Hierarchical Network of Multan Reigon
advertisement

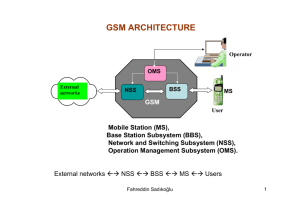
Hierarchical Network of Multan INTRODUCTION:We will study Hierarchical network of Multan on the basis of three Tier model. In three tier model we will design the network by dividing the network into three layers. CORE LAYER (Backbone PTCL Multan) DISTRBUTION LAYER (ZONG & PTCL Exchange) ACCESS LAYER (Mobile User, Land Line & Rise College Network) In Core layer we will study the Central Exchange Dera Adda Multan as a backbone network .Which distribute its services on the various ISPs, exchanges or different mobile companies of Multan. In Distribution layer we will study the distribution end networks which are taking the services from backbone network and provide it to the user end. We will study Zong Mobile Company and PTCL Exchange Multan as a distribution end network. In Access layer we will see how users are facilitate their self by taking the services from distribution end. In this layer we will take RISE College Multan, landline users and mobile users. CORE LAYER Now we will come on the Core layer. First of all we have to know that what Core layer is. And what services they provide. The core layer is the network's high-speed switching backbone that is important to company communications. The core provides wide area link between remote sites and other companies that connect to form a WAN. It is where the enterprise touches the world. The core layer provide following services: Fast transport High reliability Redundancy Fault tolerance Low latency and good manageability Avoidance of slow packet manipulation caused by filters or other processes. Quality of services Backbone Network: The network backbone exists in the Core Area. Here we will see Central Exchange Dera Adda Multan as a backbone network. We will divide this topic on the following points. Network Topology Transmission media Working Redundancy Scalability and Adaptability Management Network Topology: The topology which is used in backbone network is dual ring topology. In dual ring topology dual lines are deployed, one is called active ring and other is called passive ring. The line which is called active ring is currently sending the data and the line which is called passive ring is used as redundancy purpose All the central exchanges of Pakistan are interconnected with the help of Ring topology. If there are any kind of problem occurs in media of topology. The topology is shifted from Active ring to passive ring. In the result transmission is never broke down. Network Topology Transmission media: The media which is used in the backbone network is Fiber optic cables. This is deployed under the earth in the form of ring, where several central exchanges are interconnected. An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of very pure glass not much bigger than a human hair that acts as a waveguide, or light pipe, to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. Optical fibers are widely used in fiber-optic communications, which permits transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than other forms of communication. DAT RATE: - Its data rate is about 1giga bit/sec. Working: Now we will see how system works in backbone network. We will divide this portion into two parts: ODF (Optical distribution frame) System Racks ODF (Optical distribution frame): When optic fiber comes into central exchange, it first comes into ODF. Optical distribution frame is a fiber optic management unit used to organize the fiber optic cable connections. Optical distribution frame is usually used indoor and the ODF could be very big size frame or small size similar like the patch panel boxes. ODF properly designed to control the bend radius of the cable inside the enclosure to avoid extra optical loss. These optical distribution frames are ideal for indoor fiber optic cable connections storage, distribution and management. SYSTEM RACKS: After coming to ODF, optical fibers then come into system racks. Every vendor has their own system racks. System racks contain sub racks inside it. Modules are placed on that racks. Fiber optic cables are attached to those modules with the help of S.C connectors. Module is a hardware component or a card placed in sub racks which are dealing with transmission, signaling and other main functionalities. Here fiber optic cables are multiplexed by multiplexer device which is also attached in system sub rack. It controls the lines in on one single optic line by multiplexing it. After controlling it, it will distribute the line by demultiplexing it through demultiplexer which is also attached in the system sub racks. In the result multiple optical line are send to different distributors at distribution end. Redundancy: Modules are playing very important role in backbone network. If there any problem occurs in it. Then back up modules are replaced by faulty ones by detaching it through racks. Scalability and Adaptability: The devices which are used in backbone network are highly scalable and adaptable. Sub racks are provided in system racks for installing a new feature module in it. Management: Network management would allow for more rapid isolation and resolution. It contains following protocols SNMP (simple network management protocol) RMON (remote monitoring) In central exchange NMS (network management software) are installed in computers. NMS is basically software which is dealing with faults