunication Group CO.,LTD Aiming at the shortcoming of the difficulty to fully reflect the effects of individual differences, maintenance and health state on the equipment failure rate curve based on statistical analysis, the modification methods taking the factors of long-term development and short-time variations into account are put forward in this paper. The least square method is used to esti- In the field of high-voltage electric equipments, the SF6 gas as insulation material is widely used in various kinds of Gas Insulated Switchgears (GIS). And the decomposition of SF6 gas under discharge would generates various kinds of gases, which may seriously result in worse insulation performance of the November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Guangzhou electricity Supply Company Guangzhou electricity Supply Company Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. Huazhong Univ. of Science and Tech. 76 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) mate the parameters of Weibull distribution function and the Marquardt method is combined to deduce the demarcation point and distribution curve of the failure rate. On this basis, the equipment failure rate curve is modified to accord better with the actual operation situation from three aspects of individual defect, maintenance situation and healthy state evaluation respectively. By the example analyzing, the validity of the research is illustrated. TuB05.17 Analysis Correlation Modeling of the O il Flow of Transformer and Temperature pp. 1549-1553 Dongri Yan Changsha univ. of science and tech. Rui Ma Changsha univ. of science and tech. Haijing Yang State Grid HAEPC Electric Power Research Inst. Yongchao Liang Human Electric Examine and Repair Company TuB05.15 Research on Operation Condition Monitoring and Security early Warning System of Distribution Substation pp. 1541-1544 Xinyuan Liu Shuyong Song Dongping Li Zhang Cheng Transformer oil is the main insulation and heat dissipation medium of oil immersed transformer, its flow velocity, pressure and density distribution has a significant effect on transformer insulation and heat dissipation performance. Based on this, this paper has deduced the relationship between the oil flow velocity and the instantaneous temperature field of the transformer, and the mathematical model. The simulation results reveal the relationship between the fault of the transformer and the flow velocity of the oil, and provide the theoretical basis and simulation platform for the study of the digital gas protection based on the fault characteristics. In addition, analyze the relationship between the temperature of inlet oil flow and the load factor and the temperature rise in the transformer, providing a good base for studying the setting value of the transformer gas relay. State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Department of Art and Design Communication University of Shanxi Qingpu Electric Power Supply Company of Shanghai The key state information index and sensing scheme of distribution substation are established, and a software and hardware scheme is designed and developed for the monitoring and safety warning system of power distribution substation. This new system can greatly improve the intelligent and automatic level of distribution substation, which has the advantages of simple operation, powerful function and low cost, which has great practical value. TuB06.1 Adaptive Communication Resource Allocation for W ide Area Measurement System pp. 1554-1558 TuB05.16 Design of New MOA Arrester Tester pp. 1545-1548 Qiao Wang Lixing Zhou Weixian Chen Lijian Xu Junhui Zhao Zhong Chen Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. Zhuzhou State Grid Power Company Farmingdale State Coll. Univ. of New Haven Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. Phasor measurement units (PMUs) in a wide area measurement system (WAMS) environment offer precise estimates, improved post-disturbance analysis, and efficient advanced control. When communication resources are limited, WAMS data transmission network design must consider accuracy as a critical limitation. Focusing on the optimal resource allocation, this paper studies the system accuracy and its relation to transmission protocol design. An adaptive communication time division based assignment is investigated. Algorithms are developed and they are shown to achieve the optimal resource usage. Illustrative examples demonstrate significant advantages of our accuracy-based time division allocation methodologies over traditional TDMA strategy. Now the most used detecting method of MOA is the full current and resistive current on-line test. And the test method of existing instrument needs to get voltage signal from the second terminal of voltage transformer. This method is dangerous because an improper operation will cause a short-circuit in voltage transformer and even endanger personal safety. Therefore, in order to solve the above problems, a new MOA arrester tester is developed in this paper. It uses a new way to obtain voltage phase signal and it gets voltage signal from the high voltage side of primary equipment and then sends it to the tester developed in this paper through wireless transmission to convert it to low voltage signal and then outputs to the original arrester tester to complete the resistance current testing. The device developed can finish arrester electrified test safely, accurately and conveniently. It can overcome the limitation of getting voltage signal from the second terminal of voltage transformer and the effect of interphase interference on test results can be effectively solved. TuB06.2 Chinese Energy Supply and Demand Structure 77 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) into the network is one of the development priorities of the integrated energy system. For the control method of the energy storage system, the most important part is the dispatchment control strategy of the energy storage system. It is expected that the energy system can discharge more energy during the peak load period and discharge less during the valley load period. Directing at this aim, this paper uses fixed threshold and dynamic threshold method to calculate the discharge threshold power to control the discharge power of the storage system respectively. Comparing the energy management results, the dynamic threshold method is confirmed to have higher energy management efficiency. Model and Power Grid Benefit Analysis pp. 1559-1564 Xiaoxia Wei Jie Liu Tiezhong Wei Lirong Wang State Grid Energy Research Inst. Heilongjiang State Grid Company Heilongjiang State Grid Company Heilongjiang State Grid Company With the energy source amount of exploitation and usage, the accelerating of energy consumption gross, source and environment can affect the energy system restrict affection are stronger. The energy source amount per person is lower. Primary energy storage and structure problem is standing out. Energy usage can pollute seriously. Chinese energy supply and demand problem is research key point. This paper researches Chinese energy supply and demand pattern system and evaluation methodology, gives out the inner and outer influencing elements. And evaluate Chinese energy supply and demand pattern from energy gross, structure, distribution and transportation. Give the energy supply synthesize radar comparison chart in certain time period. From the energy security, economy, clean and efficiency, analyze the benefit comparisons of Chinese energy supply and demand pattern. This energy supply and demand pattern model will give one certain theoretical analysis and practice reference. TuB06.4 Power System Fault Simulation in SG-OSS DTS pp. 1570-1574 Wenhui Wei Jie Chen Chengjie Zhao Changnian Li Rui Ge Guodong Li TuB06.3 With the increasing complexity of grid dispatching, it becomes an inescapable trend to implement a full dynamic simulation of DTS while fault simulation is a key component in dynamic simulation. This paper describes the design and implementation of fault simulation in a new generation of DTS based on multi-threaded multi-core processor architecture of parallel computing algorithm. Firstly describes the core design calculations for the fault, then describes the characteristics and features of fault simulation in the DTS environment. A numerical example was given to show the feasibility and practicability in large-scale power grid. Energy Management Method Applying in Integrated Energy System pp. 1565-1569 Yiru Chen Ke Jia Bohan Liu Guozeng Yan Dongfang Wang Chunlai Li North China Electric Power Univ. North China Electric Power Univ. State Grid AC Project Construction Co., Ltd State Grid AC Project Construction Co., Ltd Qinghai Province Key Laboratory of Photovoltaic Grid Connected Power Generation Technology State Grid Corporation of China Qinghai Province Key Laboratory of Photovoltaic Grid Connected Power Generation Technology State Grid Corporation of China The development and utilization level of energy is an important symbol of the technology and living standards of the society. Integrated Energy System (IES) is important to improve energy efficiency and promote the large-scale development of the Renewable Energy Source (RES). In the meanwhile, it also can improve the utilization of the social infrastructure and secure the energy supply. It has become a significant research topic in the international energy field. Photovoltaics, wind turbines and other renewable energy source of electricity are coupled with energy storage system to supply power to the local consumers in the IES, which can reduce the energy transmission losses and the large disturbances impact from the main grid. Since the inverse distribution of the output power of some renewable energy distributed generation and the load demand, the research of the energy storage system control to achieve the target of high efficient local utilization of the renewable energy and avoid a large excess power flowing November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Co. Ltd Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Co. Ltd Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Co. Ltd Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Co. Ltd State Grid Dispatching Control Center State Grid Dispatching Control Center 78 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) nology TuC01.1 High Frequency Modeling Technique for ThreePhase Power Electronics Module pp. 1575-1579 A.Cataliotti D.Di Cara G.Marsala A.Pecoraro A.Ragusa G.Tinèi Univ. di Palermo National Research Council, Palermo, Italy National Research Council, Palermo, Italy National Research Council, Palermo, Italy National Research Council, Palermo, Italy National Research Council, Palermo, Italy Nowadays, the high integrated power electronicsmodules (PMs), characterized by high speed, low loss and hardware miniaturization, represent a new technology that meets the emerging demands of many applications, such us vehicle and home appliance, renewable energy sources in smart grid. The integration process and the high switching speeds increase thePM electromagneticemissions that can createelectro- magneticinterference(EMI) withelectric/electronic devices near the PMs. For this reason, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) have to be carefully considered, yet in the design phase, to guarantee the reliability of PM systems. In this paper a method to develop a high frequency (HF) model, useful to study EMI phenomena of a three-phase PM, is presented. The method is based on experimentalmeasurements at the PM external pins and it allows to extract internal inductive and capacitive parasitic coupling without the knowledge of structural and physics parameters of the device. The PM HF model, developed in the 150kHz-30MHz frequency range, has been implemented in MATLAB® environment. The method has been experimental validated comparing the frequency responses of the PM characteristics with that obtained by the model. TuC01.2 A Problem about TF/SF Technique in the FDTD Simulations of Cylindrical Waves and Spherical Waves pp. 1580-1582 Jianyong Wang Cuihong Liu Hohai Univ. Hohai Univ. The finite difference time domain methods(FDTD methods) are the most popular simulation methods of the electr- omagnetic waves, and the total field/scattered field technique(TF/SF technique) is the main source technique of the FDTD methods. The amplitude of the electric fields and the amplitude of the magnetic fields are considered as invariant in the connection interface between the total field regions and the scattered field regions, when cylindrical waves and spherical waves are simulated by the FDTD methods and the TF/SF technique is applied. But this consideration is wrong because that the amplitude of cylindrical waves and the amplitude of spherical waves are both not constants on the direction of propagation, and thus C: High Voltage Transmission Tech79 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) the computational results are effected. A new method for applying TF/SF technique in the FDTD simulations of cylindrical waves and spherical waves is brought forward. The method considers the variations of the amplitude of cylindrical waves and the amplitude of spherical waves on the direction of propagation, and thus the problem is solved. Numerical experiments were done, and the experiments indicate that the new method can effectively improve the simulation results. ture or thermal aging state on the voltage initial slope by changing charging and discharging time. Then the examples are analyzed when the moisture content in the transformer increase, the initial slope of the decay voltage significantly increased; the initial slope of the recovery voltage also increases obviously when the thermal aging degree of the transformer increased. The results show that it really has some effect on the initial slope of decay voltage when oil paper insulation damp, so as the initial slope of the return voltage when oil-paper insulation thermal aging. TuC01.3 TuC02.2 Parallel Computing of Electromagnetic Field Based on Domain Decomposition Method pp. 1583-1586 Tianwei Li Tian Wu Simulation of Propagation Characteristic of Ultra High Frequency Signals in Power Transformers Using Finite Difference Time Domain Method pp. 1591-1594 Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. Bin Xu Yanming Li Junhong Zhao Xinjun Wang Ruixiang Zhang The computing velocity and memory storage of Single PC are often limited in large-scale electromagnetic simulation by finite element method (FEM), parallel processing is an important means to overcome such problems. The domaindecomposition method (DDM) which decomposes the domain by nodes dominating and suits for parallel computing was illustrated first in this paper; A 2D electrostatic model was built and decomposed by the DDM; And the FEM linear system of equations was solved by using parallel CG method on the distributed parallel system composed of 6 PCs, the effective speed up reaching 97.5% was satisfying. Especially for large-scale simulation which consists of more than millions of freedoms, the parallel processing reduces computing time and increases the computing velocity greatly, it’s the base on which large-scale 3D electromagnetic parallel computing. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Xi’an Research Inst. of Hi-Tech. Xi’an Research Inst. of Hi-Tech. Xi’an Research Inst. of Hi-Tech. In order to study the propagation characteristics of Ultra High Frequency (UHF) signals excited by partial discharge in an actual power transformer, a simulation model of the power transformer is established using Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) method to simulate the propagation progress of the UHF signals. The receiving signals in different points and planes are analyzed by time domain and frequency domain methods. The results show that due to the complicated structure, the magnitude of the receiving signals vary greatly with places and the distribution of energy also varies very much. The higher the frequency, the greater the attenuation. TuC02.1 The Impact of Oil-paper Insulation Moisture and Aging on the Initial Slope of the Voltage pp. 1587-1590 Xiaorui Tan Tao Zhang Qian Zuo Qi Zhang TuC02.3 Experimental Research on minimum approach distances and complex gaps for Live Working in Substation pp. 1595-1599 Three Gorges Univ. Three Gorges Univ. Three Gorges Univ. Shiyan Power Supply Company Hubei Electric Power Company Bin Xiao Kai Liu Tian Wu Ting Liu Yong Peng Xinglie Lei Ziming Su Pan Tang The polarization spectrum method based on the recovery voltage is a non-destructive method for insulation diagnosis and lifetime evaluation. It has been used to evaluate the insulation condition of the transformer. The main time constant is often used for diagnosis of oil paper insulation moisture state, and the initial slope of the voltage is used to diagnose the thermal aging state of oil-paper insulation by return voltage measurement method, but the results are not accurate. Since the initial slope is closely related to the polarization conductivity, based on the basic method of return voltage, the paper analyze the effect of oil-paper insulation with different mois- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China China Electric Power Research Inst . China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. Live working in substation is of importance to ensure the reliability of power system. Minimum approach distance and complex gaps are key parameters for safety of workers and electric equipment in substation. The discharge characteristic curves corresponding to four live working gap configuration in 80 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) substation ,such as "equalpotential personnel-grounding structures", "equipotential personnel-adjacent phase bus", "live phase bus-working personnel-grounding structures", "live phase bus-working personnel-adjacent phase bus" were obtained by the switching impulse discharge test in this article . Combined with overvoltage level of 220 kV typical substation design scheme ,the minimum live working electrical minimum approach distances were calculated : phase to ground safe distance 1.2 m, phase to phase safe distance2.1 m ,and a safe distance, phase to ground complex gaps 1.3 m, phase to phase complex gaps2.2 m . The minimum approach distances comply with relevant regulations for 220 kV substation live working by comparative analysis. TuC02.5 The finite element simulation analysis and test study of insulator ground icing flashover pp. 1606-1611 Min China Electric Power Research Inst. Bin Xiao China Electric Power Research Inst. Yong Peng China Electric Power Research Inst. Xinglie Lei China Electric Power Research Inst. Ziming Su China Electric Power Research Inst. Pan Tang China Electric Power Research Inst. of Te c h . Dan Li Hunan University of Tech. Jinhui Zeng Hunan University of Tech. State Grid Hunan Electric Power Construction The icing phenomena occurred in south China has seriously affected the safe and stable operation of the power grid. Some research results in this field has been reported in China and some other countries. However, there are rare results related to the parallel flash gap insulator ground icing network. This paper used the finite element analysis software to simulate the parallel gap distance icing flashover voltage, conducted icing tests to the RCSE 100C-2 insulator in artificial climate laboratory, and quantitative analyzed the impact of the parallel gap distance icing flashover voltage. The results show that flashover voltage shunt size and the gap size were intimately related after the icing bridge is formed up between the ground insulators. The flashover voltage was higher when the gap in parallel was larger, and the dry flashover voltage is higher than the wet flashover voltage in the same gap conditions. T ian Wu China Electric Power Research Inst . Ting Liu University Supervision Insulation Property of Wire-plane Gap under Fire Condition: Effects of Vegetation Flame Conductivity pp. 1600-1605 China Electric Power Research Inst. Hunan Wanli Yang TuC02.4 Kai Liu Lei TuC02.6 Diagnosis and Analysis for A Typical Defect of Partial Discharge in GIS pp. 1612-1616 Energy distribution and economic development level of our country are imbalance, and a large number of EHV and UHV transmission lines pass through high forest fire risk zone, and insulation property of transmission under mountain fire condition is a critical issue needed to be considered during survey, design and operation and maintenance. Gap discharge under mountain fire condition is affected by high temperature, flame conductivity (electron and ion) and large particles (smoke fog and ash), etc. This article studied characteristics of leakage current of different vegetation flames and the effect of flame conductivity on wire-plate gap breakdown characteristics with the sample of typical vegetation that causes line trip under transmission line. Research result show that conductivity of three kinds of typical vegetation flame is quite high, breakdown voltage is decreased obviously with rising of flame conductivity, and discharge pattern is transited from streamer discharge lead to electric arc discharge. Discharge characteristic of different vegetation flames can be identification basis of mountain fire risk region and dangerous vegetation, which improves reliability of line under mountain fire condition. Zhumao LuState Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Tianzheng Wang State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Hua Yu State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Jichong Liang State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Yutong Chen State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Dongdong Yang State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Yanpeng Li State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. GIS equipment is widely used in electric power system, however, partial discharge affect the normal operation of the equipment. The paper introduces the principle of ultra-high frequency and acoustic emission partial discharge living detection methods and SF6 gas decomposition detection. And this paper introduces typical defect cases of partial discharge in GIS equipment using different living detection method, combined with on-line monitoring. The living detection result is verified correctly after dismantlement, and analyses the reason of partial discharge. The final conclusion is that combined with ultra-high frequency on-line monitoring and a variety of living detection methods can improve the detection efficiency for insulation defects such as partial discharge in GIS equipment. 81 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuC02.7 TuC02.9 Fault Simulation and Diagnostic Test for Abnormal Voltage of Secondary Coil of Capacitor Voltage Transformer pp. 1617-1623 Fault Analysis and Structure Optimization of 40.5kV Wall Bushing pp. 1628-1631 Hua Yu State Grid Shanxi ElectricPower Research Inst. Hongkui Zhang Gang Yang State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Rongyan Shang Yutong Chen Fucheng Lang State Grid LiaoningElectric Power Research Inst. Corp Shenyang Research Inst. Hua Qiao Univ. Based on the explosion fault of wall bushing used in a 35kV substation, analyzing operation environment, appearance inspection of bushing and electrical test on other bushings operating well, the key causes which lead to this failure were found: design defects and high non-uniform electrical field distribution, simultaneously, heavy operation condition and high humidity are the exterior factors resulting in the explosion fault. For improving the electrical performance of bushing and electrical field distribution, the new design with shield ring was presented. At the same time, improvement solutions, adding the heater and fan in busbar compartment, used to reducing the humidity inside busbar compartment of switchgear were present ed in this paper. After these improvement measures were carried out, the switchgears operate very well in safe condition. State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Zhumao Lu State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Yongxin Liu State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. The transformer protection action is investigated and studied caused by over-excitation due of capacitor voltage trans -former secondary coil voltage that is increased. In order to find the reasons of the transformer protection action, routine tests, diagnosis tests are conducted and theses data are accord with national standards. According to infield inspection, faults simulation and analysis method are proposed which results indicated that the protection action caused by electromagnetic interference of the secondary loop. In order that prevent the occurrence of similar failures, some suggestions for operation and maintenance of capacitor voltage transformers are concluded. TuC02.10 Characteristics of Gas-production and Electrical Signal of Column-plate Model Under High- frequency Voltage pp. 1632-1636 TuC02.8 Study on Artificial Contamination Test of Typical Transmission Line Insulators pp. 1624-1627 Chunhui Gu Sihua Liu Guangzhou Power Supply Co., Ltd. Guojun Lu Guangzhou Power Supply Co., Ltd. Mancheng Yi Guangzhou Power Supply Co., Ltd. Jiangtao Li China Coal Technology & Engineering Group Qingmin Li North China Electric Power Univ. Ying Zhang North China Electric Power Univ. To elaborate the problems emerging from high frequency stress on insulating system clearly and to provide assistance in detection and measurement of high-frequency transformer, a column-plate model is adopted as the test model under high voltage both of high frequency voltage and power frequency voltage. Electrical signal was captured with Rogowski coil linked to the test model in the ground strap to measure the induced voltage and the contents of key gases were measured using Zhongfen 2000A gas-phase chromatographic instrument. In this paper, the partial discharge inception voltage, phase-amplitude diagram, the content and the proportion of key gases generated under the constant high frequency voltage are analyzed. Conclusions can be drawn from the tests that high frequency stress boosts the degrading process of oil-paper insulation system, and increases the content of key gases produced by oil-pressboard insulation system, indicating that insulating oil deteriorates severer than pressboard, but both were much worse than those under the power frequency voltage. Furthermore, the partial discharge signals were increased in frequency and reduced in amplitude, verifying the characteristics of gas-production. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Insulator contamination is an important technical problem because contamination-caused insulator flashovers may cause great damage to power system. Dust, waste, condensation and so on give rise to serious influence to flashover accident. In order to investigate the contamination distribution law of typical transmission line insulators, artificial contamination test is carried out and equivalent salt deposit density (ESDD) is measured under different conditions in pollution cycle device. The influence of different wind speed, wind direction, number of pieces is investigated to find the rules, which enables us to better understand the contamination conditions of the insulators and take effective measures to prevent the pollution flashover accidents. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China N o r t h C h i n a E l e c t r i c Po w e r Un i v. 82 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuC02.11 TuC03.2 The Study on the Partial Discharge and Insulation Aging Detection of Cable Based on the Chaotic Characteristic Parameter pp. 1637-1642 Review of the Research on Icing Mechanism of Transmission Lines and Ice-melting Technologies pp. 1648-1652 T a o L i u C h a n g s h a U n i v . o f S c i e n c e a n d Te c h . We iw e i H a o C h a n g s h a Un i v. o f S c ie n c e a n d Te c h . Lixing Zhou Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. Yu n fe n g Z h a iC h a n g s h a Un i v. o f S c ie n c e a n d Te c h . Partial discharge (PD) and water tree is the important reason to insulation deterioration of XLPE cable, So PD monitoring and locating is an important means of cable operation and maintenance. On the basis of the mechanism of cable’s PD and the research of cable aging diagnosis, the Matlab Simulink simulation model of XLPE is built, and the variation law of the chaotic characteristic parameters of PD signal is studied. The simulation results show that: with the increase of transmission distance, the correlation dimension decreases with the decreasing of the logarithmic function, and the new method based on chaotic characteristic is proposed. The ultra-voltage background of the ice storm is briefly introduced, the formation mechanism of lines icing and influencing factors are elaborated to provide a reference for Icing forecasts and anti-icing methods; Ice-melting for icing lines is reviewed, the applicable voltage levels for current method of Ice-melting is given, and various methods of Ice-melting is comprehensively evaluated in terms of security, economical efficiency, operability, and the results indicate that for all of the Ice-melting technologies, no one can possess all satisfactory security, economical efficiency and operability. Combined with the Ice-melting principles and engineering needs, the simulation calculation and test research of Ice-melting current and time should be emphasized, so that better Ice-melting and energy saving can be achieved. It is suggested that forecasting and Ice-melting be laid as a core, and also the research can be studied from icing mechanism and models, icing monitoring and early warning, anti-melting, so that the ability of anti-icing and mitigation can be continuously enhanced. Shurong Peng Changsha Univ. of Science and Tec h . TuC03.1 Application Effect Evaluation of Demon- stration Project of Thyristor-controlled Phase Shifting Transformer in 500kV Grid pp. 1643-1647 TuC03.3 Yong Cui Electric Power Research Inst., SMPEC. Yinghui Yu Electric Power Research Inst., SMPEC.Zenghui Yang R e s e a r c h I n s t . , An On-load Test Method for the Y/Δ Converter Transformer Base on Inrush Current pp. 1653-1656 Electric Power S M P E C . Haosheng Huang The considerably uneven distribution of power flow on 500kV Anhui-Jiangsu cross province interface during peak hours may contribute to overload conditions in case of outages on one of the four transmission lines of this interface. Export of electric power from Anhui province through this interface to Yangze Delta load center is restricted to 4800MW. Installation of thyristor-controlled phase shifting transformer (TCPST) on each of the 500kV cross province transmission lines from Dangtu substation to Huifengshan substation is reviewed to be effective solution for interface power flow control under various possible grid operation conditions. This paper evaluates the application effect of the demonstration project, which involves power flow control impact on the interface and neighboring system, short circuit current limiting effect with respect to the impedance of TCPST under varying phase shifting angle as well as system stability performance related issues. The evaluation is expected to provide theoretic basis for the implementation of the demonstration project. Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Yu Liu Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Xiangping Kong Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Peng Li Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst . Yi Yang Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. For the Y/Δ converter transformer in the converter station, the transformer has only two windings, and the on-load test cannot be implemented to test the polarities of current transformers’ (CTs’) secondary loops. In order to fill this gap, a novel polarity determination method for the CTs of the Y/Δ converter transformer is presented in this paper. Firstly, the configurations of CTs and relay protections for converter transformer are introduced. Besides, the characteristics of the inrush currents caused by charging the converter transformer is also analyzed. Based on that, a polarity determination method of CTs is proposed. The impact of harmonics on the on-load test data of the converter transformer can be effectively avoided with the proposed method. The proposed approach is validated with the on-load test data of the practical converter transformer. 83 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuC03.4 TuC03.6 Series-CompensationParameter Determi- nation Method of Transmission Lines with Consideration of Unbalance Degree pp. 1657-1662 S-Transform Based Pilot Protection Method for HVDC Transmission Lines pp. 1667-1672 Wenzhe Guibin Zou Chen Xi’an Jiaotong Z h a o Univ. Zhiguo Hao Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Tao Du Jun Guan Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Wenjia Yang Baohui Zhang Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Xianguo Jiang China Electric Power Research Inst. Xingguo Wang China Electric Power Research Inst. L i S h a n d o n g U n i v . Shandong Univ. Shandong Univ. State Grid Shandong Power Supply Company Traditional traveling wave protection of HVDC line is easily influenced by fault resistance, and the current differential protection as backup protection has disadvantages of slow operation speed and data synchronization, so this paper proposes a pilot protection method for HVDC line based on S transform. Theoretical analysis shows, for a fault occurring on the forward direction of the protection, the polarities of the fault components of voltage and current detected by protection are opposite, but for a backward direction fault, they are the same. According to these characteristics, a new method based on S transform angle differences to identify the fault direction is presented. In addition, for a pole-earth fault in bipolar HVDC systems, the faulted line can be distinguished from the healthy line in terms of ratio differences of S transform transient voltage energies. Simulation results show that the proposed method can effectively identify internal and external faults, the faulted line and lightning disturbance in different fault conditions. This paper discusses the formation of unbalance current when series-compensated transmission lines operate normally, studies the principle of improving unbalance degree by adjusting the series-compensation capacity within relatively tight bounds of each phase, proposes the method of series compensation parameters based on Nelder-Mead algorithm. A simulation model of 750kV transmission lines was constructed. The results show that this method can minimize zero sequence unbalance degree and negative sequence unbalance degree respectively. Moreover, the transfer capability of transmission lines almost stays the same before and after the adjustment. TuC03.5 TuC03.7 Research on DC Ice-melting Technologies for 500kV AC Transmission Lines pp. 1663-1666 Measurement and Calculation of Potential Shifting Current in ±800kV HVDC Converter Station pp. 1673-1678 We iw e i H a o C h a n g s h a Un i v. o f S c i e n c e a n d Te c h . Shurong Peng Jiazheng Lu Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. Hunan Electric Power Company T ian Wu China Electric Power Research Inst . Some technical details of DC ice-melting device and its application is introduced.And core components and structural program of DC Ice-melting device are studied from performance and price aspects.The practical functions of lines drawing, shorting scheme and the related knife gate are described.The harmonic analysis and calculation of the related parameters are carried out under the establishment of matlab simulation model according to the ice-melting needs for 500kVAC transmission lines,and accordingly the DC ice-melting plan is given.In conclusion,the combing method of the uncontrolled and controlled rectifier can address 500kV AC transmission lines icing of different line types,different ice thickness and different distance under complex climatic conditions. