UNIT 1: Living cells
advertisement

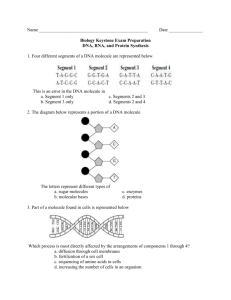
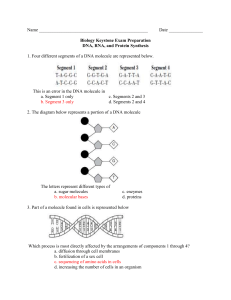
UNIT 1: Cell Function and Inheritance Topics 1-8 UNIT 1: Living cells TOPIC 1: Structure and variety of proteins Amino acid Conjugated protein Fibrous protein Nitrogen Globular protein Hydrogen bond Polypeptide Peptide bond ssssssssssssssssssss Molecule consisting of polypeptide chain folded into a ball with a non-protein chemical One of 20 different types of organic compound that are the basic building blocks of protein Weak chemical link holding a polypeptide chain into a coil by linking adjacent amino acids in the helix Molecule consisting of long, parallel chains arranged like a rope Strong chemical link joining adjacent amino acids in a poly peptide chain Molecule consisting of polypeptide chains arranged like a ball of string Chain-like molecule composed of several amino acids Chemical element present in protein but absent from carbohydrates TOPIC 2: Role of enzymes Active site Co-factor Digestion Denaturation End product Enzyme Inhibitor Substrate Lock-and-key mechanism Synthesis ssssssssssssssssssss Substance formed as a result of an enzyme acting on its substrate Process by which an enzyme’s structure is changed and it’s active site is destroyed Biological catalyst composed of globular protein Building-up of large, complex molecules from simpler ones by an enzyme-controlled reaction Region on an enzyme where the complementary surface of the substrate becomes attached Substance upon which an enzyme acts, resulting in the formation of an end product Non-protein substance needed by some enzymes to bring about their catalytic effect Substance that decreases or halts the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction Breakdown of large, complex molecules to simpler ones by an enzyme-controlled reaction Hypothesis which proposes that substrate and enzyme molecules fit together in a precise and specific way TOPIC 3: Nucleic acids and protein synthesis Adenine Cytosine Deoxyribose DNA Double helix Nucleotide Ribose Thymine Uracil Amino acid Codon Genetic code Polypeptide Ribosome Guanine Anticodon Translation mRNA 2-stranded molecule of DNA wound up into a spiral Base present in mRNA that is complementary to adenine Base present in DNA and RNA that is complementary to thymine Basic unit of which nucleic acids are composed Sugar present in DNA Base present in DNA that is complementary to guanine Nucleic acid present in chromosomes Sugar present in RNA Base present in DNA and RNA that is complementary to cytosine Sub-cellular structure that is the site of protein synthesis Process by which a complementary molecule of mRNA is made from a region of DNA template Type of nucleic acid that conveys information from DNA to a ribosome Long chain of amino acids formed at a ribosome during translation of RNA The conversion of the genetic code into a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide Molecular language made up of 64-codewords called codons Unit of genetic code consisting of 3 mRNA bases Type of nucleic acid that acts as an amino acid carrier Triplets of bases on a tRNA molecule that is complementary to an mRNA codon One of 20 different types of sub-unit that make up protein molecules TOPIC 4: ATP and energy transfer Acetyl CoA ATP Central matrix Citric acid Crista Cytochrome system Cytoplasm Glycolysis Krebs cycle Oxygen Pyruvic acid Water Phosphorylation Glucose Mitochondrion Stage of respiratory pathway common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration Series of hydrogen (electron) carriers located on cristae of mitochondrion Folded extension of inner membrane of mitochondrion Organelle responsible for aerobic respiration The location in a cell where glycolysis occurs Part of a mitochondrion containing enzymes needed for the Krebs cycle Final hydrogen acceptor in aerobic respiration High energy compound formed by phosphorylation using energy released during respiration Stage of respiratory pathway that occurs in central matrix of mitochondrion Process by which high energy ATP is formed from low energy ADP + Pi 2-carbon compound formed from pyruvic acid when oxygen is present 3-carbon compound formed from glucose during glycolysis Product of aerobic respiration when oxygen combines with hydrogen 6-carbon compound formed when 4carbon and acetyl coA combine 6-carbon sugar that acts as a common respiratory substrate in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration TOPIC 5: Sources of energy Disaccharide Non-reducing sugar Glucose Glycogen Polysaccharide Maltose Monosaccharide Reducing sugar Starch Sucrose General name for insoluble carbohydrate composed of many monosaccharide molecules General name for sugar consisting of 2 monosaccharide molecules joined together Soluble carbohydrate whose molecules can donate electrons to other substances Monosaccharide produces following complete digestion of starch General name for soluble carbohydrate unable to donate electrons to other substances Polysaccharide stored in human liver cells Disaccharide reducing sugar produced by action of amylase on starch Non-reducing disaccharide sugar composed of glucose and fructose General name for ‘single’ simple sugar Polysaccharide stored in plant cells TOPIC 6: Cell membrane and transport of materials Active transport Diffusion Exocytosis Hydrophilic part Hydrophobic part Pinocytosis Osmosis Globular protein Phagocytosis Phospholipid Component of cell membrane whose molecules make up a fluid bilayer Form of endocytosis by which lipids are taken into a cell in small vesicles Water-loving head end of a phospholipids molecule Form of endocytosis by which solid particles are engulfed and taken into a cell Net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of lower concentration of that substance Component of cell membrane whose molecules form a patchy mosaic amongst the phospholipids bilayer Movement of ions across the plasma membrane against a concentration gradient Net movement of water molecules from high to lower water concentration through a selectively permeable membrane Water-hating tail end of a phospholipids molecule Process by which intracellular vesicles discharge their contents from the cell TOPIC 7: Cellular response in defence Active immunity Agglutination Allergy Antibody Autoimmunity B cell Vaccination Cell-mediated response Humoral response Killer T cell Memory cells Antigen Macrophage Passive immunity Clumping together of red blood cells by becoming bound to antibodies Failure of immune system to tolerate its own antigens resulting in it attacking its own cells Injection or ingestion of harmless form of pathogen to produce immunity Over-reaction by hypersensitive immune system to harmless substance Type of phagocytic cell especially numerous in liver, spleen and lymph nodes Protection gained by receiving readymade antibodies from another person or animal Mobilisation of cell products (antibodies) to deal with antigens Complex molecules (e.g. protein) recognised by lymphocytes as foreign B- and T-lymphocytes formed during first exposure to antigen which produce secondary response in future Y-shaped protein made by Blymphocytes in response to antigen Mobilisation of killer T-cells to deal directly with foreign antigens Protection gained by producing antibodies in response to natural or artificial exposure to pathogen Lymphocyte that brings about cellmediated response to alien material Lymphocyte that produces and releases antibodies as free molecules TOPIC 8: Viruses AIDS Bacteriophage Host Lysis Capsid Retrovirus Helper T cell HIV Reverse transcriptase Virus General name for a micro-organism that exhibits living and non-living characteristics Bursting of host cell releasing copies of viruses Virus that destroys T helper cells General name for virus containing RNA and reverse transcriptase Protective coat surrounding a virus Enzyme that transcribes viral RNA into DNA Type of virus that attacks bacteria Type pf white blood cell that plays host to HIV Organism whose cells are attacked by a virus Acquired immune deficiency syndrome