occurs in backbone network. Every vendor has its own network management software. If there any fault occurs in backbone network. NMS inform us where the problem exists. Then operators deals with it easily with the help of NMS. These softwares installed in a computer systems from where the operator checking and managing the devices in backbone network. Thus the backbone network distributes the multi fiber optics to different distributive networks which is operating on distribution layer. Distributive networks which we have to deal with are Zong mobile network Multan, PTCL Exchange Multan. DISTRBUTION LAYER PTCL Exchange The Exchange is the building where the local exchange switch resides. A CO’s switch may serve telephone service subscriber in a very narrow geographic area such as a single large building. Conventionally, you can tell which central office user belong to which exchange by looking at the first three digits of seven-digits telephone number. In Ptcl Exchange Dera Ada, Switch resides that is used for call switching to Destination. (DP) Distribution Point From user to Distribution Point Drop Wire is used. And low- medium density copper cable (2-300 pairs) from DP to Distribution Frame. New building can be built and Dp are used to provide them connection Instead to direct connection to Exchange. (DF) Distribution Frames Distribution fames surround the CO. They are high density copper cable (501500 pair ) Primary Cable. Usually all connection to a distribution frame are copper. It allow the telephone company to use High Density Copper Cabling. (MDF) Main Distribution Frames MDFs are distribution frames that have some smart switching in them. Usually, this equipment has been placed to provide the facility of DSL for access to use Internet. With the help of DSLAM Internet is enable in MDFs for particular user. Rise College Network Topology Rise Network is consist of more than 60 Pcs and 3 Server Machines. Ptcl DSL is used to provide the facility of Internet and connected to 14 Port Switch. 3 PCs , 1 Server and Tp Link is connected to this Switch, furthermore 16 Port switch is connected to 14 port Switch. 24 Port switch is connected with 16 Port Switch and both handle 38 PCs and 2 Server Machines. Tp Link provide Wireless facility to Campus. They are using 3 backup for Electricity, 1 Generator, 2 Rent Generator and 3 UPS. Each and every device and computer is connected with UPS. GSM System Architecture Overview A GSM network is made up of three subsystems: 1. The Mobile Station (MS) 2. The Base Station Sub-system (BSS) – comprising a BSC and several BTS’s 3. Network and Switching Sub-system (NSS) – comprising an MSC and associated registers. A GSM network is divided into cells. A group of cells is considering a location area. A mobile phone in motion keeps the network informed about changes in the location area. If the mobile moves from a cell in one location area to a cell in another location area, the mobile phone should perform a location area update to inform the network about the exact location of the mobile phone. 1. The GSM Mobile Station (MS) The Mobile Station is made up of two entities: A: Mobile Equipment (ME) B: Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) Mobile Equipment Each mobile station has its own identification number, i.e., the International Mobile Equipment Identifier (IMEI). IMEI mainly consists of the type permission code and the related manufacturer product number. E.g. Dial *#06# to check IMEI number of any mobile phone. Voice and data transmission Monitoring power and signal quality of surrounding cells 160 character long SMS The IMEI may be used to block certain types of equipment from accessing the network if they are unsuitable and also to check for stolen equipment. Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) Mobile stations are not fixed to one user. On any mobile station in the system, we can identify the subscriber with the SIM card (Subscriber Identity Module). Main features of SIM card: Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) Smart card has its own international mobile subscriber identifier (IMSI), which is stored in SIM card & in HLR. Location Area Identity (LAI) Allows user to send and receive calls and receive other subscribed services Encoded network identification details Mobile Station International Standard Data Network (MSISDN), (optional). Can be moved from phone to phone – contains key information to activate the phone. SIM is Protected by 4-8 digit PIN to validate the ownership of SIM PUK – Personal/Pin Unlocking Key Base Station Subsystem (BSS) The base station subsystem (BSS) is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem. The BSS communicates with the MS over the digital air interface and with the MSC via 2 Mbit/s links. The BSS consists of three major hardware components: 1. Base Transceiver Station (BTS) 2. Base Station Controller (BSC) 3. The Transcoder – XCDR Base Transceiver Station (BTS): The BTS contains the RF components that provide the air interface for a particular cell. The base transceiver station, or BTS, contains the equipment for transmitting and receiving radio signals (transceivers), antennas, and equipment for encrypting & decrypting communications with the (BSC).This is the part of the GSM network which communicates with the MS. The antenna is included as part of the BTS. The purpose of the BTS is to: Communicates with Mobile station and BSC Provide radio