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Kai Liu China Electric Power Research Inst. TingLiu China Electric Power Research Inst. Bin Xiao China Electric Power Research Inst. Yong Peng China Electric Power Research Inst. Ziming Su China Electric Power Research Inst. Pan Tang China Electric Power Research Inst. Xinglie Lei China Electric Power Research Inst. The reliable and stable operation of ultra HVDC transmission system contributes to the safe operation of the power grid, thus to carry out live working is of great significance in converter station. Shift of potential is the most important aspects of entering equal-potential. At the moment of shift of potential, the strong arc and large pulse current will occur between the bus 84 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) and operation worker. Research on the characteristics of the potential shift current is benefit to take appropriate protective measures. Based on NI9165 wireless data acquisition card pulse current measurement system was applied to measure potential shifting currents during the process of entering +800 kV DC converter station bus. According to the characteristics of access to DC converter station polar bus equal-potential, potential distribution and capacitor between worker and polar buses were studied using the electromagnetic analysis software in the process of entering the equal potential. Equal potential transfer analysis model was built according to these parameters and potential shifting current were calculated in UHV DC converter station. Entering potential shifting current pulse is of the highest value 150 A with positive and negative polarity pulse, pulse width for dozens of μs in the process of entering equal-potential. Potential shifting current simulation calculation results is that maximum is 190 A, pulse width of 10 μs. Calculation and measurement results show that the potential shifting current UHV DC converter station is far less than UHV AC lines. such as potential in the process of potential shifting current pulse is mainly caused by the arc extinguish and renewed between bus and workers repeatedly, and workers should be quick into and out of the equal-potential during contacting and out of a live conductor, in order to avoid arc burns damage to workers, potential shifting bar is recommended to use during into and out of the bonding process. TuC03.9 Vibration Modal Analysis and Calculation of A New HVDC Converter Transformer with Inductive Filtering Method pp. 1683-1688 Yuehui Chen State Grid Hunan Electric Power Company Yong Li Hunan Univ. Yanjian Peng Hunan Univ. Longfu Luo Hunan Univ. In this paper, the vibration modal characteristics are investigated for a new high-voltage direct current (HVDC) converter transformer with inductive filtering method. A 3-D finite element model of the transformer is established by means of ANSYS and used to extract natural frequencies and vibration modes of the windings and cores of the converter transformer. First, a new converter transformer based on the inductive filtering is proposed, and its physical structures are described in brief. Then, 3-D model of windings of the new converter transformer is established to calculate the vibration mode. Then, the vibration mode of iron core is investigated, and an effective method of installing pre-tighten clamping is proposed to reduce the vibration of iron core. Finally, the vibration mode of whole transformer is investigated and the results show that proposed transformer has a good performance in vibration. Besides, the proposed vibration modal analysis is useful for the design of the new HVDC converter transformer. Based on the vibration analysis results, we can take the corresponding method to reduce the possibility of resonance caused by harmonic currents. TuC03.8 Study on Reactive Control Strategy of UHVDC Transmission Project pp. 1679-1682 P e n g We i J i a n g s u E l e c t r i c P o w e r R e s e a r c h I n s t . Qian Zhou Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Jiankun Liu Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Chenggen Wang Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. TuC03.10 Transformer model with Hysteresis characteristic for Electromagnetic transients based on PSCAD/EMTDC pp. 1689-1694 To keep normal running of UHVDC in addition to the active control reactive power control were needed to maintain a normal commutation voltage of converter valve. Reactive power control need coordinate with priority of each level control when considering filtering and voltage stability. Traditional reactive power and voltage control does not generally consider the priority issues of reactive power control. In order to analysis the mechanism of reactive power and voltage control of UHVDC. Take the ±800kV Jinsu UHVDC as background, based on the study on the filter configuration, detailed analysis of the relationship between the priority of the five control levels for reactive and voltage control as well as the its control principles were make. Research results indicates that the reactive power control strategies of UHVDC have five levels as abs min filter control, Umax/Umin control, Qmax control, min filter control and U/Q control under priority from low to high. Xiaohua Li Electric Power Col. South China Univ. of Tech. Jiaqi Wu Electric Power Col. South China Univ. of Tech. Chao Ye Electric Power Col. South China Univ. of Tech. Lizhu Wu Electric Power Col. South China Univ. of Tech. Dongyi Zhang Electric Power Col. South China Univ. of Tech. Xiaobing Ding Power Dispatching and Communication Center of CSG To analyze the complex sympathetic inrush characteristics of HVDC and study the methods of suppression, making up the blank of Electromagnetic transient simulation software of PSCAD/EMTDC not considering the hysteresis characteristics 85 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) of ferromagnetic material of transformer cores as well, a new three-phase transformer model with hysteresis characteristic for electromagnetic transients based on the PSCAD/EMTDC is presented, which derives from the ideas of the transformer model considering hysteresis characteristics in ATP-EMTP, it consists of Type96 and BCTRAN. This model adds magnetizing branch considering hysteresis characteristics based on UMEC model. It's full use of the advantages of UMEC model, without using winding turns, the core cross-sectional area, the core length, etc, and the hysteresis characteristics of transformer can be described when using experimental data obtained. The simulation results show that the model both have high simulation accuracy, and because the parameters readily available, it's easy for user to use in PSCAD/EMTDC and to promote the use of the transformer model in engineering application when considering transformers with hysteresis characteristics. TuC03.12 Wind Accident Analysis of Transmission Line in China Southern Power Grid’s Coastal Regions pp. 1700-1704 T ianwei Li Electric Power Research Inst ., CSG Bing Luo Lei Liu Tian Wu Electric Power Research Inst., CSG Electric Power Research Inst., CSG China Electric Power Research Inst. There are some transmission lines in China Southern Power Grid suffered from frequently typhoon in recent years. That is, typhoon will threaten power system’s safe and steady operation for long. It’s necessary to analyze statistically wind accidents in China Southern Power Grid’s Coastal Region, including Coastal Region in Guangdong, Guangxi and Hainan province. In this paper, the wind accidents of transmission line are systematically generalized and summarized according to dif- TuC03.11 ferent voltage classes, including trips, collapsed tower, broken line, damaged fitting, etc. The reasons are further and con- Research on Excitation Deicing for Transmission Line with Considering the Deicing Power Attenuation pp. 1695-1699 cretely analyzed from design, construction and operation. Q u n w e i J i n g C h a n g s h a Un i v. o f S c i e n c e a n d Te c h . against typhoon. Yusheng Zhou Then, The impact of two powerful typhoons “Ute” and “Usagi” to transmission lines are analyzed in detail. The results above will provide reasonable basis on reinforcing transmission lines Changsha Univ. of Science and Tech. L i a n g L i u C h a n g s h a U n i v. o f S c i e n c e a n d Te c h . TuC03.13 Transmission line icing is a common natural disaster in southern China with great harm to the security operation of power systems. Deicing method with high-frequency excitation has the advantages of small ice-melting current and high ice-melting efficiency, but over high operating frequency and voltage would produce electromagnetic interference to the surrounding radio communication, cause corona loss to reduce the effect of melting ice, and may increase the cost of manufacture high-frequency excitation equipment. In this paper, uniform transmission line theory is used to determine the optimum operating frequency and voltage of the excitation source with considering the deicing power attenuation. The excitation deicing method with parameters 3kHz/11kV and deicing effect are identified, using MATLAB and ANSYS simulation to verify its feasibility and comparing the deicing effect with DC shorted deicing. The research result shows the superiority of deicing that it reduces ice-melting current and power capacity, and reduces the ice-melting time to improve deicing efficiency. The electromagnetic interference, corona loss, and the manufacturing cost of the excitation source are also reduced. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Analysis on HVDC Start-up in System Black-start pp. 1705-1709 Guanghu Xu China Southern Power Grid Liang Tu China Southern Power Grid Haiwen Lan South China Univ. of Tech. Chengjun Xia South China Univ. of Tech. The start-up of HVDC will bring impact of active and reactive power to the grid, causing voltage and frequency disturbances. This paper analyses the effects of different HVDC start-up modes to AC system and selects the most appropriate one. Besides, the paper puts forward the method of estimating short circuit ratio and effective inertia constant of AC system to meet the operation requirements of voltage and frequency in both transient and steady states and verify the accuracy by the simulation of Yunguang HVDC. 86 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) reclose overvoltage was lower than that of close overvoltage. It’s appropriate to close the circuit breaker on source side after closing the circuit breaker on the load side to avoid damaging the potential transformer joint with the bus of load. The amplitude of close overvoltage when the transmission line was whole headline was lower than that when the transmission line was headline and cable. It’s really possible to occur resonance overvoltage if the transmission line was the whole cable. The amplitude of the over-voltage can be reduced only if the suitable operation types and running types. TuC03.14 Principle Research on Suppressing Harmonic Instability of HVDC Transmission by Using an Inductive Filtering Method pp. 1710-1714 Guandong Zhou State Grid Hunan Electric Power Company Yong Li Yuehui Chen Longfu Luo Yicheng Zhou TuC03.16 Hunan Univ. State Grid Hunan Electric Power Company Combined Fault Location Algorithm for HVDC Transmission lines Based on Natural frequency pp. 1720-1725 Hunan Univ. Fujitsu Corporation Duan Harmonic stability is easily excited once there are non-characteristic harmonics in HVDC transmission, who operates on the unbalance condition or has disturbance of converter control system. This paper concerns the core-saturation-type harmonic instability, and presents a new concept that using inductive filtering method to solve harmonic instability fundamentally. First, the mechanism of harmonic instability generation is analyzed. Then, a new HVDC transmission based on inductive filtering method is introduced briefly, and its equivalent impedance network is established. Based on this, a frequency scanning method is presented to get the impedance-frequency characteristics of the new HVDC transmission. Besides this, for comparative study, the CIGRE HVDC benchmark model is also analyzed. Research results indicate that the application of inductive filtering method changes the resonance frequency, and it can avoid the harmonic instability caused by low-order harmonic resonance. Xi’an Zhao Zhao Un iv. of Te c h . Xi’an Univ.of Tech. Liu Jing Xi’an Univ. of Tech. In frequency domain, there is a certain mathematical relationship between the natural frequency and the fault distance. But model mixing is still the problem haven’t been solved well yet, it brings difficulty in gaining the natural frequency. A combined fault location algorithm for HVDC transmission line based on natural frequency is proposed in this paper, in which time domain and the frequency domain is combined together. On the one hand, in time domain, wavelet analysis was used to calculate rough fault distance. Then through the relationship between the fault distance and the natural frequency, the rough natural frequency was obtained. On the other hand, wavelet packet was used to divide the frequency into several specific ranges, and then find out the range of rough frequency. At last, multiple signal classification algorithm was used to obtain the frequency, and the fault distance was obtained. The algorithm has been performed a lot in PSCAD. The validity of the algorithm has been verified. TuC03.15 Differentiation Research on Closing Overvoltage of Headline-cable Comprehensive Transmission Type with Double Circuit Transmission Lines on Same Tower pp. 1715-1719 TuC03.17 Field Study of A Novel Dynamic Rating System for Power Transmission Lines pp. 1726-1731 Fucheng LangState Grid Liaoning Electric Power Research Inst. Hongkui Zhang Jiandong China Coal Tech. & Engineering Group Corp Shenyang Research Inst. Wei Bao State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Yuehao Yan To research the close overvoltage transient characteristic of headline-cable comprehensive transmission type with double circuit transmission lines on same tower, a 220kV power system was selected to build the transient model of headline-cable comprehensive transmission type with double circuit transmission lines on same tower by EMTP, the characteristics of the close overvoltage and the reclose overvoltage after single phase grounding fault were researched totally. Ultimately, the main factors effect on close overvoltage were analyzed. The results demonstrated that the amplitudes of overvoltage were mainly related to close phase angles with its range from 1.17p.u to 2.14p.u. It’s best to close at the phase angle from 210°-240° considering the characteristic of arrester. The amplitude of State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company WeizhengZhangState Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Jun Xin State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Zhengrong Li Shanghai Hinner Tech. Co., Ltd Rui Tang Shanghai Hinner Tech. Co., Ltd In the modern power grid, the dynamic rating technology of transmission line has been drawing more and more attention. Through on-line monitoring devices installed on transmission lines, the conductor temperature, environment temperature, wire current and sunshine intensity are monitored in real-time, 87 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) frequency sinusoidal alternating current, to analyze the mechanism of DC bias caused by GIC impacting the system voltage in this paper. Based on the simulation model, the variations of transformer reactive power consumption and system voltage are recorded. In addition, the impact of GIC on the generator output is studied. The results indicate that the consumption of transformer reactive power increases periodically with the increasing of GIC, which results in the periodic reduction of system voltage and decrease of generator output. which provides solid theoretical basis of raising line short-term transmission capacity Developing dynamic rating system can effectively and safely raise short-term transmission capacity of transmission lines, to satisfy the demands for power supply under emergency. By the analysis of the principle, structure, and functions of transmission line dynamic rating system. The risk aversion strategy are derived based on the simulated research and field test data to improve the ampacity. The proposed method such as safety current under the limited time and safety operation time under the limited current provide feasible measures for dynamic rating of transmission lines. TuC03.18 TuC04.1 Based on the LCC calculation method of the economic current density pp. 1732-1735 Investigation study for double circuit lightning trip incident at 275kV overhead line network in Malaysia pp. 1740-1745 Wa n g we i J i N o r t h C h i na E l e c t r i c Po w e r Un i v. Yajing Gao North China Electric Power Univ. Qing Xie North China Electric Power Univ. Jing Li North China Electric Power Univ. Boniface. H.K. Chia Lightning outage has always been a major concern for power utilities operating tropical region which is experiencing high level of lightning activities. Syarikat SESCo Berhad in Malaysia is one of the utilities facing the challenge in achieving decent lightning performance of the lines. This paper presents an investigation study on the suspected double circuit lightning trip incident at 275kV overhead line network in Malaysia. The lightning outage will be investigated based on four study aspects, vitz. shielding failure flashover, backflashover, induced flashover and mid-span flashover.The input to the calculation will be based on recorded data and the typical design parameters for existing 275kV line. Selection of total cross-section and split type for transmission line conductor is an important factor in obtaining good economic benefits during the entire life-cycle of AC power transmission projects. Economic current density is an important reference for line cross-section selection. The traditional economic current density algorithm exist the following problems: 1. Traditional algorithm ignores the influence of line maintenance cost, spare parts cost and the retirement cost. 2. Electricity price and wire price are important factors affecting current density. Obviously the current price is different with the 80s. The method of traditional ignores the time value of money and think the price as constants. This paper presents a method which is based on the theory of LCC to solve the above problems. Each cost function expression of line section is fitted out with plenty of practical engineering data. Finally, a practical case study is employed to verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the method and model proposed on the completed transmission line. TuC04.2 Study on the Affection of Ground Grids with Varied Aspect Ratio on Frequency Characteristics of Grounding Impedance pp. 1746-1751 TuC03.19 The Impact of GIC on System Voltage and Generator Output pp. 1736-1739 Hanli WengChina Three Gorges Univ. Guowen Yang China Three Gorges Univ. Xuehua Li China Three Gorges Univ. Xiangning Lin China Three Gorges Univ. Chunjiang Hu Gansu Electric Power Research Inst. Dingjun Wen Gansu Electric Power Research Inst. Yaming Sun Gansu Electric Power Research Inst. Kang Liu Gansu Electric Power Research Inst. Zhijie He Southwest Jiaotong Univ. Lijun Zhou Southwest Jiaotong Univ. In order to study ground grids with varied aspect ratio impact on grounding impedance, this paper considers the characteristics of the transient electromagnetic conductors and compares frequency characteristic curve of grounding impedance, after the simulation and calculation based on the CDEGS,which is famous for measuring the grounding resistance in the world. The results show the inductive component of grounding impedance is related to injecting point of ground short-circuit current. As the aspect ratio of ground grids decrease at power frequency, the resistive component of grounding impedance Aiming at the phenomenon of the system voltage decrease in the case of geomagnetic storms, a Geomagnetically Induced Current (GIC) -Direct Current (DC) bias simulation model with 2 generators and 5 buses based on the PSCAD/EMTDC platform is established, in which the GIC is simulated by low November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Syarikat SESCo Berhad 88 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) lished. Through the calculation of the traditional distribution transformer model parameters and the study of energy equivalence principled, this paper puts forward a method to calculate the resistance, inductance and distributed capacitance parameters of the lighting transient model. And the parameters of S-11-M-100/10 distribution transformer are calculated as an example. This paper simulates the simple distribution network with a distribution transformer model in lightning stroke using PSCAD.By analysis on the waveforms of distribution transformer for both high and low voltage side in three kinds of lighting stroke,this paper shows the lightning hazards of distribution transformers. becomes greater and greater. The impact of grounding impedance under five different aspect ratio is compared at several frequencies other than power frequency, by parameter calculation and simulation analysis, the results indicate the design of large substation ground grids should be made with an aspect ratio of 6/5:5/6, and perhaps could be set as a standard in grounding system design and modification in distribution substations. TuC04.3 TuC04.5 Study on the Frequency Characteristics of Grounding Resistance in Non-uniform Soil Regions pp. 1752-1756 Chunjiang Hu Gansu ElectricPowerResearch Inst. Dingjun Wen Gansu Electric Power Research Inst. Yaming Sun Gansu Electric Power Research Inst. Yushuo Wu Gansu Electric Power Research Inst. Ying Chen Southwest Jiaotong Univ. Lijun Zhou Southwest Jiaotong Univ. Simulation Study on Lightning Protection of Distribution Transformer with Z inc Oxide Arrester pp. 1763-1767 Mengqian Hou Shandong Univ. Houlei Gao Shandong Univ. Shuai Zhang Shandong Univ. Fei Wang Shandong Univ. Currently, few researches related to lightning protection of distribution transformer with zinc oxide arrester are reported on both home and abroad. This paper establishes a model of zinc oxide arrester and distribution transformer under lightning stroke. In order to verify the lightning protection of zinc oxide arrester to distribution transformer, two distribution network simulations are carried out by using PSCAD. One is the condition without zinc oxide arrester, another one is with zinc oxide arrester to be installed in distribution transformer’s high voltage side. Besides, this paper also carries out a distribution network simulation with zinc oxide arrester installed in both high voltage side and low voltage side of a distribution transformer. The importance of zinc oxide arrester for preventing distribution transformer from damage of lighting is shown by comparison of different simulation results. The grounding system is an important measure to maintain reliable operation of power systems and ensure the safe of equipment and human body. Grounding resistance is an important parameter to judge whether the grounding system meets the requirements. This paper aims to study the frequency characteristics of grounding resistance in non-uniform soil regions. By using the software CDEGS, a three-layered soil model was made,and the simulations of the influence of upper soil resistivity, upper soil layer thickness, middle soil resistivity, middle soil thickness and lower soil resistivity on grounding resistance based on horizontal three-layered soil structure were carried out. And the frequency characteristics of grounding resistance under several situations were studied. It is concluded that frequency has a greater effect on grounding resistance in the areas with higher resistivity and smaller thickness of upper soil. TuC04.6 Study on Lightning Characteristics of Mountain Transmission Line pp. 1768-1771 TuC04.4 Establishment and Simulation of Distribution Transformer Transient Model under Lightning Stroke pp. 1757-1762 Yong Sun Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. Linli Zhang Shandong Electric Power Research Inst. Mengqian Hou Shandong Univ. Houlei Gao Shandong Univ. Xiaogang Gao Jibei Electric Power Company Xiaobo Wu Jibei Electric Power Company Zhange Liu Jibei Electric Power Company Dexuan Sun Jibei Electric Power Company Muwen Li Jibei Electric Power Company Huimin Gao Jibei Electric Power Company Lightning accident is an important cause of transmission line failure. Although the study on lightning characteristics of transmission line have conducted a lot both at home and By analyzing the characteristics of the lightning current and traditional distribution transformer model, a transient distribution transformer model under the lightning stroke is estab- 89 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) abroad, safe and reliable operation of the transmission line must depend on the design of tower grounding and lightning protection measures according to the structural characteristics of the transmission line itself. In this paper, the researchers study the transmission line in Qinglong mountain area and carry out the relevant fundamental research and analysis on the mountains lightning performance of transmission line, which provides a reference for design and operation of transmission line mountain area. charge detection for cable insulation is an important means to find the cable insulation defects and assess state of the cable insulation. Partial discharge signals from different sources have great harm to the power equipment, so pattern identification is an important purpose in this research. First, the four kinds of discharge waveforms are processed by de-noising preprocessing, then discharge waveforms are decomposed by wavelet packet, and finally the energy percentage in different frequency bands can be obtained. Studies show that when the type of discharge signal is different, the wavelet packet coeffi- TuC04.7 cients in the distribution of each band is also different. So energy percentage of the wavelet packet coefficients can be used Fault Diagnosis of Substation Grounding Grid Based on the Signal Distance Function pp. 1772-1775 Liqun Shang Xi’an University of Science & Tech. Wenli Liang Xi’an University of Science & Tech. for discharge signal feature recognition. In this paper, SVM binary classification is first extended to multi-classification by M-ary algorithm, then the feature vectors composed by energy percentage of the wavelet packet coefficients are inputted into SVM for recognition. The recognition results of test samples show that feature vectors composed by the percentage of en- Good grounding condition is great important to keep the safety of staff and stable operation of electrical equipments in the substation. Electric power system is an urgent need for practical and effective diagnostic method without excavating the grounding grid and affecting the normal operation of the system, which can look for the location of corrosion and diagnose the degree of corrosion of grounding grid, so as to evaluate safety performance of grounding. This paper adopts the electromagnetic induction principle, pours the excitation current of different frequency sine wave into the grounding through CDEGS analysis software of grounding grid, simulates and analyzes the distribution of magnetic induction intensity in the surface; diagnoses the defects state of grounding grid conductors according to the change of distributional characteristics; calculates the value of the signal distance function for the distribution of magnetic induction intensity when the grounding grid conductors is in the corrosion and breakage; and finds out the specific difference of the each waveform according to the value of mutual distance, to achieve the fault diagnosis of grounding grid. ergy of wavelet packet coefficients can well reflect the characteristics of the original signal, and the method based on SVM has better recognition performance. TuC05.2 Evaluation of the Calculation Method for Stray Losses in Structural Parts of HVDC Converter Transformers pp. 1780-1785 TuC05.1 The Feature Extraction and Pattern Recognition of Partial Discharge Type Using Energy Percentage of Wavelet Packet Coefficients and Support Vector Machines pp. 1776-1779 Jia Xu South China University of Tech. Haiqing Niu South China University of Tech. Riliang Hu Yaqing Liu Huazhong University of Science and Tech. Dandan Zhang Huazhong University of Science and Tech. Zhenbiao Li Huazhong University of Science and Tech. Qinqing Huang Huazhong University of Science and Tech. Menghu Li Huazhong University of Science and Tech. Bin Li Huazhong University of Science and Tech. Jian Liu Huazhong University of Science and Tech. Stray losses in structural parts are calculated separately during determining load losses of HVDC converter transformers, but the calculation method proposed by IEC 61378-2 standard shows significant difference from the experimental results. The nonlinearity, hysteresis losses, and frequency characteristic are thought as the sources of errors in this paper, and then an electromagnetic-circuit coupling FEM analysis is performed to investigate them. It is shown that the frequency characteristic Southern Power Grid of the stray losses is the major factor that causes the errors, Partial discharge is an important cause of the deterioration of and the material characteristic should be considered. The the cable insulation condition, and also an important manifes- magnetic and nonmagnetic materials are suggested to be cal- tation of the deteriorated insulation condition. Partial dis- culated separately. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China 90 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuC05.3 TuC05.5 Research of VFTO in 110kV Minimized GIS pp. 1786-1789 Zhiguo Hao Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. The Research and Application of Ultrasonic Imaging Technology in Transformer Internal Fault Detection pp. 1795-1799 Jie Guo Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Zhipeng Wang Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Xuan Wang Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Tianzheng Wang Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Hua Yu Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Tao Jin Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst. Qifei He Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 110kV minimized gas insulated substation (GIS) has been widely used in China, due to its great electrical properties. The closing or opening operation of disconnector switches (DS) and circuit breaker (CB), and single-phase ground fault are all probable to cause the very fast transient overvoltage (VFTO), which is a threat to the power system. Compared to the structure of higher voltage GIS, three-phase electrical equipment in 110kV minimized GIS is placed in the same box. So we must establish the three-phase model of GIS and then calculate its VFTO. This paper referred to 110 kV minimized GIS power system. Using the Electro-magnetic Transient Program (EMTP), numerical simulation and analysis of VFTO in different DS, CB operation modes and single-phase grounding fault were carried out. And the data of VETO under different operation modes, including the frequency, amplitude, steepness and waveform were obtained. Then it calculated and analyzed the influence on VFTO of length of branch bus and transformer entrance capacitance, in order to provide reference basis to the structure design of GIS and analysis of VFTO. In view of the complex internal structure of the transformer, this paper presented the theoretical foundation of high sensitivity ultrasonic sensor signal receiving mechanism, and the relationship between ultrasonic signal amplitude modulation information and the location and shape information of the transformer internal structure. Through the study of ultrasound folding and reflection law in different internal media of transformer, the relationship between ultrasonic signals and the transformer internal structure is revealed, and the internal structure of transformer is imaged. TuC05.6 TuC05.4 Research on Control Technology of Permanent Magnetic Operating Mechanism for Vacuum Circuit Breaker pp. 1800-1803 Development and Experiment of Fast Breaker-Type Fault Current Limiter pp. 1790-1794 Feng Gao Ningxia Electric Power Company Shaogui Ai Ningxia Electric Power Company Ran Ding Ningxia Electric Power Company Yongning Huang Ningxia Electric Power Company Fucheng Lang Electric Power Research Inst. of Liaoning High Voltage and Large Current Laboratory of State Grid Corp. Hongkui Zhang China Coal Tech. & Engineering Group Corp. In order to improve the reliability of mining electrical equipments and to ensure the safe operation of power system in coal mine, a design scheme of mining permanent magnet sealed vacuum circuit breaker operating mechanism control system was proposed. Hardware circuit and software program of control system were designed on the basis of PIC single chip microcomputer, including IGBT drive circuit and the control Fault current limiter (FCL) is one of the efficient technological measures to solve the increasingly serious problem of excessive short-circuit current in power grid. A fast breakertype fault current limiter with modularized design is developed on the basis of 12kV fast-speed vacuum breakers and shortcircuit current perfect forecast and zero-cross point precise phase controlled breaking technologies. Zero-loss of the FCL is obtained under normal condition and up to 80 kA short-circuit current could be limited within 20ms to the safe breaking level of the system circuit breaker. The security, efficiency and reliability of the device are verified by field operation and two single-phase transient short-circuit experiment in a 330 kV network. signals transport circuit. Research the IGBT action over voltage buffer technique and hardware anti-jamming technique. The experiment shows that the system can control the permanent magnetic actuator to drive mine permanent magnet sealed type vacuum circuit to complete the breaker switching operations, which meets the design expectations. 