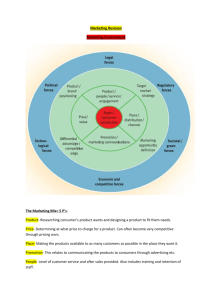
Adoption process The mental process through which an individual
advertisement

Management of Technology GLOSSARY Acquisition The purchase of one company by another Adoption process The mental process through which an individual passes from first hearing about an innovation to final adoption. Advertising Any paid form of nonpersonal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods, or services by an identified sponsor. Behavioral segmentation Dividing a market into groups based on consumer knowledge, attitude, use, or response to a product. Benchmarking The process of comparing the company’s products and processes to those of competitors or leading firms in other industries to find ways to improve quality and performance. Benefit segmentation Dividing the market into groups according to the different benefits that consumers seek from the product. Brand A name, term, sign, symbol, or design, or a combination of these intended to identify the goods or services of one seller or group of sellers and to differentiate them from those of competitors. Brand equity The value of a brand, based on the extent to which it has high brand loyalty, name awareness, perceived quality, strong brand associations, and other assets such as patents, trademarks, and channel relationships. Break-even pricing An approach to pricing in which the price of a unit of the product is set high enough to cover the variable costs of producing that unit as well as the fixed costs of producing the product. Benchmarking Process by which a company implements the best practices from its own past performance and those of other companies to improve its own products Branding Process of using symbols to communicate the qualities of a product made by a particular producer 1 Management of Technology Business ethics Ethical or unethical behaviors by a manager or employer of an organization Catalog marketing Direct marketing through print, video, or electronic catalogs that are mailed to select customers, made available in stores, or presented online. Co-branding The practice of using the established brand names of two different companies on the same product. Competitive advantage An advantage over competitors gained by offering consumers greater value, either through lower prices or by providing more benefits that justify higher prices. Countertrade International trade involving the direct or indirect exchange of goods for other goods instead of cash. Forms include barter, compensation (buyback), and counter purchase. Consumer behavior Various facets of the decision process by which customers come to purchase and consume products Corporate culture The shared experiences, stories, beliefs, and norms that characterize an organization Demarketing Marketing to reduce demand temporarily or permanently; the aim is not to destroy demand but only to reduce or shift it. Differentiated marketing A market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to target several market segments and designs separate offers for each. Direct marketing An approach to marketing that uses one or more advertising media to affect a measurable response. Dumping Practice of selling a product abroad for less than the cost of production Early adopters Consumers who buy a product early in its life cycle and influence other people to buy it. 2 Management of Technology Early majority Consumers who wait and watch others before adopting a new product. Enlightened marketing A marketing philosophy holding that a company’s marketing should support the best long-run performance of the marketing system; its five principles include consumer oriented marketing, innovative marketing, value marketing, sense-of-mission marketing, and societal marketing. Exclusive distribution Strategy by which a manufacturer grants exclusive rights to distribute or sell a product to a limited number of wholesalers or retailers in a given geographic area Extranet Intranet allowing outsiders access to a firm's internal information system Flat organizational structure Characteristic of decentralized companies with relatively few layers of management and relatively wide spans of control Futures contract Agreement to purchase specified amounts of a commodity at a given price on a set future date Focus group Market research technique in which a group of people is gathered, presented with an issue, and asked to discuss it in depth Foreign direct investment Arrangement in which a firm buys or establishes tangible assets in another country Franchise A legal contractual relationship between a supplier and one or more independent retailers. The franchisee gains an established brand name while the franchisor gains financial remuneration as well as some control over how the business is run. Firewall Software and hardware system that prevents outsiders from accessing a company's internal network Functional departmentalization Departmentalization according to group’s functions or activities Goodwill Amount paid for an existing business above the value of its other assets 3 Management of Technology General partnership Business with two or more owners who share in both the operation of the firm and in financial responsibility for its debts Hybrid marketing channel Multichannel distribution system in which a single firm sets up two or more marketing channels to reach one or more customer segments Innovators Consumers who are ready and willing to adopt a new idea. Intranet Private network of internal Web sites and other sources of information available to a company's employees Interactive marketing Nonstore retailing that uses a Web site to provide real time sales and customer service Industrial Revolution Major mid-eighteenth century change in production characterized by a shift to the factory system, mass production, and the specialization of labor International Monetary Fund (IMF) United Nations agency consisting of about 150 nations that have combined resources to promote stable exchange rates, provide temporary short-term loans, and serve other purposes Joint venture Strategic alliance in which the collaboration involves joint ownership of new venture Just-in-time (JIT) production Production method that brings together all materials and parts needed at each production stage at the precise moment they are required Local area network (LAN) Network of computers and workstations, usually within a company, that are linked together by cable Laggards Consumers who are strongly oriented toward the past and very suspicious of new concepts, they are the last to adopt a new product. Market penetration A strategy for company growth by increasing sales of current products to current market segments without changing the product. 4 Management of Technology Marketing mix The set of controllable tactical marketing tools-product, price, place, and promotion that the firm blends to produce the response it wants in the target market. Mission statement A statement of the organizations purpose what it wants to accomplish in the larger environment. Marketing The process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives Marketing research The study of consumer needs and wants and the ways in which sellers can best meet them Mission statement Organization's statement of how it will achieve its purpose in the environment in which it conducts its business Monopoly Market or industry in which there is only one producer, which can therefore set the prices of its products Niche marketing Focusing on sub segments or niches with distinctive traits that may seek a special combination of benefits. Perfect competition A competitive situation in which there are many buyers and sellers, perfect market information, few or no barriers to entry, and homogeneous products. Personal selling Person-to-person communication in which the receiver provides immediate feedback to the source’s message. Positioning A process in which a marketer communicates with consumers to establish a distinct place for its product or brand in their minds. Product life cycle (PLC) The course of a product's sales and profits over its lifetime. It involves five distinct stages: product development, introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. 5 Management of Technology Pull strategy A promotion strategy that calls for spending a lot on advertising and consumer promotion to build up consumer demand. If the strategy is successful, consumers will ask their retailers for the product, the retailers will ask the wholesalers, and the wholesalers will ask the producers. Push strategy A promotion strategy that calls for using the sales force and trade promotion to push the product through channels. The producer promotes the product to wholesalers, the wholesalers promote to retailers, and the retailers promote to consumers. Penetration pricing Setting an initial low price to establish a new product in the market Promotion Aspect of the marketing mix concerned with the most effective techniques for selling a product Pricing Process of determining what a company will receive in exchange for its products Product Good, service, or idea that is marketed to fill consumer needs and wants Strategic planning The process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between the organization's goals and capabilities and its changing marketing opportunities. It involves defining a clear company mission, setting supporting objectives, designing a sound business portfolio, and coordinating functional strategies. Scenario analysis A forecasting technique in which researchers develop a subjective picture of several possible futures by identifying cause-and-effect relationships and following them to their logical conclusions. Strategic alliance (or joint venture) Arrangement in which a company finds a foreign partner to contribute approximately half of the resources needed to establish and operate a new business in the partner's country Target market A set of buyers sharing common needs or characteristics that the company decides to serve. Total quality management (TQM) Programs designed to constantly improve the quality of products, services, and marketing processes. 6 Management of Technology Telemarketing Nonstore retailing in which the telephone is used to sell directly to consumers Vertical marketing system (VMS) A distribution channel structure in which producers, wholesalers, and retailers act as a unified system. One channel member owns the others, has contracts with them, or has so much power that they all cooperate. Word-of-mouth influence Personal communication about a product between target buyers and neighbors, friends, family members, and associates. 7