A2000_CAL_en - Array Solutions
advertisement

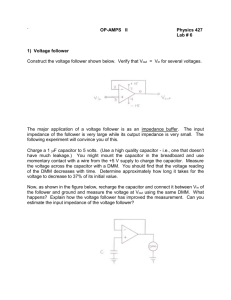
Calibration procedure for ACOM2000A INTERFACE and CPU PCB ========================================================= SAFETY FIRST! ------------It is presumed that the personnel to follow the instructions trained and acquainted with all the general safety rules and operation and handling HIGH VOLTAGE circuits as well as with and operation of the ACOM 2000A amplifier, and how he should while handling the amplifier! below is properly measures for the construction ward off the danger PLEASE DO NOT PROCEED --------------------if you don't feel comfortable with handling HIGH VOLTAGE circuits! Contact your nearest dealer for an advise! Please read the whole instruction below before to start. Carry out the following safety procedure of discharging the HV capacitors inside the amplifier each time before opening the top cover of the amplifier. WARNING HIGH VOLTAGE! --------------------The amplifier works with high voltages up to 3000V which is LETHAL! You should never work alone in the room and you should always have somebody nearby, who is capable of rendering FIRST AID in a case of any unfortunate accident! For your safety pull the amplifier power plug out of the mains wall outlet and WAIT AT LEAST 30 minutes EACH TIME BEFORE you remove the cover of the amplifier! Do not touch any part inside before ensuring, as described below, that no residual voltage is present inside the amplifier! A. Switch off the amplifier and disconnect the power cord from wall outlet. Wait at least 30 minutes for HV safety before to continue. B. After removing the top cover, make sure that no residual DANGEROUS VOLTAGES are still present inside. For the purpose, take approximately 1m (3ft) of WELL INSULATED wire (adequate for 3000V). Bare and tin about 10-15mm (1/2") at its both ends. Connect one end FIRST to the GROUND STUD (on the rear panel), and AFTERWARDS, holding the wire BY THE INSULATION ONLY, at a distance of minimum 10cm/4", touch with its second tinned end the following points on the HV&SG PCB (be ready to see an electrical discharge on each point in case of residual charges presence): - the spade Fast-On contact J3 labelled "HV +2850V"; - each lead of the wire-wound resistor R12 (10 Ohm 10W); - each lead of the four HV diodes D1-D4. CAUTION! -------The calibration procedure described below requires high skill and knowledge in order not to damage the amplifier. 1 1. Preset all 15 trimmer potentiometers in the INTERFACE PCB to point to the following positions: RP1 - 1 o'clock; set plate idling current 375mA (SERVICE IP) c.w. RP2 - 2 o'clock; set plate idling current 50mA (SERVICE IP) c.w. RP3 - not available; RP4 - 8 o'clock; cal. forward RF power measurement (fwd) FWD_P c.c.w. RP5 - 11 o'clock; cal. reflected RF power measurement (rfl) RFL_P c.w. RP6 - 1 o'clock; cal. plate current measurement (ipm) I_PLATE c.c.w. RP7 - 10 o'clock; cal. bias voltage measurement (g1vm) BIAS c.c.w. RP8 - 2 o'clock; cal. screen-grid current measurement (g2c) I-SCREEN c.w. RP9 - 12 o'clock; cal. input RF power measurement (inp) DRIVE c.c.w. RP10 - 12 o'clock; cal. Alt. RF anode voltage measurement (aav) PLATE-RF c.c.w. RP11 - 12 o'clock; cal. screen-grid voltage measurement g2vm SCREEN-V c.c.w. RP12 - 12 o'clock; cal. high voltage measurement (hvm) HV c.c.w. RP13 - 4 o'clock; cal. mains voltage measurement (linevm) MAINS c.w. RP14 - 2 o'clock; cal. heater current (front) measurement (hcf) IF-FRONT c.w. RP15 - 11 o'clock; cal. heater current (rear) measurement (hcr) IF-REAR c.c.w. RP16 - 4 o'clock. cal. heater voltage measurement (htrvm) FIL-V c.w. Above are listed the trimmer function, the signal name according to the schematic diagrams (in brackets), the measurand name in the MEASURE sub-menu, and the rotation direction to increase the measurand. Please look at fig.1 for potentiometers layout. An older PCB version is shown but the potentiometers layout and schematic diagram in later versions are the same. Presetting all trimmer potentiometers is needed to make it possible turning on the amplifier without tripping any protection due to any large mis-calibration. Further calibration as described below is needed for precise measurement and normal amplifier function. You should know that precise calibration of RP4 (fwd), RP5 (rfl), and RP10 (aav) is important for proper antenna-impedance matching in the AUTO TUNE procedure. 