91 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) partial discharge in the environment with low SNR and strong electromagnetic interference, thus it can improve the sensitivity and anti-jamming ability to detect power transformer operation of the system. TuC05.7 Design and Simulation of Cylindrical Linear Induction Motor Mechanism Based on F inite Element Analyze pp. 1804-1808 Hongkui Zhang Fucheng Lang TuC06.1 China Coal Tech. & Engineering Group Corp. Shunt Capacitor Bank Protection in UHV Pilot Project pp. 1813-1817 Electric Power Research Inst. of Liaoning High Voltage and Large Current Laboratory of State Grid Corp. According to the requirements on operating mechanism of movement characteristics during the opening and closing of 40.5 kV vacuum circuit breaker, a new type of motor drive operating mechanism- cylinder linear induction motor (CLIM) mechanism was designed in this paper. And magnetic field and some characteristics of (C-LIM) was analyzed using finite element method, and (C-LIM) design validity is proved. Based on higher requisition of the characteristics of breaker operating mechanism when operating and closing the motor mechanism movement characteristics was built and load model of system is analyzed, and the optimized velocity curve of the contacting also planned in the paper. Pointing at ending effect of C-LIM mathematical model of vector control system is built when consider dynamic vertical ending effect, and simulated of the mechanism control system for driven by (C-LIM) in MATLAB environment. C-LIM model is successful in putting it through a test on circuit breaker rated 40.5kV and satisfy requirements. The results show that it can get a good dynamic performance, small vibration and perfectly meet the requirements of mechanism movement characteristics during the opening and closing of circuit breaker when the linear motor direct drive circuit breaker actuator operating shaft, and still lay the foundations of circuit breaker intelligence control. ZheZhao Zeng Changsha University of Science & Tech. China Southern Power Grid The Research of Live Working Gap Discharging Characteristics on UHV Steel Tubular Tower Transmission Lines pp. 1818-1821 Xinglie Lei China Electrical Power Research Inst. Kai Liu China Electrical Power Research Inst. Ting Liu China Electrical Power Research Inst. Bin Xiao China Electrical Power Research Inst. Yong Peng China Electrical Power Research Inst. Tian Wu China Electrical Power Research Inst. Ziming Su China Electrical Power Research Inst. Pan Tang China Electrical Power Research Inst. Along with the construction and development of UHV project, the steel tubular towers have been widely used in projects of UHV transmission lines. In order to ensure the safety of live working on UHV steel tubular tower transmission lines, this article compares the electric field distributions around UHV steel tubular tower and angle-steel tower through simulating calculation; obtained the impulse discharging characteristics of various typical live working conditions through 1:1 steel tubular tower model test, and determined the safety distance for live working under various conditions; through impulse discharging test of both steel tubular tower and angle-steel tower, analyzed the difference of impulse discharging characteristics between the two typical structures. The research result can provide a technical support for live working on UHV steel tubular tower transmission lines. It is significantly difficult to make well detection of transformer operating conditions in the environment with strong noise and electromagnetic interference. This paper presents Duffing oscillator model transformation based on the generalized time scale and the weak partial discharge signal can be detected by the use of ultra high frequency (UHF) partial discharge detection on the model, thus the operation of transformers is acquired. The theoretical analysis and simulation results show: this new method not only with chaos and noise immunity of the good, but also can detect faint pulse signals of transformers November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Taoxi Zhu TuC06.2 Transformer 's UHF Partial Discharge Signal Detection Based on Converted Duffing Oscillator Model pp. 1809-1812 Changsha University of Science & Tech. China Southern Power Grid The configuration and setting of shunt capacitor bank protection is very important to ensure the safety of power system and power equipment. This paper introduces the shunt capacitor banks connection and shunt capacitor banks protection configuration of the UHV pilot project from Southeast Shanxi via Nanyang in Henan province to Jinmen in Hubei province. The application principle on the configuration and setting of this 110kV shunt capacitor banks protection is studied and discussed in detail. The principle to ensure the safety of power equipment is chiefly taken into account in order to achieve a reasonable configuration and setting. TuC05.8 ZhenYuan Yang Qing Tian 92 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuC06.3 TuC06.5 Application of Long Tonnage Composite Insulators on UHVDC V-Type Strings pp. 1822-1826 Research on Impacts of Bipolar Blocking in Jinsu UHVDC on Stability of Receiving-end System pp. 1830-1833 Guanjun Fu Peng Wei Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Jiankun Liu Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Yongxin Gong State Grid Energy Research Inst. CEC Huada Electronic Design Co.,Ltd. Qian Zhou In UHVDC transmission projects, long tonnage composite insulators with mechanical strength of 300kN and above will be widely used for V-type strings. Research on operating mechanical characteristics of long tonnage composite insulators is the basis for properly insulator selecting. In this paper, finite element model of overhead transmission line as well as mechanical model for V-type composite insulator verified by load test was constructed. In view of the application of composite insulator FXBZ-800/550 on UHVDC V-type strings, the dynamic tensile and compressive loads under the dynamic operating conditions such as ice shedding, wind swaying and conductor galloping were studied through numeric simulation, so were the influences of ice thickness, wind velocity and galloping amplitude to the insulator loads, and furthermore, the amplification ratio of dynamic peak loads relative to their corresponding static loads was obtained. This research results can provide theoretical references for developing long tonnage composite insulator dynamic load reliability test and selecting its safe coefficient. Chenggen Wang TuC06.6 Research on Impacts of UHVDC Transmission on Operating Stabilities of Receiving-end Power Gr i d pp. 1827-1829 Peng Wei Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Jiankun Liu Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Chenggen Wang Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. For receiving-end system that has larger percent of power from outside, if UHVDC bipolar blocking occur, there must have some impact on grid security and stability. Take Jinsu UHVDC as background, based on the typical summer peak data of Jiangsu power grid, electromagnetic transient model of Jinsu UHVDC project was established in ADPSS containing detailed DC control system; In addition, the remaining part of Jiangsu power grid and electromechanical transient model of the sending equivalence grid were established, the influence of Jinsu UHVDC bipolar blocking on angle of power plant surrounding power, surrounding reactive power, voltage and grid frequency. Results shows that: After the bipolar blocking, power angle of plant near the placement unit stability can be maintained, reactive power of the plant is reduced after shortly increase first, 500kV voltage nearby fluctuate maximum of 30kV, frequency of Jiangsu grid drop slightly, can maintain stable operation. TuC06.4 Qian Zhou Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Analysis on the Operating Characteristic of UHVDC Hierarchical Connection Mode to AC System pp. 1834-1837 Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Research on interaction impacts on UHVDC after fault in receiving-end power grid is important for improving stability. In order to research the running stability of the receiving end grid under typical fault take Jinsu UHVDC project as background, the sending grid and also the entire main grid of Jiangsu outside Jinsu UHVDC were established base on ADPSS. In accordance with the actual project DC line, filters, converter transformer and other DC electromagnetic transient model. The influence of typical faults on the receiving end grid such as AC bus fault, three-phase short circuit on line and bipolar locking were analyzed. Finally, restart procedure of bipolar locking were studied. Simulation results shows that serious fault may lead to DC bipolar locking, bipolar blocking or typical fault in AC system; Jiangsu power grid can restart smoothly after bipolar blockin, but the receiving end power grid can keep stable operation after bipolar locking. Wanqian Sun Nanjing Univ. of Posts and Tele. Rong Fu Nanjing Univ. of Posts and Tele. Zhenkai Zhou Nanjing Univ. of Posts and Tele. Xiaojuan Huang Nanjing Univ. of Posts and Tele. Chenggen Wang Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Ke Xu Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Bing Xie Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Zhaowei Li NARI Technology Co.Ltd. Ming Ni NARI Technology Co.Ltd. In this paper, the mathematical method of the MIIF (multi-infeed interaction factor) under UHVDC hierarchical connection mode is analyzed, and the correctness of the method is verified by PSCAD simulation. In hierarchical connection mode, it was analyzed that one inverter in a bus which has been in the condition of commutation failure has effect on another inverter in another bus with the change of MIIF. 93 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) D: New Energy Power Generation and Microgrid Technology TuD01.1 A Research on Design and Evaluation of BIPV pp. 1838-1843 QiangZeng JingpengChen Guangdong Grid Company hanghai Jiao Tong University Jianmo Ni hanghai Jiao Tong University Qian Ai hanghai Jiao Tong University ZhaoyuWang hanghai Jiao Tong University RuicongZhai PingXu Electric Power Research Institute of Guangdong Grid Company Guangdong Grid Company of Jiangmen Power Supply Bureau ChengzhiMa Guangdong Grid Company of Jiangmen Power Supply Bureau PengminWang Shanghai Huali Software System Company Limited Building Integrated Photovoltaic (BIPV) systems are expected to increase significantly in the forthcoming years because of its friendliness with natural environment. This paper discusses design and evaluation of BIPV. A novel way to calculate tilt angle is presented to reduce the impacts of shading and maximize power output, followed by a design example to show its effectiveness. In system evaluation, levelized cost of energy (LCOE) method is used to evaluate the economy of designed system and output optimized tilt angle and LCOE optimized tilt angle are obtained. Government’s incentives are more crucial for the improvement of BIPV’s LCOE. Life-cycle emission analysis is used to quantify environmental benefits of BIPV systems. TuD01.2 Research on correlation evaluation and joint probability model of multi-wind generation scenarios pp. 1844-1847 TaoShi China Electric Power Research Institute LingzhiZhu China Electric Power Research Institute XiangyanWang China Electric Power Research Institute In this paper, in order to quantify the correlation and joint probability character between different wind farms, the relativity analysis theory is used in the correlation evaluation of multi- wind farms, located in different positions. And then a method for modeling the joint probability distribution of wind November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China 94 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) resource in multi-wind farms is provided, which is based on the copula function. The availability of this method are demonstrated by an actual case with two wind farms, located in northwest of China . error has obvious effect on optimized scheme of power flow calculation, unit commitment and operation in the power system with wind power. The wind forecast error is different under the power dimension and correlative under time dimension, so it can describe the actual wind power attributes more accurately on the basis of fitting the forecast error divided into different groups according to the power-time attributes. The parameters distribution like normal distribution can not describe the error in different bins accurately, but this paper proposed non-parameter kernel density estimation (NKDE) to fit the error data in various bins, which is also suitable for various forecast methods. If ignoring the characteristic of NKDE, it has poor fitting effect because of too many bins and too few data in some bins. This paper proposed a method to reduce the number of bins to improve the fitting effect and reduce calculation time. Results for this case show the proposed probability density function (pdf) is more close to the actual wind power error distribution. TuD01.3 Comprehensive Evaluation of Renewable Energy for Power Projects Based on CA-DEA Model pp. 1848-1853 XiaochuanMa North China Electric Power Univ. BoZeng North China Electric Power Univ. YuxiZhang North China Electric Power Univ. YingziLi North China Electric Power Univ. ZongqiLiu North China Electric Power Univ. This paper presents a two-phase evaluation model called cluster analysis data envelopment analysis (CA-DEA) for renewable energy in power generation projects which combines cluster analysis and data envelopment analysis, to achieve the optimal resource exploitation sequence in the stage of planning and the effective evaluation during the period of operation. On the basis of a designed comprehensive evaluation index system, the fuzzy AHP is introduced to analyze the qualitative indices, such as the coordination level with local condition. The dominant factors can be determined by applying cluster analysis (CA); the non-parametric DEA model is adopted for the assessment of project input-output efficiency, which makes the production function determination easier. According to the comprehensive values of the ratio of input to output, the effective assessment to the performance of the projects could be implemented. Finally, a practical case is presented to verify the effectiveness and practicability of the model. TuD01.5 Chaotic Time Series Prediction Model of Wind Power pp. 1860-1863 The Fitting Method of Wind Power Forecast Error under Power-time Dimension pp. 1854-1859 Intelligent Dispatch and Control of Ministry of Education XueliWan State Grid Shandong Electric Power Maintenance Company LibinYang Deyang Electric Supply Company of State Grid HuaqianLi Sichuan University LanWang Sichuan University Wind Power Prediction Errors Model and Algorithm Based on Non-parametric Kernel Density Estimation pp. 1864-1868 Intelligent Dispatch and Control of Ministry of Education JunLiang ZhijianYuan TuD01.6 Intelligent Dispatch and Control of Ministry of Education ChengfuWang Deyang Economic and Tech Research Inst In order to reveal the interval laws of wind power time series, the phase space reconstruction which is on the basis of chaotic time series theory is used to identify the chaotic feature of wind power time series. Considering the different effects of different coordinate of phase points on predicted point, this paper improves the distance criterion and the evolutional trend criterion by weighting. In addition, this paper proposes an improved local Volterra adaptive filter to predict wind power by proposing a comprehensive criterion to select the neighbor points as the training set. The simulation of the measured data of a certain wind farm shows the proposed model is accurate and fast. TuD01.4 ZhaoqingWang ZhijianYuan State Grid Qinghai Electric Power institute Randomness and volatility are the inherent attributes of wind power, and the present method for forecasting wind power is not accurate enough. However, the exact description of forecast 95 GuodongLiao Economic & Technical Research Institute GuodongLiao Jie Ming Boyuan Wei Hongji Xiang Nan Jiang Peng Ai Chaohua Dai State Grid Hunan Electric Power Corporation Southwest Jiaotong University Southwest Jiaotong University Southwest Jiaotong University Southwest Jiaotong University Southwest Jiaotong University Southwest Jiaotong University November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Xintao Xie Xintao Xie MengjiaoLi MengjiaoLi model proposed in this paper has higher prediction accuracy compared to another model and has certain application value. Economic & Technical Research Institute State Grid Hunan Electric Power Corporation Economic & Technical Research Institute State Grid Hunan Electric Power Corporation TuD01.8 For the high randomness and fluctuation of wind power, as well as the low precision of the power prediction, the traditional prediction of wind power point is not able to describe the uncertainty of wind power. A normal distribution is usually used to model wind power forecast error, but it is not valid in some special cases. In this paper, non-parametric kernel density estimation is adopted to calculate the probability density errors of wind power prediction at different levels. According to system reserve capacity requirements, safety and economy of power generation dispatching, a wind power prediction interval with three spline interpolation is acquired which satisfies the certain confidence interval. The three spline interpolation is the wind power error’s distribution function. An equality constrained optimization problem was simplified into an unconstrained optimization problem and Newton with the characteristics of non-parametric kernel was presented. Given a probability value at a certain precision, it’s useful to use Newton to search for arguments. Then, the upper and lower range are obtained. The calculation results show that the used wind power interval forecasting method can provide wind power prediction curve and its variation range, and is more suitable for wind power uncertainly. Longitudinal Moment Markov Chain Model of Wind Power and Its Application on Ultra-short-term Prediction pp. 1874-1878 Zhong Chen Changsha University of Science & Technology Dongyang Yin Shandong University Libin Yang Shandong University Communication Shandong NormalUniversity State Grid Qing Hai Electric Power Research Inst XueliWang State Grid Shandong Electric Power Maintenance Company In this paper, a longitudinal moment Markov chain model of wind power time series based on the longitudinal time concept is proposed. This model emphasizes the transition characteristics related to different moments by providing a set of transition probabilities matrices. This matrices set, describing the inherent transition information of moments, gives the necessary probabilistic conditions for optimization decision of power systems containing wind farm. Besides of rapid calculation as conventional Markov chain model has, the proposed model makes the transition information more detailed and accurate. To illustrate the effect of improvement, a wind power prediction (WPP) method on ultra-short-term horizon using the longitudinal moment Markov chain model is put forward. The case study based on actual wind power data under multiple time scales shows that the proposed method achieves a higher prediction precision. Huitong County Power Supply Co., Ltd, TuD01.9 State Grid Hunan Electric Power Company Qi Li Zhihao Yun XiaojuanYang A new combination Model for short-term wind power Prediction pp. 1869-1873 Changsha University of Science & Technology Shandong University Jun Liang TuD01.7 Zizhong Yin JingwenSun Electric Power Economic and Technical Research Short Term Wind Speed Forecasting Using Wavelet Transform and Grey Model Improved by Particle Swarm Optimization pp. 1879-1884 Institute, State Grid Bengbu Electric Power Supply Company Short-term wind power prediction is important to the dispatch and operation of power system. A prediction model based on the rough set, principal component analysis (PCA) and Elman neural network (ElmanNN) is constructed for short-term wind speed forecasting to improve the prediction accuracy of short-term wind power. The wind speed prediction model is established by using ElmanNN, and PCA is used to extract the feature of wind speed data, which optimizes the inputs of ElmanNN. Furthermore, excitation function and the structures of network are improved to search for the optimum solution to function of convergence rate and prediction accuracy. To solve large error and prediction accuracy fluctuations of the ElmanNN model at the peak value of wind speed, the rough set theory is proposed to compensate and correct the predicted values to further improve the forecasted results. Finally, the predictive value of the wind power is obtained by the power conversion. Experiment results show that the new combination November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China MianGuo Hohai University ZhinongWei Hohai University HaixiangZang Hohai University GuoqiangSun Hohai University Huijie Li Alston Power Grid Technology Center Co., Ltd Kwok W. Cheung GE Grid Solutions lnc. Nowadays wind energy is one of the most important source of renewable energy worldwide. Wind power generation is an important form of wind energy utilization. The energy problem has become increasingly prominent, which requires to speeding up the development of wind energy industry. However, the existing wind speed forecasting using grey model is in- 96 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) eration is the key to master the change law. In order to explore the direct or indirect-cross influence of various environmental factors on PV generations, this paper collects the continuous generation data of Changzhou practical engineering cases and meteorological data in the first quarter of year 2014 and 2015, analyzes the effects of radiation, temperature, weather ty-pe, wind indices, air quality and other factors on system generation based on mathematical regression method, deduces the prediction formula of system generation, and verifies the prediction error. Studies have shown that various environmental factors have different effects on PV generation, and the photovoltaic power generation forecasting model based on regression analysis has good precision. accurate. Direct prediction of original wind speed sequence produces large error because of the randomness of wind power. To solve the above problems, a novel method for short term wind speed forecasting based on grey model is proposed in this paper. In order to reduce the error of short term wind speed forecasting, one of the most successful approaches is particle swarm optimization algorithm, which chooses the parameters of grey model to avoid the man-made blindness and enhances the efficiency and capability of forecasting. In the present paper, the wavelet decomposition and reconstruction are used to separate the high frequency signal and the low frequency signal. To verify its efficiency, this proposed method is applied to a wind farm’s wind speed forecasting in China. The result confirms that the performance of the method proposed in this paper is much more favorable in comparison with the original methods studied. TuD02.1 TuD01.10 Increasing Maximum Penetration of Distributed Generation by Voltage Regulation in Smart Distribution Grid pp. 1894-1898 Experimental Study on Biological Removal of Malodorous Gas Containing Hydrogen Sulfide pp. 1885-1888 Lu Bai State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst Shizhong Yan Shanxi Electric Power Survey and Design Insti TianzhengWan State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst Hua Yu State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Inst Zhipeng Wang State Grid Shanxi Electric Power Research Institute Shanshan Zhao TuD01.11 Hui Jie Hohai University Ni Ying Hohai University Xiaohui Song China Electric Power Research Institute, TuD02.2 Study on the Photovoltaic Power Generation Prediction Methods Based on Comprehensive Regression Analysis of Environmental Factors pp. 1889-1893 Hohai University China Electric Power Research Institute, With the increasing pressures on energy conservation and emission reduction, the urgent need arises to increase the maximum penetration of distributed generation (DG) without violating the voltage limits. This paper proposes a two-dimensional multi-resolution model of smart distribution grid (SDG) to analyse dynamic changes of DG and load at first. And then based on the model, an analytical methodology is presented to determine and increase the maximum DG penetration without voltage violations by voltage regulation. IEEE Comprehensive Test Feeder is used to prove the feasibility and validity of the proposed model and method. The simulation results show that voltage regulation is proved to be a good solution to increase the maximum penetration of DG, but a compromise must be made between higher penetrations of DG and fewer adjustments of voltage regulation devices. This will have major implications for the development of DG in SDG. Biomass power generation is the next essential part of green power generation, and in the future its proportion of the power industry will be bigger and bigger. Concomitant with the biomass power generation is producing a large amount of mainly hydrogen sulfide gas. Selecting hydrogen sulfide as a research object which is the main odor pollutant, the management of odor gas hydrogen sulfide was investigated by using the combined process Bio-Trickling reactor in this paper. Meanwhile, diverse factors which might influence the operation of bio-trickling reactor were inspected and the reacting mechanism of biological deodorization was analyzed as well. Technical route in this paper would provide new methods and thinking for management of pollution composed of multicomponent gases which is represented for odor waste gas. Similarly, research conclusions would offer basic data and reference for further application study. Jinrong Shen China Electric Power Research Instit, Xiaoli Meng Scenario Model and Algorithm for Distribution Network Reconfiguration with Wind Power Generators Embedded pp. 1899-1903 Yuqing He Jingjing Liu Chao Xu Accurate mastering the changes of photovoltaic power generation system is the base to achieve scientific scheduling of power stations. Conducting comprehensive analysis on the direct and indirect effects of environmental factors on system power gen- Lilin Mao Hunan Electric Power Corporation Econl & Techl Research Inst Hunan Electric Power Corporation Econ & Techl Research Inst Hunan Electric Power Corporation Econ & Tech Research Inst Hunan electric power transmission A novel scenario distribution network reconfiguration model 97 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) improve the wind power conversion efficiency. This paper establishes the mathematical models of Doubly Fed Induction Generator, wind turbine and rotor side converter, designs the MPPT control strategy controller and the rotor side converter controller, and uses the double steps hill climb searching algorithm to develop the simulation model of DFIG-based wind turbines based on MATLAB/SIMULINK platform. Simulation results show that double steps hill climb searching algorithm is a good method to achieve the maximum power point tracking of DFIG-based wind turbines. considering wind power generators (WPG) is presented in this paper. Scenario analysis is applied to describe the influences of random output from WPG through scenario selection and scenario voltage in this model. A dynamic reactive power compensation strategy is put forward to satisfy the passive reactive demand of WPG. An efficient hybrid algorithm combined physical optimization and genetic algorithm is presented for the scenario distribution network reconfiguration model. Through the no-unfeasible-coding rule in the initial population strategy, recombination strategy and eugenic strategy, individuals in the evolution always form feasible solutions. Physical optimization based on scenario voltage reduces the optimization time and the dependence of the population size. Test results verify the efficiency of the proposed model and algorithm. TuD02.5 Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine’s Converter Based with SOM Net pp. 1915-1918 TuD02.3 A Distributed Real Time Power Allocation Strategy for Dispersed Energy Storage Systems pp. 1904-1909 Jun Xie Nanjing University Lu Wang Nanjing University Kaixuan Chen Nanjing University ChongxinHuang Nanjing University Yaping Li China Electric Power Research Institute Ke Wang China Electric Power Research Institute Baohui Zhang Xi'an Jiaotong University TuD02.6 A Method to Improve the Efficiency of Asymmetric Parallel Converters for PV Generation pp. 1919-1923 TuD02.4 MPPT Control Strategy of DFIG-based Wind Turbines Using Double Steps Hill Climb Searching Algorithm pp. 1910-1914 Junhua Yan Tongji University Longhua Mu Tongji University This paper proposes an efficiency-based current distribution scheme to improve the overall efficiency of PV parallel converters with asymmetric circuit parameters. At the beginning, an efficiency optimization model with explicit objective function and restrictions is built based on the analysis of common efficiency model of DC/DC converters. The particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm with inertia weights is used to solve the efficiency optimization model, which determines the optimal phase current of parallel converters. Furthermore, a linear interpolation method is used to obtain continuous target value of optimal phase current. Case study demonstrates the validity of the proposed current distribution scheme for PV parallel converters with asymmetric circuit parameters. South China University of Technology South China University of Technology Recently DFIG-based wind turbines have become the dominant wind turbines for its mature control technology and high stability. And maximum power point tracking control strategy (MPPT) of DFIG-based wind turbines is very significant to November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Xi'an Jiaotong University Nowadays, most provinces of China like Xinjiang, Gansu, Ningxia, Inner Mongolia, Zhejiang, Heilongjiang, Jiangsu, Guangdong are constructing windfarms on a large scale. After all these windfarms are completed, the maintenance of them is very commercially valuable. Therefore, a fault diagnosis system of wind turbine's converter is studied in this paper on the basis of Xinjiang's windfarm. Firstly, the structure of wind turbine and converter are introduced, and the reasons of converter's faults are analysed in this paper. SOM net was used to diagnose wind turbine converter’s fault and it’s effect was verified by using data. This paper combine traditional fault diagnosis technology of power electronics' device with the fault diagnosis technology of xinjiang wind turbine's converter in a creative way, and it can have some active effect on using wind power largely. This paper presents a distributed consensus strategy that regulates the power outputs of dispersed energy storage systems (DESS) in power distribution network, which can be used to smooth the renewable power fluctuations. The algorithm is based on the consensus algorithm in graph theory and it satisfies both the smooth of the renewable power fluctuations and the equity allocation among DESS. The most distinct feature of the algorithm is that there is no “dispatch center” or “leader” to collect the global information in real-time power allocation process, each DESS obtains the global information and allocates its power outputs and realizes the target of smoothing the global renewable power fluctuations according to the local information interaction among DESS. Simulation on the IEEE 34-bus distribution system demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm. Xiaoyan Du Huajie Yin Xiaobo Zhang 98 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) more, the paper also investigates the influence on the power loss considering different positions the photovoltaic connected along the low-voltage feeder. From the perspective of decreasing the three-phase unbalance factor, some advice for the photovoltaic connected to the distribution networks is proposed at last. The simulation results show that the proposed advice can effectively reduce the losses caused by the three-phase unbalance. It also provides effective guidance and recommendations for the electricity company to carry out loss reduction work and to deal with large-scale single-phase photovoltaic connection in the future. TuD02.7 Fault Ride-Through Capability Enhancement by Adapative Voltage Support Control for Inverter Interfaced Distributed Generation pp. 1924-1928 Dehui Zeng South China University of Technology Jingmei Guo South China University of Technology Maosheng Ding Ningxia Electric Power Corporation State TuD02.9 Grid Corporation of China Duo Geng Ningxia Electric Power Corporation State Coordinated Optimal Operation of Hybrid Energy Storage in Power System Accommodated High Penetration of Wind Power pp. 1935-1941 Grid Corporation of China In order to meet the grid code of distributed generation and avoid intolerable over-voltage of dc-side on the occurrence of grid faults at the same time, an adaptive voltage support control strategy for low voltage ride-through (LVRT) of inverter interfaced distribution generation (IIDG) is proposed. Firstly, according to the request of German grid code, the basic control strategy and the fault current characteristic of IIDG are studied. Then, based on analyzing the effect of reactive power supplied by IIDG to the point of common coupling (PCC) voltage, this paper proposed an adaptive voltage support control strategy to enhance the fault ride-through capability of IIDG. Finally, simulation results demonstrate the proposed control strategy has advantage of improving to PCC voltage support capability and helping to ensure the safety of the IIDG equipment. Guangxi University Guangxi University Tangshan Cui Guangxi University Wanxia Bi Guangxi University Huazhong Univ of Science and Tech State Key Laboratory Suhua Lou Huazhong Univ of Science and Tech Xiangcheng Zhang Qinghai Province Key Laboratory Xu Tia Qinghai Province Electric Power Company Zuoxia Bai Qinghai Province Electric Power Company The variability and nondispatchable nature of wind power presents sustainable challenges for power system’s steady operation and security. In order to accommodate high penetration of wind power and increase the utilization rate of renewable resources, a model of hybrid energy storage system consisting of battery energy storage system and pumped storage power station is proposed in this paper, and a coordinated optimal operation method in the power system is presented. Based on the restriction of upper wind power fluctuation rate limit, a determination method of grid-connected wind farm power output is presented, which can improve the scheduling performance of wind power. The power difference between the original wind farm power output and grid-connected wind farm power output is mitigated by BESS due to its quick response capacity. Pumped storage power station is used for peak regulation in power system. The proposed model and operation method are verified on a modified RTS-96 system, the results are presented to prove the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed model and method. Power Loss Analysis for Low-voltage Distribution Networks with Single-Phase Connected Photovoltaic Generation pp. 1929-1934 Lei Ye State Key Laboratory Tianmeng Yang, Suhua Lou TuD02.8 Biyun Chen Tianmeng Yang Currently, the photovoltaic generation has been paid highly attention to and has obtained policy encouragement. With the increasing popularity of single-phase photovoltaic in low-voltage distribution networks, it may deteriorate the overall grid performance including power flows, losses and voltage profiles. On the other side, single-phase photovoltaic connected to the distribution networks will have some influence on the balance of three-phase that may bring additional losses under a three-phase unbalanced situation. In this paper, the concept of three-phase load current unbalance factor is introduced and additional losses in circuits and transformers induced by the three-phase unbalance are firstly analyzed. Secondly, the variation characteristics of the power loss and the three-phase unbalance are studied when single-phase photovoltaic is connected to different phases and different capacities. Further- TuD02.10 Multi-Types of Distributed Generators Planning Based on Free Search Algorithm pp. 1942-1947 Jin Wang Wei Dai Yuxuan Zhou 99 Changsha Univof Scie & Tech Changsha Univof Scie & Tech Changsha Univof Scie & Tech November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) Distributed generators (DG) brings about great environmental benefits which makes it worth researching. In order to optimize the grid-connected positions and capacities of various types of DG, a multi-objective model is established. The total generation cost of DG, the network loss and static voltage stability indices are synthetized in the model. Additionally, a kind of improved multi-objective free search (IMOFS) optimization method is proposed. This algorithm adaptively adjusts searching radius and step to improve searching efficiency. According to the period of evolution, the previous searching radius and step do not change much in searching for the overall situation, while they change relatively greatly in the later stage in local exploration by the algorithm. At the same time, in order to make the distribution of Pareto front more even, dynamic adaptive mesh strategy is adopted to maintain the non-dominated set, thus good candidate schemes are provided for terminal decision. TuD02.12 Study on Control Characteristic of Grid-connected Solar Photovoltaic Plant Based on Simulation pp. 1954-1958 China Electric Power Research Institute China Electric Power Research Institute Dajun Jiang China Electric Power Research Institute Dawei Zhao China Electric Power Research Institute Yanzhang Liu China Electric Power Research Institute China Electric Power Research Insti China Electric Power Research Insti Dongfang Wang State Grid Qinghai Electric PowerCompany Haining Zhang State Grid Qinghai Electric PowerCompany TuD02.13 Accurate wind turbine model is the basis of studying its dynamic physical process and performance characteristics. In order to resolve the difficulties in modeling direct-drive permanent magnet wind turbine (DD-PMWT) because of the absence of permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG) model in some existing power system analysis software, the method to interconversion between electrical excitation synchronous generator (EESG) and PMSG was presented as well as the parameter conversion formulas and procedure were provided on the basis of their mathematical model and equivalent circuit in this paper. In additon, the model of DD-PMWT was built in DIgSILENT PowerFactory by means of replacing PMSG with EESG. Finally, based on the typical test system provided by Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC), the dynamic characteristics of DD-PMWT were analyzed. The simulation results verified the validity of the proposed method and the rationality of the established DD-PMWT model. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Lei Zhang Along with the advancement of renewable energy development strategy, photovoltaic (PV) power technology has gained rapid progress in recent years. Due to the rapid growth of PV power penetration in power system, the research with PV power grid integration are drawing more and more attention, such as low voltage ride through (LVRT), automatic voltage control (AVC), voltage stability and so on. This paper investigates on voltage and reactive power control characteristic of grid-connected solar PV plant based on simulation. The voltage and reactive power control strategy uses the grid-connected inverters and static VAR compensation (SVC) device as flexible and controllable source of reactive power to regulate the voltage and reactive power of large-scale PV power plants. The PV inverters and SVC both have a variety of control mode generally, such as constant voltage control mode, constant reactive power control mode, constant power factor (PF) control mode and so on. The coordination control characteristic between PV inverter and SVC is analyzed in this paper. Through in-depth study of the characteristics of different combinations of control modes, the operating characteristics of PV power plants are summarized. The research results of this paper are helpful to the development of AVC system. Modeling and Implementation of Direct-drive Permanent Magnet Wind Turbine Based on Generator Parameter Conversion pp. 1948-1953 Dongping Hu China Electric Power Research Insti Dawei Zhao TuD02.11 Lei Zhang Yanzhang Liu The Impact of Dynamic Behaviors of Distributed Grid-connected Photovoltaic System on Distribution Network Transient Voltage Stability pp. 1959-1964 Liuhan Huang Shandong University Wen Zhang Shandong University Hao Yang Shandong University Due to the increasing capacity of grid-connected photovoltaic systems in distribution networks, its impact on the voltage security can’t be ignored. In this paper, based on the voltage stability criterion of maximum transmission power, and considering induction motor voltage response characteristic, the impact of dynamic behaviors of grid-connected photovoltaic systems on transient voltage stability is investigated. Three scenarios have been analyzed, respectively corresponding to three kinds of photovoltaic system’s dynamic behaviors: stopping operation after voltage sags, low-voltage ride-through capability and dynamic voltage support. In addition, P-V curve 100 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) is applied to do theoretical interpretation for the simulation results in the revised IEEE 33-bus distribution network, and it is testified that grid-connected photovoltaic systems equipped with low-voltage ride-through capability can remarkably improve distribution network transient voltage stability, and the effectiveness would be more prominent with the dynamic voltage support of photovoltaic systems. taking the integrated optimal of operating cost, voltage deviation and power loss as the target and adopting multi-state model to build a multi-objective model based on chance constrained programming. An adaptive reactive power control strategy is employed to solve the voltage regulation problem of grid-connected nodes. Moreover, non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II) based on elitist is proposed to solve multi-objective model and technique for order preference by similarity to an ideal solution (TOPSIS) based on entropy is adopted to choose the optimal solution from Pareto solution set. Finally, the simulation results on IEEE 33-bus distribution system demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. TuD02.14 Harmonic Current Suppression of Grid-connected PV Power Plant LCL Filter Based on PR Control Strategy pp. 1965-1969 Chao Xiong TuD02.16 Shenyang Univ of Tech Yun Teng Shenyang Univ of Tech Chunlai Li Shenyang Univ of Tech MPPT Control for Photovoltaic System Based on T-S Fuzzy Reasoning pp. 1976-1980 Qinghai Electric Power Research Inst Zhongjie Zhang State Grid Tongliao Power Supply Company Xin Yu State Grid Dandong Power Supply Company L.L.WANG North China Electric Power Univ The output characteristics of the photovoltaic cell are a nonlinear and easily affected by external environment. The maximum power point tracking (MPPT) control is an effective method to improve the conversion efficiency of the photovoltaic system. In order to solve the problems of conventional fuzzy control algorithm, a new control strategy based on T-S fuzzy reasoning is proposed. This algorithm can avoid the oscillation near the maximum power point and reduce the energy loss with good dynamic and static performance. The model of the photovoltaic system is established and simulated by Matlab/Simulink. The simulation results show the effectiveness of the proposed control algorithm. The repetitive control technique based on the internal model principle, can achieve low steady-state tracking error and total harmonic distortion in AC systems, so it is widely adopted in the inverter systems. The new PR current control strategy is developed and implemented to a grid-connected three-phase inverter with LC filter. The controller resulted in a low current total harmonics distortion (THD) of 3% to meet the grid requirement. Proportion-integral values above which can achieved output controller and proportion resonant controller are adopted to control the power adjustment and zero error control of harmonic restrain. The result of the simulation shows that the improved inverter control system can effectively control the grid current waveform which tends to sine wave. The detail design of the proposed controller is presented. TuD02.17 Method for Wind Farm Cluster Active Power Optimal Dispatch under Restricted Output Condition pp. 1981-1986 TuD02.15 Research of Optimal Hosting Capacity of Small Hydropower Considering Adaptive Reactive Power Control pp. 1970-1975 Di Li State Grid Henan Economic Research Inst Shiqian Wang State Grid Henan Economic Research Inst Wang Lei State Grid Henan Economic Research Inst Nannan Xing North China Electric Power Univ Chunzheng Tian State Grid Henan Economic Research Inst Zongqi Liu North China Electric Power Univ Hongqi Yang State Grid Henan Economic Research Inst Pengcheng Xu North China Electric Power Univ Guo Xu State Grid Nanyang Power Supply Company Daogui Shi North China Electric Power Univ Due to the inconsistent development of power grid and wind power farm, as well as insufficient power transmission capability, wind-abandon problem is becoming increasingly serious in China, and no effective solution can be found in a short time. With consideration of large scale wind farm construction in China, a method is proposed in this paper for wind farm cluster active power optimal dispatch under output restriction condition, which is based on the ultra-short-term wind power In order to promote the coordinated development of runoff small hydropower and the regional distribution network, this paper introduces a method for calculating the optimal hosting capacity of runoff small hydropower considering adaptive reactive power control. For the purpose of improve the security and economy of the operation of the distribution network, 101 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) forecasting. In this method, the active power maximization and the line loss minimization are assumed as the objective functions on the condition of output restriction, with power system security, output power of wind farm, frequent turn-on and turn-off of wind turbines, and the low forecasted power as the function constrains. In addition, the active power loss and short term active power forecasting error are also considered. A case study of a wind farm cluster located in the north-west of China has verified the effectiveness and feasibility of this method. the decoupling between the output power and the frequency. Moreover, DFIGs also lack power reserve margin because of the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) operation. In this paper, a virtual inertial control strategy of the DFIG based wind turbines called supplementary control loop for inertial response is investigated. When the system frequency is changing severely, the output power of DFIG should respond to it rapidly through the virtual inertial controller at the same time. The rotor speeds of wind turbines can also be adjusted into this procedure. The inertial control methods proposed in this paper can supply controllable virtual inertia of DFIGs to the power system so that the system frequency stability can be strengthened through inertial control of wind turbines on the basis of damping torque analysis. TuD02.18 Dynamic Power Flow Calculation Method of Power System with Wind Power pp. 1987-1991 TuD02.20 Ruohan Wang Shandong University Hengxu Zhang Shandong University Analysis of Distributed Generation Effect on System Losses in Distribution Network pp. 1998-2002 Changgang Li Shandong University Yifei Guo Shandong Univ Houlei Gao Shandong Univ Jian Wang Shandong Univ Changhui Ma Shandong Electric Research Inst High penetration of renewable energy nowadays makes it necessary to take wind power plants and solar power plants into consideration when calculating dynamic power flow. The paper mainly focuses on the approach to deal with wind turbine in power flow calculation and the power-frequency characteristics of it after attaching it to power system. Firstly, the concept and major steps of dynamic power flow calculation are illustrated. The whole procedure is programmed in Fortran language and ready for case study. By ignoring some negligible variables, the simplified model of wind turbine which considers it as PQ bus is put forward. This model brings convenience to dynamic power flow calculation with wind power and its rationality can be guaranteed to a certain degree. With this model, the power-frequency relationship of wind turbine is obtained through mathematical deduction and the complex static frequency modulation coefficient of wind farm is calculated in order to execute dynamic power flow calculation. In a specific case, IEEE 30-bus system is modified to be used to test the presented algorithm. Zhigang Wu State Grid Shandong Electrical Power Comp Chunpeng Han State Grid Shandong Electrical Power Comp Distributed generation (DG) connected to the distribution network changes the network power flows, voltage profiles and losses. In this paper ,the effects of DG on distribution network active losses are studied in three factors including the DG penetration, location and dispersion levels. The loss sensitivity factor (LSF) is adopted to analyze the effect of location on active losses. In multi-DG cases, a new approach is presented to analyze the effects caused by different DG dispersion levels. It is the combination of enumeration method and Monte-Carlo method. And in order to give a quantitative conclusion, plenty of simulations are tested on the IEEE 33-bus test system. The simulation results provide suggestions and references for DG optimization allocation. TuD02.21 Probabilistic Load Flow Analysis Considering the Correlation for Microgrid with Wind and Photovoltaic System pp. 2003-2008 TuD02.19 Damping Torque Analysis of Virtual Inertia Control for DFIG-Based Wind Turbines pp. 1992-1997 C. Lv Queen’s University Shanye Tian Shandong University T. Littler Queen’s University Hui Wang Shandong University W. Du North China Electric Power Univ Xiaohan Xie The increasing penetration of large-scale wind generation in power systems will challenge the power system inertia due to the reason that the converter based variable speed wind turbines have no contribution to the system inertia. Traditionally, a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG)-based wind power plant naturally does not provide frequency response because of November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Shandong University With the distributed energy system widely used, quite a few microsources have been connected to the microgrid recently. Due to the randomness, uncertainty and correlation of microsources, the models of typical power flow calculation are not suitable for the microgrid. A probabilistic load flow analy- 102 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) sis is proposed based on third-order polynomial normal transformation(TPNT) combining three-point estimate method in this paper. And the probabilistic models of microsources, such as wind energy system, PV/wind hybrid system, are established according to the control characteristics and various random factors. The correlation of input random variables in the same area is also taken into consideration. In order to deal with input random variables, the TPNT is used to transform correlated non-normal random variables into uncorrelated normal random variables. Then the independent input variables can be estimated by three-point estimate method and calculated by deterministic power flow algorithm. The proposed method is tested in a typical microgrid system containing multi-type microsources. By comparing three different cases, the simulation results show that the proposed method is generic, effective and correct. Besides, the microgrid system consisting of multi-type microsources can obtain the optimal performance characteristics. with DC series-parallel collection systems. Due to wake effect considerations, the power generated among the series connected wind turbines does not remain the same and the series connection causes the output voltages of the turbines to be dis-tributed in proportion to their power output. Power curtailment is required in order to prevent the turbines being subjected to over-voltage and under-voltage conditions. In this paper, a voltage adjustment procedure is proposed to eliminate over-voltage and under-voltage of wind turbines. Based on the voltage adjustment procedure and the power generation model of wind turbines, the energy curtailment of a wind farm is analyzed with the consideration of wake effect due to series connection. A case study on several DC series-parallel collection configurations is presented to analyze the energy curtailment of wind farms using the voltage adjustment procedure. TuD02.22 A Novel Photovoltaic MPPT Controller Based on Fuzzy Sliding pp. 2009-2013 Fu Shen Hongyu Li Peng Xue Weiguang Sun Youjun Ren Changqing Feng TuD02.24 Calculation Method and Analysis of Power Flow for Distribution Network With Distributed Generation pp. 2020-2024 Hohai Univ Hohai Univ Hohai Univ Hohai Univ Hohai Univ Hohai Univ With different load and weather conditions, the output characteristics of photovoltaic (PV) cells are various. There is no Chao Cheng Shandong University Houlei Gao Shandong University Yanqiu An Shandong University Xueqi Cheng precise mathematical model of PV cells. To make full use of PV cells, the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) is a necessary unit in PV system. This paper proposes a novel MPPT controller based on the combination of fuzzy control method and sliding control method. Compared only with fuzzy controller and sliding controller, the proposed controller has more advantages, such as fast response speed, strong anti-interference, strong robustness, and a higher stability, etc. The advantages of the proposed controller have been verified Weifang Power Supply Company State Grid Shandong Electrical Power Company Jingjing Yang Weifang Power Supply Company State Grid Shandong Electrical Power Company A simplified power flow calculation method for distribution network with distributed generation is proposed in this paper. Based on loop analysis method, this proposed calculation method can theoretically transform the complex power flow equations into linear algebraic equations. In addition, node voltages of PV-type and PQ(V)-type distributed generation are calculated by calculating and correcting their reactive power generated by them, and finally branch loss is compensated to by simulation in the Matlab. TuD02.23 make the calculation method more accurate. Case study results show that this method demonstrates shorter computing time and good accuracy,which can meet the engineering demand of fast power flow analysis and real-time scheduling. Simultaneously, different node types of distributed generation are inserted in different positions of distribution network and their voltage profiles expose the effect of locations and node types of distributed generation on power of distribution network. Energy Curtailment Analysis of Offshore Wind Farms with DC Series-parallel Collection Systems pp. 2014-2019 Jingli Guo Xi’an Jiaotong University Xiuli Wang Xi’an Jiaotong University Zece Zhang Xi’an Jiaotong University Hui Li Beijing Information Scie & Tech Univ Padmavathi Lakshmanan Cardiff University Jun Liang Cardiff University Voltage balancing among the series connected wind turbines is one of the main technical challenges of offshore wind farms 103 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuD02.25 TuD02.27 Research on the LVRT of DFIG’s Wind Power Generation with Experimental Demonstration System pp. 2025-2030 Static Security Risk Evaluation Of The Power System With Wind Speed Correlation pp. 2035-2040 Jun Zhuan China Electric Power Research Institute Liangzhong Yao China Electric Power Research Institute Bo Yang China Electric Power Research Institute Yuanzhi Cao China Electric Power Research Institute Hao Luo Li Zhang Junyong Liu Sichuan University Sichuan University Because of the close geographic location of wind farms in the same power grid, the correlation of their wind speeds and the correlation of the generated wind power are obvious. This study proposes a novel method which provides the static security risk evaluation of the power system with wind speed correlation. In this study, Ranked Set Sampling Monte Carlo simulation (RSMCS) which is based on the Nataf transformation and Ranked Set Sampling is involved for the investigation of the impacts of wind speed correlation on probabilistic load flow. The proposed method provides a low computation intensive mechanism to generate a high accurate solution with a relative easy implementation. The proposed method is validated with a modified IEEE-30 bus system which consists of four wind farms. The static security risk of current operating state with wind speed correlation is also analyzed in validation work. Nanjing Institute of Technology This paper introduces the verification experiment on the LVRT capability of wind power generation system in laboratory environment. A new LVRT system is designed in which contains chopper and crowbar subsystem, by adopting the IGBTbased fast switches instead of half-controlled thyristor, to realize the wind power generation system ride through when voltage dip happens. Based on the DSP & CPLD control system platform, a novel control strategy is proposed to achieve the fast detection of voltage dip, efficient separation of positive and negative voltage component, soft excitation of DFIG’s rotor. A 30kW prototype DFIG system is built to verify the topology design and corresponding control strategy of LVRT system, for demonstration of realization and stability. TuD02.28 The Impact of Distributed Generation and Its Parallel Operation on Distribution Power Grid pp. 2041-2045 TuD02.26 Research Status of Electricity-stealing Identification Technology for Distributed PV pp. 2031-2034 Xiaodong Yuan Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst. Kai Zhang Qinghuangdao Power Supply Company Kexue Liu Qinghuangdao Power Supply Company Naipeng Yao Qinghuangdao Power Supply Company Yuhong Jia Qinghuangdao Power Supply Company Wenjun Li Qinghuangdao Power Supply Company Lihan Qin Qinghuangdao Power Supply Company Mingming Shi Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst. Zhengyang Sun The trend of distributed power application is more and more obvious Aiming at the problem of the lack of effective argument and the corresponding technical analysis in access system. Focus on all kinds of distributed power supply access after the results of the influence of the power grid operation. First of all, from the operation mode and the way of interface for distributed power supply is analyzed, so that the classification to study the effect of different results is easy. Then, analyse the connection way of the distributed power grid, build a typical distribution network model, as the basis of analysis of the distributed power access. Finally, by the theoretical calculation of the access model, analyse the effect on the steady state characteristics and power quality, thus providing theoretical basis for distribution network planning technology principle of modified. Nanjing University of Science and Tech. With the development of photovoltaic (PV) industry, some methods of defrauding PV subsidies appeared because of the way it generates power and the government subsidy policy. These behaviors of defrauding PV subsidies are called electricity stealing of PV. This paper summarizes the research status of the traditional anti-electricity stealing technology and electricity stealing of PV. Four typical methods of photovoltaic electricity stealing are introduced in principle and analyzed on economic costs from aspects of cost of electricity stealing, quantity of electricity stealing, earning of electricity stealing and time of recovering cost. Finally, on the basis of related research, several ideas to distinguish electricity stealing of PV are proposed in this paper. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China 104 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuD02.29 TuD02.31 The Comprehensive Evaluation of Impact of Distributed PV on Distribution Network pp. 2046-2050 A Joint Probabilistic Analytical Model with Consideration of Wind Power and Load Uncertainties Xinghua Dong Yunhui Gao Tianshun Ma Jinlong Liu Rongsheng Xia Yichen Huang Qinhuangdao power supply Comp. Qinhuangdao power supply Comp. Qinhuangdao power supply Comp. Qinhuangdao power supply Comp. Qinhuangdao power supply Comp. Jibei Economic and Tech. Inst. Beijing pp. 2056-2062 This paper starts with the impacts of distributed PV on distribution network in power quality, supply quality, network losses and security, establishes the comprehensive evaluation model. According to different indicators data, deal with the high-priority indicators, low-priority indicators and neutral indicators. Then, analyzing the weight factor of different indicators by using the combination of analytic hierarchy process(AHP) and entropy method. At last, take a distribution network of a certain area for example, testing the feasibility and practicability of the method. pp. 2051-2055 Tsinghua University Yajie Liu Tsinghua University Jinqing Luo Tsinghua University China Electric Power Research Inst.Beijing Center for Power Grid Technology Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Institute Nanjing Dan Liu TuD02.32 Center for Power Grid Technology Jiangsu Comprehensive Evaluation of Impacts of Distributed Generation on Voltage and Line Loss in Distribution Network Electric Power Company Research Institute Nanjing Xiaodong Yuan Center for Power Grid Technology Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Institute Nanjing Ping Ge Libao Shi A joint probabilistic analytical model for modeling wind farm power output and load demand considering uncertainties is proposed in this paper. Compared with traditional numerical solutions, the proposed model can improve computational efficiency remarkably while keeping the accuracy. Firstly, based on a series of typical wind speed distributions whilst considering the wake effect of wind farm, the probabilistic analytical models of wind farm power output via introducing the concept of impulse function in the signal system are proposed. In order to better reflect the effects of wind power and load uncertainties simultaneously, in accordance with the convolution method described in probability theory and combined with the normal probability density function (PDF) of load, a joint probabilistic analytical model for describing the uncertainties of wind farm power output and load is deduced. Finally, the comparisons with numerical simulation method are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness and validity of the proposed model. Solutions for Peak Regulation of Jiangsu Power Grid Incorporated with Large-scale Renewable Power and Its Comparison with Germany Yi Liu Tsinghua University Liangzhong Yao TuD02.30 Qiang Li Ren Wang pp. 2063-2067 Nanjing College of Information Technology Jiangsu Yangzhou Power Supply Company Up to June 2015, the total wind and PV capacity of Jiangsu has amounted to 6600 megawatts, which is expected to increase to 20000 megawatts in 2020. Due to the intermittency and randomness of renewable power, the reserve capacity and regulation ability of conventional generator appear to be insuffic-ient for Jiangsu power grid with the increasing penetration level of renewable power. For the purpose of seeking for the appropri-ate solutions for peak regulation, methods for enhancing the regulation ability of Jiangsu power grid including inter-province tie-line control, constructing rapid regulation power sources, exploiting the existing conventional generators potential and optimizing unit commitment by wind power forecast are investi-gated. Meanwhile, the comparison of renewable power grid-integration of Jiangsu and Germany are analyzed, and some experiences in the peak regulation of Germany are presented, which may be useful for Jiangsu power grid. Jian Wang Shandong University Houlei Gao Shandong University Guibin Zou Shandong University Zhigang Wu State Grid Shandong Electrical Power Company With the high penetration of distributed generation (DG), the power quality, protection and control of the distribution networks will be affected. This paper mainly studies the impacts of DG on both voltage and line loss. To quantitatively evaluate the impacts, a set of quantification indices are adopted. To take comprehensive evaluation of the impacts, a principal component analysis (PCA) method is proposed in this paper. Considering different capacities and different locations, the evaluation indices are calculated based on IEEE 33-bus test system. The results are presented and analyzed to illustrate the usefulness of proposed method and indices. 105 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) tinuous quantity with the double-optimization strategy; Introduced the fuzzy satisfaction-maximizing method to reaching a decision for Pareto solution and also nested into each dynamic solution; Through simulation for 10 units of wind power, the result show that this method is an effective way to optimize the Multi-objective unit commitment modeling in wind power integrated system with Mixed-integer variable. TuD02.33 Credible Capacity of Wind/PV Hybrid System Research Based on Hybrid Algorithm pp. 2068-2073 Pei Zhang Shandong University Weixing Zhang Shandong University Chunjuan Jia Shandong University Xiao Yang Shandong University Fengjun Yi Shandong University TuD02.35 Stochastic Optimal Power Flow with Wind Generator Based on Stochastic Response Surface Method (SRSM) and Interior Point Methods pp. 2079-2083 In view of the unstable reliability of the power grid due to the integration of various intermittent power sources with power grid, this paper intends to discuss the credible capacity of the wind/PV hybrid system to research the complementarity of the wind power and PV power. Based on sequential Monte Carlo simulation, this paper develops the reliability evaluation models of wind and PV power and analyzes the complementarity and probability of output power of them. To tackle the misconver-gence with a high calculation accuracy in the secant method and the slow iterative speed in the dichotomy, this paper presents a hybrid algorithm to calculate the credible capacity. By combin-ing the secant method with fast iterative speed and the dichoto-my with no misconvergence, this algorithm avoids the miscon-vergence when the fast iterative speed and realizes the high cal-culation accuracy. Modified IEEE RTS-79 system is utilized to verify the validity of the proposed hybrid algorithm. The result shows that the hybrid algorithm has a fast iterative speed and has no misconvergence. Moreover, this paper analyzes the ef-fects of the proportional ratio between installed capacity of wind power generators and that of PV arrays, the penetration of the renewable energy generations and the reliability level of the original system without renewable energy on the credible capac-ity of hybrid system. Ying Tan Rui Ma Changsha University of Science and Technology Changsha University of Science and Technology In order to describe the randomness of the wind speed, analyze its influence to the optimal power flow with wind power generator,and reduce simulation time, this paper proposes a calculation method for stochastic optimal power flow with wind generator based on stochastic response surface method (SRSM) and interior point methods. The stochastic response surface method is applied to transform the problem of probability evaluations of the output power to the deterministic problem and shorten calculation time. The interior point method is used to deal with the randomness of wind speed and solve the deterministic problem stochastic optimal power flow with wind generator. Compared with the Monte Carlo method on IEEE 14-bus systems, the stochastic response surface method requires smaller amount of computation and achieves higher accuracy. The results also indicate that the proposed compound method are more practical and effective in reducing simulation time. TuD02.36 TuD02.34 Research on Discrete PR Controller with LCL Filter Based on DRNN for Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter pp. 2084-2088 Multi-objective Dynamic Unit Commitment Optimization for Energy-saving and Emission Reduction with Wind Power pp. 2074-2078 Jin Wang Yuxuan Zhou Zhenxiong Zhou Shuo Shi Changsha University of Science&Technology Changsha University of Science & Technology The single-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverter with LCL filter is studied as the research object in this paper. Based on the nonlinear and time-varying characteristics of photovoltaic grid-connected system, the double closed-loop control strategy of PR control is presented. For the PR controller of fixed parameters is unable to adapt to changes in power network parameters, and the system control performance cannot be optimized. A PR control method based on DRNN of dynamic self-tuning is presented and its control algorithm is given. DRNN is based on the two-step RPE algorithm, which has a faster convergence rate than the BP algorithm using the first-order gradient algorithm. The simulation results prove that this control strategy has a good quality of the output cur- As a clean energy, wind power is massively utilized in net recent years, which significantly reduced the pollution emission created from unit. This article referred to the concept of energy-saving and emission reducing; built a multiple objective function with represent of the emission of CO2& SO2,the coal-fired from units and the lowest unit fees of commitment; Proposed a algorithm to improving NSGA-Ⅱ(Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm-II) for the dynamic characteristics, consider of some constraint conditions such as the shortest operation and fault time and climbing etc.; Optimized and commitment discrete magnitude and Load distribution con- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Beihua University Beihua University 106 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) rent and fast performance in dynamic response, the resonance of grid current is effectively avoided and high in-grid power factor is achieved. isolated microgrid in north China is used for verification. The results indicate that the above proposed energy scheduling strategy could play the complementary advantages of two storage components more adequately. And comparisons between QPSO and traditional particle swarm optimization (PSO) are made by analyzing the configuration results, which proves that using QPSO algorithm can find the optimal solution more quickly and save the daily cost of HESS. TuD03.1 A Novel Control Strategy of Super Capacitor-Battery Energy Storage System pp. 2089-2093 Yuqiang Ou Jiangmen Power Supply Company Jianzhong Wen Jiangmen Power Supply Company Liguo Wang Jiangmen Power Supply Company TuD03.3 Zhiwen Yu Shanghai Jiaotong University Economic Analysis of Applying the Used EV Battery to Commercial Electricity Customer pp. 2100-2103 Jiantao Huang Shanghai Jiaotong University Kuan Zheng State Grid Energy Research Institute Zhanghua Zheng State Grid Energy Research Institute Qian Ai Liukai Fen Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai Holley Software System Storages are usually used to absorb the fluctuation power produced by distributed generators such as wind turbine (WT) and photovoltaic (PV). The SC-battery hybrid energy storage system (HESS) has attracted more and more attention because of the advantages of high power density and high energy density. In this paper, a typical ac power grid is presented which consists of WT, PV, super capacitor (SC) and battery. A novel cooperative control strategy for HESS is proposed to control the SC to rapidly absorb or release power and the battery to exchange slowly fluctuating power. It is proved that the proposed control strategy can prevent the SC from saturation and low voltage, which can make full use of SC and battery. Finally, a wind-solar power example is proposed to verify the effectiveness and correctness of the control strategy. The results show that the control strategy can make SC and battery run normally and restrain the fluctuation power. State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Jie Ren State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Electric vehicles have indeed contributed a lot to the energy savings and environment protections, while it leaves a worldwide problem that is how to recycle its core component- the battery. A specific economic analysis of applying the used EV battery to the commercial electricity customers is carried out based on actual data of the real-time load curves and the electricity prices collected from the State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company. Obtained results show that the secondary utilization of the EV battery as a storage technology is justified in load shifting application and its cost effectiveness is decided mainly by the volatility of electricity prices. Furthermore is reasonable for commercial application and the benefits can be improved with capital cost being lower and lifetime being longer. In addition, its benefits include not only the monetary savings from the load shifting, but also the improvement of network congestion by reducing the peak demand. Subsidy to storage technology market is also reasonable if savings from network congestion improvement is significant. TuD03.2 Optimal Capacity Configuration of Hybrid Energy Storage for an Isolated Microgrid Based on QPSO Algorithm pp. 2094-2099 Xiaohan Xie Hui Wang Shanye Tian Yaodong Liu Haiyun Jiang TuD03.4 A Novel Energy Storage for PFC by EV Motor/Generator pp. 2104-2107 Shandong University Shandong University Shandong University Shandong Jianzhu University The capacity configuration of energy storage de-vices not only affects the power supply reliability of an isolated microgrid, but also directly relates to its economic operation. In allusion to an isolated microgrid which includes typical loads, a hybrid energy storage system (HESS) and renewable energy resources, a new quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization (QPSO) is proposed in this paper to optimize the capacity of the HESS. A rational energy scheduling strategy is also put forward. Additionally, a mathematical model is established which the lowest daily cost of HESS is taken as the objective. A case of an Hui Wang Shandong University Chenghui Zhang Shandong University Wenlong Qi University of Hong Kong Khai D. T. Ngo Virginia Tech Blacksburg, UA The size of dc-bus capacitor is the key contributor for the volumes of PFC and battery charger, whose important characteristics is the 2nd order low-frequency ripple power on the DC bus. The motor in an electric vehicle can be used to store the ripple power, thus significantly reducing the size of the dc-bus capacitor. In this pa- 107 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) per, a novel principle for Energy Storage in PFC by EV motor/generator is proposed. A digital controller is used to regulate the converter by using PWM, resulting in small volume, low noise and high power density. The size of the dc-bus capacitor is reduced 10 times. K.J. Tseng An Online Calibration Algorithm of SOC for LiFePO4 Battery by using Characteristic Curve pp. 2108-2112 China Electric Power Research Institute Jizhong Chen China Electric Power Research Institute Juan Hu China Electric Power Research Institute Huanling Wang China Electric Power Research Institute Shouping Xu China Electric Power Research Institute C.C. Sun Hohai University Modeling and Simulation of Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) Used in Power System pp. 2120-2125 Tian Xia China Electric Power Research Institute Muyi Li China Electric Power Research Institute Peng Zi China Electric Power Research Institute Liting Tian China Electric Power Research Institute Xiaohui Qin China Electric Power Research Institute Ning An China Electric Power Research Institute For reflecting grid connected operation control strategies, modeling of Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) was studied. The BESS models include two parts according to the infection to control results of State of Charge (SOC) of batteries. One is the electromechanical transient model, and the other is the long-term dynamic model. The convertor section of the models consider power control segment in normal operating mode, and fault crossing and protection segment reflecting output external characteristics in abnormal operating mode. In the capacity limit aspect, the actual voltage-SOC curve of battery is introduced in the models. Meanwhile, the charging and discharging character-istics can be simulated accurately. The validity of the proposed models is proved according to calculation results after taking BESS models into single generator system for simulation. In this paper, BESS models are established from the perspective of power grid and to realize the target of grid connected control, the models have generality, and they are suitable for electromecha-nical transient and long-term dynamic simulation. Therefore, the problems of present BESS models, that is being complex, reflect-ing charging / discharging characteristics of different batteries but no grid connected characteristics, and being not suitable for engineering application, can be solved. TuD03.6 Design of Energy Storage Scheme for the Smoothing and Dispatch Planning of Large-Scale W ind Power Generation pp. 2113-2119 Nanyang Technological University Singapore November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Hohai University TuD03.7 Battery Monitoring is very important for most of the electric vehicle(EV) and battery energy storage system(BESS)since the safety, operation and even the life of the passenger/operator depends on the battery system. Checking and controlling the status of battery within their specified safe operating conditions is exactly the major function of battery management system (BMS). The state of charge (SOC) is a critical parameter of a Li-ion battery, an accurate on-line estimation of the SOC is important for forecasting the EV driving range and BESS power dispatching. A widely used method to estimate SOC is based on coulomb counting, due to the uncertainty, including unit-to-unit variation, measurement noise, operational uncertainties, and model inaccuracy, it’s difficult to estimate the SOC by using coulomb counting, an online inference of open-circuit voltage (OCV) is used to calibrate the SOC, however, a relatively flat OCV curve of LiFePO4 will lead to the error of SOC is large. In this paper, an algorithm using the derivation curve (dV/dQ vs Q) to calibrate the SOC on-line is bring out. The SOC estimation has been implemented using coulomb counting and derivation curve methods thereby eliminating the limitation of the stand-alone coulomb counting method. Finally, by utilizing the actual operation data, experiments and numerical table were conducted, show that this SOC calibrate algorithm based on characteristic curve has better robust performance of the practical application of LiFePO4 battery energy storage system. M.T. Li, S.S Y. Yuan The paper examines the use of energy storage system to smoothen the output power from wind farms, and to make dispatch planning from the wind power generators possible. Firstly wind power is segregated into components through the use of filters designed from the application of empirical mode decomposition technique. Buffering of the high- and mid-frequency components of the wind power is then effected through the use of battery-supercapacitor banks, while the low-frequency components of the wind power are used in conjunction with a pumped-hydroelectric storage system to realize short-term dispatch planning. The proposed method is illustrated using data obtained from an existing wind farm. TuD03.5 Chaoyong Hou Nanyang Technological University Singapore 108 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuD03.8 TuD04.2 Compound Energy Storage Control of W ind Power Base on Wavelet Decomposition A Novel Control Method for Islanding Mode Microgrid with Unbalanced Load pp. 2126-2129 pp. 2134-2138 Huanhuan Jia Inner Mongolia University Tianyi Ma Beijing Institute of Graphic Communication Zhiyuan Qi Inner Mongolia University Guangyao Cheng Zhifeng Li Inner Mongolia University Beijing Institute of Graphic Communication Single-phase load in microgrid brings about negative sequence voltage and current, deteriorating the stability of microgrid system. The difference of microsource(MS) parameters influences the sharing negative current and reduces the reliability of MS. Negative sequence voltage reduces power quality and stability of microgrid. In this paper, a comprehensive control method is proposed to improve the power stability of unbalanced load microgrid. The adjustable negative sequence virtual impedance is included in the method, which is regulated by the negative current amplitude of MS. Through the design of adjustable negative sequence virtual impedance, the accurate negative current sharing is realized under islanding mode. The effect of negative sequence virtual impedance character on unbalanced voltage factor of Point of Common Coupling (PCC) is also analyzed. In order to reduce PCC unbalanced voltage factor, a kind of secondary voltage compensation method is proposed in this paper. