Treaty
advertisement
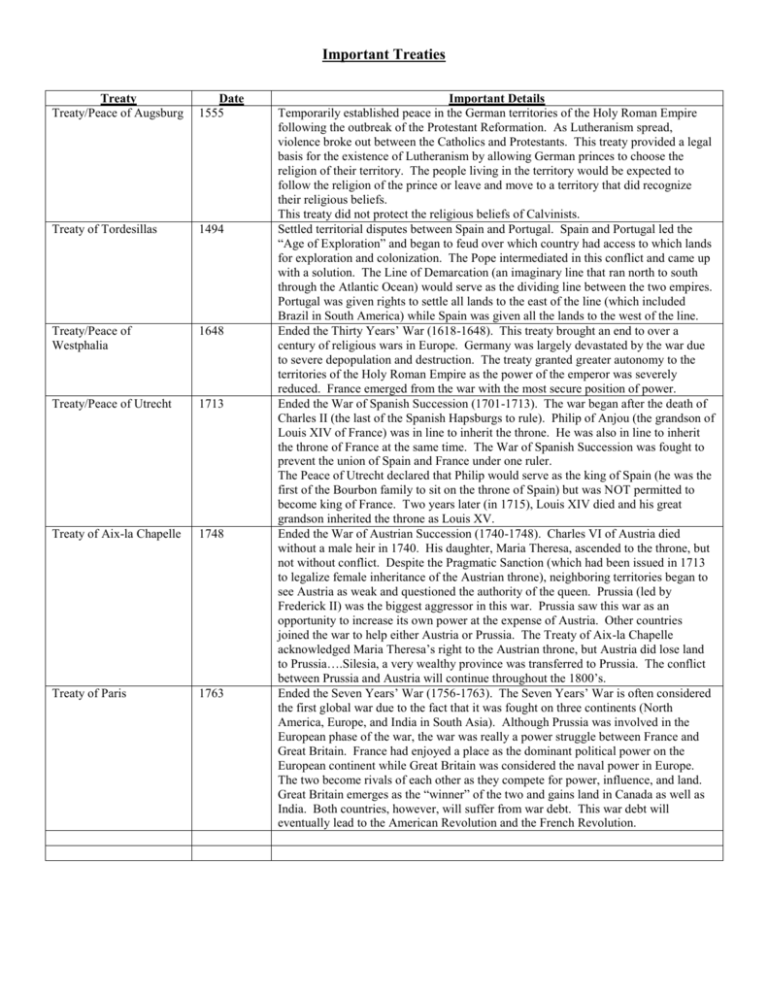
Important Treaties Treaty Treaty/Peace of Augsburg Date 1555 Treaty of Tordesillas 1494 Treaty/Peace of Westphalia 1648 Treaty/Peace of Utrecht 1713 Treaty of Aix-la Chapelle 1748 Treaty of Paris 1763 Important Details Temporarily established peace in the German territories of the Holy Roman Empire following the outbreak of the Protestant Reformation. As Lutheranism spread, violence broke out between the Catholics and Protestants. This treaty provided a legal basis for the existence of Lutheranism by allowing German princes to choose the religion of their territory. The people living in the territory would be expected to follow the religion of the prince or leave and move to a territory that did recognize their religious beliefs. This treaty did not protect the religious beliefs of Calvinists. Settled territorial disputes between Spain and Portugal. Spain and Portugal led the “Age of Exploration” and began to feud over which country had access to which lands for exploration and colonization. The Pope intermediated in this conflict and came up with a solution. The Line of Demarcation (an imaginary line that ran north to south through the Atlantic Ocean) would serve as the dividing line between the two empires. Portugal was given rights to settle all lands to the east of the line (which included Brazil in South America) while Spain was given all the lands to the west of the line. Ended the Thirty Years’ War (1618-1648). This treaty brought an end to over a century of religious wars in Europe. Germany was largely devastated by the war due to severe depopulation and destruction. The treaty granted greater autonomy to the territories of the Holy Roman Empire as the power of the emperor was severely reduced. France emerged from the war with the most secure position of power. Ended the War of Spanish Succession (1701-1713). The war began after the death of Charles II (the last of the Spanish Hapsburgs to rule). Philip of Anjou (the grandson of Louis XIV of France) was in line to inherit the throne. He was also in line to inherit the throne of France at the same time. The War of Spanish Succession was fought to prevent the union of Spain and France under one ruler. The Peace of Utrecht declared that Philip would serve as the king of Spain (he was the first of the Bourbon family to sit on the throne of Spain) but was NOT permitted to become king of France. Two years later (in 1715), Louis XIV died and his great grandson inherited the throne as Louis XV. Ended the War of Austrian Succession (1740-1748). Charles VI of Austria died without a male heir in 1740. His daughter, Maria Theresa, ascended to the throne, but not without conflict. Despite the Pragmatic Sanction (which had been issued in 1713 to legalize female inheritance of the Austrian throne), neighboring territories began to see Austria as weak and questioned the authority of the queen. Prussia (led by Frederick II) was the biggest aggressor in this war. Prussia saw this war as an opportunity to increase its own power at the expense of Austria. Other countries joined the war to help either Austria or Prussia. The Treaty of Aix-la Chapelle acknowledged Maria Theresa’s right to the Austrian throne, but Austria did lose land to Prussia….Silesia, a very wealthy province was transferred to Prussia. The conflict between Prussia and Austria will continue throughout the 1800’s. Ended the Seven Years’ War (1756-1763). The Seven Years’ War is often considered the first global war due to the fact that it was fought on three continents (North America, Europe, and India in South Asia). Although Prussia was involved in the European phase of the war, the war was really a power struggle between France and Great Britain. France had enjoyed a place as the dominant political power on the European continent while Great Britain was considered the naval power in Europe. The two become rivals of each other as they compete for power, influence, and land. Great Britain emerges as the “winner” of the two and gains land in Canada as well as India. Both countries, however, will suffer from war debt. This war debt will eventually lead to the American Revolution and the French Revolution.