access to the mobile station Encodes, encrypts, multiplexes, modulates and feeds RF signals to antenna. General Architecture A BTS in general has the following units: Radio Transceivers (Transmitter/Receiver) (TRX) units Combiner Duplexer Antennas and feeder cables Transceiver (TRX): TRX basically does transmission and reception of signals. Also does sending and reception of signals to/from higher network entities (like the base station controller (BSC) in mobile telephony) Combiner(CMB) : Combines feeds from several TRXs so that they could be sent out through a single antenna. Allows for a reduction in the number of antenna used Duplexer(AEM): For separating sending and receiving signals to/from antenna, does sending and receiving signals through the same antenna ports (cables to antenna) Antennas and feeder cables: Antenna is also considered a part of the BTS. This provides signals to MS. Base Station Controller (BSC) The BSC as its name implies provides the control for the BSS. The BSC communicates directly with the MSC. The base station controller (BSC) provides, classically, the intelligence behind the BTSs. Typically a BSC has tens or even hundreds of BTSs under its control. The databases for all the sites, including information such as carrier frequencies, power reduction levels are stored in the BSC. Main functions of BSC: Manages Radio resources for BTS Assigns Frequency and time slots for all MS’s in its area Allocates a channel for the duration of a call Handles call set up maintains the call monitoring quality Generating Handover for each MS to another cell when required It communicates with MSC and BTS, Network Switching Subsystem (NSS) Controlling the Radio power transmitted by the BTS or MS. Controls one or more BTSs. Switches traffic and signaling to/from the BTSs and the MSC The Transcoder – XCDR The Transcoder is used to compress the signals between the BSS and MS (64 Kbit/s to 16 Kbit/s and vice versa) so that they are more efficiently sent over the universal interfaces. The transcoder is used to reduce the rate at which the traffic (voice/data) is transmitted over the air interface. Although the transcoder is part of the BSS, it is often found physically closer to the NSS to allow more efficient use of the universal links. The 64 Kbit/s Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) circuits from the MSC, if transmitted on the air interface without modification, would occupy an excessive amount of radio bandwidth. The required bandwidth is therefore reduced by processing the 64 Kbit/s circuits so that the amount of information required to transmit digitized voice falls to a gross rate of 16 Kbit/s. Network and Switching Sub-system (NSS) Key elements of the NSS are Mobile Switching Center (MSC) Home Location Register( HLR) Visitor Location Register( VLR) Equipment Identity Register(EIR) Authentication Center( AUC) Gateway Mobile Switching Centre (GMSC) Echo Canceller (EC) Billing Zong MSC Mobile Switching Center (MSC) Heart of the network Manages communication between GSM and other networks Call setup function and basic switching Call routing Billing information and collection Mobility management - Location Updating - Inter BSS and inter MSC call handoff MSC does gateway function while its customer roams to other network by using HLR/VLR. Home Location Registers (HLR) Permanent database about mobile subscribers in a large service area Database contains Subscriber ID Current subscriber VLR Subscriber status Authentication key Visitor Location Registers (VLR) Temporary database which updates whenever new MS enters its area, by HLR database Controls those mobiles roaming in its area Reduces number of queries to HLR Database contains Mobile Status Location Area Identity(LAI) Equipment Identity Register (EIR) Database that is used to track handsets using the IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) Made up of three sub-classes: The White List, The Black List and the Gray List White List The terminal is allowed to connect to the network Black List The terminal is under observation by the network for possible problems Grey List The terminal has either been reported stolen, or is not a type approved for a GSM network The terminal is not allowed to connect to the network Authentication Center (AUC) Protects against intruders in air interface Maintains authentication keys and algorithms and provides security . Generally associated with HLR Gateway Mobile Switching Centre (GMSC) A Gateway Mobile Switching Centre (GMSC) is a device which routes traffic entering a mobile network to the correct destination. The GMSC accesses the network’s HLR to find the location of the required mobile subscriber. A particular MSC can be assigned to act as a GMSC. The operator may decide to assign more than one GMSC. The GMSC routes calls out of the network and is the point of access for calls entering the network from outside. Echo Canceller An echo canceller models the voice signal passing through it As the voice passes back through the canceller it applies signal to remove it dynamically. Billing The MSC/GMSC that originates a call generates a record (Call Detail Record which contains: >User identity >Number called >Call length >Routing of the call This record acts as a ‘ toll ticket’ which tracks the cal l on its route through various networks The record passes along the backbone to the home network Billing computer generates bills to be sent to the user