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of the proposed methods. A compound energy storage system in which lead acid battery combines with super capacitor is used to balance the fluctuation of wind power in this paper. A wavelet decomposition method is put forward to extract control signal that contains slowly variable low frequency signal and fluctuant high frequency signal. The slowly variable signal is applied to control the charge or discharge of the battery. The fluctuant signal is applied to control the super capacitor to absorb rapidly changing energy. A control way that voltage loop combines with current loop is used to keep the DC bus voltage steady. A simulation study based on MATLAB is presented to verify the correctness of proposed control strategy. Simulation results show that the battery can be charged steadily and discharged reasonably. In addition, the super capacitor can extract rapidly fluctuant wind energy, and the DC bus voltage of wind power system can be keep in steady at different wind speed and loads. Therefore, the proposed compound energy storage control method can satisfy the energy balance requirement in wind power system. TuD04.3 Based on Hybrid Algorithm of Micro-grid Islanding Detection TuD04.1 A Novel DG Integration and Coordination Control Method for Hybrid Microgrids pp. 2139-2143 Chao Xiong pp. 2130-2133 Biyun Chen Guangxi University Zhiyue Mo Guangxi University Shenyang University of Technology Yun Teng Shenyang University of Technology Chunlai Li Shenyang University of Technology Qinghai Electric Power Research Institute Xin Lia This paper presents a research on the integration and coordination control of distributed generation (DG) in a hybrid microgrid (MG). This approach integrates DGs by the direct current (DC) power lines added to the local power distribution system, while the alternating current (AC) power lines take charge of providing the conversional power energy for the local loads, and an energy conversion station is designed to mix energy from the DC generation line with energy from the utility grid. The voltage stability logic controller makes it easier and more convenient for the coordinated control between the DGs and the utility grid, as well as avoids coping with AC integration problems, AC stability and line synchronization for instance. Matlab/Simulink simulation tool was used to show the robust operation performance and to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method above. Shenyang University of Technology Qinghai Electric Power Research Institute Zhongjie Zhang State Grid Tongliao Power Supply Company Xin Yu State Grid Dandong Power Supply Company Micro-grids are being developed as a building block for future smart grid system. Islanding detection is a great challenge in connecting distributed generation (DG) in electrical power systems. Islanding detection methods are categorized into three groups, i.e., communication based methods, active, and passive methods. Communication based methods are established upon communication between utilities and DGs and have the inconvenience of being expensive and are limited in use. Active methods perturb the system with a disturbance and the system response to the disturbance is analyzed. This paper proposes a hybrid islanding detection method which uses voltage unbalance (VU) and high-frequency (HF) impedance. The proposed 109 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) method merges the advantages of both active and passive techniques. In addition, since the active method used in this paper does not change any of the system variables as a disturbance, it will not lead to any instability. TuD04.6 IEC 61850 Based Testbed for Micro-grid Operation, Control and Protection pp. 2154-2159 TuD04.4 Wei Deng Chinese Academy of Sciences Evaluation of the Standardization Needs of Wei Pei Chinese Academy of Sciences Microgrids Technology Ziqi Shen Chinese Academy of Sciences Zhenxing Zhao Chinese Academy of Sciences pp. 2144-2148 Hui Yu Wenpeng Luan Wanxing Sheng Test of system operation, control and protection is becoming an China Electric Power Research Institute important part of the micro-grid technology. This paper presents a testbed for operation, control and protection of micro-grid based on IEC 61850 with RT-LAB. A hierarchical system architecture for testbed including a system level, a bay equipment level, and a power device level is presented, and the design for testbed is proposed in detail. Then, experiments are performed based on the proposed testbed to verify its validity. China Electric Power Research Institute China Electric Power Research Institute Haitao Liu China Electric Power Research Institute Wenyuan Ma China Electric Power Research Institute Microgrid has played a crucial role in solving problems caused by integration of distributed generation and therefore becomes an effective and efficient means for promoting renewable energy utilization and improving power supply reliability. This paper summarizes the key technologies and standardization needs for microgrid development and applications, based on the market needs and industry status. Some key features of a microgrid that distinguish it from traditional power grid and smart grid are described. After review of the relevant activities currently undergoing in IEEE and IEC, recommendations for microgrid standardization based on the existing work are proposed. TuD04.7 The Improved Control Strategy of Inverters Output Power Equipartition in Micro Grid pp. 2160-2165 TuD04.5 Research on Autonomous Control Strategy for DC Microgrid PLA University of Science&Technology Pengfei Hou PLA University of Science&Technology Ye Xu PLA University of Science&Technology Jianke Li PLA University of Science&Technology Jun Yan Jianhui Su Hefei University of Technology Haining Wang Hefei University of Technology Yong Shi Hefei University of Technology based on the droop control method are analyzed, and a measurement method of micro grid line impedance based on clock synchronization and Micro Grid Central Controller-(MGCC) coordinated control is presented. Secondly the output power ability of inverters, the active and reactive power decoupling ability, the system dynamic property and stability are served as the conditions of virtual impedance designed, therefore the optimal design method of virtual impedance values is proposed. PLA University of Science&Technology The DC microgrid has the advantages of simpler control, higher power conversion efficiency and lower cost compared with AC micro grid, which is the future development direction of smart grid. The method of autonomous control requires no communication bus, it can improve reliability of the system and reduce the cost of the system. Therefore, this paper studies the key control problems of the autonomous control system of the non-communication bus. In this paper, the design method of DC microgrid autonomous control system is studied and improved, several working modes are defined, with case studies in a typical DC microgrid system, the effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by Matlab / Simulink. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Hefei University of Technology The output power of inverters should be precise equipartition in micro grid ,because that is the basic conditions that the micro grid system works stably for a long time. This paper proposes a improved control strategy of inverters output power equipartition in micro grid based on virtual impedance method. Firstly, the output power equipartition conditions of inverters pp. 2149-2153 Jinquan Wang Wenjin Wu The system simulation model was set up in MATLAB, and the simulation experiment results show that the proposed method has the effectiveness and practicability. 110 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) limit the reactive power sharing errors and improve the power quality, which can be applied in complex microgrid configurations. Finally, the performance of the proposed control strategy is verified by digital time-domain simulation in PSCAD/EMTDC software. TuD04.8 The Study of Power Electronic Transformer on Power Flow Control and Voltage Regulation in DC Micro-grid TuD04.10 pp. 2166-2172 Ke Zhou Guangxi Grid Co., Ltd Qingren Jin Guangxi Grid Co., Ltd Zheng Lan Hunan University Chunming Tu Hunan University Ming Guo Guangxi Grid Co., Ltd Guangshi Liu Guangxi Grid Co., Ltd Flywheel Energy Storage System Based on DC/DC Converter with Integrated Magnetic Structure pp. 2179-2184 Xuhong Wang Dan Li Changsha university science and technology Changsha university science and technology The AC and DC distribution grids between different voltage levels coexist in smart grids, and a reliable connector was needed between them. Power Electronic Transformer (PET) was suitable for being used as public interface to control power flowing between different electricity networks and regulated DC bus voltage, because of its abundant functions and electrical interfaces. In order to take advantage of PET served as a power balance junction, an improved droop control method for DC micro-grid was proposed. Power can flow bi-directionally between DC micro-grid and AC grids by using this method. Then the power distribution was achieved in DC micro-grid and the stability of the DC bus voltage was enhanced. The simulation studies were carried out in three cases: system load mutation, power fluctuation of distributed generation and voltage sag in high voltage distribution network. The simulation results showed that the DC micro-grid was still on stable operation in the cases above, and proved the good performance of the improved droop control method. Xiaofei Mai Changsha university science and technology Xiangqian Li Puyang Power Supply Company TuD04.9 TuD04.11 An Novel Hierarchical Control of Microgrid Composed of Multi-Droop Controlled Distributed Power Resources Optimal Operation of Microgrid Composed of Small Hydropower and Photovoltaic Generation W ith Energy Storage Based on Multiple Scenarios Technique Aiming at the DC power supply instability in micro-grid, a Flywheel Energy Storage System (FESS) based on magnetic integrated structure bidirectional DC/DC converter is proposed. In this system, for the convertor, three magnetic elements (isolation transformer, resonant inductor and transformer) are integrated into a single core via magnetic integrated technology. The FESS can not only supply the energy shortfall of micro-grid, but also stabilize the voltage of DC bus, improve power quality and reliability. A DC/DC converter 10kW prototype with 460-560V input and 320V output is produced. Through experimental analysis, the project has the advantages of less components, smaller size etc, and can reduce the current ripple effectively, will be suitable for high power applications. pp. 2173-2178 Wei Bao State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Yuehao Yan State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Changchun Cai Hohai University Bo Kong State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Shucheng Cheng Hohai University Yuanhong Chi State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Bing Jiang Hohai University Weili Dai Hohai University Min Wu Hohai University Jianyong Zhang Hohai University Lu Xin pp. 2185-2190 Zhengzhou Xinli Electric Power Co.,Ltd. To improve power sharing and power quality in ac microgrid based on droop controlled voltage source converter, a novel hierarchical control of ac micro-grid according to different time scales is proposed in this paper. In short time scale, larger droop gains is adopted to improve power sharing. In long time scale, the no load frequency and voltage set points of droop characteristics are adjusted to improve the voltage and frequency quality. The proposed hierarchical control can both Microgrid is an effective way to improve the utilization of distributed renewable energy. In order to improve the operational efficiency of the microgrid, this paper proposes an optimal control strategy for the microgrid composed of small hydropower and photovoltaic generation with energy storage based 111 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) on multiple scenarios technique. The probabilistic models of distribution generation are discussed, and the optimal cutting technology is used to reduce the sample number of microgrid operation which can simplify the operation optimal problem of microgrid. Based on the operational characteristics of the photovoltaic generation and small hydropower, a mathematic model for the optimal operation of microgrid is presented and the objective function is the income of the power from distributed generation. Improved particle swarm algorithm is used for the calculation of the optimal problem. The simulation results show that the optimal model of microgrid is suitable for the operation of microgrid in different conditions and can obtain maximum benefit from the distributed generations. concepts are evaluated by simulation results. TuD05.3 Power Losses Analysis and Efficiency Evaluation of High Boost Converters for PV and Fuel Cell Applications pp. 2201-2206 Voltage-Balancing Method for Series-Connected IGBTs Based on FPGA pp. 2191-2194 Univ of Shanghai for Scie and Techy Chaoli Wang Univ of Shanghai for Scie and Techy Dongyuan Zhao State Grid Smart Grid Research Inst Aiming at the problems of voltage sharing failure and overvoltage when Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) are utilized in series, a novel voltage-balancing method for series-connected IGBTs based on Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the collector-emitter voltages of IGBTs are gathered and send to FPGA. Secondly, FPGA generate control signals by using the feature that a high level voltage is applied to gate while the collector-emitter voltage goes to down. The total signal of control signal by FPGA and original switching signal from original power electronic device is acted as the input of gate driver. Lastly, simulation results verify the validity of the method in this paper. Antonella Ragusa I.S.S.I.A – C.N.R. U.O.S Zilong Xiao Huazhong University of Science and Technology Dan Wang Huazhong University of Science and Technology Qing Xiong Department of Power System Research Electric Power Research Institute Chengxiong Mao Huazhong University of Science and Technology Jiming Lu Huazhong University of Science and Technology Linglong Cai Huazhong University of Science and Technology In renewable energy power conditioning system (PCS), like photovoltaic and fuel cell sources, the low input current ripple represents a very important issue to improve the source efficiency. This paper proposes a topology of a DC-DC high gain boost converter with a zero input current ripple condition. In particular, this result is obtained by using coupled inductors. A detailed mathematical analysis on the operating principle, the steady-state analysis and the comparison with the same topology without coupled inductors is presented. The proposed November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China I.S.S.I.A – C.N.R. U.O.S Efficient Modeling of Cascaded-Multilevel Static Synchronous Compensator on Electronicmagnetic Transient Simulation Program pp. 2207-2214 Free Ripple Input Current High Boost Converter with Coupled Inductors pp. 2195-2200 I.S.S.I.A – C.N.R. U.O.S Antonella Ragusa TuD05.4 TuD05.2 Giuseppe Marsala I.S.S.I.A – C.N.R. U.O.S In renewable energy power conditioning system (PCS), like photovoltaic (PV) and fuel cell sources, the low input current ripple represents a very important issue to improve the source efficiency. This paper presents an analysis of the power losses and efficiency of two high boosting converters for PV and fuel cell applications, designed by the authors. The two converters are characterized by a single switching device and, the first topology, by a reduced input current ripple and, the second one, by a zero input ripple condition. In particular, the free ripple condition of the second topology is obtained by coupling the two inductors that are uncoupled in the first topology. A detailed mathematical analysis of the power losses and efficiency is presented together with an evaluation of the effects on the efficiency caused by coupling the inductors. The proposed concepts are demonstrated by simulation. TuD05.1 Ranyue Li Giuseppe Marsala Cascaded-Multilevel STATCOM (CM-STATCOM) is of great development potential in reactive power compensation device. But it consists of large number of semiconductor devices which significant increases the simulation time in electromagnetic transient simulation program. This paper proposes an efficient model of CM-STATCOM based on Dommel algorithm, which replaces the arm circuit with Thevenin equivalent circuit and numerical calculation block. This paper also introduces ideal switching devices to reduce computation quantity in calcula- 112 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) tion block. The proposed model that preserves the individual identity of H-bridge and interface to control system is of wide applicability and high accuracy. Besides, the size of nodal admittance matrix is reduced by several orders of magnitude so that the simulation time is reduced drastically. The proposed model is validated in PSCAD/EMTDC under different condition by comparisons with traditional model. ble. Use the simulation software FEMM, the magnetic flow distribution and magnetic circuit structure are analyzed. This method is convenience to the magnetic flow analysis. With the data comparison between the magnetic flow and magnetic potential, the magnetic circuit model and magnetic potential equations can be found out. Through comparison with different magnetization curve models, this paper gives a mixed separated magnetization curve fitting method, which is very suitable to orthogonal extinction coil. And this simulation method is very important to the research on the orthogonal core. Based on this curve research, this paper also analyzes the control characteristic control ex-characteristic and adjustment characteristic. TuD05.5 Instantaneous Compensation Strategy of DC Voltage Component in the Digital-Analog Integrated Simulation Interface pp. 2215-2220 Linglong Cai TuD05.7 Huazhong University of Science and A Design for High Voltage DC Power Supply pp. 2227-2231 Technology Chengxiong Mao Huazhong University of Science and Technology Jie Zeng and Technology Jiming Lu and Technology Junlin Li Huazhong University of Science Huazhong University of Science Huazhong University of Science and Digital-Analog integrated simulation combines the advantages of digital simulation with the advantages of physical simulation. The applicability of traditional simulation system is increased. The DC component of output voltage restricts the versatility of Digital-Analog integrated simulation. Unlike general inverters, the inverter of Digital-Analog integrated simulation interface (DAISI) has its unique features. A new control strategy is put forward to restrain the steady and transient DC component without additional hardware circuit. The feedback control loop along with the output voltage control loop adjust the duty cycle of sinusoidal pulse width modulation which compensate for the DC voltage component in the DAISI. Simulation and experiment verify the effectiveness of the control strategy. TuD05.8 A Research and Implementation of DigitalTechnologies of Natural Sampling SPWM for Three-Level NPC Inverter Based on FPGA Technology pp. 2232-2237 TuD05.6 Analysis of Orthogonal Controllable Extinction Coil Characteristic pp. 2221-2226 Jie Liu Hebei University of Science and Technology A novel DC high voltage power supply is presented. The device takes 220V AC as input, through the AC inputrectifier-inverter boost-doubler rectifier to get DC high voltage. The device obtains about 300V DC voltage through the fullbridge rectifier. The pulse-width modulation DC/DC links makes DC voltage adjustable. Then the DC voltage is converted into high-frequency AC square wave voltage which will be boosted by the high frequency high voltage transformer. Finally, the doubler rectifier circuit outputs the required 0~30kV adjustable DC voltage. AT89S51 is adopted as the control core. LCD screen displays the current voltage. The AT89S51 microcontroller PWM wave is generated through software programming as the control signal of the chopper. Two complementary PWM wave were generated to control the inverter circuit. The AT89S51 compare the feedback voltage and reference voltage required, modulation PWM wave that is to change the duty cycle to achieve highperformance adjustable DC. Simulation and experimental results verify the correctness of theoretical analysis and design. Technology Xiaoxia Wei Hebei University of Science and Technology Zhaowen Dong Electric Power Research Institute of Guangdong Power Grid Co. Ltd. Dan Wang Jianye Liu State Grid Energy Research Institute Heilongjiang State Grid Company Tiezhong Wei Heilongjiang State Grid Company Lirong Wang Heilongjiang State Grid Company Jian Liu Wuhan Institute of Technology Wei Tang Wuhan Institute of Technology Hao Zhang Wuhan Institute of Technology Hua Zeng Wuhan Institute of Technology Yao Zhou Wuhan Institute of Technology KaiCheng Xiong The orthogonal extinction coil is reliable and easily controlla- 113 Wuhan Micro Hydrogen Newenergy Co., Ltd November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) With the application of digital sinusoidal pulse width modulation (SPWM) control technologies, we can improve the output accuracy of the pulse width control signal, shorten the control respond time, and reduce the harmonic content of the output waveform. In this paper the digital theory of natural sampling SPWM is study with the combination of characteristics of high voltage and high power three-level NPC inverter. A framework of full digital natural sampling SPWM is set up. The digital realization method of triangular carrier wave and sinusoidal modulation wave generation, switching states combination and dead time configuration are studied in detail. And there comes up with a FPGA based hyper-real-time duty cycle calculation method, by using this method the Taylor series expansion and convergence judgment could be avoid. The output waveform can be achieved through the effect of natural sampling, compared with regular sampling, which is less harmonics in output waveform. At the end of this paper, the theory research has been realized by using VHDL language and a FPGA chip. The software simulation and experiment results prove the correctness and the feasibility of the digitization theory. VSC-HVDC system, such as in offshore wind farms, will be widely used in the next few years. The controller parameters of both rectifier and inverter will have a great impact on both the system itself and the other parts of the transmission system due to the connection of DC transmission line. Usually, the controller parameters on each side are designed and tested separately. Therefore, the performance of the whole system can hardly achieve the best operation state. In this paper, a new method of coordinated optimization considering DC line is proposed. A united transfer function model is also established. Then, according to ITAE (integral of time multiplied by the absolute value of error) criterion, the parameters of both converters are optimized simultaneously. Simulation results verify the correctness and effectiveness of the proposed optimization method. TuD05.11 Design of soft start in self-powered circuit for IGBT power modules in series pp. 2249-2252 TuD05.9 Single Carrier SPWM Grid-Connected Inverter Hybrid Cascade pp. 2238-2242 Yuan Jin State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Xiu Lan Liu State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Shuang Zeng State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Zhongyuan Chen Smart Grid Research Institute of SGCC Zhixia Wang Smart Grid Research Institute of SGCC Zou Ge North China Electric Power University Series-Connected insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is the important basis in the high voltage and power converter application. A long duration of the excessive inrush current occurs in self-powered circuit when IGBT power modules in series start working. A design method of soft start of self-powered circuit is presented in this paper. The rise time of voltage of the capacitance stored energy is extended, the inrush current is reduced and easing the current stress IGBT module in series and diode can withstand by this method. The simulation model of soft start is realized by Saber and experimental results are used to illustrate both correctness and defensiveness of the proposed method to reduce the inrush current, protecting IGBT module and diode in self-powered circuit. This paper describes a hybrid cascaded inverters, which can be applied to low power energy storage system. The working mode of the circuit and the dead-time effect are analyzed. Base on the traditional control mode, a new way is given to control the auxiliary capacitor voltage. In order to solve the problem that multilevel SPWM method take up to much system resources, this paper put forward a single carrier SPWM method, which can be implemented efficient for the inverter. To verify the feasibility of the system, a simulation model and a low power inverter was constructed and results are provided. TuD05.12 TuD05.10 A Novel Comprehensive Control Scheme of Modular Multilevel Converter-Based Power Electronic Transformer pp. 2253-2258 Coordinated Optimization of VSC-HVDC Controller Considering DC Line pp. 2243-2248 Beibei Qi Hohai University Chong Li Jiaxing Electric Power Company Yuqing Jin Hohai University Ke Tao Hohai University Qian Chen Hohai University Ping Ju Hohai University Hongyu Li Shandong University Guangzhu Wang Shandong University Jiangzhou Feng Shandong University Xiujuan Shang Shandong University In this paper, the modular multilevel converterbased power electronic transformer (MMC-based PET) is studied. This topology is suitable for high voltage and large power capacity Hohai University November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Qin Wu 114 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) situations, such as DC power distribution network. Only one medium frequency transformer is used in the PET structure, reducing the size and weight. A series inductor is added to the DC side of MMC which can improve the characteristics of the topology. By analyzing the structure of MMC stage, a comprehensive control scheme is proposed. Based on the small signal model of output stage, a phase shift closed-loop control scheme is designed for output stage. The control schemes of MMC stage and output stage are independent of each other. A Simulink model is built in Matlab, and the simulation results verify the effectiveness of the topology and the proposed control scheme. Jinmu Lai JianDai Zhe Zhang Minghao Wen Combining switching characteristics of power electronic devices and state transitions in carrier phase-shifted SPWM (CPS-SPWM), this paper uses graphic Stateflow toolbox of Matlab/Simulink to design the process of CPS-SPWM. Then it is applied to STATCOM which is integrated with distribution transformer (DT-STATCOM) for PWM signal generation. Simulation results are presented to prove that the method is valid and effective for reactive power compensation. Meanwhile, softwarein-loop (SIL) test and automatic code generation are also carried out. Results of experimental test with DSP TMSF28335 have validated the theoretical contributions of the paper. PWM signal comparison of both simulation and experiment result shows that this method has both the feasibility and effectiveness of software and hardware design. With this method, design of CPS-SPWM can be more rapid, efficient and convenient. TuD05.13 Low Output Frequency Operation of Modular Multilevel Matrix Converter pp. 2259-2264 Xiujuan Shang Shandong University Guangzhu Wang Shandong University Feng Li Shandong University Qin Wu Shandong University Jianzhou Feng Shandong University TuD05.15 When the multilevel modular matrix converters (MMMC) operate at low frequency, sub-module (SM) capacitors voltage mainly contains doubling-output frequency component inversely proportion to output frequency, especially when MMMC operate at zero frequency, the voltage ripple of SM capacitor can be infinite in theory. This paper proposes two methods to solve the voltage ripple problem of MMMC operating at low frequency, even near zero. The first one injects high frequency zero-sequence voltage on the neutral point and injects high frequency negative-sequence currents to each phase. To suppress low frequency fluctuation, the magnitude and phase angle of the zero-sequence voltage changes according to low frequency power, without complicated calculation. The second method is called following feedback low frequency ripple envelope method. The low frequency ripple voltage is calculated by difference between the reference voltage value and the average voltage value of each phase, then got eliminated by use of feedback close-loop control. In this way, low frequency ripple can be detected and minimized. The Matlab/simulink simulation is built and the results have confirmed the validity and effectiveness of these methods. Study On the Optimal DC Voltage Control For Power Electronic Transformer pp. 2270-2275 Guangxi Grid Co., Ltd Hongbo Chu Guangxi Grid Co., Ltd Yangkai Hu Hunan University Hunan University Zhiyuan Sun Guangxi Grid Co., Ltd Mosi Liu Guangxi Grid Co., Ltd Power electronic transformer (PET), the key equipment for future smart grid, is vital for the whole power grid to be in normal operation. The mathematical relationship between the DC-link voltage and the system parameters for PET were analyzed in this paper. Based on the analysis, the optimal DC-link voltage for PET is obtained by mathematical deduction. Then, a novel adaptive voltage regulation method is proposed, in which the DC-link voltage reference value will be maintained in the required optimal voltage level, and it also can be adaptively changed according to different grid voltage levels and load levels. Therefore, PET can avoid the grid voltage and load level fluctuation impact on the input current distortion and output voltage stability. Finally, representative simulation results in PSCAD/EMTDC verify the validity and effectiveness of the optimal DC-link voltage design and the proposed adaptive voltage regulation method. Stateflow Based Carrier Phase-Shifted SPWM and its Application in DT-STATCOM pp. 2265-2269 Xianggen Yin Ke Zhou Zheng Lan TuD05.14 Haihuan Wu Huazhong University of Science and Technology Huazhong University of Science and Technology Huazhong University of Science and Technology Huazhong University of Science and Technology Huazhong University of Science and Technology Huazhong University of Science and Technology 115 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) archy control method, which keeps voltage balance of SM capacitors better than that with the nearest level control; thirdly, circulating current is suppressed inherently, removing the need of the standalone circulating current suppressing controller. Simulation results based on PSCAD/EMTDC prove the effectiveness of proposed strategies. TuD05.16 The Research on Security and Stability of PWM Technology of High-Voltage Three-Level NPC Inverter High-Power pp. 2276-2280 TuD06.1 Jian Liu Wuhan Institute of Technology Hua Zeng Wuhan Institute of Technology Wei Tang Wuhan Institute of Technology Yao Zhou Wuhan Institute of Technology A Hybrid Compensation Method for Electric Railway’s Power Quality Improvement pp. 2287-2292 Hao Zhang Wuhan Institute of Technology Yuanyuan Sun Shandong University Chuankai Dai Shandong University Kaicheng Xiong Wuhan Micro Hydrogen New Energy Co., Ltd Jiaqi Li The security and stability operation mechanism is the key problem of the high power and voltage three-level neutral point clamp inverter[1]. As the security and stability of PWM is very important for normal operation of system, the control strategy and algorithm are the basis for the safety operation of the inverter. In the process of starting up the inverter, the optimal settings of minimum pulse width and secure access are the most important problems needed to be solved. In the normal operation process of the inverter, the accuracy algorithm of PWM output region identification and the dead zone insert need to be fully considered. The treatment method during the emergency stop time of the inverter is also one of the key contents of improving security and stability. And the theoretical innovation through the multi-disciplinary overlapping (such as power electronics, intelligent technology) should be adopted. Combined with existing achievements, this paper carries out research in the aspects of improving security and stability of PWM of high-voltage and high-power three-level NPC inverter. The results lay a theoretical and experimental foundation for the following theoretical research. Qingdao Electric Power Company Electric railway brings many power quality problems to the public power system. In this paper, a new power quality improvement method is proposed which can alleviate the voltage unbalance and low power factor problem of electric systems. The method is composed of a specially connected three phase to two phase transformer and a phase balancing device. The specially connected transformer has the following common characteristic: secondary voltages are equal in magnitude and differ 90 degrees in phase angle. Such transformers include Scott Transformer, Le-Blanc Transformer, and modified Wood-bridge Transformer and so on. The phase balancing device consists of two parts: one is used to regulate the power factor to unity; the other part is to transfer power flow between the two feeders, thus balancing their loads. With the proposed scheme, negative current can be eliminated and power factor can be regulated to unity. The advantage of the new method is that it is very simple and cost-effective. Validity of the proposed method is verified by simulation results. The capacity of the compensation device is also analyzed in the paper. TuD05.17 TuD06.2 Two Control Strategies of Modular Multilevel Converter in Rectifier Side Based on Arm Current Under Unbalanced Voltage Condition pp. 2281-2286 Three-level APF Control Strategy Based on the Double Sampling T iming Comparison pp. 2293-2298 Jian Wu Harbin Institute of Technology Zhujian Ou Shandong University Yanfei You Harbin Institute of Technology Guangzhu Wang Shandong University Yue Qi Harbin Institute of Technology Jianzhou Feng Shandong University Dianguo Xu Harbin Institute of Technology Two control strategies for MMC in rectifier side based on arm current control are proposed in this paper. The strategies work well both under balanced and unbalanced voltage conditions. The proposed strategies have the following advantages: firstly, ac side current is well balanced under unbalanced condition by adjusting the active power flowing from arms to dc bus; secondly, arm current reference is obtained by using multihier- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China High frequency harmonics generated by active power filter (APF) play a negative role on the power quality of grid. To eliminate the impact without reduction on harmonic compensating effectiveness, this paper proposed a three-level diode-clamped APF topology. Besides, the double sampling and the neutral voltage balancing technology based on the short 116 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) vector switching were utilized to accomplish the timing comparison control strategy proposed in this paper. Moreover, the influence of feedback current sampled position and the system delay on APF performance were also analyzed in this paper. Finally, an experimental prototype was established, and the whole scheme was validated by the experimental results. variation in each cycle, the stuff can assess the state of the windings. This technique does not call for any special equipment and has clear judgment standard. Thus, it is possible to realize on-line monitoring. Finally, PSCAD simulation and dynamic simulation experiment verified the practicality and validity of the proposed method. TuD06.3 TuD06.5 Thevenin Equivalent Circuit Parameter Estimation for the PCC Upstream System pp. 2299-2303 Yuanyuan Sun Shandong University Chuankai Dai Shandong University Jiaqi Li Online Monitoring Of W inding Deformation And Error Analysis Based On Transformer Impedence Circle Character pp. 2310-2315 Fei He Qingdao Electric Power Company The Thevenin equivalent circuit parameters for the upstream system seen at a load bus plays an important role in the power system operation