Please follow the following guidelines for group discussions: I
advertisement

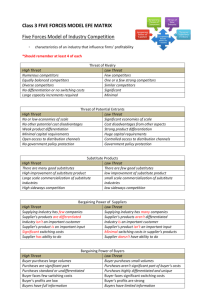
Please follow the following guidelines for group discussions: I) Present basic facts about the assigned companies and their competitors. II) Discuss the assigned companies and competitors over the given factors. III) Answers to the questions that you feel are relevant for your assigned company. I) Present basic facts about the assigned companies and their competitors: Facts (History, Financial performance- Revenue, Profitability, Stock price movement (if applicable), Growth rate, etc. ) about the companies assigned Competitors of companies assigned both online and offline II) Discuss the assigned companies and competitors over the following factors: 1. Key Elements of a business model : 2. Key industry analysis and strategic factors (industry level): Barriers to entry; Power of suppliers; Power of customers; Existence of substitute products; Nature of intra-industry competition (Porter’s 5 forces) The threat of substitute products: The existence of close substitute products increases the propensity of customers to switch to alternatives in response to price increases (high elasticity of demand). buyer propensity to substitute relative price performance of substitutes buyer switching costs perceived level of product differentiation The threat of the entry of new competitors: Profitable markets that yield high returns will draw firms. This results in many new entrants, which will effectively decrease profitability. Unless the entry of new firms can be blocked by incumbents, the profit rate will fall towards a competitive level (perfect competition). the existence of barriers to entry (patents, rights, etc.) economies of product differences brand equity switching costs or sunk costs capital requirements access to distribution absolute cost advantages learning curve advantages expected retaliation by incumbents government policies The intensity of competitive rivalry: For most industries, this is the major determinant of the competitiveness of the industry. Sometimes rivals compete aggressively and sometimes rivals compete in non-price dimensions such as innovation, marketing, etc. number of competitors rate of industry growth intermittent industry overcapacity exit barriers diversity of competitors informational complexity and asymmetry fixed cost allocation per value added level of advertising expense Economies of scale Sustainable competitive advantage through improvisation The bargaining power of customers: Also described as the market of outputs. The ability of customers to put the firm under pressure and it also affects the customer's sensitivity to price changes. buyer concentration to firm concentration ratio bargaining leverage, particularly in industries with high fixed costs buyer volume buyer switching costs relative to firm switching costs buyer information availability ability to backward integrate availability of existing substitute products buyer price sensitivity differential advantage (uniqueness) of industry products RFM Analysis The bargaining power of suppliers: Also described as market of inputs. Suppliers of raw materials, components, and services (such as expertise) to the firm can be a source of power over the firm. Suppliers may refuse to work with the firm, or e.g. charge excessively high prices for unique resources. supplier switching costs relative to firm switching costs degree of differentiation of inputs presence of substitute inputs supplier concentration to firm concentration ratio threat of forward integration by suppliers relative to the threat of backward integration by firms cost of inputs relative to selling price of the product. This 5 forces analysis is just one part of the complete Porter strategic models. The other elements are the value chain and the generic strategies. 3. Business Strategy: SWOT a. How can we Use and Capitalise on each Strength? b. How can we Improve each Weakness? c. How can we Exploit and Benefit from each Opportunity? d. How can we Mitigate each Threat? Four generic strategies- Differentiation; Cost; Scope; Focus 4. Strategic factors that pertain to firm include: Firm value chain; Core competencies; Synergies; Technology; Social and Legal challenges 5. Consumer profile & parameters that can potentially influence her decision makingDemographic profile, Technical know-how, Customer behavior- cultural, social (opinion leaders, effect of friends, peer-pressure, acceptance in society), habits, lifestyle, psychological, security concerns, etc. 6. Five stages in the consumer decision making process: Awareness of need; Search for more information; Evaluation of alternatives; Actual purchase decision; Post-purchase contact with firm 7. Dealing with information asymmetry- reviews & rating mechanisms; Recommendation systems 8. Various fee models for using certain platform such as eBay- Listing fees, Percentage of the final transaction amount, Fixed fees if product sold 9. Social cause support element- such as for every blah-blah product sold, company will donate some amount for some cause. III) Food for thought: 1. Why do you think blah-blah succeeded/failed or will succeed/fail? 2. What are the key success factors/failure reasons for blah-blah? 3. Do you think blah-blah would work for you? 4. Why are competitors (old, contemporary, forthcoming) succeeding/failing or will succeed/fail? 5. How has blah-blah impacted its industry domain? 6. Who are/would be the customers of blah-blah? 7. Why would customers pay for the product/service? 8. What changes would you suggest to blah-blah? 9. What strategies would you suggest to competitors in the similar domain? [Please also discuss strategies for conventional competitors (competitors without online presence) in the domain of assigned companies.]