2. Turn ON the amplifier and wait for the 150s warmup period to expire. The amplifier should enter the STBY mode automatically after that. Enter the MEASURE sub-menu on the RCU and select the measurand to be calibrated according the instructions below. If any protection trips meanwhile, you should turn the corresponding potentiometer slightly in a direction desired to correct the respective measurand, in order to make it possible to continue operation. 2 Fig.1 Interface PCB - measurements calibration If the message concerns any DC supply voltage, check the corresponding monitoring voltage on the INTERFACE PCB JP7: pin 24 for +5V, pin 19 for +12V, pin 18 for -12V, pin 7 for 24V MOTOR VOLTAGE, pin 6 for +24V, and pin 21 for +48V. All these monitoring voltages should be about +2V to the chassis. For +5, +12, and -12V it should be between 1.9 and 2.1V while for +24 and +48V it might be between 1.7 and 2.3V, deviated proportionally to the current deviation of the mains voltage from its nominal. For instance, if the protection states "HEATER VOLTAGE TOO LOW", you should turn the trimmer potentiometer RP16 (htrvm) slightly in clock wise position in order to increase the measured value. This should permit further operation until the measurand is calibrated in next steps. 3. CPU-PCB ADC full-scale check. This procedure is to be run only after a repair in the ADC circuits (located on the CPU PCB). It should be verified however before to continue with the INTERFACE PCB calibration. Enter OPER mode and select SCREEN-V on the RCU. Using a precise voltmeter (0.2% or better) check the voltage on INTERFACE JP7:11 "g2vm". The SCREEN-V should be exactly 200 times higher than the real voltage "g2vm". For instance, if "g2vm" 3 is found 1.710V, the SCREEN-V should read 342V. If needed, adjust the RCU reading by the trimmer potentiometer RP2 "Full Scale" on the CPU PCB, located near the ADC integrated circuit - look at fig.2. Fig.2 CPU PCB - ADC full scale calibration Normally the CPU PCB is pre-calibrated in the factory and no calibration should be needed. Return to the STBY mode after the check. 4. Heater AC voltage measurement calibration. The heater voltage is to be monitored with an external AC voltmeter connected directly to either tube socket, between pins 3 and 7. Please look at fig.3 for socket contacts layout. About 12.6V AC voltage is expected there. For this purpose open the small aluminium cover under the tube deck. Connect provisionally two neat wires to pins 3 and 7 and thread them through either screw hole in the small cover. Install the cover in order to let the cooling air pressurizing the tube deck when you turn on the amplifier after that. Be careful not to grip any wire when you close the cover. 4 Fig.3 Tube socket 4CX800A / GU74B Turn ON the amplifier and when STBY mode appears after 150s, enter the MEASURE sub-menu. Select the FIL-V to be monitored on the RCU. The nominal heater voltage is 12.6V AC but it depends on the mains-voltage deviation. Calibrate the RCU reading according to the external voltmeter, using the trimmer-potentiometer RP16. 5. Heater AC current measurement calibration. Remove the front tube. Connect an external 3.3 Ohm / 50W dummy-load resistor, with an external AC ampermeter connected in series, between the socket pins 3 and 7. It should replace the filament of the missing tube. Make the connection from the top side of the socket, using two hard metal pins of 1.2-1.3mm (AWG16 or 1/20 Inch) diameter, 25mm (one Inch) long, with two heavy connection leads pre-soldered to the pins. The connection-leads cross section should be 0,5 sq.mm (AWG20) minimum. You may use the filament of the removed tube as a load resistor (between pins 3 and 7) but you should provide a small fan to cool the tube during the procedure. It is advisable to limit the total testing time to about 5 minutes per tube in this case. 5 Turn ON the amplifier and when STBY mode appears after 150s, enter the MEASURE sub-menu. Select the IF-FRONT to be monitored on the RCU. The nominal heater current is 3.6A but it depends on the tube specimen and the mains-voltage deviation. Calibrate the RCU reading to the external ampermeter, using the trimmer-potentiometer RP14. Switch off the amplifier and move the external load and ampermeter combination to the rear socket. Install the front tube since the amplifier would trip with "heater current too low ..." message otherwise. Turn ON the amplifier and when STBY mode appears after 150s, enter the MEASURE sub-menu. Select the IF-REAR to be monitored on the RCU. Calibrate the RCU reading to the external ampermeter, using the trimmer-potentiometer RP15. Switch off the amplifier, remove the heater dummy load and install the tube. Check the wiring. 