and planning. In order to accurately estimate the Thevenin equivalent parameters for the upstream supply system, an estimation method not requiring synchronized measurement is used in this paper. The characteristics of the probability curves of load voltage and impedance fluctuations have been analyzed, based on which the data selection criteria has been established. The field measurement data from different substations are processed by the proposed methods, and abnormal data has been filtered out in order to increase the accuracy of the estimated parameters. The validity and accuracy of the proposed method has been verified by both the simulation and field measurement data. Xiaojing Zhang Xi'an Jiao tong University Haiyang Song State Grid Jiangsu Power Supple Company Yu Zhang State Grid Jiangsu Power Supple Company Zhiguo Hao Xi'an Jiao tong University Qifei He Xi'an Jiao tong University Peng Wu State Grid Jiangsu Power Supple Company Guozhen Chen State Grid Jiangsu Power Supple Company Xi'an Jiao tong University This paper introduced the main point of three winding transformer impedance circle characters that is constructing the 3D locus between the voltage differences in the highand low-(or middle-) sides of a particular phase against the currents of this two windings. In additional, error terms caused by exciting current of both two winding and three-winding transformer have been analyzed. Current compensation was employed to reduce error. A Matlab code was developed to calculate the feature parameter of the impedance circle character. Winding deformation can be diagnosed by comparing the index with the fingerprint. PSCAD simulation and fault recorder analysis results show that the technique is free from load, does not call for any special equipment and enable on-line monitoring. Transformer Impedence Circle Character Based W inding Deformation Online Monitoring pp. 2304-2309 State Grid Jiangsu Power Supple Company Xiaojing Zhang Zhiguo Hao TuD06.4 Guozhen Chen State Grid Jiangsu Power Supple Company TuD06.6 Construction Programs and Applications of AVC System for Regional Power Network pp. 2316-2319 Xi'an Jiao tong University This paper introduced a novel on-line transformer winding deformation monitoring technology. That is constructing the locus of the voltage difference on both sides of the transformer changes with the primary side current. Results show that the locus is an ellipse and we name it the transformer impedance circle character. Mathematical methods were applied to analyze the characteristics of the impedance circle, as well as the factors that influence the shape of it. Indicators such as eccentricity ratio and deviation angle, which is free from of running condition but sensitive to internal fault, were established to evaluate the state of winding. Indexes established in normal condition are determined as fingerprint. By comparing the Lei Guo Jinshan Power Supply Company Shiwei Gao Jinshan Power Supply Company Feng Gao Jinshan Power Supply Company Dan Zhou Jinshan Power Supply Company In recent years, the AVC technology has been widely used as a main method of centralized monitoring, analysis and calculation for reactive power and voltage state in the whole power grid. It’s optimally controlled from an overall angle for wide-area distributed power grid reactive device. The AVC system of Jinshan District is based on the OPEN3000 platform. In the process of system running, we are faced with many 117 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) problems. We propose the Voltage and Reactive Power closed-loop control system should aim at reducing the whole network loss and onload voltage regulating joint adjustment numbers, ensuring each node voltage qualification and the most reasonable compensation of Capacitor equipment operation, while it should also keep in the core of the Centralized Control Center (Dispatching Center or Distribution Center), to the principle of Expert system and Fuzzy control, and as a mean of on-load voltage regulating joint gear in each substation and capacitor switching regulator control and coordination. The solution effectively improved the bus voltage qualification rate and reduced the equipment operation numbers and the reactive power loss. The AVC system is running in good condition at present. phase-shifting transformer, the proposed topology is composed of cascaded H-bridge diode rectifier and boost circuit modular units, by which the high power factor rectify, the output of stabilized voltage of cascaded modular units and voltage-sharing control can be implemented. The basic working principle of the proposed topology, mathematical modeling and phase diagram of the circuit and its steady state characteristics are discussed, and corresponding control strategy is given. The feasibility of the proposed topology and control strategy is validated by simulation results and experimental results. TuD06.9 Overview of the Instantaneous Reactive Power Theory in Three-Phase Systems pp. 2331-2336 TuD06.7 The Electromagnetic Transient Modeling andSimulation of 10 kV/400 V EPT pp. 2320-2325 Xiang Liang Huazhong University of Science and Technology Yiran Liu Huazhong University of Science and Technology Yun Yang Huazhong University of Science and Technology Chengxiong Mao Xiangping Kong Research Institute Yubo Yuan Haosheng Huang Dan Wang Huazhong University of Science and Technology Ye Wang The wide application of power electronic equipment results in severe non-sinusoidal phenomena, making the conventional steady-state reactive power theory no more applicable. In order to deal with the harmonic compensation and power factor correction under the non-sinusoidal condition, scholars have carried out lots of research works. This paper discusses and compares several commonly used instantaneous reactive power theories, and pointes out the relationships and differences of them. The work of this paper contributes to better understanding of the instantaneous reactive power theories. TuD06.10 Assessing the Harmonic Current Emission Level of the Residential Loads Based on the Impedance Gathering Trend pp. 2337-2341 TuD06.8 New Cascade Diode H-bridge Multi-level Rectifier pp. 2326-2330 China University of Mining & Technology In allusion to current circulation through the switch and the corresponding diode rectifier bridge in certain conditions leading to other cascaded diode rectifier bridges withstand the full supply voltage in traditional cascaded diode H-bridge multi-level Rectifier,a novel cascade diode H-bridge multi-level structure is proposed. Not needing power frequency November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Institute Electronic Power Transformer (EPT) is capable of improving power quality without additional devices; hence it has the potential of pervasive application in prospective utility grid. Ahead of field test, transient analysis of EPT is necessary to verify power supply reliability as well as ensure safety. In this paper, the Electro-Magnetic Transient (EMT) simulation model of an industrial prototype of 10kV/400V/500kVA unidirectional EPT is built in PSCAD/EMTDC. Then the validation of the model and case studies under fault conditions are carried out. Simulation results show that the prototype can withstand phaseto-phase and phase-to-ground faults and sustain regular output after timely adjustment. Xiangbei Jiang Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Institute and Technology Huazhong University of Science and Technology Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Institute Huazhong University of Science Jiming Lu Jiangsu Electric Power Company Yang Fu Shanghai University of Electric Power Guang Chen Shanghai University of Electric Power Bo Tang Shanghai University of Electric Power Shunfu Lin Shanghai University of Electric Power Bo Tang Shanghai University Due to the widespread applications of new energy and the power electronic residential loads in the distribution network, it is very necessary to assess the harmonic current emission 118 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) distribution method. The analysis results of practical cases prove that the cloud transform is capable of fitting the harmonic current distribution curves in high precision, and presenting the multi-modal characteristics of the distribution curves well. level since the impact of the collective harmonics cannot be ignored. The calculation of the harmonic impedance is a crucial task to determine the harmonic responsibilities at the point of common coupling (PCC). This paper presents a method to quantify the harmonic current responsibilities of the system side and customer side based on the impedance gathering trend, and then to calculate the emission level of the residential loads. This study has a sparked phenomenon on the evaluation of current emission level of the residential loads and can reflect the residential load harmonic emission characteristic precisely. TuD06.13 Influence of Distributed Generation on Distribution System Voltage Stability pp. 2352-2355 TuD06.11 Meimei Xu Identification of Transient Power Quality Disturbances Based on FCM pp. 2342-2346 Hehong Guo Jinzhong Electric Power Company Qingsheng Zhao Taiyuan University of Technology Yuhuan Han Taiyuan University of Technology Guizhou Power Grid Co., Ltd. Zuyi Ren NARI-Relays Electric Co., Ltd. Yong Xiao Guizhou Power Grid Co., Ltd. Yang Bai NARI-Relays Electric Co., Ltd. Xiankui Wen Guizhou Power Grid Co., Ltd. Junfang Zhang Nanjing University of Science and Technology Zhiqian Bo XUJI Group of SGCC Interconnected operation of distributed generation (DG) will become the future trend. This paper studies the voltage stability of distribution network with DGs. According to different network interfaces and operating modes, DGs are classified into four different node types. The processing methods in power flow calculation are also analyzed in this paper. Then voltage stability condition of distribution network is derived out based on the power flow solution. According to four types of DGs, simulations and analysis of the impact on the voltage stability index are conducted. Simulation results show that the voltage stability is reduced by accessing PV-type DGs, and the quantity of PV-type DGs should be limited. Additionally, the voltage stability of distribution network is improved by accessing PQ-type DGs on different location and capacity. This paper presents a new hierarchical identification method for transient power quality disturbance based on fuzzy C-mean clustering (FCM) algorithm. The method consists of five function modules. By use of the ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) and singular value decomposition method, we can extract effective feature vectors layer by layer, which are used as the input of FCM. In this way the optimized classified matrix and clustering centers are obtained. According to the Euclidean distance between the unknown-sample records and the known-sample ones, the disturbance type is identified. Simulation results of common kinds of transient disturbances indicate that this method is accurate and has a potential application in engineering. TuD06.14 TuD06.12 Current Control of Active Power F ilters Assisted by three-state hysteresis pp. 2356-2359 A Study On The Probability Distribution Of The Residents Load Harmonic Collective Effect Based On Cloud Theory pp. 2347-2351 Bo Tang Shanghai University Shiwei Ma Shanghai University Guang Chen Shanghai University of Electric Power Shunfu Lin Shanghai University of Electric Power Xuan Sun Changsha University of Science and Technology Xin Tang Changsha University of Science and Technology In this paper, repetitive control is employed to design the current controller of active power filter for reducing the steady-state error due to periodic command. Zero steadystate error for current harmonics is realized. Harmonic reduction and power factor correction will both be carried out by the proposed filter. Discussions on the design of the current and voltage control loops are given. Experimental results verified the feasibility of the proposed method, obtained from a 10KW shunt active power filter. This paper introduced the cloud theory briefly firstly, then presents a method based on the cloud theory to access the collective harmonic influence of the residential loads, which can identify the harmonic sources so as to determine the harmonic suppression scheme. For the residential harmonic current probability distribution has multiple peak values, the cloud transformation method has more advantages than the normal 119 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) modeled as an event-driven system using SimEvents® toolbox and energy grid is modeled as a time-driven system using SimPowerSystems® toolbox. Co-simulation results are obtained by combining different communication scenarios and time-varying irradiance scenarios for the PV plant when this one is required to provide a certain power in response to a power reference received from SCADA over the communication network. The analysis aims at illustrating the impact that stochastic behavior and delays due to network communication have on the global system behavior. E: Smart Grid Technology TuE01.1 A Reliability Evaluation Model for Intelligent SubstationSecondary System based on Variation Coefficient Method pp. 2360-2364 Zhongqing Li Wei Li Hao Li Kun Yu Hang Zhao Xiangning Lin China Electric Power Research Inst China Electric Power Research Institute Huazhong Univ of Science and Tech Huazhong Univ of Science and Tech Huazhong Univ of Science and Tech Huazhong Univ of Science and Tech TuE01.3 WDM Switch Technology Application in Smart Substation Communication Network pp. 2373-2376 It is important to establish reliability analysis model of secondary system for the intelligent substation. In this paper, a method is proposed to evaluate the reliability of secondary system in smart substation. Firstly, according to the reliability indices of secondary system structures for different smart substations,the evaluation matrix are determined andthe matrixcan beorthogonalized to makes it non dimensional. Secondly, the mean, standard deviation, coefficient of variation, and weighted vector of the matrix are calculated. Then, the weighted data matrix of ideal sample and negative sample is determined. Finally, according to the correlation degree ranking method, the reliability evaluation of each index is obtained. Forpractical examples, this method can be used to identify the factors influencingrealiability of intelligent substation. The method can be used to select an appropriate network topology, improving the reliability of the design level of substation communication system. Co-simulation of a Low-Voltage Utility Grid Controlled over IEC 61850 protocol pp. 2365-2372 Info and Comm Inst China Smart Grid Rese Zhansheng Hou Info and Comm Inst China Smart Grid Rese Min Xu Info and Comm Inst China Smart Grid Rese Lin Peng Info and Comm Inst China Smart Grid Rese Haiyun Han Info and Comm Inst China Smart Grid Rese TuE01.4 Grenoble Alpes University Grenoble Alpes University “Dunărea de Jos” University of Galaţi Bratcu Grenoble Alpes University Substation Alarm Information Processing Based on Ontology Theory Analysis Correlation Modeling of the O il Flow of Transformer and Temperature pp. 2377-2382 This papersis Correlation Modeling of the Oil Flow of Trans presents a co-simulation model using MATLAB® toolboxes to illustrate an interaction between the communication system and the energy grid, coherent with the concept of smart grid that employs IEC 61850 communication standard. The MMS (Manufacturing Message Specification) protocol supported by IEC 61850, based on TCP/IP, is used for the vertical communication between the Supervisory and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system and Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) embedding the local control of different parts of the smart grid. In this paper an IED supporting the power control of a photovoltaic (PV) plant connected to a low-voltage (LV) utility grid is considered. Communication system consisting of the transport layer and a router placed on the network layer is November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Info and Comm Inst China Smart Grid Rese Gang Wang By analyzing the typical communication networking method of Process Layer in Smart Substation, this paper proposes the problems of current widely used Process Layer communication isolation network by using VLAN Technology. This paper expounds the basic principle and advantage of using WDM technology to realize the Switch, proposes the Security isolation communication networking method of using WDM Switch in Smart Substation Process Layer. This method has obvious advantages than the current VLAN logic isolation method in theory, truly meets the "Three Networks In One" needs of Smart Substation Process Layer communication network. TuE01.2 Ekanki Sharma Claudiu Chiculita Yvon Besanger AntonetaIuliana Xingchuan Bao Zhiwei Liao Sheng Liu South China University of Technology South China University of Technology Logical alarm information is the key to mining the knowledge that hidden in the power system equipment operation and maintenance information. In this paper, a knowledge mining method of association rules based on ontology is proposed in order to realize the intelligent analysis of substation alarm information. Firstly, the alarm information ontology is based on the structure of substation configuration language, and it uses the methods of short text classification and data generali- 120 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) zation, which lays the foundation for hierarchical database of the Apriori algorithm. Secondly, this paper uses the ontology method to construct ontology class tree that integrates the unstructured records based on three dimensions of time, frequency and range. And then we traverse data, attributes, and relationships in the tree, so as to generate the data sources that computer can use for algorithms in data mining. Finally we use the improved Apriori algorithms based on alarm ontology to calculate and draw conclusions. Experimental results show that the efficient generation of association rules and assertions rules verify the validity of the method. method (PDIPM). This new OPF model is constituted of current source converter (CSC), VSC and its coupling transformer which is considered to be a tap-changing transformer. The new model represents well both AC system and DC system where the VSC is not assumed as idealized, controllable voltage sources but compound transformer devices which take account of VSC internal switching losses, ohmic losses and reactive power design limits. Finally, the accuracy and effectiveness of the proposed OPF model are demonstrated on a modified IEEE-14 Bus system. TuE02.2 TuE01.5 DC Side Line-to-line Fault Analysis of VSC-HVDC and DC-fault-clearing Methods pp. 2395-2399 Relay Adaptive Testing Research in Smart Substation Process Level Based on EPON Network pp. 2383-2388 Zhihua Zhan China Electric Power Research Institute Zhengguang Chen China Electric Power Research Institute Rongrong Zhan China Electric Power Research Institute Chunxia Zhou China Electric Power Research Institute Danhua Liu TuE02.1 A Novel Hybrid MTDC Model for Optimal Power Flow Using Interior-Point Method pp. 2389-2394 Hohai University Hohai University Guoqiang Sun Hohai University Qun Li State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Company Jiankun Liu State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Company Tongzhen Wei Chinese Academy of Sciences Qunhai Huo Chinese Academy of Sciences Lixin Wu Chinese Academy of Sciences As the fault voltage and current change raptly in case of DC side line-to-line fault of voltage source converter, it's a serious threat to the whole system. Aiming at this problem, the mechanism of DC side line-to-line fault in three kinds of converters including two-level converter, three-level diode-clamped converter and Modular Multilevel Converter, was analyzed firstly. Without converter blocked, the calculation of fault overcurrent and voltage collapse expressions was proposed as well. Finally, theoretical analysis of the short-circuit fault process was validated through the RT-LAB simulation. The derivation and simulation waveform provide a reference for disconnecting the faulty branch. The results indicate that quick removal of the fault is better to be done by DC circuit breaker or converter with self-clearing. A low-voltage low-current laboratory prototype of hybrid DC circuit breaker has been built in the laboratory, which verify DC circuit breaker can disconnect the fault current absolutely. Through describe the principles and characteristics of EPON network, Proposed EPON communications network applying smart substation process level, and test the adaptability of protection under the EPON network. The paper has constructed smart substation relay protection dynamic simulation model test platform based on EPON network. Selecting 220kV smart substation busbar protection, transformer protection, line protection for test object, and analyzed the test results. The result shows that relay protection operation performance has not affected by the process layer by using EPON network. The research work can provide the basis for the smart substation layer applying EPON network and the subsequent technology Application. Weimin Huang Zhinong Wei University of Chinese Academy of Sciences TuE02.3 Accelerated Model of Alternate Arm Voltage Source Converters pp. 2400-2404 Original optimal power flow (OPF) model of hybrid multi-terminal high voltage direct current (hybrid MTDC) system ignores the converter transformer of voltage source converter (VSC). The modulation of VSC may reach the upper limit losing regulation and VSC station works in the nonlinear modulation area. This paper presents a novel model of hybrid MTDC for OPF solutions using primal-dual interior-point Wenlong Liu Chinese Academy of Sciences Jin Zhu Chinese Academy of Sciences Qunhai Huo Chinese Academy of Sciences Tongzhen Wei Chinese Academy of Sciences For the purpose of drastically reducing the computational time of alternate arm voltage source converters in electromagnetic transient simulations, an accelerated model of AAMC is proposed based on Thevenin's theorem. This real-time simula- 121 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) tion model is fast and efficient, and it has strong universality. The simulation results validate the simulation accuracy and acceleration ratio of the new model. TuE02.6 A Study on Damping Low Frequency Oscillation in Power System by VSC-HVDC pp. 2415-2419 TuE02.4 Analysis of Oscillation Modes in A VSC-HVDC System pp. 2405-2410 Shan Jiang Changsha University of Science and Technology Xin Tang Changsha University of Science and Technology Mao Xiao Changsha University of Science and Technology Xin Tang Changsha University of Science and Technology The low frequency oscillation occurs in power system is mainly due to the insufficiency of the system damping. A voltage source converter based high voltage direct current (VSC-HVDC) system with traditional control strategy can not supply damping. To increase the system damping, two damping control strategies for a VSC-HVDC by modulating the active and the reactive power respectively are proposed. Then the VSC-HVDC with the proposed control strategy connected Harmonic instability may occur when a controlled voltage source converter interacts with the local power grid in a power system. In this paper, oscillation modes are analyzed in a voltage source converter based high voltage direct current (VSC-HVDC) system. The impedance models that are seen from the point of common coupling (PCC) for the rectifier ac system are also derived. The output impedance models consider the parameters of the inner current control loop and the outer power control loop. The obtained impedance models are then used to analysis the oscillation modes of the system. Simulation is built in the time-domain program (PSCAD/EMTDC) and the results validate the analysis. with a single-machine infinite-bus system is analyzed theoretically. Finally, based on the PSCAD / EMTDC simulation software, the simulation platform of the system is established and the simulation results show that both two kinds of damping control strategies can increase the system damping effectively, suppress the low frequency oscillation rapidly, and enhance the stability of power system. TuE03.1 TuE02.5 A Review of Different UPFC Steady Models in Power Flow Algorithm pp. 2420-2424 DC-side Small-signal Model of a PWM Converter W ith a DC Voltage Controller pp. 2411-2414 WeiTan Changsha University of Science and Technology XinTang Changsha University of Science and Technology Ningyu Zhang Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst Jiankun Liu Compared to AC distribution network, DC distribution network has a significant technical and economic advantages in the new energy grid connect, power supply to the load driven by converters and transmission loss. DC distribution network usually connects with AC grid by PWM inverter, thus establishing the DC side model of the PWM converter station is very important. In this paper, the fixed DC voltage control model of the converters is presented and the active balance equation is linearized, then the DC side Small-signal model is built. Furthermore, the DC-side input impedance of the converter can be constructed by a resistor in parallel with an inductor. The circuit model is useful not only for analyzing the DC micro-grid’s stability, dynamic and static characteristics but also for analyzing and designing the parameters of the DC circuit in new energy generation systems. Finally, the PSCAD simulation results show the effectiveness of the proposed equivalent circuit model. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst Qian Zhou Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst Haoming Hu Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst Chen Jing Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst Haiyun An Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Ins As the most powerful FACTS (flexible alternative current transmission systems) device, UPFC (unified power flow controller) could be considered as a multi-function controller which is capable of providing the performance of one or two FACTS device. This paper presents various UPFC steady models in load flow algorithms. Based on acquired achievement, UPFC has been researched by load injection technique, decoupled technique, π load injection technique, indirect technique, ideal transformer technique for different analysis purpose. It also discusses advantages and disadvantages of each method. In the end, based on analyzing current methods, a discussion for future is proposed. 122 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) has taken the use of the principle of multi-resolution structural elements to complete feature extraction by choosing different kinds of linear structure element. By the simulation experiment, compared with the fault feature component extracted by wavelet transform, it shows that this measures has a good effect on the fault feature extraction of single phase grounding fault in neutral ineffective grounding system. TuE04.1 Comparison Study on Restoration Strategies of Chongqing Power Grid pp. 2425-2430 Tao Chen Chongqing Electric Power Corporation Li Feng Chongqing Electric Power Corporation Xinyu Liu Chongqing Electric Power Corporation Lin Zhang Chongqing Electric Power Corporation Lingyun Tao Beijing Jiaotong University Ying Wang Beijing Jiaotong University Pei Zhang TuE04.3 Study of The Disturbance Propagation in The Discrete Model of Power Networks pp. 2436-2441 Beijing Jiaotong University The efficient restoration after large-scale electric interruption is an important subject for ensuring the secure operation of power systems. This paper applies the concept of “generic restoration milestones (GRMs)” to develop two different restoration strategies of Chongqing power system. One adopts build-outward approach that utilizes internal hydropower as black-start units. Another adopts build-inward approach that utilizes external power source as black-start units. Comparison study results show that the build-inward strategy uses less time than the build-outward strategy, thereby promotes the process of restoration. It can assist system operators in selecting an optimal restoration plan. Haihan Li North China Electric Power University Baoding State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Hui Zhang State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Bing Liu State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Zhengzhou Xinli Electric Power Co.,Ltd The study of the characteristics of disturbance propagation in the interconnected power networks is of great importance to control the spreading of disturbance and improve the security level of power systems. In this paper, the characteristics of disturbance propagation in a one-dimensional chained power network are studied from the electromechanical wave point of view. The electromechanical wave equation is built based on the discrete inertia model of power networks. The wave transfer function which can describe the variations of amplitude and the phase is derived. Then, the propagation characteristics of different frequency disturbances are analyzed. The corner frequency of the discrete inertia model is proposed. Furthermore, the frequency dispersion and local oscillation are considered and their relationships with the corner frequency are revealed as well. Computer simulations for a 50 generators chained network are carried out to verify the propagation characteristics of disturbances with different frequencies. North China Electric Power University Baoding North China Electric Power University Baoding Wei Bao Lu Xin Improved Mathematical Morphology Transformation and Application to Single Ground Fault Feature Extraction in Small Current System pp. 2431-2435 Qiang Li State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Jun Xin TuE04.2 Guping Zheng Yuehao Yan TuE05.1 Single phase grounding fault occurs in small current grounding power system frequently, fault signal caused by which contains a large number of feature information, which is an important basis for the fault location. However, due to the weakness of the fault signal, collecting the fault feature information becomes a difficult point to detect the fault line and solve the fault location. In this paper, combining with the idea of multi-resolution structural elements, an improved mathematical morphology method to accomplish the extraction of the characteristics of the fault signal has been proposed. Firstly, the consistency distribution level has been introduced to ameliorate the traditional morphological filter, which reassigned the individual treatment effect of the signal of Open-Closing and Close-Opening operation and optimized the proportional coefficients of these two kinds of operations in this filter. As a result, it makes these two operations have a more thorough and effective influence on the feature signal extraction results. Then, it Analysis on the Measures Employed to Deal with Abnormal Faults of Intelligent Electric Meters pp. 2442-2446 Ke Wang Central South University Rui Huang Hunan Electric Power Company Hao Chen Hunan Electric Power Company Haiyuan Wang Hunan Electric Power Company Xianyong Xu Hunan Electric Power Company Liman Shen Hunan Electric Power Company All kinds of faults would occur during the operation of the intelligent electric meter including burnt-out electric meter; black screen; voltage loss; communication fault; battery fault; 123 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) display malfunction and relay malfunction. In this paper, two kinds of abnormal faults encountered by the author during work are listed for research and analysis so as to propose measures for dealing with these two kinds of faults as well as provide useful suggestions for future work. tion and maintenance of power grid. To weaken the influence above, the technology named Vehicle to Home is proposed, which can control EV charging load to a specific value as well as control the EV discharge to grid. In order to actively respond to the impact of EV and distributed PV application access to the power grid, based on the actual home users, the data of household electricity load and the user level transformer are collected and analyzed. At the same time with the peak and valley price, based on the quantitative analysis of the influence of electric cars, solar access to the grid, the interactive applications is put forward. Calculation and interactive analysis results show that the implementation of V2H can not only bring economic benefits to users but also reduce the peak valley ratio and the risk of peak on peak which result on the electric vehicle charging in disorder. TuE05.2 Research on Active Demand Response Based on Multi-agent Simulation pp. 2447-2453 Na Yu Northeast Dianli University Lezheng Yu Northeast Dianli University In view of the characteristics of active demandresponse, a multi-agent simulation system of active demand response behavior is proposed in the paper. We take reside-nt user as an example, a multi-agent simulation system an-d the interaction mechanism contains two kinds of scheduli-ng with electrical equipment is designed. Taking electricity cost minimum as the goal, electricity plan decision mode is established according to operation characteristics of each ki-nd electric equipment and considering the price signals and the user electricity habit; in order to avoid the “rebound peak”, the indicator variables to evaluate the active demandresponse behavior are proposed, taking the maximum powerlimitation as demand response signal and formulating real-ti-me adjustment rules. Taking a residential user as a case, we analyze their participation in active demand response inelectricity plan decision and real-time adjustment and studie-s the influence of electricity usage satisfaction on the use o-f electricity and evaluation indexes. The rationality of the proposed model and method are verified. TuE05.4 Research on Integrated Utilization of Multi-resources Energy in Intelligent Building DC Microgrid Based on OpenADR pp. 2459-2464 XiangtanUniversity Minghui Fan, XiangtanUniversity Jijun Li Genping Wang XiangtanUniversity Shenzhen Polytechnic In distributed energy hybrid power system of intelligent building , Multi-input DC/DC converter has many advantages ,simplifying the dynamic interface to the system for distributed power and playing voltage Boostor Buck more effectively in the system. Based on OpenADR communication protocol and according to electricity prices, the system load can be adjusted by the intelligent controller for the economic optimal goal. Besides, an intelligent building DC Micro-grid simulation in which the Wind-PV-diesel battery hybrid power system also realized will be presented so as to increase accesses of distributed energy. TuE05.3 Study on the Impacts and Analysis of EV and PV Integration Into Power Systems pp. 2454-2458 Cheng Gong Lingzhi Yi State Grid Beijing Power Research Institute Longfei Ma State Grid Beijing Power Research Institute Zhongjun Chi State Grid Beijing Power Research Institute Baoqun Zhang State Grid Beijing Power Research Institute Rui Shi State Grid Beijing Power Research Institute Ran Jiao State Grid Beijing Power Research Institute Shuang Zeng State Grid Beijing Power Research Institute Jianshu Chen State Grid Beijing Power Research Institute TuE05.5 Multi-objective K inetic-molecular Theory Optimization Algorithm W ith Application to Automatic Demand Response pp. 2465-2470 Lingzhi Yi Shengbing Li Chaodong Fan Yahui Wang EV (Electric vehicle) and PV (photovoltaic) load will bring about some influence to the power system when is connected to gird, such as the change of load characteristics, increase the peak valley difference and etc. At the same time the application of inverter will bring about reverse power threat to the opera- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Xiangtan University Xiangtan University Xiangtan University Hunan University Intelligent household as an extension of smart grid in the user side highly integrates loads management and control. Home energy management system (HEMS) with automatic demand 124 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) response (ADR) is a key part of intelligent household, which is able to fit their electricity demand without changing the residents' habits too much. Furthermore HEMS schedule their power consumption to save energy, reduce emission, shift peak load and reduce the financial burden. The characteristics of various electrical devices were analyzed in this paper, and a mathematical model of ADR was established. Multi-objective kinetic-molecular theory optimization algorithm was used to optimize the solution of the ADR model. Implementation results showed that the KMTOA was more accurate and reliable than other algorithms for the complexities of model and data size considered in this study. Compared with some similar algorithms, the multi-objective kinetic-molecular theory optimization algorithm shows more advantages. Research of Electricity Stealing Identification Method for Distributed PV Based on the Least Squares Approach pp. 2471-2474 Nanjing Univ of Science and Technology Xiaodong Yuan Jiangsu Electric Power Company Min-gming Shi Jiangsu Electric Power Company State Power Smart Grid Research Institute Zhansheng Hou State Power Smart Grid Research Institute Min Xu State Power Smart Grid Research Institute As unified communications systems used in the power industry that has special security requirements on the communications industry, the security issues in urgent need. Security issues through the analysis of a typical unified communications system, the communication level, combined with the complex network environment in the power industry, power industry security requirements for unified communications. Reference to domestic and foreign advanced communications security technology and unified communications security issues and the special needs of the power industry, from hardware, software and other aspects, this paper presents unified communications security solutions for the power industry transformer and temperature. TuE06.1 Zhengyang Sun Wang Gang TuE07.1 Bi-level Distributed Optimal Dispatch of Micro Gird Clusters Based on Mutual Communication pp. 2480-2485 Jie Yu Southeast University Yiping Jiao With the photovoltaic (PV) subsidy policy of China, the installed capacity of distributed PV is increasing rapidly. However, as the amount of subsidy is in proportion to PV power generation, few dishonest users take some methods to increase the value of PV meter and get extra subsidy. These behaviors are called electricity stealing of PV. This paper introduces four typical methods of electricity stealing of PV and proposes an electricity stealing identification method using measured value of PV meter and gate meter. The least squares approach is adopted to fit the linear functions between PV meter data and gate meter data of electricity stealing model and none-electricity stealing model. The slopes of the two linear functions are different, which can be used to identify the behavior of electricity stealing. Finally, simulations are performed, and the results show that the method based on the least squares approach can identify the stealing behavior effectively if the solar array simulator is used. Southeast University Xiaolong Wang Ming Ni Southeast University NARI Technology Co. Ltd Micro Gird Cluster (MGC), connecting to the medium or low voltage distribution network, usually contains certain number of Micro Grids, distributed generators, energy storages and loads. Considering coordinated operation in MGC, this paper proposes a hierarchical control architecture- the upper layer operated in distributed mode among multiple MGs and the lower layer were controlled by each micro grid center. This hierarchical architecture not only shows the excellent features of distributed control, but also integrates the advantages of centralized control. According to this hierarchical architecture, bi-level distributed optimal dispatch of MGC is analyzed. With the aim of minimizing MGC total costs in upper layer and minimizing each Micro-Grid costs in lower layer, bi-level op- TuE06.2 timal mathematic model take global and local aims into account synthetically. The distributed primal-dual sub-gradient Research on the Security of Unified Communications System’s Applications in the Power System pp. 2475-2479 Liang Zhu State Power Smart Grid Research Institute Lin Peng State Power Smart Grid Research Institute Haiyun Han State Power Smart Grid Research Institute Xingchuan Bao State Power Smart Grid Research Institute algorithm is designed to solve the upper layer optimal model, alternating gradient iteration algorithm for the lower optimization model. Simulation cases show that bi-level distributed optimal mathematic model successfully fulfill the aim of coordinated operation in MGC, and distributed primal-dual sub-gradient algorithm is an effective solution to this optimal model. 