Big Bang and Cosmology Exam Review answers
advertisement

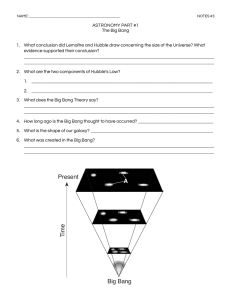
Big Bang and Cosmology Exam Review 1) One light year is about 9.5x1012 Km 2) What does the red shift tell us about the motion of the universe? It is expanding 3) What is currently the most accepted theory about the origin of the universe called? Big Bang 4) What can I tell about a star based on its color? What elements are present 5) What is the most common unit for measuring the distance of cosmic objects? Light Years 6) Who first proposed that the universe is expanding and what made him think so? Edwin Hubble, distant objects were redder than they should have been. 7) Which cosmic objects are moving faster, the near or the far? The farther away they are the faster they are moving 8) What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory? A theory has been thoroughly tested, attempts to explain, and is generally accepted 9) True or False: Although you spent all of elementary school learning that being a tattle tale wasn't acceptable, it is precisely what you are supposed to be in a lab setting. True 10) Who first proposed the dual nature of light? Einstein 11) Name one experiment that 'proves' light is a particle. Photoelectric effect 12) Name one experiment that 'proves' light is a wave. Double slit experiment 13) What are the two competing theories that describe the fate of the universe? Big Freeze and the Big Crunch 14) Which one does the scientific community generally regard as most likely, given what we currently know? Big Freeze (dark energy > dark matter) 15) What was the first of the four fundamental forces to emerge from the big bang? Gravity 16) How would I define the unit light year? And why is it a measure of distance, not time? It is the distance light travels in a year. D = v * t 17) What other forms of electromagnetic radiation join visible light in the electromagnetic spectrum? Radio, micro, infrared, ultraviolet, x-rays, & gamma 18) What is the Doppler effect and how does it relate to astronomy? The observed frequency is effected by the relative motion of the source and observer 19) True or false the big bang produced more antimatter than matter? False. more matter than antimatter 20) What crazy-small unit of time do cosmologists use when speaking about the fractions of a second immediately after the big bang? Planck time 21) How does an atom become ionized? Gaining or losing electrons 22) What are spectral emission lines? Specific and unique frequencies of EMR given off by an element or molecule 23) What are absorption lines? Specific and unique frequencies of light absorbed by a substance (usually a gas) leaving gaps in the spectrum 24) Which has more energy, a photon of a radio wave or a photon of a gamma wave? Gamma wave 25) Which moves faster a microwave or an infrared wave? Same speed 26) Why do different elements have different colors of characteristic light? It takes different amounts of energy to move their electrons to different energy levels