6. Bias DC voltage measurement calibration. Connect an external DC voltmeter between the INTERFACE PCB JP2:15 (BIAS) and chassis. Turn ON the amplifier and when STBY mode appears after 150s, enter the MEASURE sub-menu. Select the BIAS to be monitored on the RCU. The nominal bias voltage during RX is -124V but it depends on the Zener-diodes specimens. Calibrate the RCU reading according to the external voltmeter, using the trimmer-potentiometer RP7. 7. Mains (line) AC voltage measurement calibration. Connect an external AC voltmeter to the mains power outlet. While in MEASURE sub-menu, select the MAINS to be monitored on the RCU. Calibrate the RCU reading according to the external voltmeter, using the trimmer-potentiometer RP13. 8. Screen-grid DC voltage measurement calibration. Connect an external DC voltmeter between the HV&SG PCB D32 cathode (+340V) and the chassis - fig.4: Fig.4 HV&SG PCB - Screen-Grid Voltage and Current Monitoring 6 Turn ON the amplifier and when STBY mode appears after 150s, change to the OPER mode. Enter the MEASURE sub-menu and select the SCREEN-V to be monitored on the RCU. The nominal screen grid voltage during OPER mode is 340V. If the real value shown by the external voltmeter is more than 2V different from 340, adjust it to 338-342V using the trimmer potentiometer RP1 on the HV&SG PCB. Then calibrate the RCU reading according to the external voltmeter, using the trimmerpotentiometer RP11 on the INTERFACE PCB. 9. Screen-grid DC current measurement calibration. Connect an external regulated DC power source (0 to 2V/0.15A) with the (-) pole to the non-grounded lead of the resistor R29 on the HV&SG PCB - fig.4. Connect the (+) pole of the DC power source through a DC ampermeter to the chassis. Set the output voltage of the source to zero before turning on the amplifier. The resistor R29 is a 15 Ohm (5%) screen-grid current measurement shunt resistor. Turn ON the amplifier and when STBY mode appears after 150s, change to the OPER mode. Enter the MEASURE sub-menu. Select the I_SCREEN to be monitored on the RCU. Increase slowly the voltage from the external DC power source while monitoring the external ampermeter. Set the current to 100mA (about 1.5V from the external DC power source should be needed for this purpose). Calibrate the RCU reading according to the external ampermeter, using the trimmer-potentiometer RP8 on the INTERFACE PCB. 10. Plate (anode) DC current measurement calibration. Connect an external regulated DC power source (0 to 15V/1.5A) with the (-) pole to the soldering point "HV-" on the HV&SG PCB. A suitable connection lead is the resistor R14F or the anode of diode D5 in older units, which are connected to the "HV-" point see fig.5. Connect the (+) pole of the DC power source through a DC ampermeter to the chassis. Set the output voltage of the source to zero before turning on the amplifier. This soldering point is connected to the chassis through a 10 Ohm (5%) plate-current measurement shunt resistor. (Early PCB revision) 7 Fig.5 HV&SG PCB - Anode Voltage and Current Monitoring Turn ON the amplifier and when STBY mode appears after 150s, change to the OPER mode. Enter the MEASURE sub-menu. Select the I_PLATE to be monitored on the RCU. Increase slowly the voltage from the external DC power source while monitoring the external ampermeter. Set the current to 1.2A (about 12V from the external DC power source should be needed for this purpose). Calibrate the RCU reading according to the external ampermeter, using the trimmer-potentiometer RP6 on the INTERFACE PCB. 11. High (anode) DC voltage measurement calibration. WARNING HIGH VOLTAGE! --------------------The expected DC voltage is 2800V which is LETHAL! Get