125 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuE07.2 TuE07.4 Fast Calculation of Available Transfer Capability Incorporating Uncertainty of W ind Generation pp. 2486-2490 Yunfei Chu Hohai University Zhinong Wei Hohai University Guoqiang Sun Hohai University Yichi Li Research on Reliability Evaluation Model and Path Optimization for Power Communication Network pp. 2495-2500 Yunfei Guo Ming Xu Hohai University power system derived from intermittent and randomness of wind speed, which has impact on calculation of power system index such as ATC. In this paper, a probabilistic ATC calculation model containing doubly fed induction generator is proposed. Then, a fast ATC calculation method based on UT technique is proposed, which has proved to be efficient with a high accuracy, and it is convenient to deal with correlations among input variables. Finally, effectiveness and practicality of the proposed method are verified with test examples of IEEE-30 system. TuE07.3 Researches on Data Processing and Data Preventing Technologies in the Environment of Big Data in Power System pp. 2491-2494 State Grid Smart Grid Research Institute Min Xu State Grid Smart Grid Research Institute Wantian Cao State Grid Smart Grid Research Institute Peng Gao Pactera Technology International Ltd Article based on the topological structure of power optical communication system, analyzes the main factors that affect the reliability of optical transmission equipment and optical fiber links, and consider the bearer of the electric power business of importance weights. At the same time, a kind of electric power communication business route evaluation model and risk calculation method is proposed, the communication risk probability of power business can be early warning based on the proposed method, and through the GMPLS dynamic routing constraint algorithm with time delay parameters, the traffic channel of the communication risk is optimized. So preventive measures can be taken in advance to reduce the risk of power business interruption. Finally according to the topological structure of Subei stable system as an example, the business risk path simulation and verification calculation and risk aversion can be carried through the defense system of power communication security. This method can automatically determine the business risk and realize path rerouting automatically through business communication network dynamic routing constraint algorithm to avoid the risk in advance, but also can provide important reference for the development of the security and stability of power grid strategy. Wind power has brought about many uncertain factors to Nige Li State Grid Smart Grid Research Institute TuE07.5 Dynamic Partitioning Technology Based on Trend Information of Bulk Power System pp. 2501-2505 State Grid Smart Grid Research Institute In this paper, we mainly focus on the problems of the data Yi Tang Southeast University Lei Shi Southeast University processing and data security in the environment of the elec- Mingming Cai, Southeast University tricity big data systems. Firstly, we focused on the security of Feng Li Southeast University big data storage, as well as the big data applications, including Dengfeng Li Chongqing Power Corporation Guoping Liu Chongqing Power Corporation the classification, aggregation and data mining demands. We proposed several practicable schemes to the big data applica- Xiancheng Ren tions. After that, we studied on the problem of the privacy prevention in big data processing. In this paper, we analyzed Trend information of the bulk power system reflects the operating status of the power grid and could be utilized to predict the threats to the security and stability. A new technology called dynamic partitioning is proposed to increase the power system’s stability based on the trend information in this paper. Firstly, the emergency state of power system is identified according to some trend information, which is related to some the demands of the big data privacy prevention in smart grid, and also proposed several methods. Based on the previous researches, we put forward the outline of the research hotspots for the data protection. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China State Grid Electric Power Research Institute 126 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) factors such as equipment overload, voltage over-limit, low frequency oscillation, short-circuit current over-limit and so on. Then some control methods could be used as dynamic partitioning technologies to prevent stability problem under the emergency condition, including transferring load, switching standby lines, changing the operation mode of electromagnetic looped network and so on. Finally, auxiliary decision-making strategy is proposed to specify which dynamic partitioning scheme should be selected among the optional solution space. The simulation results illustrate the effectiveness and rationality of the proposed method. communication delay on current differential protection with a probabilistic method, and a false-trip probability model is proposed. First, the mechanism of false-trip of current differential protection is introduced and the quantitative relationship between differential current and power grid operation state and communication delay is derived. Then a false-trip probability model based on current differential protection action criterion is proposed with a probabilistic method. Simulations show the validity of the model. Based on the false-trip probability model, the key factors affecting false-trip of current differential protection are analyzed, and some useful conclusions are drawn transformer and temperature. TuE07.6 TuE07.8 Study of the Evaluation and Design Method for the Control Structure of Power System Stability Control System pp. 2506-2511 Yuhang Liu Model the Real-time Failure Rate of Protection Channels Due to Communication Latency and Bit Error pp. 2517-2522 NARI Technology Co. Ltd Ming Ni NARI Technology Co. Ltd Zhou Li NARI Technology Co. Ltd Wenjie Yu NARI Technology Co. Ltd Manli Li Ming Ni The regional security and stability control system is an important tool to ensure the safe and stable operation of modern power system. The communication system can provide information exchange among the stations for the regional security and stability control. Hence, the reliability of communication system is one of the important factors that need to be considered in the design of the control system. In this paper, firstly, the regional security and stability control system is divided into centralized control structure and distributed control structure using the decision-making method. Secondly, the evaluation index of the communication status for the control system is given. Thirdly, the differences of the communication networks based on centralized control and distributed control structure are analyzed comparatively. And finally, the design method of the control system based on centralized control as well as distributed control structure is proposed. NARI Technology Co. Ltd NARI Technology Co. Ltd Yi Tang Southeast University Jie Wu Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications Yingjun Wu Nanjing University of Posts and Tele The safe and reliable transmission of relay protection signal is essential to the normal operation of relay protection device. Based on the characteristics of the protection signal transmission, this paper proposes a method to model the real-time failure rate of the protection communication channel introduced by the communication latency and bit error. First of all, by using the decision tree method and processing the history fault data of the protection channels, communication equipment, board equipment and various function blocks, get the channel failure rate based on historical data. On this basis, according to protect channel signal delay and error performance requirements for the protection signal, propose a real-time channel failure rate model due to communication time delay and bit error. Finally, the application and effectiveness of the proposed channels real-time failure rate model are demonstrated on a typical example. TuE07.7 TuE07.9 False-tirp probability model for the current differential protection considering power grid operation state and communication delay pp. 2512-2516 The Achieve of Power Manager Application Honeypot Based on Sandbox pp. 2523-2527 ManliLi NARI Technology Co. Ltd. MingNi NARI Technology Co. Ltd. YuecenLi NARI Technology Co. Ltd. YiTang Southeast University YingjunWu Nanjing Univ of Posts and Telecommunications Qian Guo Jie Fan Nige Li State Grid Smart Grid Research Inst. State Grid Smart Grid Research Inst. State Grid Smart Grid Research Inst. Honeypot is a common method of attack capture, can maximize the reduction of cyber-attacks. However, its limited application layer simulation makes it impossible to use effectively in power system. Through research on sandboxing technology, The paper studies the impact of power grid operation state and 127 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) this article implements the simulated power manager applications by packaging real power manager applications, in order to expand the honeypot applied range. ony algorithm to find the optimal circuitous route. Simulation results show that the method is fast, which can accelerate the recovery of the communication network. Besides, this paper does some research on the dead end problem, and analyses relationship between degree of adjacency and ratio of coming to a dead end. The result shows that the efficiency of ant colony algorithm can be improved only if it tries to avoid coming to dead ends. TuE07.10 Novel AGC Strategy Considering Communication Failure Possibility for Interconnected Power Grids pp. 2528-2531 Zhou Li Southeastern Univ. Jie Yu Southeastern Univ. Haoyu Qi Ming Ni TuE07.12 Research and Application of Interactive Technology between Microgrid and Distribution Grid pp. 2536-2538 Nanjing University of Science and Tech. Xiaohui Xu NARI Technology Inc. The conventional automatic generation control (AGC) strategy only takes the economic factors into consideration. However, for interconnected power grids, under the condition of communication failure, there will be high risk that the AGC control signal be blocked and then some AGC units will not adjust the generating power following the load fluctuation due to the interrupt of the control signal. In this paper, the strategy of economic dispatch (ED) as well as load frequency control (LFC) has been investigated and a novel AGC strategy considering the communication failure possibility has been proposed. The ED control of the novel AGC strategy is designed to drains the power margin of those AGC units with high risk of communication failure according to the load forecasting and the evaluation of communication system. While the LFC strategy of the novel AGC strategy is designed to employ those AGC units with low risk of communication failure to balance the unpredictable short-term load fluctuation. As a result, the communication failure would cause slightest affect to AGC. The IEEE 118-bus benchmark system is employed to verify the effectiveness of the novel AGC strategy, and the simulation results indicate that, the novel control strategy can improve the dynamic performance, stability as well as economic performance of AGC under the condition of communication failure. It has excellent economy and engineering application value. The China Electric Power Research Inst. Hao Ding State Grid Ningxia Electric Power Company Longyu Yang State Grid Ningxia Electric Power Company Tiantian Wu School of Southeast Univ. Based on 330kWp Yinchuan solar power station, the overall framework of interactive microgrid was firstly designed. Then subsystems including microgird monitoring system and energy storage system were constructed. According to our interactive microgrid system, the output and operation mode of the photovoltaic and energy storage system can be adjusted through the energy management system to smooth the output curve of photovoltaic and supply power for station load at off-grid status. The wireless communication based on GPRS is used between interactive devices (including isolation devices) and the Ningxia electric power company. Finally, through constructing and upgrading necessary facilities, the microgird demonstration project was built, which provided a good platform for the study of microgrid and the practice interactive test with distribution grid. The renewable energy and loads can be integrated as much as possible into the platform. Meanwhile, the platform shows excellent energy-saving characteristics due to the use of electric load, which greatly reduce the energy losses in the testing process. TuE07.13 TuE07.11 Reliability Assessment of Line Protection Based on Reliability Graphs and Monte Carlo Simulat i on pp. 2539-2544 Analysis of Ant Colony Algorithm for F inding the Optimal Circuitous Route in the Communication Network of Power System pp. 2532-2535 Xin Chen Zhiqian Bo Yingjun Wu Nanjing Univ. of Posts and Tele. Tsinghua Univ. Manli Li NARI Technology Inc. Xuji Group Corporation Ming Ni NARI Technology Inc. Xinzhou Dong Tsinghua Univ. Shenxing Shi Tsinghua Univ. Qiang Zhang A reliability assessment methodology for transmission line protection systems is presented, which is based on a probabilistic modeling of the protection system’s successful operation, The communication network of power system is often damaged after a disaster. To solve this problem, this paper uses ant col- November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China State Grid Huaian Power Supply Company 128 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) tablished; information entropy theory has been introduced to weigh the comprehensive impact of these six meteorological factors in real-time objectively and quantitatively; linear penalty function has been used in amending meteorological entropy value to define comprehensive meteorological factors, which can quantify the influence weather risk sources have on dispatching operation. Finally, the model's validity is verified based on the practical calculation of Guangzhou City, the result showing the model can reflect the actual weather situation of the devices in the being operated area and accurately assess the potential risk which multiple meteorological factors have on power grid dispatching operation. Through the joint between the model and numerical weather prediction, automation level of risk sources identification in power grid dispatching operation is enhanced greatly. So far, the model has been put in use in Guangdong Power Grid. and considering both the availabilities of the line protection hardware and the failure function of the current differential protection caused by communication delay. The system successful operation is described by reliability graphs, and solutions are obtained from Monte Carlo simulation. The developed methodology is applied to three protection schemes to show its effectiveness. TuE07.14 Z igBee W ireless Networking for the Intelligent Protection Center Research pp. 2545-2548 Fanfan Ding Zhiqian Bo Dahai Zhang Tsinghua Univ. Xuji Group Corporation TuE07.16 Beijing Jiaotong Univ. Xin Chen Tsinghua Univ. Xinzhou Dong Tsinghua Univ. Shenxing Shi Tsinghua Univ. Communication Channel Reconstruction Based on W ireless Sensor Network for Pilot Differential Protection pp. 2554-2560 This paper introduces the basic structure and functions of the Intelligent Protection Center, and besides, it describes rapid reconstruction of power grid and rapid recovery of communication channel, both based on the Intelligent Protection Center. In this paper, we have compared the characteristics of various wireless communication modes and discussed unique advantages of ZigBee technology in reconstructing of power system after disaster. We intentionally proposed the rebuilding of the wireless channel based on the ZigBee technology for "information island" where there was not any circuitous channel around, and have carried out the simulation about this project. Entropy Theory Based Weather Risk Source Quantified Model for Power Grid Dispatching pp. 2549-2553 Guangdong Power Grid Co., Ltd Zhu Chao Guangdong Power Grid Co., Ltd Huazan Zhong Guangdong Power Grid Co., Ltd Min Xie South China University of Tech. Yijiang Yin South China University of Tech. Mingbo Liu South China University of Tech. Hunan Province Power Company of State Grid Liqiang Xu Hunan Province Power Company of State Grid Xu Chen Huazhong University of Science and Tech. Xianggen Yin Huazhong University of Science and Tech. Bin Yu Huazhong University of Science and Tech. This paper discusses communication channel reconstruction based on wireless sensor network for pilot differential protection. Considering communication characteristic of WSN module, this paper further studies and analyzes redundant arrangement and communication performance under hazard from the perspective of practical application. A redundant arrangement algorithm of nodes based on reliability and optimal cost of the whole communication network is proposed. And the influence of communication distance, line span and hop counts to communication delay and is studied under ADOV routine by pilot differential protection digital simulation test. The results of pilot differential digital simulation test shows that emergency protection channel constructed by wireless sensor network which uses redundancy arrangement method to do network panning can achieve strong reliability and meet the need of pilot differential protection under extreme disaster. TuE07.15 Jianing Liu Wei Pan Weather is one of the main risk factor in power grid dispatching operation and this paper studies how to identify and establish a model of weather risk sources during power system dispatching operation for smart grid. A qualified weather risk sources model, which can comprehensively reflect temperature, wind speed, visibility, rainfall, relative humidity, thunder and lightning harm degree these six meteorological factors, is es- 129 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) (ESS) PI controllers’ parameters. The performance of ESS active and reactive power PI controllers is very important in applying ESS to improve power systems stability in smart grid in which the ESS is required to adjust its active and reactive power quickly. Therefore,an improved PSO algorithm with the idea of the simulated annealing algorithm is applied to optimize the ESS active and reactive power PI controllers’ parameters. On the basis of PSO with chaotic initialization, iteration by adding chaos disturbance and adaptive inertia weight factor, the algorithm becomes more efficient because of both location limits and step out locally optimal solution by adding the idea of the simulated annealing. The nonlinear simulation results test and verify the effectiveness of optimization by a 4-machine power system installed an ESS with optimization PI controllers. F: Energy Internet and New Emerging Technologies TuF01.1 Analysis of Technical Strategies Towards a Low Carbon Electricity System in Europe pp. 2561-2565 Yue Zhang Xi,an Jiaotong Univ. Xiuli Wang Xi,an Jiaotong Univ. Wentao Zhang Xi,an Jiaotong Univ. Furui Hou Xi,an Jiaotong Univ. Zechen Wu Xi,an Jiaotong Univ. Facing energy crisis and climate changes, transition towards a low carbon electricity system has aroused great concern around the world. As pioneer in CO2 emission reduction, European Union (EU) is planning all-round transformation in electricity system. This paper analyses and concludes European decarbonization strategies from four aspects, with the aim to explore approaches to a low carbon electricity system. At generation level, exploitation of large scale renewable energy sources (RES) is the key to a low carbon energy supply. At transmission level, a pan-European transmission grid is essential for the integration and transportation of RES across Europe. At consumption level, great importance will be attached to demand response (DR) to reduce supply variability. At technology level, promising breakthrough technologies are summarized. Inspired by European plans, the paper ends by providing suggestions for a future low carbon electricity system in China. TuF01.3 A Daily Operation Arrangement and Peak Load Regulation Algorithm Based on Multi-state Renewable Energy Simulation pp. 2571-2575 Optimization of ESS PI Controllers Parameters Based on PSO in Smart Grid pp. 2566-2570 Hohai Univ. Chenyu Zhao Hohai Univ. Feng Wu Hohai Univ. Hongying Zhao Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Jingjing Shi Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Xiaoxue Jiang Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Junhua Deng Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Yue Li Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. An improved PSO is proposed to tune Energy Storage System November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Xiuli Wang Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Yue Zhang Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Zechen Wu Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Furui Hou Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. Large-scale integration of wind power makes the peak load regulation become more and more serious. As a result, the analysis of daily operation manner plays an important role in determining the power architecture. Based on traditional generation expansion planning method focusing on economic and reliability indices, this paper proposes a daily operation arrangement and peak load regulation algorithm, which is established on the basis of multi-state renewable energy simulation, and is used to test the running feasibility of the power generation planning result. The algorithm proposes a sequential multi-state wind generation model established on a Markov process with state transition matrices and initial distribution based on historical data. Also, the algorithm proposes an efficient multi-state energy function forming method based on equivalent energy function method to analyze the power and energy balance and peak load regulation of the system using a deterministic production simulation. So the algorithm can ensure the economy, reliability and feasibility of the power generation planning. Test system was used to verify the rationality and feasibility of the proposed models and algorithm and the results of this paper may provide some suggestions for the generation planning. TuF01.2 Linjun Shi Wentao Zhang 130 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuF01.4 TuF01.6 Load Prediction for Large-Scaled HAWT Based on a Nonlinear Structural-Aerodynamic Coupled Method pp. 2576-2580 Sustainable value analysis of smart grid and a prospective case study of China grid 2020 pp. 2587-2590 Hongyu Lin Harbin Institute of Tech. Pin Lyu Northwestern Polytechnical Univ. Bo Yu Harbin Institute of Tech. Mingfu Liao Northwestern Polytechnical Univ. Bo He State Grid Energy Research Inst. Yaojie Yin Northwestern Polytechnical Univ. Han Huang State Grid Energy Research Inst. Load prediction is becoming difficult due to the larger, lighter and more flexible blades of large-scaled horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT), which leads to the nonlinear aeroelastic responses. Based on geometrically exact beam (GEB) theory for blade structural dynamics, a free-vortex wake (FVW) model for the prediction of unsteady aerodynamic loads and a partitioned loosely coupled methodology to exchange the data at the interface, a nonlinear FSI model has been developed in this study. Through comparison of NREL UAE Phase VI experimental data and the load predicted by the nonlinear model, the capability to accurately predict the aerodynamic loads is validated. The nonlinear beam model is also validated by several cases which all show a good agreement with results obtained by other authors. Finally, dynamic responses for NREL 5 MW RWT are estimated and compared with results from linear model. The results show that the coupled method is capable of evaluating blade nonlinear responses for large-scaled HAWT. Reduce the consumption of exhaustible natural resources is an important feature of smart grid. By integrating power generated from renewable resources and implementing environmentally benign end-devices such as electric vehicles, smart home appliances and etc, smart grid creates sustainability values. This article proposes a value analysis model of smart grid from the view point of sustainable development. The EI-serafy model is adopted to measure the user-cost of exhaustible natural resources. Then, the sustainable value of smart grid is quantified to be the reduction of user-cost of exhaustible natural resources that consumed in power industry. A prospective case study of China grid 2020 demonstrates that smart grid would creates significantly sustainable value by reducing the consumption of exhaustible natural resources. TuF02.1 TuF01.5 Energy policy and market space research in electricity of European Commission pp. 2591-2595 The Dynamic Stability Analysis of W ind Turbines under Different Control Strategies pp. 2581-2586 Yaojie Yin Mingfu Liao Pin Lyu Northwestern Polytechnical Univ. Northwestern Polytechnical Univ. Northwestern Polytechnical Univ. The control strategies have influences on the dynamic stability of modern wind turbines. This article presents a theoretical investigation on this topic. The investigation is motivated by a vibration measurement of wind turbines in a wind farm. The mechanisms of control strategies influencing the dynamic stability have been discussed and the stability enhancement by means of time delay in pitch control is investigated. The results show that the optimum control of rotational speed for maximizing energy capture below rated power can improve the dynamic stability by suppressing the axially unstable vibrations of the wind turbines. At above rated wind speed, the control mode of fixed-speed variable-pitch can cause unstable axial vibrations of the wind turbines; variable-speed variable-pitch can suppress the unstable vibrations. Additionally an appropriate time delay in pitch control can effectively enhance the dynamic stability of wind turbines. Fuqiang Zhang State Grid Energy Research Inst. Junshu Feng State Grid Energy Research Inst. Jianhua Bai State Grid Energy Research Inst. Yanming Jin State Grid Energy Research Inst. According to the EU's energy strategy, the future EU will reduce the size of conventional fossil fuel generation capacity, gradually decommission nuclear power, and while vigorously develop renewable energy. However, the EU's electricity load will continue to grow. Due to the randomness and intermittent of the output of renewables, and the consequent lower effective capacity, there are needs to accept external power. Based on the future forecasting of power load and power installed capacity change by Entso-E, market space of electricity of the European Union (EU) and Germany were estimated. The results gave preliminary judgment of market space of electricity for the intercontinental transmission vision between Asia and Europe. 131 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) TuF02.2 TuF03.1 Evidence of Significance of Graph Energy Interlinks in Topological Form of the Power Grid pp. 2596-2602 Research on Multi-objective Optimization Coordination of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle and Distributed Generation pp. 2608-2613 Xin Li Univ. of Oklahoma Milad Javadi Univ. of Oklahoma Boshi Zhao Univ. of Oklahoma Di Wu Univ. of Oklahoma John N. Jiang Univ. of Oklahoma Huiling Li China Electric Power Research Inst. Chao Zheng China Electric Power Research Inst. Xin Zhang China Electric Power Research Inst. Xiang Chen China Electric Power Research Inst. Xiqiang Chang State Grid Xinjiang Graph energy is the form of energy often used in a simple sysWith large integration of plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) and distributed generation (DG), a good regulation ability of the power grid is required for PHEVs random charging and DG’s intermittency. Considering safe and economic operation of the power grid and charging cost of PHEV owners, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) is a multi-objective and multi-constrained optimization problem by nature. A multi-objective optimization coordination model is proposed for PHEV and DG integration. Objectives of this model are maximum synthetic load ratio, minimum node voltage deviation and power loss ratio, lowest V2G service cost of the grid and charging cost of PHEV owners. By dynamic regulating PHEV charging and discharging power, power fluctuation between load and DG can be matched well and the impact of DG intermittency on the power grid will be decreased. A real 10kV feeder is simulated. tem of physics, typically expressed with the potential energy in springs and the kinetic energy of interlinked moving particles. In this paper, we present a study to show a new piece of evidence of the significance of graph energy interlinks in topology of the power grid, which is formed under the specific reliability principles of power system engineering. Particularly, based on the comparisons of the graphs, generated with a modified graph energy based layout method, to the physical layouts of three real power grids, it is found that the generated graphs are highly consistent with the actual layouts. The result is an important piece of evidence, showing that the graph energy interlinks play an important role in the topology formation of the power grid. TuF03.2 TuF02.3 Research on Quantitatively Evaluating System Acceptance Capacity of Electric Vehicles Considering Coordinated Strategy pp. 2614-2619 Design of A Hierarchical Infrastructure for Regional Energy Internet pp. 2603-2607 Dan Liu Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Xiaodong Yuan Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Qiang Li Jiangsu Electric Power Research Inst. Motivated by the success of the information technologies and new energy technology, the energy internet comes into being. Qi Zuo North China Electric Power Univ. Ming Zhou North China Electric Power Univ. Hailei He China Electric Power Research Inst. Caihao Liang China Electric Power Research Inst. Qinyong Zhou China Electric Power Research Inst. Wenjie He This paper focus on the implementation of regional energy Beijing Hyundai Technical Centre internet. Firstly the hierarchical architecture of regional enerBy studying on the coordination between the system reliability level and the EV grid-integration scale, the system acceptance capacity of EVs can be assessed from a new point of view. In this paper, a model for the charging loads of three types of EVs and a coordinated strategy with time-of-use price (TOU) are established. Then, the maximum acceptable capacity, reliability sensitivity and other indicators are proposed to quantitatively characterize the system ability to accommodate EVs. Subsequently, by combining the acquired EV charging load gy internet is proposed, secondly the collaborative optimization scheduling of multi-energy sources is clarified, then the framework of energy management and public service center is given, finally the construction of demonstration in Jiangsu is introduced. November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China 132 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) algorithm with the traditional reliability assessment method, the quantitative evaluation approach of the system acceptance capacity of EVs considering coordinated strategy is proposed. In order to improve the simulation efficiency, the Latin hypercube method is used to sample the system state. The feasibility of proposed indicators and method is verified with test results of the IEEE24-RTS system. Furthermore, different cases are comparatively analyzed with and without the coordinated strategy, respectively. Results prove that the coordinated strategy can improve the system reliability level, and greatly enhance the system acceptance capacity of EVs. TuF03.4 Frequency Regulation Strategy for Decentralized V2G Control pp. 2626-2629 Lijuan Chen Southeast Univ. Yuxuan Jiang Southeast Univ. Xiangjun Li China Electric Power Research Inst. Liangzhong Yao China Electric Power Research Inst. Xiaohui Xu China Electric Power Research Inst. Tianxiang Geng Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) has the potential to provide the frequency regulation service. In this paper, a frequency regulation strategy for decentralized V2G was proposed, which not only guaranteeing the primary and secondary frequency regulation, but also considering the charging demands from EV customers. According to the state of charge (SOC) of each EV, two kinds of participation patterns were presented. One is available anytime pattern. The customers can use their EVs at any time. In this pattern, EVs only participate in the primary frequency regulation. Another is fixed time pattern. EVs can only be used at a fixed time. EVs can easily switch between the primary and secondary frequency regulation according to the current SOC. Simulations on a two-area interconnected power system with wind power have indicated the effectiveness of the proposed methods. TuF03.3 Vehicle-to-grid Participating in Frequency Regulation under Distributed Cooperative Control Based on Cloud Service pp. 2620-2625 Xiaolong Wang Southeast Univ. Jie Yu Southeast Univ. Jianqiang Hu Southeast Univ. Shumin Fei Southeast Univ. Jinde Cao Southeast Univ. State Gird Ningxia Electric Power Company The smart grid emphasizes interaction between grid-load-generation, and the electric vehicle (EV) is a kind of favorable load with controllable ability. These EVs could participate in frequency regulation when the grid is suffering from imbalance between supply and demand. According to the requirement of power dispatching center, these EVs could inhibit charging and postpone the electricity demand to other time. It could also transmit electrical power to grid reversely. However, individually frequency response of each independent EV would cause excessive communication flows, and create new impact to power grid. This paper based on cloud service, assembled every EV in an area into a cluster agent, and proposed a kind of distributed cooperative control strategy to harmonize their frequency response. Firstly, the power dispatching center issues the demand request to a leader node named cooperative pinning node. Then, such pinning node releases the adjustment demand to the network consisted of EV cluster agent nodes. Through communication and calculation on each agent nodes, the goal of fair EV load shedding would reach. Case study shows that the method could organize multiple EV cluster agents effectively and the system would be regulated faster than the original system with vehicle-to-grid participating. TuF03.5 Research And Discussion On Electric Vehicles Charging Cable Testing Methods In Different Standard Systems pp. 2630-2633 Xin Li Technology Center Nari Group Corporation Hongsheng Xu Technology Center Nari Group Corporation Pan Dai Technology Center Nari Group Corporation Yichuan Bai Technology Center Nari Group Corporation Jinda Zhu Technology Center Nari Group Corporation Yan Chen Jiangsu Academy of Safety Science and Technology With the increasing use of plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs) which has environmental and economic benefit, some institutes have published some standards to verify the quality of electric vehicles cables. However, these standard systems have some differences confusing the industry manufacture and customs. In this article, some similar and difference are founded and discussed in order to clarify the test detail in UL and TÜV electric vehicles charging cable standards. The test methods of PEV cables are stated clearly to help cable industry produce and inspect useful electric vehicles cables. 