general HV safety measures. Use only special HV probe to the multimeter or a special HV voltmeter, adequate for 3kV minimum. Do not use normal multimeters directly neither their leads since they are only intended for 500-1000V maximum. Switch off the amplifier and get safety measures described in the WARNING notes (A) and (B) in the beginning of the present instruction. Connect the HV probe grounding to the chassis BEFORE connecting the HV tip to the HV+ pole. On the HV&SG PCB, connect the HV probe tip to the HV rectifier output HV+. A suitable connection can be made to the lead of the wire-wound resistor R17F or the cathode of the diode D20 in older models as shown in fig.5. Turn ON the amplifier and when STBY mode appears after 150s, enter the MEASURE sub-menu. Select the HV to be monitored on the RCU. The nominal HV voltage during RX is 2800V but it depends on the mains voltage deviation. Calibrate the RCU reading according to the external HV voltmeter, using the trimmerpotentiometer RP12. Turn off the amplifier. Disconnect the HV probe and install the top cover of the amplifier with at least 5 screws on top. 12. Tubes idling current adjustment. In STBY mode, select the SERVICE menu. Do not apply any drive during adjustment. Using the UP and DOWN arrow buttons, select the following screen : 8 PLATE CURRENT: GRID BIAS : mA V The grid bias voltage is monitored for information only. You should be monitoring the plate current while adjusting the two trimmers RP1 and RP2 on the INTERFACE PCB. Note that RP1 will affect both idling levels, while RP2 - only the low level. That is why the high level is adjusted the first. At this point, an automatic procedure is started when you press the ENT button. The tubes are first controlled to the high-level idling current, then a pause follows, and the low-level appears the last. At the first step, the high-level idling current must be adjusted between 370 and 380mA using the trimmer potentiometer RP1 marked "375mA". You will have about 15 seconds for this adjustment, after which the tubes are automatically cutted off. You may note a 0/10mA flicker on the display, which is normal. After a 15 seconds pause, the tubes are controlled to the low-level idling current for another 15 seconds. Now the current must be set to 50mA using the trimmer potentiometer RP2 "50mA". After this second session, the amplifier automatically leaves the SERVICE menu. 13. Forward power measurement adjustment. Connect the transceiver with a coaxial and the control cable to the amplifier RF INPUT and KEY-IN connectors (and KEY-OUT if used). Connect a dummy load or good antenna (SWR below 1.05 for 7MHz) through an external in-line wattmeter (up to 2kW, 5% or better accuracy) to the amplifier RF OUTPUT. Turn ON the amplifier and when STBY mode appears after 150s, enter the MEASURE sub-menu. Select the FWD_P to be monitored on the RCU in the left field of the LCD. While monitoring the external wattmeter, in OPER mode apply 7.0-7.1MHz RF drive (about 50W), until the output power reaches 1500W. Calibrate the RCU reading according to the external wattmeter, using the trimmer-potentiometer RP4. 14. Reflected power measurement adjustment. The transceiver and the load should be connected as it was for forward-power calibration. Use a "T" adapter to add a transmitting-type 400-500pF capacitor (500V minimum) in parallel to the dummy load or select an antenna with SWR between 2 and 4 for 7MHz. Keep the external wattmeter connected in line but set for reflected power. Enter the MEASURE sub-menu and select the RFL_P to be monitored on the RCU. While monitoring the external wattmeter, in OPER mode apply minimum RF drive at 7.0-7.1MHz. Increase the drive power slowly until the reflected power reaches 200W. Calibrate the RCU reading according to the external wattmeter, using the trimmer-potentiometer RP5. Remove the test capacitor from dummy load. 15. Drive power measurement calibration. The transceiver and the load should be connected as it was for forward-power calibration. An 100W-range 5% wattmeter should be connected at the amplifier input. Enter the MEASURE sub-menu and select the DRIVE to be monitored on the RCU. 9 While monitoring the input wattmeter, in OPER mode apply 50W 7.0-7.1MHz drive RF power. Calibrate the RCU reading according to the input wattmeter, using the trimmer-potentiometer RP9. 16. Alternate RF anode-voltage measurement calibration (Auto-Tune accuracy adjustment). The reference point of the AUTO TUNE procedure concerning the plate-load resonant resistance, i.e. the target load resistance aimed by the automatic procedure when you start an AUTO TUNE cycle, is controlled by the trimmer potentiometer RP10 "aav". In fact, this potentiometer adjusts the PLATE-RF amplitude reading. It should be adjusted only after a calibration of the forward and reflected power measurements has been done. The inscription at the right-bottom of the RCU should be "DEF" to start the adjustment. If it is "USR" for any reason, you should first erase the tuning memory for the frequency segment of operation (7.0-7.1MHz). For this purpose, press and hold the ESC button and press ENT, while still holding ESC. Then release them at the same time and press ENT again to erase USR. The DEF inscription should appear instead of USR on the RCU. Enter the MEASURE sub-menu and select the PLATE-RF to be monitored on the RCU. While monitoring the output wattmeter, in OPER mode apply 7.0-7.1MHz drive for 400W output power. Pre-adjust the trimmer-potentiometer RP10 for 1000V PLATE-RF reading on the RCU. The mains voltage should be very close to the nominal selection at the moment of this calibration. You should use an auto transformer to correct for any mainsvoltage deviation greather than 3% from nominal selection during this procedure. To fine adjust RP10, perform an Auto-Tune cycle. For this purpose, select the AUTO TUNE menu. Apply about 15W drive power and wait for 1-2 seconds until the auto-tune cycle finishes. Check whether "DEF" inscription has been replaced by "USR" on the RCU at the end. The output-signal envelope form should be monitored on an oscilloscope for the next adjustment. Use a -40 to -60dB RF coupler or other means to connect partly the oscilloscope probe to the RF OUTPUT of the amplifier. Select a 5-10ms/div sweep and synchronize it with the mains voltage frequency (50 or 60Hz). The output wattmeter should be not of peak-reading but an average-power reading type. Tihs makes a difference due to amplitude modulation on the CW signal during the adjustment procedure. You should be simultaneously monitoring the output wattmeter and the oscilloscope waveform. When increasing the drive power, at a certaing level a parasitic 100/120Hz saw-tooth-envelope AM on the output CW signal will appear. If you further increase the drive, the AM depth and the output power would saturate. Then decrease the drive power back until the AM depth would become half the "saturation" value. Note the wattmeter reading at this moment. When RP10 is properly adjusted, the power threshold for "half AM depth" should be between 1950 and 2000W. Please note the AM frequency - it should be twice the mains frequency (100 or 120Hz). If 50 or 60Hz AM is noted, you should stop this procedure and look for any rectifier problem in the HV, screen grid, and the bias voltage bridges (most likely half bridge is missing). If the "half AM depth" power threshold is less than 2000W, turn the trimmer potentiometer RP10 slightly c.c.w. in order to increase the PLATE-RF reading on 10 the RCU proportinally to the deviation from 2000W. This will decrease the aftertune loading resistance in order to increase the power attainable. Turn RP10 in c.w. direction if the 2000W threshold has been exceeded. Use small adjustment steps and perform Auto-Tune procedure after each step in order to gradually approach the 1950-2000W "half AM depth" power threshold. Final check. When you consider RP10 is properly adjusted, perform a two-tone test on the amplifier. The IMD3 at 1500W PEP should be better than -35dB. Up to 2100W PEP should be attainable without flat-topping the two-tone output waveform however it should flat top before reaching 2200W PEP. Also, the power GAIN with a CW test signal at 1500W output should be between 14.5 and 15.5dB. Do not forget that the mains voltage should be very close to the nominal selection during this adjustment and the final check. 11





![[11]______ No. of printed pages :04](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008230456_1-c7f17f51a590100b54beedcacca16186-300x300.png)