133 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) the effectiveness of the algorithm. This algorithm can overcome the shortcoming of the particle swarm optimization which limited to the local optimum, and realize the orderly charging and discharging of battery charging and swapping station, it can finally conduct the function of peak load shifting of grid load. TuF03.6 EV Battery SOH Diagnosis Method Based on Discrete Fréchet Distance pp. 2634-2639 Jiao Dongsheng Beijing Electric Power Research Inst. Beijing Electric Power Company Wang Haiyun TuF03.8 Beijing Electric Power Research Inst. A Reactive Power Evaluation Model for EV Chargers Considering Travelling Behaviors pp. 2646-2651 Beijing Electric Power Company The power battery of electric vehicle may be limited by battery safety issues and power problems. The key points of this paper are firstly it combines discrete Fréchet distance method with discharge curve identification method, and then it proposes a kind of new state of health diagnose method base on line testing platform. Through the CAN communication module, the system could control the power battery to finish online full charge and discharge test. And also the system could get the actual operational status data to build life cycle databases of electric vehicle, which can predict the state of health diagnose. The results of the SOH could guide power battery safety assessment and balance maintain. Through analyzing simulation results between the SOH diagnose results with returned test data results, qualitative indicates the decline of EV battery. Ting Yu XiuPing Yao Mingshen Wang Yunfei Mu Ruiye Liu Harbin Institute of Technology Ke Hua Jian Meng Key Laboratory of Smart Grid of MinKey Laboratory of Smart Grid of Ministry of Education Xiaohong Dong Key Laboratory of Smart Grid of Ministry of Education A reactive power evaluation model is proposed to estimate the available V2G capacity of reactive power provided by EV chargers during a day considering the travelling behaviors of EV users. Firstly, a generic EV charger model (GECM) is developed to describe the reactive power response characteristic of EV charger. Then, considering the travelling behaviors of EV users, a monte carlo simulation (MCS) method is implemented to build the reactive power evaluation model. Finally, the available reactive power from EV chargers is analyzed and compared under two different charging strategies (dumb charging and smart charging). Simulation results show that the reactive power evaluation model can determine the available reactive power capacity for V2G along a day, which can support the operation of the power system. Heilongjiang Electric Power Company State Grid Corporation of China As the application of electric vehicles expands, their charging power demand will influence the operation of the power grid. This paper firstly considers the relevant factors which influence the charging power demand; by using the Monte Carlo method to calculate the large-scale electric vehicle charging power demand. Based on the problem that the large-scale electric vehicle’s disordered charging may affect the stability of the power grid, this paper considers the characteristic of the electric vehicle battery charging and swapping station, which can easily realize charging and discharging dispatching, taking charging and discharging power in different periods as controlled object, taking the inhibition of load fluctuation and load peak and offpeak difference as objective function, we can build a mathematical model of dispatching strategy and use the multi-swarm cooperative particle swarm optimization to achieve the daily dispatching strategy optimization. Based on the daily load curve of a certain region, the simulation’s result verifies November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Key Laboratory of Smart Grid of Min- istry of Education Dispatching Strategy Optimization for Orderly Charging and Discharging of Electric Vehicle Battery Charging and Swapping Station pp. 2640-2645 Harbin Institute of Technology State Grid Xinjiang Electric Power Company istry of Education TuF03.7 Ting Gao China Electric Power Research Inst. TuF03.9 A Probabilistic Evaluation Method to Voltage Profile of Distribution Network Considering the EV Charging Choice pp. 2652-2657 Tong Wang Kunda Yu Nari Technology Development Limited Company Wei Feng Kunda Yu Nari Technology Development Limited Company Xiaohong Dong Tianjin University, The Key Laboratory of Smart Grid of Ministry of Education The and 134 interactions between the the distribution network transportation system become more and The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) more close due to the electric vehicles charging in the fast charging stations which are considered as a new kind of public service infrastructure and a special power load. In this paper, a probabilistic evaluation method to voltage profile of distribution network considering the electric vehicle charging choice is proposed. Firstly, a special-temporal distribution of the charging load of electric vehicles is determined considering the uncertainties of battery characteristics, travelling behaviors, and the charging choices. Then, the temporal distribution of the fast charging station load is determined. Finally, the voltage profile of distribution network is evaluated in the test case. What's more, simulation results illustrate that the effect of various electric vehicle charging choices on the voltage profile, by comparison. TuF04.1 Power Grid Diagram Automatic Mapping Algorithm for the Radial Distribution Feeder pp. 2663-2667 Boxi Zhou State Grid of Electrical Technology Coll. Youpeng Fan State Grid of Electrical Technology Coll. Hui Jing State Grid of Electrical Technology Coll. Hongwei Zhang State Grid of QingDao Power Supply Company Xinpei Hao Electrical Engineering Coll. of ShanDong Univ. This paper takes CIM_SVG based radial distribution feeder as the research object and designs an automatic mapping algorithm. Firstly, feeder’s branches belong to different levels are preliminarily arranged in vertical and horizontal direction according to CIM_SVG based data. Then, a lever-to-lever trunk-branch model and corresponding branch-regional model which confirm the object oriented programming (OOP) are proposed. By utilizing the models proposed, the extremely asymmetrical branches and the overlap/cross regions in the preliminary mapping are identified and eliminated. Finally, the mapping of a 10kV radial distribution feeder is taken as an example to demonstrate and validate of the algorithm. It is shown that the algorithm proposed is able to draw the typical distribution network in few seconds and can be expanded to the use of other application in the distribution network visual analysis. TuF03.10 Optimal Matching Strategy Based on Electric Vehicle Contactless Charging Compensation Model pp. 2658-2662 Shuang Zeng Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Yuan Jin Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Xiulan Liu Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Cheng Gong Electric Power Research Inst. TuF04.2 State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Longfei Ma Electric Power Research Inst. Research of Marketing-Distribution-Dispatching Integrated System in Rural Grid pp. 2668-2671 State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Compensation mode has an important influence on the efficiency and power characteristics of contactless charging system. Analyze the necessary of power compensation for the loosely coupled transformer based on electromagnetic inductive contactless charging system structure of electric vehicle. By analyzing the four kinds of compensation models, the S/S model is selected due to its high system efficiency and easy control, and the matching relationship between the system frequency and the equivalent load is put forward. In the premise of considering the system efficiency and the user experience, the efficiencypreferred operating frequency selection strategy of the electric vehicle electromagnetic inductive contactless charging system is proposed, which contributes to produce a new idea to maintain the system to work efficiently by the operating frequency adjusting. The correctness of the analysis and optimization strategy is verified by examples. Lu Wang Nari Group Corporation State Grid Electric Power Jin Zhu Nari Group Corporation State Grid Electric Power Research Institute Research Institute With the development of smart grid, the key to solve the problem of intelligent development of rural grid is information integration. This paper proposes to make a MarketingDistribution-Dispatching integrated System in rural grid with the data acquisition and analysis of the electric energy data acquisition system, dispatching and distribution integrated system and marketing system, by the use of information sharing and data exchange technology. This system which contains power grid operation and enterprise management will provide technical support for enhancing the leader’s capacity of management and decision-making. 135 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) algorithm is proposed to produce the optimal scheduling strategy of the ADS, and the solution algorithm for ADS is introduced in detail. Finally, the case study demonstrates the validity of the proposed optimal scheduling model and the IHS algorithm for ADS. TuF04.3 A Study on Short-term Trading and Optimal Operation Strategy for V irtual Power Plant pp. 2672-2677 Chunfa Dong North China Electric Power Univ. Xin Ai North China Electric Power Univ. Shuai Guo North China Electric Power Univ. Kunyu Wang North China Electric Power Univ. Yiran Liu North China Electric Power Univ. Le Li North China Electric Power Univ. TuF04.5 Pseudo-Sequential Monte Carlo Simulation for Distribution Network Analysis with Distributed Energy Resources pp. 2684-2689 A virtual power plant (VPP) model, which consists of a wind power plant, interruptible loads, a pumped storage plant and a gas turbine, is built considering the uncertainty of the power output of renewable energy sources (RES) as well as the participation of demand response (DR) resources. Multi-scenario method is used to deal with the uncertainty of day-ahead market price and power output of wind power plant. A short-term trading model, which is based on multi-stage stochastic programming with the objective of maximization of VPP bidding profits in dayahead market combined with penalty in balancing market, is constructed considering the characteristic that the uncertainty of stochastic variables reduces when time approaches. It is shown that the model constructed could notably promote the certainty gain of VPP. Optimization Schedule of Active Distribution System Based on Improved Harmony Search Algorithm pp. 2678-2683 Xi’an Univ. of Technology Fuping Yan Xi’an Univ. of Technology Lupeng Chen Xi’an Univ. of Technology Kaiyu Wang Xi’an Univ. of Technology Yang Lei Xi’an Univ. of Technology Southeast Univ. Yu Liu Southeast Univ. Multi-phase Distribution State Estimation W ith Only Direct Measurements pp. 2690-2694 The optimization schedule strategy of the active distribution system (ADS) is the core technology required to actively manage distributed energy resources (DERs) and to guarantee the economical utilization and safe operation of renewable energy generation. This paper investigates an optimal scheduling model for the ADS on the basis of ADS itself and DERs features, whose purposes are minimizing voltage deviation and minimizing the operational expenditures of a complete dispatching cycle by means of controllable DERs. In addition, the harmony search (HS) algorithm is improved by using uniform distribution of the initial harmony library and variable dimension harmony memory, the improved harmony search (IHS) November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Shan Gao TuF04.6 Xi’an Univ. of Technology Teng Mu Southeast Univ. The high penetration of distributed energy resources (DER) in future Active Distribution Network (ADN) will bring great challenges to distribution network analysis. This paper presents a new methodology based on pseudo-sequential Monte Carlo (PSMC) simulation for the reliability assessment of distribution network with wind farms, photovoltaic generators and batteries. The proposed approach retains the computational efficiency of non-sequential Monte Carlo simulation and the accuracy of sequential Monte Carlo simulation for it considers the chronological aspects of load, DER and batteries when evaluating failure sequences. Micro-grid operation, DER use strategy and optimal load shedding strategy are also considered in this method. Case study on the line 4 of IEEE RBTS-BUS6 is presented to prove the practicability of the method. The effects of DER integration on the distribution network reliability indices are also discussed. TuF04.4 Jiandong Duan Le Yu Yuntao Ju China Electric Power Research Inst. Wanxing Sheng China Electric Power Research Inst. Xiaohui Song China Electric Power Research Inst. Jing Wang China Electric Power Research Inst. Wenchuan Wu Tsinghua Univ. There are mainly two kinds of state estimation measurements' model in recent research. One model considers that direct measurements and indirect measurements are uncorrelated, the other model considers that indirect measurements have strong correlation with the direct measurements where they are derived, and the correlation can be described as covariance elements in weight matrix. In fact, without using the indirect measurements, state estimation can already be solved with only 136 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) direct measurements. This paper proposes a state estimation method which only adopts direct measurements. Its efficiency and accuracy are certified by numerical tests. TuF05.1 Experimental Study of the Online Monitoring of the Mechanical Characteristics of a Hydraulic HighVoltage Circuit Breaker pp. 2706-2709 TuF04.7 Day-ahead Active Distribution Network Optimal Schedule with EV Penetration pp. 2695-2699 Zhenxing Zhao Xianjun Ge Hao Xiao Chengyou Wang Candong Liu Inst. of Electrical Engineering Chinese Academy of Sciences Inst. of Electrical Engineering Chinese Academy of Sciences With the popularization of electric vehicles, electric vehicles in the active distribution network continue to expand the scale. Electric vehicles access to the active distribution network to participate in the economic dispatch with other distributed powers. This can reduce the total cost of active distribution network. In addition, the owners of the electric vehicle can make profit when their vehicles paticipating the dispath. This paper presents an active distribution network operation optimization model. The target of this model is to take the lowest operating cost of the active distribution network, in each calculation period. The algorithm is used to control the distributed generation units and the flexible load in the active distribution network, and optimize the electric vehicle charging and discharging. Changes of the number of electric vehicles and changes of charge and discharge cost of electric vehicles are discussed. The accuracy of the results is verified by using IEEE 13 node test feeders. TuF05.2 Realization of A Simulation Test Method for Feeder Automation of Power Distribution Automation System pp. 2710-2714 TuF04.8 Active Distribution System State Estimation Considering the Characteristics of DGs pp. 2700-2705 Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst. Qiang Li Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst. Xiaodong Yuan Jiangsu Electric Power Company Research Inst. R & D Center Taikai Electric Automation Co., Ltd Online monitoring of primary equipment such as circuit breakers is widely used in smart substations. By analyzing the data acquired from online monitoring systems, the circuitbreaker status can be monitored, and the health of the breaker can be determined comprehensively. Using an online monitoring system, tests were carried out to measure the mechanical characteristics of a hydraulic high-voltage circuit breaker. Opening and closing coil current curves and distance curves were experimentally obtained by applying 0, 10, 20, and 50 kA of instantaneous load current. The main eigenvalues of the mechanical characteristics were calculated using the online monitoring system. Although varying the load current does not impact the motor or circuit-breaker closing performance, the experimental results show that large load currents will impede breaker opening, a phenomenon that had not been reported prior to the online monitoring tests described here. China Electric Power Research Inst. Xiong Yang University of Jinan Shilei Guan China Electric Power Research Inst. Wenbo Fan China Electric Power Research Inst. Haoliang Lei China Electric Power Research Inst. Lan Liu China Electric Power Research Inst. Dongliang Li China Electric Power Research Inst. According to the lack of unified, standardized testing methods for the feeder automation function of distribution automation system, this paper introduces a kind of simulation testing method realization of feeder automation function, which can provide technical reference for the bidding, and strengthen the quality control and operation management of power distribution automation system. This method setups testing environment by using the DATS–1000 distribution network automation master station injection testing system, simulates feeder and typical fault under the actual working condition and evaluates the feeder automation function conformed to the standard requirements. Through the actual products testing, this simply operated method was verified, it can reduce physical impact and testing cost effectively, which indicates that can be used for feeder automation function testing and also can be acceptance for the power distribution automation system simulation test and site. In this paper, an active distribution system state estimation (ADSSE) method with considering the characteristics of distributed generations (DGs) is proposed, in which the running and controllable characteristics of DGs are discussed and analyzed. The mathematical model which can reflect realtime monitoring of the running and controlling state of DGs is established, and their running state variables and controllable parameters are introduced into ADSSE based on weighted least squares (WLS), then the state estimation model of the proposed ADSSE method is obtained, which can accurately estimate the running state variables and controllable parameters of DGs. Finally, it follows from the simulation results that the proposed ADSSE method is successful and effective. 137 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) object on the application layer is represented by the FSM. In each FSM, the communication drives the FSM from state to the other which is also called state transition. The event set includes all of the events which have impacts on the communication procedure. As a novel method to model the communication based on IEC60870-5-101/104, the DES accurately describes the behaviors of the system and enhances the reliability of the communication by using the supervisory controller. TuF05.3 Data Quality Analysis and Improved Strategy Research on Operations Management System for Electric Vehicles pp. 2715-2720 Lu Zhang Electric Power Research Inst. TuF06.1 State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Yanxia Chen Electric Power Research Inst. The Influence Factors Experiment of Poor Contact Discharge in Indoor Power Grid pp. 2725-2729 State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Jie Zhu Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Mingyu Pan Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Zhou Sun Electric Power Research Inst. Chengjiang Wang China Three Gorges Univ. Qiang Liu China Three Gorges Univ. Qi Zhang China Three Gorges Univ. Yi Yang Power Supply Bureau of WanZhou State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company Weixian Wang Electric Power Research Inst. In order to achieve monitoring on poor contact in indoor power grid and avoid electrical fires, the discharge phenomenon caused by poor contact is experimented systematically. A discharge experiment model of poor contact is developed, in which the influence of the structural parameters of contact type and the gap distance on poor contact discharges are experimented, and the influence of the operating parameters of load type (cos ϕ ), load current and voltage phase are experimented too. The influence factors of initial discharge and the influence regular patterns with various parameters have been obtained from a large number of experiments. Statistical results show that the discharge trend increases first and then decreases. In the range of experiment load, poor contact discharge is very sensitive to the structure parameters of contact model, in comparison, it is not sensitive to operation parameters such as load type and load current. When the phase of experiment-voltage is in the vicinity of 0°, 60°, 120°, 180°, 240°, 300°, it has intensive discharge region of poor contact, and this phenomenon has the similarity under different factors. State Grid Beijing Electric Power Company It is very important for Operations Management System (OMS) and big data analysis application to improve the data quality of Electric Vehicle (EV) charging service. This paper focuses on the charging transaction record data from the Beijing EV charging OMS, and analyzes error types and distributed locations of the abnormal data. Based on the mathematical logic among various kinds of operation data, the data selection rules and processing method are proposed, and the system improved scheme is given. Through the design and application of data selection and processing module, the abnormal data can be timely detected and corrected. It is also beneficial for the system operation and maintenance to improve the acquisition data quality. The comparative analysis results verify the feasibility and effectivity of the proposed scheme. This research is a necessary guarantee for the big data technology application. TuF05.4 TuF06.2 Event System Based Automatic Testing Method for Intelligent Terminal Communication Protocol pp. 2721-2724 Zhong Chen Changsha Univ. of Science and Technology Junhui Zhao Univ. of New Haven Xiaopeng Yu Changsha Univ. of Science and Technology A Two-Stage Tradeoff-PCA Method for Assessing Environmental Benefits of Smart Distribution System pp. 2730-2735 A novel method based on the Discrete Event System (DES) theory is proposed to solve the compatibility and interoperability issues among devices from different manufactures for the application of IEC60870-5-104 in distribution networks. In this paper, the DES method, which is described by a Finite State Machine (FSM), is employed to model the communication procedure based on the IEC60870-5-104. In the model, each November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China Yingzi Li North China Electric Power Univ. Bo Zeng North China Electric Power Univ. Pengcheng Xu North China Electric Power Univ. Zongqi Liu North China Electric Power Univ. Focusing on the absence of systematic indicators and methodologies for evaluating environmental benefits of urban network planning quantitatively, this paper studies and proposes a new 138 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) comprehensive evaluation index system and method for urban TuF06.4 power grid planning. The model is mainly composed of two parts: (1) A new quantitative index system including pollutant Construction Mode and Embodiment of Dispatching Automation System for Distribution Network pp. 2741-2746 emission, carbon emission, environmental coordination, landscape aesthetics, as well as economic feasibility,in which the impacts of DG integration are also considered; (2) A two-stage evaluation method, which combines multiple attributes Tao Han tradeoff analysis and principal component analysis, to deal Beibei Zhang with excessive dependence on the subjective judgment in the traditional evaluation methods. The simulation results of a real Hongwei Du urban network in China are presented and discussed, illustrating that the proposed model is effective and superior, which Yinghua Song helps guide the urban power grid towards an eco-friendly fu- Xianghao Wang ture. Yanghao Zhou Huichao Wu TuF06.3 In order to adapt to system requirements of “Operation” and achieve a high degree of integration about the county two grid business, Proposed a set of principles to differentiate construction to achieve a modern grid with automation, information technology, interactive features targeted distribution network dispatching automation system building programs. For distribution automation management needs and characteristics,analyzed of differences between energy management system (EMS) and distribution anagement system(DMS) from modeling,basic functions,analysis applications and information interactive applications of distribution network. From the perspective of the integration of EMS / DMS functional integration or independent construction, according to the scale of construction in different areas, proposed two kinds of construction ideas includes EMS / DMS independent and integration,and given in detail construction mode. Depending on the construction model, discussed the problem to be solved such as data collection,fault handling, electronic wiring diagram and implementation methods. Analysis of the risks to upgrade existing areas dispatching system into integration of dispatching system which includes distribution network. A New Approach for Fast Reliability Evaluation of Composite Power System Considering W ind Farm pp. 2736-2740 Pengcheng Xu North China Electric Power Univ. Yingzi Li North China Electric Power Univ. Qi Chen North China Electric Power Univ. Wenxia Liu North China Electric Power Univ. Zongqi Liu NARI Technology Co.,Ltd NARI Group Corporation NARI Technology Co.,Ltd NARI Group Corporation NARI Technology Co.,Ltd NARI Group Corporation NARI Technology Co.,Ltd NARI Group Corporation NARI Technology Co.,Ltd NARI Group Corporation NARI Technology Co.,Ltd NARI Group Corporation NARI Technology Co.,Ltd NARI Group Corporation North China Electric Power Univ. Due to fluctuation and randomness of wind speed, reliability of power system will be affected severely with increasing wind energy injected into power grid. In order to evaluate reliability of composite power system with wind farms, this paper proposes a new approach based on non-sequential Monte Carlo TuF06.5 simulation (MCS) and the cross-entropy (CE), the basic idea is to find an optimal distortion for probabilistic parameters of Construction Policies of Distributed Power Generation pp. 2747-2751 components using the CE concepts. A fault set based on linked list is utilized to enhance the retrieval speed as well. As a result, the computational efforts of the CE can be greatly reduced Fang Luo Dansheng Li Ning Chen Dawei Zhao Xiangyan Wang Minhui Qian while retaining many of its main advantages. Comparisons with CE, and non-sequential MCS are carried out using the modifications of IEEE-RTS-79 (Reliability Test System) that include wind farm. The results demonstrate that the improved CE (ICE) method is of relatively high efficiency for reliability China Electric Power Research Inst. State Grid Corporation of China China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. China Electric Power Research Inst. This paper is about the construction policies of distributed power generation. The distributed generation develops quickly in the whole world. The construction policies of each country can influence the industry development essentially. Con- evaluation of composite power system with wind farms. 139 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) struction policies of distributed generation can be considered from three aspects: the distributed power generation admission policy, the grid construction costs policy and the governments encourage policy. The governments adjust policies to influence the developing direction of distributed power generation. Good results are obtained in the practice. Maturity Assessment Model of Smart Grid Project pp. 2752-2757 State Grid Energy Research Inst. Xiaojun Li Tianjin Univ. Wenjin Qi Tianjin Univ. Qiming Zhao Tianjin Univ. Hongjie Jia Tianjin Univ. Han Huang Tianjin Univ. Yuan Zeng Tianjin Univ. Yanli Liu Tianjin Univ. State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Hao Zhong State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company In the modern power system, the dynamic rating technology of transmission line has been drawing more and more attention in power system operation research. Developing dynamic rating system can raise short-term transmission capacity of transmission lines effectively and safely to satisfy the demands for power supply under emergency. The dynamic rating model based on thermal circuit is derived through the foundation of steady state model and transient state model of thermal circuit. The overhead transmission line temperature at any time is obtained through the first-order thermal circuit model. The field test data of dynamic rating system is analyzed. The effectiveness of the proposed model and dynamic rating system is verified by the simulation test and field test. TuF06.6 Xiaoling Jin Zhaohui Li TuF06.8 Forecast of Line Ice-coating Degree Using Circumfluence Index & Support Vector Machine Method pp. 2764-2768 From the point of view of project maturity, this paper builds the maturity assessment model of smart grid project. Based on the general rules of the smart grid project, the assessment model evaluates smart grid project comprehensively, including technical maturity of key technology of the project, project policy and environment, project management level and project business model. In this paper, the project maturity assessment system is built, with the joining between technical maturity and the project maturity, where the technical maturity of the key technology project is one of the first grade indexes of the project maturity. This paper uses sequence relations method to assess the indexes of the project maturity, and analyze the influence on the project maturity brought by the uncertainty of bottom evaluating index, by using Gram-Charlier expansion. Then this paper analyzes the uncertainty of the result. Finally the national wind- photovoltaic-energy storing pilot project verifies the effectiveness and the rationality of the proposed evaluation model. Jingjie Huang Changsha University of Science and Tech. Hongming Yang Changsha University of Science and Tech. Yi Wang Changsha University of Science and Tech. Forecast of line ice-coating plays an important role for reducing the damage of power grid from ice rain efficiently. Aiming at the climate feature and forecast purpose in Hunan area, forecasts for ice-coating number of days and ice-coating thickness are transformed into forecasts for ice-coating degree. According to the calculated ice-coating degree coefficient, ice-coating degree is indicated and divided. Because normal climate information and ice-coating forecast method are hard to satisfy the requirement of de-icing schedule and financial risk reducing, circumfluence indexes as atmosphere information and support vector machine (SVM) as forecast method are presented to forecast lines ice-coating degree. Through correlation analysis about 74 circumfluence indexes to ice-coating degree, correlation coefficient and associated correlation coefficient are calculated and listed. These 8 circum- TuF06.7 fluence indexes of higher coefficients are chosen as independ- A Thermal Model Based Dynamic Rating System for Overhead Transmission Lines pp. 2758-2763 weeks or months. SVM models based on two kinds of kernel ent variables to be used to forecast the ice-coating degree in Yuehao Yan State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Wei Bao State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company Jun Xin Hui Lin functions for forecasting degree are built. adopted in Hunan. The parameters of two kinds of SVM models are got through Particle Swarm optimization. The forecast results show that polynomial kernel function SVM model is State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company more efficient and suitable than radial basis function to winter State Grid Zhengzhou Power Supply Company November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China ice-coating Ice-coating samples and circumfluence indexes of 30 years are ice-coating forecast. 140 The IEEE 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT 2015) ability to deal with power grid collapse. TuF06.9 TuF06.11 Application of the Principal Component Analysis and Cluster Analysis in Comprehensive Evaluation of Thermal Power Units pp. 2769-2773 Design of Main Circuit and Control System for Connecting Series and Parallel Interface of W ind Power Generating Unit pp. 2780-2784 Liqun Shang Xi’an University of Science and Tech. Shoupeng Wang Xi’an University of Science and Tech. Shiping Su Yimin Su Guiying Liu In order to improve the operational level of safety, reliability, economy and environmental protection of thermal power units, the principal component analysis (PCA) and cluster analysis (CA) method were combined and proposed to assess the operating condition of fossil-fired power plants comprehensively, which can resolve the problem on the evaluation of multiple indicators. This method utilizes principal component analysis to perform the standardization, dimension-reduction and de-correl ation of multiple evaluation indicators system for thermal power unit and abstracts the principal components. Moreover, the principal components were extracted as a new data matrix by cluster analysis. Finally the principal component scores and cluster classification were combined for comprehensive evaluation. It can provide the high reference value for the power generation group on how to implement energy saving, optimal operation, index evaluation and competition in thermal power units. The practical example shows that the proposed method is effective. Changsha University of Science and Tech. Changsha University of Science and Tech. Changsha University of Science and Tech. Since the wind is random, intermittent and uncontrollable energy, conventional grid is difficult to adapt to the requirements of grid connected wind power. We can use inverter interface to improve quality and safety when wind power generation connected to grid. In this paper, a detailed study of the wind power on the series and parallel interface and topology, a detailed analysis the working principle and mathematical model of the series and parallel interface, and a detailed analysis of the power characteristics of the wind power generation are done. And also, the paper gives the series and parallel signal generation principle, a detailed analysis of serial and parallel output interface control hysteresis control method, and the harmonic and reactive power signal simulation. What’s more, the paper studied signal detection method in the dq0 coordinate, the working process of the power and hysteresis control of PWM signal. Theoretical analysis and simulation results show that the method and the control method of signal detection is feasible. TuF06.10 Simulation and Deduction System for Complex Power Grid Collapse and Restoration Process pp. 2774-2779 Jiabing Han Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Wenhui Wei Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Qihai Yuan Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Changnian Lin, Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Guoping Wang,Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System Shujin Zhou Beijing Kedong Electrical Power Control System The power grid large-scale blackout and collapse always puts our society in risk. Power grid companies must strengthen the ability to deal with blackout and collapse. The complex power grid collapse and restoration process simulation and deduction system is designed. System structure and system functions are described. This paper focused on the key technologies including power system simulation oriented to the collapse and restoration process, relay protection and automatic device simulation, and multi-agent simulation deduction. The system can achieve accurate and complete simulation of complex power grid collapse and restoration process, to reappear the whole process. It can provide simulation and training tools for power grid dispatchers and operators, to enhance the emergency 141 November 26-29,2015 Changsha,China